Pathology Laboratory
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Macule
circumscribed flat area of color change <1cm diameter.
Patch
circumscribed flat area of color change >1cm diameter.
Papule
solid elevated lesion <1cm diameter.
Plaque
flat elevation in skin >1cm.
Pustule
circumscribed elevation of skin containing pus; may be intraepidermal, subepidermal or follicular in location.
Vesicle
sharply circumscribed elevation of epidermis filled with clear fluid, <1cm diameter, intraepidermal or subepidermal
Bulla
sharply circumscribed elevation of epidermis filled with clear fluid, >1cm diameter.
Wheal
sharply circumscribed raised lesion consisting of edema
Nodule
circumscribed solid elevation >1cm in diameter that usually extends into deeper layers of skin
Cyst
epithelium-lined cavity containing fluid or a solid material. It is a smooth, well-circumscribed, fluctuant to solid mass.
Alopecia
complete loss of hair
Hypotrichosis
thin hair coat/partial loss of hair
Scale
accumulation of loose fragments of stratum corneum.
Crust
accumulation of dried exudate, serum, pus, blood, cells, or scales adherent to skin
surface
Follicular casts
accumulation of keratin and follicular material that adheres to hair shaft
extending above surface of follicular ostia.
Comedo
dilated hair follicle filled with cornified cells and sebaceous material
Pigmentary abnormalities
changes in skin color due to a variety of pigments or lack of
pigment such as melanin.
Epidermal collarette
special type of scale arranged in a circular rim of loose keratin flakes
or peeling keratin
Scar
area of fibrous tissue that has replaced damaged dermis or subcutaneous tissue
Excoriation
erosion or ulcer caused by scratching, biting, or rubbing
Erosion
shallow epidermal defect that does not penetrate basal laminar zone Ulcer: break
in continuity of epidermis with exposure of underlying dermis
Fissure
linear cleavage into epidermis or through epidermis into the dermis. May be single or multiple, curved, branching or straight
Lichenification
thickening and hardening of skin characterized by exaggeration of superficial skin markings. Often hyperpigmented. Hyperkeratosis is increased thickness of stratum corneum.
Callus
thickened, rough, hyperkeratotic, alopecic, often lichenified plaque
integument
It serves as the anatomic boundary between the body and the ambient environment.
epidermis
prime example of an adult tissue that undergoes continual and rapid flux. It also maintains homeostasis by constant proliferation of a single inner (basal) layer of rapidly dividing progeny of stem cells.
stratum basale (basal layer)
This is the deep germinative layer of the epidermis and is composed of a single layer of cuboidal to low columnar cells resting on the basement membrane zone.
stratum spinosum/prickle cell layer
This is characterized by prominent intercellular bridges that are the desmosomal attachments between cells.
stratum granulosum
variably apparent on light microscopy in haired skin and appears only 1-2 cells thick.
stratum corneum / SC
This is composed of >20 overlapping layers of bland, polyhedral, anucleate cells sandwiched between layers of lipid.
Melanocytes
These are located in the basal layer of the epidermis and outer root sheath of hair follicles; and in hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) sections, they appear as clear cells with a small dark-staining nucleus because of shrinkage artifact.
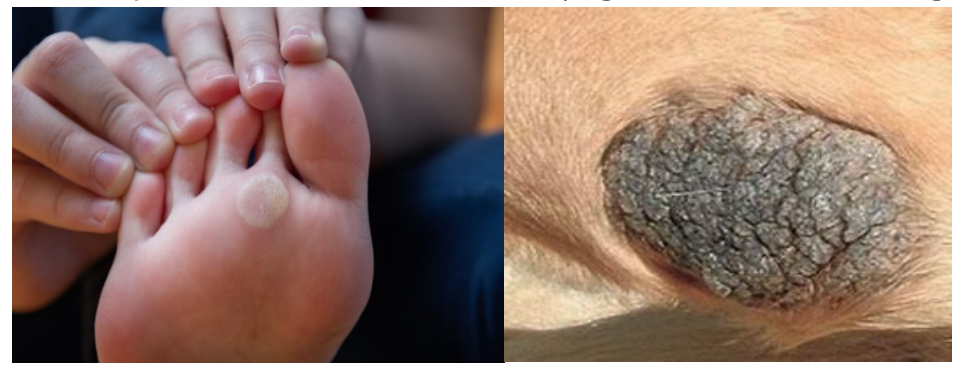
Acanthosis nigricans
What is this ds?
