C1.3 Photosynthesis
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
photosynthesis
energy conversion process converting light energy into chemical energy in carbon compounds (carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids), supplies chemical energy needed for life processes in ecosystems
6CO2 (carbon dioxide) + 6H2O (water) -(light)→ C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2
done by plants (mainly leaves), algae, cyanobacteria; creates carbohydrates
photolysis
reaction that splits molecules of water
2H2O → 4e + 4H+ + O2
a part of the photosynthesis process that occurs in the chloroplast
only happens when light is available to provide energy
produces hydrogen needed for reduction reaction in photosynthesis that converts carbon dioxide into glucose
increases concentration of oxygen inside of chloroplasts, oxygen diffuses out of chloroplasts, out of leaf cells to air spaces inside the leaf
oxygen diffuses through stomata to air outside leaf
absorption of light
pigments - chemical substances that absorb light
white/transparent substances are not pigments
white - reflect all wavelengths of visible light
transparent - allow all wavelengths to pass through
black - pigment that absorb all wavelengths of light
other pigments absorb some wavelengths of visible light, not others
photon
particle/unit of light, discrete quantity of energy
energy related to wavelength
absorbed by pigment molecule if energy held by photon causes an electron in an atom of the pigment molecule to jump into higher energy level (excitation) - requires specific amount of energy supplied by certain wavelengths of light
chloroplasts
organelles in plants where photosynthesis occurs
chlorophylls
main photosynthetic pigments, absorbs red and blue most effectively, reflects green to avoid light fluctuation and regulate light taken in
appears green - photons in red and blue parts of the spectrum can excite an electron in chlorophyll, wavelengths in green part of the spectrum cannot, most green light is reflected
absorption spectrum
graph showing percentage of light absorbed at each wavelength of light by pigment(s)
x-axis: wavelength of light, 400 nm (violet) to 700 nm (red)
y-axis: absorption of light, can show multiple pigments on the same graph
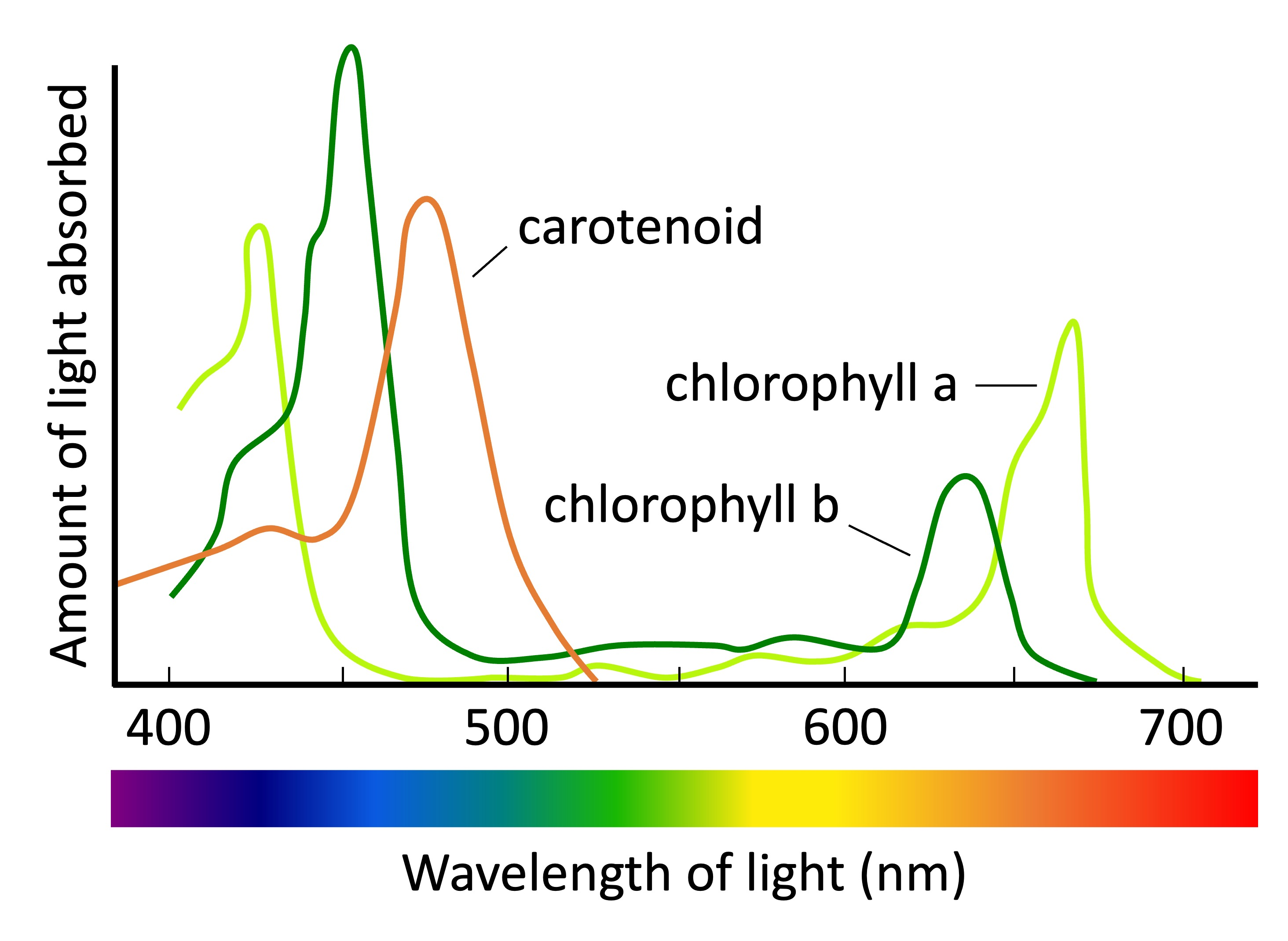
action spectrum
graph showing rate of photosynthesis at each wavelength of light
x-axis: wavelength of light, 400 nm (violet) to 700 nm (red)
y-axis: relative amount of photosynthesis, percentage of maximum rate
comparing action and absorption spectrums
similarities between curves - photosynthesis can only occur in wavelengths of light absorbed by chlorophyll or other photosynthetic pigments
differences between curves - action spectrum is less dramatic, includes photosynthesis rate considering all pigments within a plant, absorption spectrum only focuses on 1 pigment (mainly chlorophyll)
FACE experiments (free-air carbon dioxide enrichment experiments)
experiments conducted on the effect of increasing CO2 concentration on plant growth in free air because factors in experiments in labs or greenhouses differ from open conditions; circles of CO2-releasing towers and control towers
Does increased atmospheric carbon dioxide increase carbon storage within a mature woodland ecosystem?
Do mineral nutrients, especially nitrogen or phosphorus, become limiting factors on uptake of carbon?
What aspects of biodiversity, ecosystem structure, and function are altered when the ecosystem is exposed to elevated carbon dioxide levels?
How can FACE experiments be generalized to other woodlands and forests?
explain the process of photosynthesis
autotrophs perform photosynthesis
reactants CO2 and H2O required for photosynthesis
light splits water molecules/causes photolysis
releases O2 as a waste product
light energy converted to chemical energy
produces organic compounds/glucose/carbohydrates
occurs in chloroplasts
chlorophyll - photosynthetic pigment that absorbs light
different pigments absorb different wavelengths of light
chlorophyll absorbs red and blue light/ends of the spectrum
limiting factors - CO2 concentration, temperature, light intensity