7A - genes and chromosomes
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
The human __________ is contained within the nucleus of somatic cells, where each __________ is located at a fixed position along a __________. Each of these __________ are made up of specific sequences of __________ that code for the production of various proteins.
The human genome is contained within the nucleus of somatic cells, where each gene is located at a fixed position along a chromosome. Each of these genes are made up of specific sequences of nucleotides that code for the production of various proteins.
what is an allele
A particular form of a gene with a unique nucleotide sequence.
You inherit two alleles for each gene: one from your mother and one from your father.
Alleles can be:
Dominant - only one copy is needed to show the trait (e.g. brown eyes)
Recessive - two copies are needed to show the trait (e.g. blue eyes)
Label the diagram
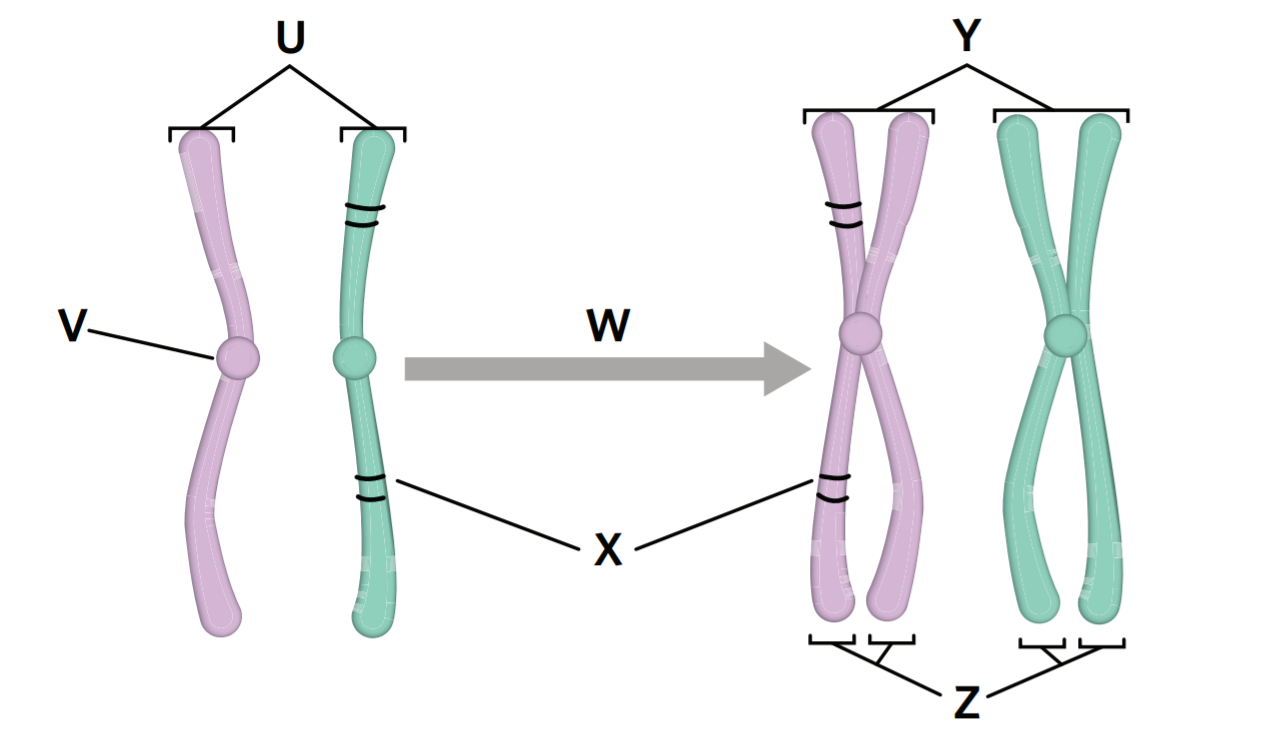
U = homologous chromosomes
V = centromere
W = replication
X = gene loci
Y = homologous chromosomes
Z = sister chromatids
what are homologous chromosomes
chromosome pairs, one inherited from each parent, that have the same genes in the same order.
they have the same:
Size and shape
Genes at the same loci (positions)
But they may carry different alleles of those genes
what are karyotypes
a visual representation of an individual's chromosomes, arranged in pairs by size and shape
what is polyploidy
a genetic condition where cells contain more than two complete sets of chromosomes
what is tetrasomy X
a genetic condition where a cell has four copies of a particular chromosome instead of the usual two.
what is trisomy 21 (Down syndrome)
a genetic condition where a person has three copies of chromosome 21 instead of the usual two
what is trisomy
a condition in which an extra copy of a chromosome is present in the cell nuclei, causing developmental abnormalities.
Match the diploid number to the corresponding genetic abnormality.
Diploid number:
2n+1
2n+2
2n-1
3n
Genetic abnormality:
Monosomy
Polyploidy
Tetrasomy
Trisomy
Monosomy = 2n
Polyploidy = 3n
Tetrasomy = 2n+2
Trisomy = 2n+1
autosomal
Autosomal refers to any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome.
Autosomes carry genes that determine most of your body’s traits (like eye color, height, etc.) but not your biological sex.
Humans typically have 46 chromosomes present in their somatic cells and 44 autosomal chromosomes
where are chromosomes found
found in the nucleus of most cells inside the human body.
what are karyotypes used to determine
species.
sex
some genetic abnormalities
what is a gene
A gene is a length of DNA that contains the coded instructions for building a gene product
they encode proteins or tRNA or rRNA molecules.
genome
refers to all the genetic information in a cell, individual, or species
chromosomes are composed of
DNA and proteins