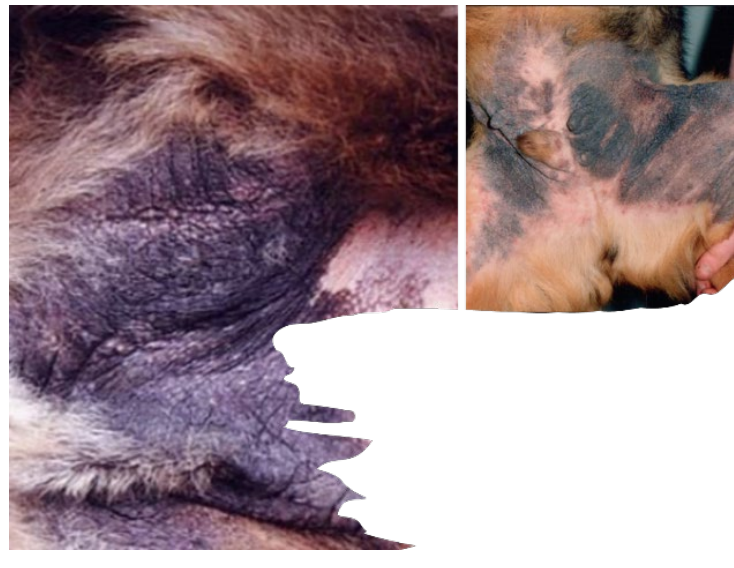
Lichenification
What is this ds?
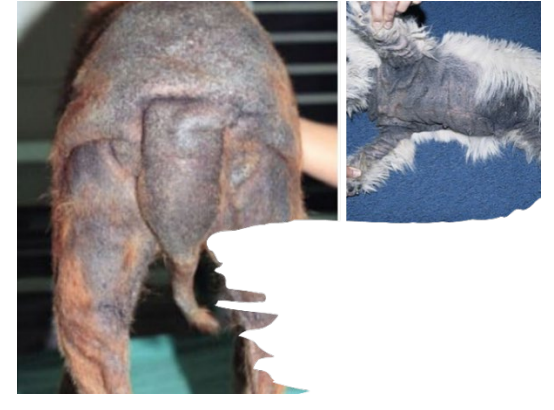
Alopecia
What is this ds?
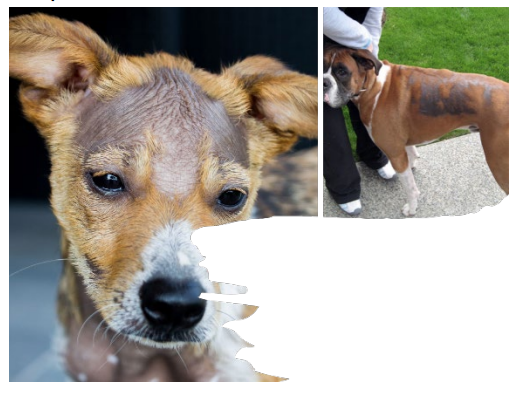

Hypotrichosis
What is this ds?

Cyst
What is this ds?
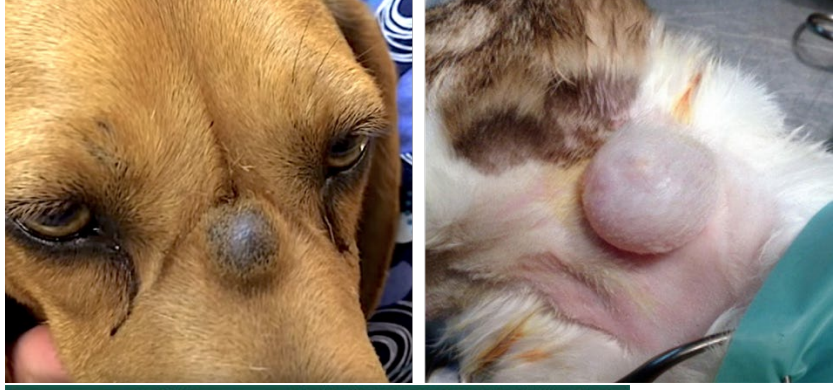
Excoriation: Ulcer and erosion
What is this ds?
