1037DOH - Oral Microbiology
1/81
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
what is a microbiome?
the collection of genomes from the total culturable and unculturable microorganisms
includes biomolecules within a defined habitat
what is a microbiota?
total collection of resident microbes within the microbiome
what are two features of microorganisms you can use classify and categorise them? briefly describe what these are
phenotype
observable characteristics/traits of an organism
genotype
organism’s complete set of heritable genes/genes that can be passed down from parents to offspring
what are the three domains of life?
bacteria (prokaryotes)
archaea (prokaryotes)
eucarya (eukaryotes)
describe the possible shapes and typical size of bacteria (MORPHOLOGY OF BACTERIA)
shapes
cocci (spherical)
bacilli (rod shapes)
spirochaetes (helical)
pleomorphic (appear as both cocci and bacillary forms)
size
0.2 - 5 microns
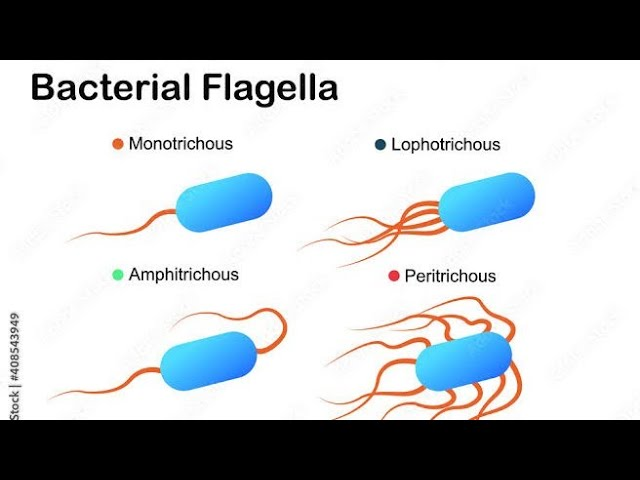
describe the flagella structure on bacteria
mono, lopho, peri
motile - whip like filaments
made of flagellin (a type of protein)
monotrichous - single + one ended
lophotrichous - many + one ended
peritrichous - all over outer surface
what are fimbriae and pili on bacteria?
pilin is a protein
both are fine, hair-like short structure
they mediate adhesion of bacteria to receptors on host (human) cell surface
what is the glycoalyx? (bacteria)
polysaccharide coating covering bacteria’s outer surface
allow adhesion to structures - eg teeth, oral mucosa, heart valves and catheters
contribute to formation of biofilms
eg streptococcus mutans - contributes to dental caries
what is the capsule layer around bacteria?
amorphous gelatinous layer surrounding bacteria
polysaccharide formed - may also contain protein
polysaccharides vary between bacteria and within a species (serological type)
what is the cell wall in bacteria?
multi-layered structure
allow rigidity
porous and permeable to substances with a low molecular weight
inner layer is peptidoglycan (protein + sugar)
inner layer varies in thickness and chemical composition (depending on gram-staining property of the bacteria)
describe gram positive, gram negative stains and LPS (lipopolysaccharide)
gram positive
dark blue/purple stain
indicates thicker peptioglycan layer (inner cell wall)
gram negative
pink stain
indicates thinner peptidoglycan layer
indicates complex outer membrane (including lipopolysaccharide (LPS), lipoprotein, and phospholipids, and porins (transportation of molecules)
LPS
toxic (endotoxin)
released when cell lysed
describe the cytoplasmic membrane of bacteria
phospholipid bilayer
similar to eukaryotic cells, but bacterial ones dont normally contain sterols
allows…
active transport + selected diffusion of molecules in and out of the cell
secretion of enzymes and toxins
electron transport
oxidative phosphorylation (in aerobic species)
has supporting receptors and other proteins of the
chemotactic and
sensory transduction systems
describe aerobes, facultative aerobes and anaerobes
aerobes
organism able to live and reproduce only in the presence of free oxygen
facultative aerobes
grow either with or without free oxygen
anaerobes
grow in absence of free oxygen
those that grow only in absence of oxygen are called obligate/strict anaerobes
describe the cytoplasm structure of bacteria
thick solution (amorphous matrix)
fills each cell
enclosed by cytoplasmic membrane
mainly composed of water, ions, metabolites and proteins
structures:
nuclear material
ribosomes
describe the nuclear material (nucleoid) of bacterial DNA
single, supercoiled and circular chromosome
2000 genes
1mm long
undergoes semi-conservative replication bidirectionally from a fixed point
describe the nuclear material (nucleoid) of eukaryotic DNA
contained within the nucleus
describe function of ribosomes
in bacterial (prokaryote) ribosomes are in the cytoplasm
in eukaryotes, ribosomes are attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum
facilitate protein synthesis
what is E. coli’s full name?
