Microbiology chapter 1-3
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Antoni Van Leeuwenhoek
Introduced us to "Animacules” or microorganisms; He began making and simple microscopes.
“Father of Microbiology”
Louis Pasteur
Disproved spontaneous generation; all living things comes from other living things, discovered Patereurization
Pasteurization
heating liquids to a special temperature to kill harmful bacterial
Robert Koch
linked certain microorganisms to disease
Edward Jenner
layed the foundation for vaccination immunity
Fleming
discovered the first antibiotics; specifically penicillin
Joseph Lister
pioneered aseptic surgery
Eduard Buchner
discovered that enzymes produced by microorganisms caused fermentation a d not the bacteria itself
Genetic Engineering
manipulation of genomes to get desired functions
Bioremediation
restores damaged environments using living bacteria, fungi, and algae to detoxify
Pathogens
disease causing germs
Recombinant DNA
genes that are manipulated for practical applications (essentially cloning)
Biotechnology
use of living organisms to develop products and technologies that improve human life and the environemnent
What is the first disease revealed to be bacteria in origin?
anthrax
Microorganisms that have no nucleus are?
Prokaryotes
Which microorganisms that are single-celled eukaryotes that are are generally motile?
Protozoa
Pateur’s experiment on fermentation led to the creation of which field of microbiology?
Biochemistry
Characteristics of prokaryotes
No nucleus
Simple, small structure
No organlles
Characteristics of eukaryotes
contains nucleus
contain organelles
Larger
All living things are composed of cells. Viruses do not have cells but are classified as microbes. Why?
they are microscopic, can infect living organisms and need a host in order function
Glycocalyses
sticky protective outer layer found on the outside of many bacterial cells
Cell wall
Rigid structure surrouding the cell membrane
Cell membrane
thin, flexible barrier that surrounds all cells, separating the inside of the cell from the external environment
Flagella
long, whip-like appendages that help with movement
Monotrichous
“mono”= one
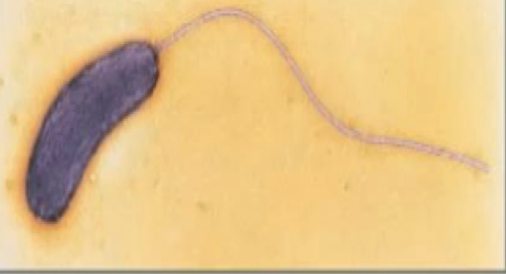
Amphitrichous
“amphi”= both

Lophotrichous
“Lopho”= crest
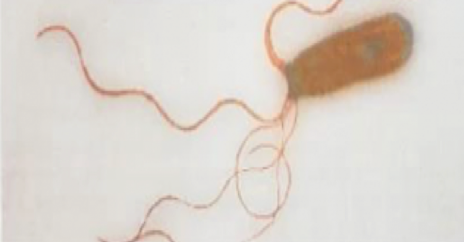
Peritrichous
“Peri” = arounds

Pili (fimbriae)
hair like structures found on the surface of many bacteria
Endospores
highly resistant, dormant structured formed by certain bacteria to survive harsh conditionsD
Diffusion
passive movement of molecules from high concentration to low concentration
Facilitated diffusion
passive transport of molecules moving down their concentration gradient with the help of membrane proteins
Osmosis
passive movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from low to high solute concentration
Isotonic
a solution with the same solute concentration as another solution
Hypertonic
a solution with a higher solute concentrationH
Hypotonic
a solution with a lower solute concentration
Passve transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without ATP
Active transport
Movement of substances requiring ATP, against the gradientG
Group translocation
a type of active transport found in prokaryotes where substances are chemically modified as it is transported across the cell membrane
Uniport
membrane transport system that moves one specific substance in one direction
Symporters
Membrane transport proteins that move 2 different substances in the same direction at the same time
characteristics of bacteria cell wall
peptidoglycan
Gram positive and Gram negative
Characteristics of Archaea cell wall
no peptidoglycan
contains hami (unique to archaea)
Characteristics of Gram- Positive bacteria
thick layer of peptidoglycan
Teichoic acids and lipoteichoic cells
Appears purple
Gram- Negative
thin layer of peptidogylcan
outside layer of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
Appears pink
What happens to a cell when peptidoglycan is disrupted or removed
the cell will die from osmotic lysis because it will loose water very fast
Structural components of the cell membrane are responsible for selective permeable function
the phospholipid bilayer
Important functions that the cell membrane performs in bacteria
selectively permeable
energy production, site of cellular respiration
The result of the Gram stain is based on differences in the cell’s…?
it is based on the structure of the cell’s wall
Which structure protects bacteria from being phagocytized?
capsule
Teichoic acids are found in what type of bacteria cell wall?
Gram positive bacteria W
What bacteria cell wall is decolorized by acetone alcohol?
Gram-negative bacteria