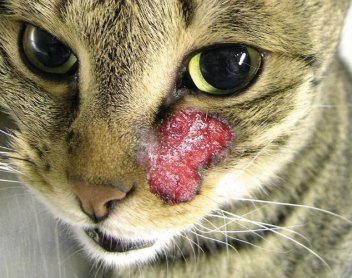
Callus
What is this ds?
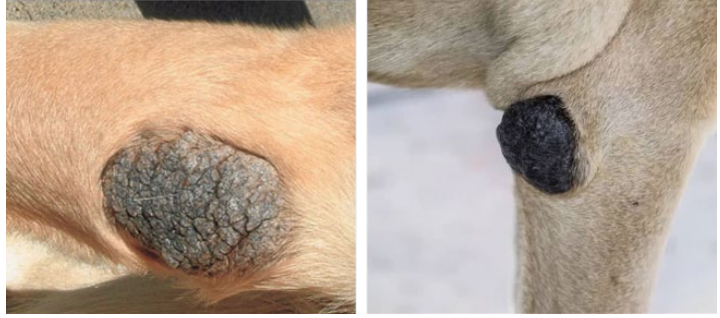
Lipomas
What is this ds?
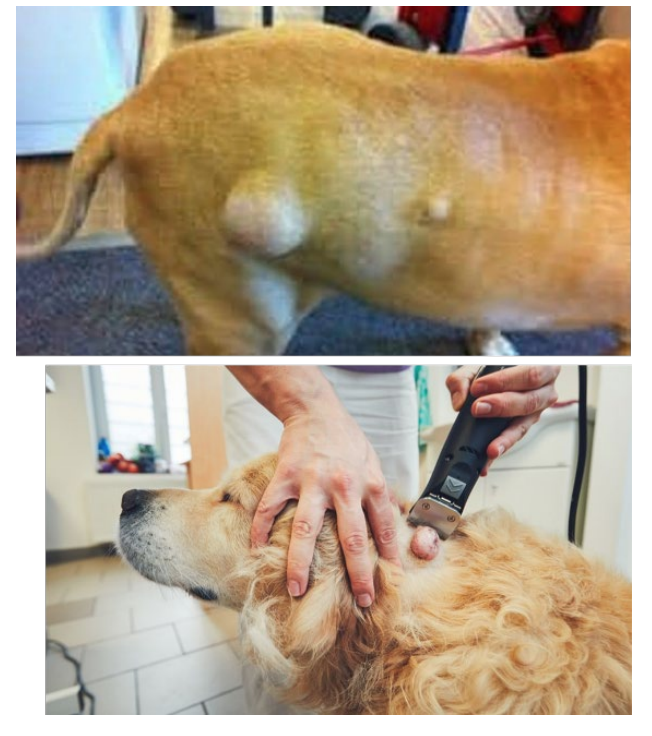
Sebaceous Adenomas
What is this ds?