escherichia coli
what is S. mutan’s full name?
streptococcus mutans
name the 3 anaerobic bacterial species identified in carious coronal dentine (GRAM POSITIVE)
peptostreptococcus (COCCI)
P. anaerobius
P. parvulus
P. micros
eubacterium (RODS)
E. alactolticum
E. aerofaciens
E. saburreum
propionibacterium
P. acnes
P. avidum
P. lymphophilum
name the 3 facultative bacterial species identified in carious coronal dentine (GRAM POSITIVE)
streptococcus (COCCI)
S. mutans
S sobrinus
S. intermedius
actinomyces (RODS)
A. israelii
A. odontolyticus
lactobacillus (RODS)
L. casei
L. plantarum
L. minutus
name 4 gram negative anaerobic bacterial species identified in carious coronal dentine
fusobacterium nucleatum (RODS)
porphyromonas (RODS)
prevotella (RODS)
veillonella (COCCI)
describe fungi
eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms
genus Candida yeasts are pathogenic
describe viruses
not living
can infect all types of life forms
exist in form of independent particles or virions
DNA or RNA is their genetic material
shapes range from simple helical/icosahedral forms to complex structure
about 1/100th the size of bacteria
when infected with a virus, a ____ cell is forced to rapidly produce thousands of identical copies of the original ______
host
virus
what is pulpitis?
inflamed pulp
pain in A-delta and C-type nerves
reversible) mild, can heal once treated (like caries), triggered by cold/sweet, brief pain
irreversible) too damaged, spontaneous, throbbing, lingers after removing stim. usually treated w. root canal/extraction
what is pulp necrosis?
pulp death
after-effect of pulpitis/trauma
partial necrosis may display pulpitis
total necrosis is symptomless
what is periapical granuloma?
affects periapical tissues
usually resulting from long-standing infection or necrotic pulp
3 stages
primary acute apical periodontitis
new, acute inflammation at the root
chronic apical periodontitis
long-term, low-grade inflammation (can lead to granuloma)
secondary acute apical periodontitis
chronic lesion that flares up
becomes acutely painful again
what is a periapical abscess?
localised collection of pus at the root tip due to bacterial infection
two types
primary acute apical abscess
occurs at the first sign of infection
usually painful
swelling may occur
secondary acute apical abscess
flare-up of chronic infection
becomes acutely infected
forms pus
what is ludwig’s angina
rapidly spreading cellulitis of the floor of the mouth, usually from infected lower molars.
can block the airway because swelling pushes the tongue up and back.
firm swelling under the chin/neck, pain, fever, difficulty swallowing, drooling.
tx) IV antibiotics + sometimes surgical drainage.
what is cerebral abscess?
pocket of pus in the brain, usually from infection spreading from the ear, sinuses, or teeth
Key features: headache, fever, neurological deficits, nausea/vomiting, sometimes seizures.
Treatment: IV antibiotics, sometimes surgical drainage.
what type of infection is oral candidiasis/candidosis?
opportunistic infection
i.e occurs in ‘compromised’ patients
where do primary and secondary oral candidiasis/candidosis occur?
primary
only in oral/perioral tissues
secondary
oral/perioral tissues
other mucous/cutaneous surfaces
what is pseudomembranous, erythematous (atrophic) and hyperplastic oral candidiasis?
PM
white creamy patches on soft tissue that wipe off and leave behind red sometimes bleeding tissue underneath
EM
red, smooth, sometimes painful areas on tongue/palate
linked to long term antibiotic/denture use
HP
thick white patches that don’t wipe off
can be chronic
associated with immunosuppression
what is candida associated denture stomatitis?
fancy for sore mouth from dentures from overgrowth of candida
very common on maxillary dentures (palate covered, warm and moist)
treatment is denture hygiene or improving its quality
medical factors (eg diabetes) contribute to this
antifungals can also help
pinpoint erythema, confluent erythema and papillary hyperplasia of oral candidiasis
PP
tiny red spots under denture
CE
red areas merge into larger patches
PH
long term inflammation causes small pebble like projections on the palate
what is median rhomboid glossitis?
papillary atrophy
can be ellipitcal or rhomboid
in the midline of the tongue and anterior to the circumvallate papillae
oral hygiene and antifungals can help this
what is angular stomatitis/cheilitis?