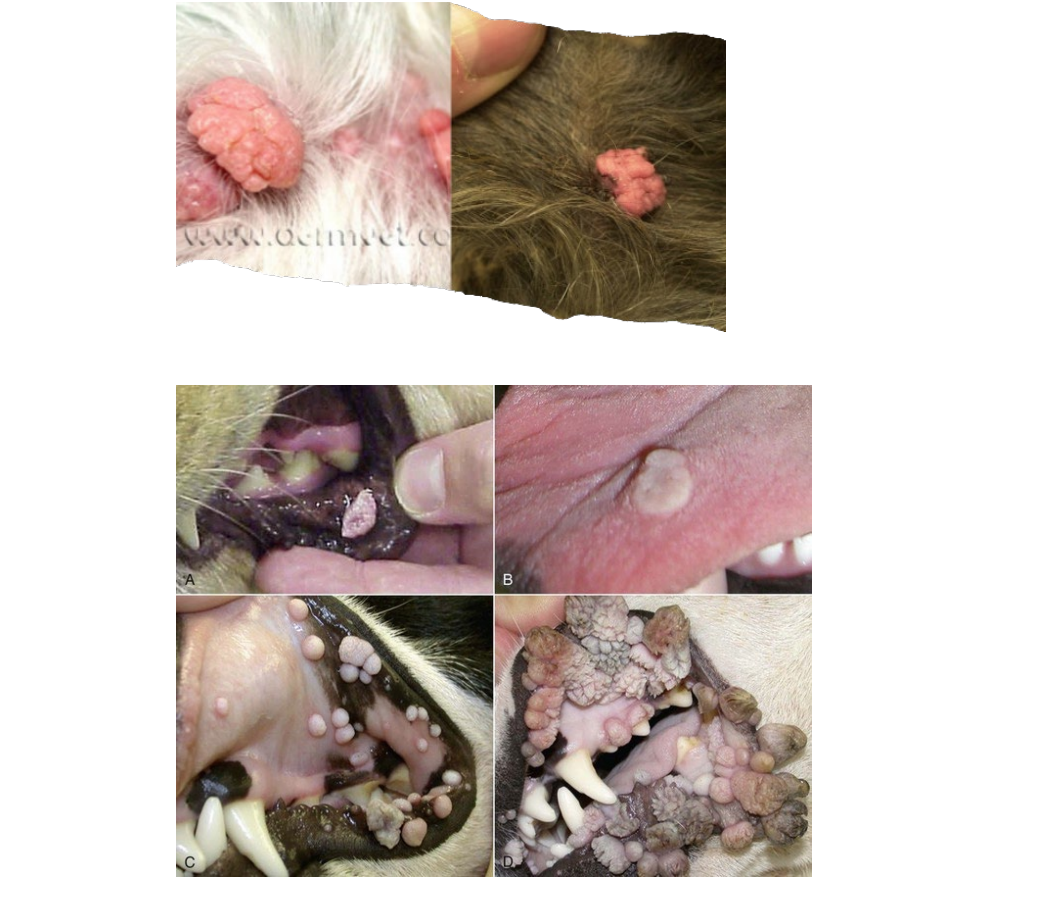
Dells
small depressions or hollows in the surface of the epidermis independent of adnexal structures. They are usually associated with focal epidermal atrophy and orthokeratotic hyperkeratosis. This term is not commonly used in veterinary dermatology
Epidermal collarette
a special type of loose scale that is arranged in a circular pattern around a central area of erythema or hyperpigmentation. Epidermal collarettes most likely represent ruptured pustules or papules from bacterial folliculitis.
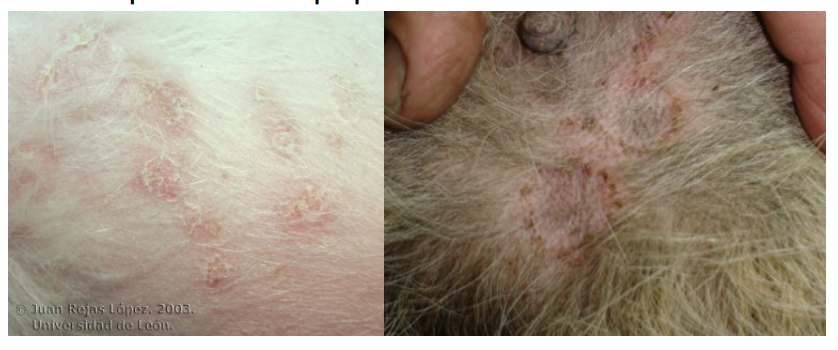
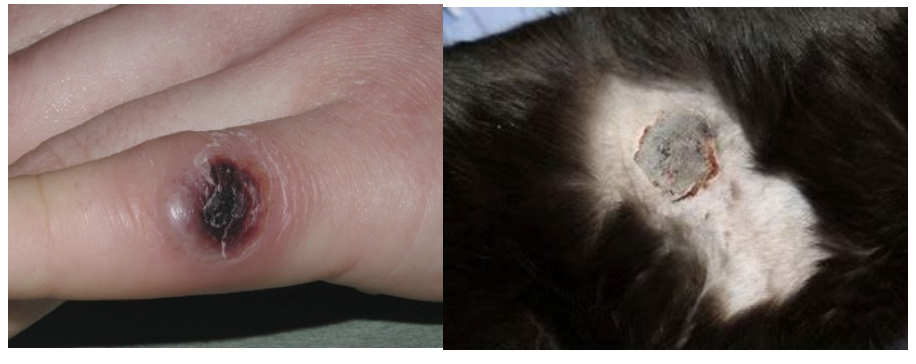
Eschar
thick crust that forms in association with an ulcer and is tightly adherent to the skin because of the incorporation of dermal collagen (e.g., thermal burn).
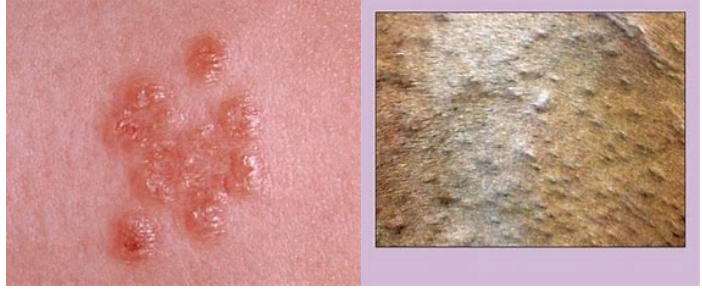
Papules
are solid, circumscribed, elevations in the skin that are <1 cm in diameter. They can be follicular (e.g., staphylococcal folliculitis) or nonfollicular (e.g., flea-bite hypersensitivity).
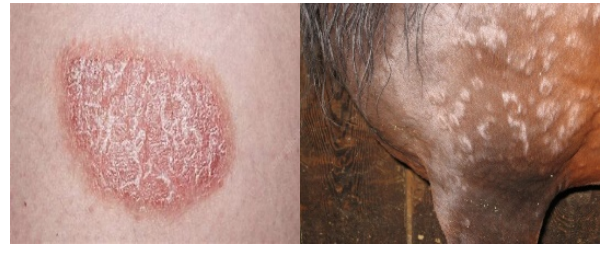
Plaques
are solid, slightly raised elevations in the skin that are >1 cm in diameter (e.g., feline eosinophilic plaque).
Pustules
can be gross or microscopic accumulations in skin that are filled with inflammatory cells, usually neutrophils or eosinophils. It can be follicular or nonfollicular (e.g., superficial pemphigus).
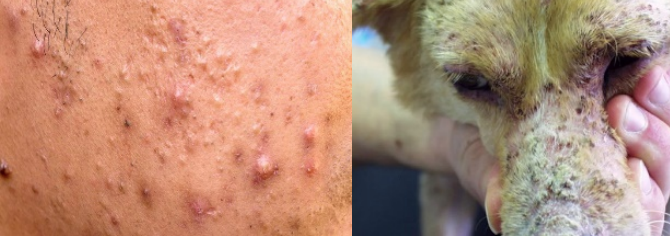
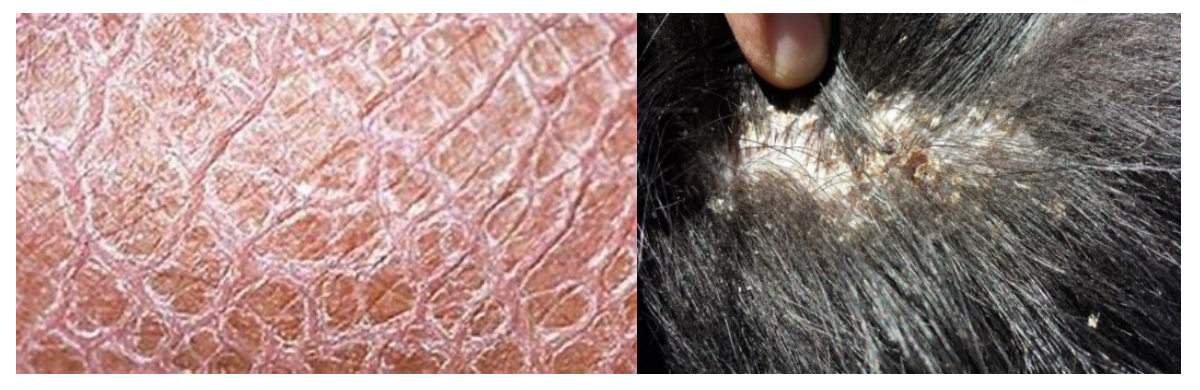
Scale
refers to a flat plate of stratum corneum (e.g., Golden Retriever ichthyosis). It is important to distinguish scale versus crust on physical examination.