lesions on the angles of the mouth
overexposure to saliva, staph aureus infections, perioral infections, poor oral hygiene contribute
zinc oxide paste, petrolatum lip balms, antifungals can help this
what is otitis media (chronic suppurative otitis media)?
infection of middle ear
appears as earache
can have discharge and pain
what is sinusitis (chronic sinusitis)?
occurs in frontal and maxillary sinuses
can occur during common cold
can appear with headache, pain, nasal obstruction, and can mimic toothache
what are some complications of a streptococcal sore throat?
rheumatic fever
chronic heart valve disease
acute glomerulonephritis
explain the rheumatic fever complication of a strep throat
symptoms are fever, pain and swelling in the joints
pancarditis: inflammation of all parts of the heart
explain the chronic heart valve disease complication of a strep throat
damage to heart valves over time, esp mitral and aortic valves
increases risk of bacterial endocarditis (infection of heart valves)
requires prophylactic antibiotics before dental procedures to prevent infection
explain the acute glomerulonephritis complication of a strep throat
kidney glomeruli are inflamed
can cause blood in urine
swelling
and high bp
describe bacterial/infective endocarditis
predominately bacteria-caused
streptococci (60%)
staphylococci (25%)
other bacteria (15%)
can happen thru periodontal treatment
identify at-risk patients
use preventive dental care
what bacteria cause bronchitis?
H. influenzae
S. pneumoniae
what is a major effect of cystic fibrosis? (infections of trachea/bronchi)
compromised natural defence mechanisms
what causes pertussis (whooping cough)? (infections of trachea/bronchi)
bordetella pertussis
happens in children
prevent via vaccinations
what bacteria causes tuberculosis?
mycobacterium tuberculosis
what is human immunodeficiency virus?
RNA virus
leads to acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)
common oral signs of AIDS (orofacial manifestations)
fungal infections
oral candidiasis (thrush) - white patches in mouth
viral infections
herpes simplex virus
herpetic stomatitis (cold sores)
human herpesvirus 8
kaposi’s sarcoma (purple/red lesions)
epstein-barr virus
hairy leukoplakia (white hairy patches on the side of the tongue)
severe, necrotising gingivitis and periodontitis
3 distinct particles of Hepatitis B
Dane particle
42 nm
complete infective virus
spherical forms
22 nm
non-infective
tubular forms
22 × 100 nm
non-infective
describe chronic persistent hepatitis B
does not develop liver damage but liver inflamed for more than 6 months
produces viral liver antigen (HBsAg)
has mild symptoms (fatigue) or no symptoms at all
describe chronic active hepatitis
extremely infectious
Dane particles present in blood
can progress to cirrhosis or liver cancer if untreated
immune system actively fighting virus = liver damage
describe HCV (hep C)
affects 3% of the population
parental route is blood products
persistent chronic infection - can progress to cirrhosis or liver cancer
dental implications of Hep C
oral tissues can show lichen planus, cancer or salivary gland disease in chronic cases
blood is main infectious media - saliva can contain viral RNA but transmission risk lower
must follow precautions to avoid sharps injuries and cross-contamination
_______ result in cell aggregation, leading to improved clearance of _______ from the oral cavity during swallowing, chewing and speaking
agglutinins
bacteria
what do lysozymes do?
breaks down bacterial cell walls
part of the defence mechanisms of the oral cavity
name some antimicrobial peptides (defence mechanisms of the oral cavity)
Histatin 5
Human beta defensin-1 (and defensin-2)
Magainin II and Magainin II amide
how do tonsils contribute to the defence mechanism of the oral cavity?
house B and T lymphocytes and macrophages
lymphoid tissue
how does epithelium defend the oral cavity?
inhibits bacterial adhesion
facilitates shedding of cells
has a keratin layer
what does connective tissue possess that makes it part of the oral cavity’s defence mechanism?
highly vascular so has lots of inflammatory response cells
why is gingival crevicular fluid a good oral cavity defence mechanism?
continuous flow of fluid
has albumin, transferrin and lysozymes
has components of the immune system (lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages)
describe how a bacterial infection spreads in the tooth and surrounding structures
dental plaque (usually supragingival)
infected enamel
infected dentin
dentinal tubule biofilm
root canal system infected
infected peri radicular/extra radicular tissues (surrounding bone and tissues)
what does dentinal tubule fluid do?