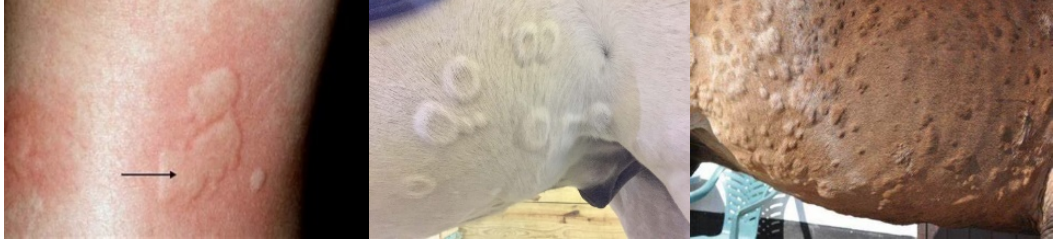
Wheal
a firm, circumscribed, raised elevation in the skin, composed of edema and is often erythematous (e.g., equine urticaria).
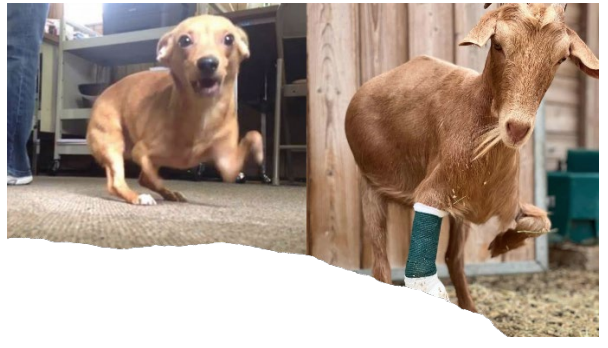
Hemimelia
What is this ds?
Umbilical Hernia
What is this ds?

Perineal hernia
What is this ds?
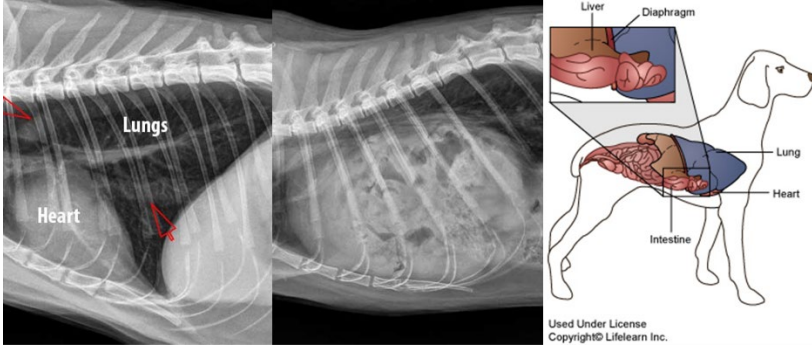
Diaphragmatic Hernia
What is this ds?
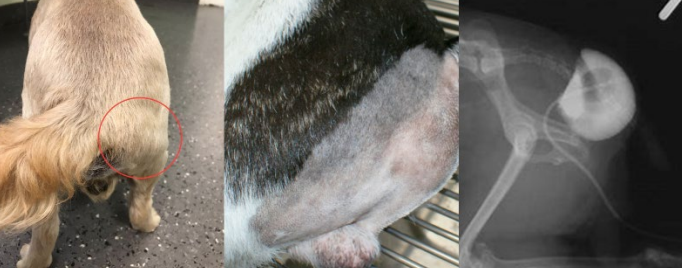
Inguinal Hernia
What is this ds?
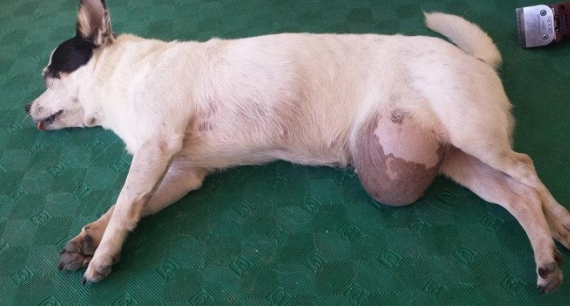
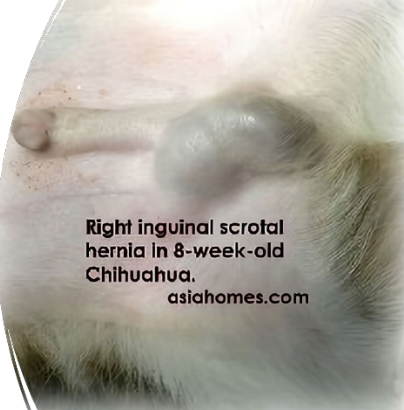
Scrotal Hernia
What is this ds?
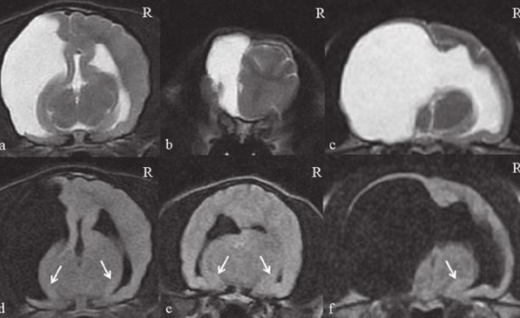
Hydranencephalus
What is this ds?
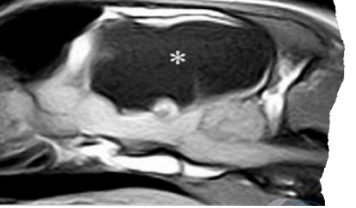
Hydrocephalus
What is this ds?
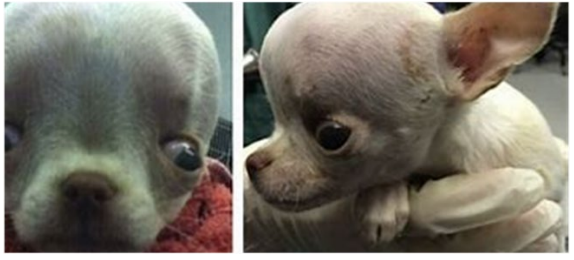
Kyphosis
What is this ds?

Microophthalmia
What is this ds?
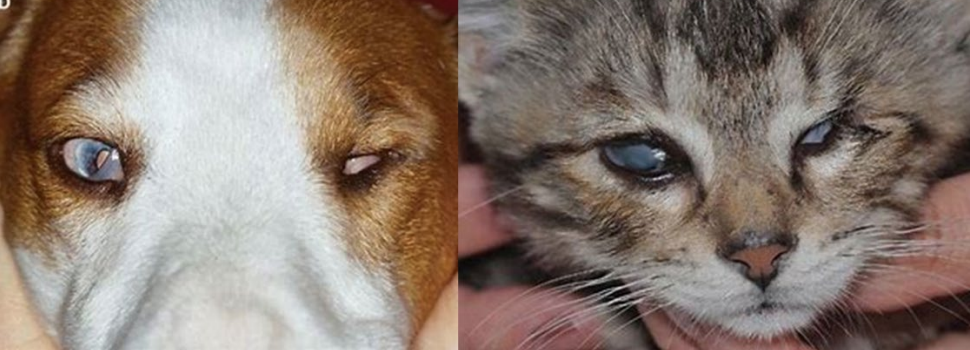
Palatoschisis
What is this ds?
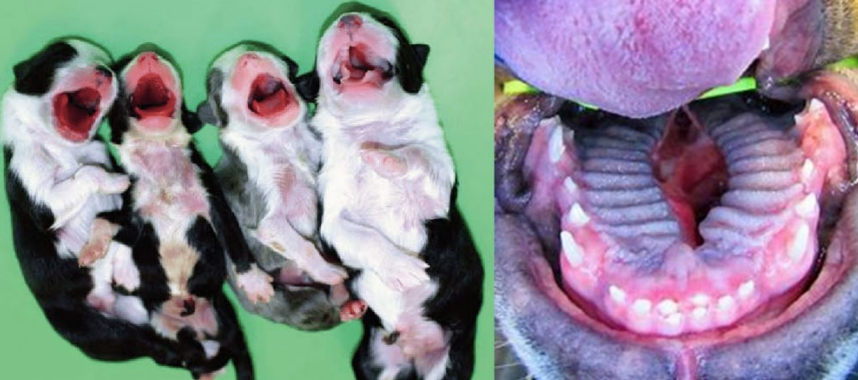
Cheiloschisis
What is this ds?