protect pulpo-dentine complex from bacterial antigens or toxic by-products
allow pulp healing
deposits serum in dentinal tubules to inhibit bacterial invasion of dentin by S. gordonii and E. faecalis
describe the colonisation of microbial biofilms
think: they get there, eat, form a gang, fight, grow
first bacteria adhere to host tissue
they utilise available nutrients
compete and co-operate with other species in the immediate environment
contend with host defence mechanisms
cells divide and grow
host becomes colonised in multiple sites
describe the biofilm benefit to cells
why are bacteria better in a biofilm than floating around on their own?
the antimicrobial chemicals get diluted in the biofilm before they even reach the tooth surface or the cells deep in the biofilm
outer layers of the biofilm act like a shield, stopping antimicrobials from getting inside
some bacteria go into a ‘sleep mode’ or change how they function (resistant phenotype) so they’re less affected by drugs that normally kill these
clin sig
makes it harder to kill harmful bacteria in plaque/root canals, meaning treatments like disinfectants, antibiotics or irrigation don’t work as well
list the 5 factors that affect the development and characteristics of biofilms
fenat
flora
ecology
nutrients
anatomy
time
flora factor of characteristics/development of biofilms
one species may supply essential nutrients for the growth of other species (like vitamin K)
strong bacterial positive interactions occur (like P. micros and P. anaerobius)
redox conditions
co-operate and compete with other species in immediate environment
nutrition factor of characteristics/development of biofilms
The oral cavity, especially in diseased areas, contains decaying tissue, root canal fluids, and serum-like substances rich in nutrients such as carbohydrates, amino acids/peptides (for protein synthesis), and growth factors like vitamin K and hemin (required by certain anaerobes).
In the early phase, sugar-metabolizing bacteria (e.g. Streptococcus) dominate, consuming available carbohydrates.
As carbohydrates are depleted, the second phase begins—bacteria capable of protein breakdown ferment peptides and amino acids, creating conditions that favor anaerobic growth.
In the final phase, protein degradation predominates, supporting the colonization of late, proteolytic species such as Prevotella intermedia, Fusobacterium nucleatum, and Eubacterium.
_______ anaerobes dominate initially and develops with ________ anaerobes
facultative
obligate
presence of _____-_______ _________ (eg prevotella) associated with advanced disease
gram-negative anaerobes
explain the community-as-pathogen theory
spg eoe
Structure: open architecture with channels → nutrient/waste flow.
Protection: resist host defenses and antimicrobials.
Gene activity: coordinated gene expression and cell-cell signaling (quorum sensing).
Environment: spatial differences allow diverse habitats and efficient nutrient use.
Outcome: enhanced virulence compared to single bacteria.
Example: S. gordonii helps P. gingivalis adhere to collagen and invade tissues.
what are macrophages?
phagocyte
detect, engulf and destroy pathogens and apoptotic cells
what are dendritic cells?
think chef
cells that process antigen material (engulf + chop em up - antigens)
present it on the cell surface to T-cells
link innate immune system to adaptive immune system
what do B and T lymphocytes do respectively?
B
make antibodies
T
help kill tumor cells and control immune responses
what does the complement system do?
tap
enhances the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells
Tagging microbes so immune cells can eat them (opsonization)
Attracting immune cells and causing inflammation (chemotaxis)
Punching holes in pathogens to kill them (membrane attack complex)
what do cytokines do?
they are small secreted proteins released by cells
tell immune cells what to do
help cells communicate, control inflammation, and coordinate the immune response
types of cytokine (list them)
lymphocytes
monocytes
chemokine
interleukin
what is PAMP (pathogen associated molecular pattern)?
small molecular motifs found on microbes (bacteria, viruses, fungi) but not on human cells.
examples include lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on gram-negative bacteria, peptidoglycan on gram-positive bacteria, flagellin, or viral RNA/DNA.
immune cells like dendritic cells and macrophages have pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that detect PAMPs. once detected, the immune system is activated to fight the invader.
what are pattern recognition receptors (PRR)?
sensors of the innate immune system
toll-like receptors (TLRs) detect bacteria, viruses, fungi
proteins or inside immune cells
once PRR binds its target, it activates immune responses: inflammation, cytokine release, and other immune cells recruitment
Summarise the development of a bacterial biofilm (10 marks)
Bacteria adhere to surface in aqueous environment
Excrete a slimy glue like substance to anchor them
Single bacterial species, but more often biofilms consist of many species of bacteria as well as fungi, algae, protozoa, debris and corrosion products
Once anchored to a surface, biofilm microorganisms carry out a variety of detrimental or beneficial reactions
functions like a tissue