Perosomus elumbis
What is this ds?

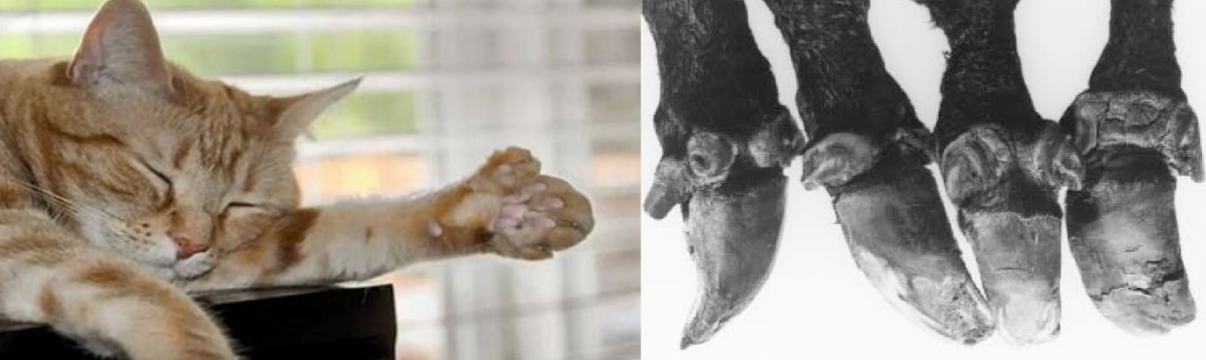
Polydactyly
What is this ds?

Porencephaly
What is this ds?
Prognathia
What is this ds?

Syndactyly
What is this ds?
Alpha-mannosidosis
a rare, autosomal, recessively inherited lysosomal storage disease caused by a deficiency of the enzyme α-D-mannosidase1. This enzyme is involved in the digestion of complex sugars derived from glycoproteins, and a defective alphamannosidase leads to the progressive accumulation of mannose-rich oligosaccharides in all tissues

Thoracoschisis
rare congenital malformation characterized by herniation of intraabdominal contents through a thoracic wall defect.
C3 deficiency
It makes an individual susceptible to severe, recurrent infections from encapsulated bacteria.
Hemophilia B
a bleeding disorder caused by a deficiency of Factor IX, a protein necessary for blood coagulation
Pyruvate kinase deficiency
an inherited metabolic disorder of the enzyme pyruvate kinase which affects the survival of red blood cells.
Von Willebrand disease (VWD)
the most common hereditary blood-clotting disorder in humans. An acquired form can sometimes result from other medical conditions.
Chédiak–Higashi syndrome / CHS
s a rare autosomal recessive disorder that arises from a mutation of a lysosomal trafficking regulator protein, which leads to a decrease in phagocytosis. The decrease in phagocytosis results in recurrent pyogenic infections, albinism, and peripheral neuropathy
Citrullinemia
an autosomal recessive urea cycle disorder that causes ammonia and other toxic substances to accumulate in the blood.
Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS)
group of 13 genetic connective-tissue disorders. Symptoms often include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation.

Photoporphyria
What is this ds?
Glycogen storage disease
Glycogen is a polymer of glucose needed to provide for a continuous source of glucose during fasting. Glycogen synthesis and degradation are tightly controlled by complex regulatory mechanisms and any disturbance in this regulation can lead to an inadequate reservoir of glycogen or an accumulation of excess or abnormal glycogen stored either in the cytosol or in the lysosomes
Malignant hyperthermia (MH)
a potentially fatal pharmacogenetic disorder of skeletal muscle calcium regulation. Triggered by exposure to certain drugs or stressors, clinical signs include sudden and dramatic rise in body temperature, muscle fasciculation, muscle rigidity, tachypnea, tachycardia, arrhythmia, myoglobinuria, metabolic acidosis, renal failure, and death.