APHUG CH10
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
10.1 Notes ( answer with “10.1” )
10.1
What is development?
Improving the material conditions of a country through an increase of knowledge and technology.
What is development measured with?
Economic statistics.
What is development NOT measured with?
Demographic Statistics
What are the characteristics of the Primary Sector?
Extraction of resources
Agriculture, mining, fishing
Von Thunen Model
What are the characteristics of the Secondary Sector?
Building or creating of products
Manufacturing : automobiles, textiles
Alfred Weber’s Least Cost Theory
What are the characteristics of the Tertiary Sector
Providing a service
Consumer, business, and public services
Walter Christaller’s Central Place Theory
What are the two categories of development?
MDCs and LDCs
What are the BRICS nations?
Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa
Describe BRICS Nations.
Near-developed countries
Almost MDCs
Has lots of resources
Ready to compete for global economic and global political power.
What is the HDI?
Calculation of a country’s development using three factors.
A long and healthy life
Knowledge
A decent standard of living
If a country is an MDC, what is the minimum HDI index value they can have?
Greater than 0.8
Where do the index values of the HDI range from?
1.0-0.0
What is in the UN HDI calculation?
1 Economic Factor - GNI per capita at PPP
2 Social Factors - Years of schooling for adults; Expected years of schooling for youth.
1 Demographic Factor - Life expectancy at birth
What economic indicators are part of HDI?
Income
Gross National Income - Values of all good and services produced
GNI per Capita - Amount of GNI per resident
Purchasing Power Parity - Adjusts GNI for differences in costs of goods.
Economic Structure
Primary sector - Extracting materials from earth
Secondary Sector - Manufacturing
Tertiary Sector - Sale of goods and services
Productivity
Productivity - Value of product compared to labor needed to produce it.
( Gross domestic product per number of people employed )
( GDP is a measure of goods and services produced, but does not included money that leaves and enters the country )
What social indicators are part of HDI?
Access to Knowledge
Years of Schooling for Today’s Adults - # of years average person over 25 spent in school.
Expected Years of Schooling for today’s Youth - # of years forecast an average 5 year old will spend in school.
Other Education Indicator
Literacy Rate - % of population that can read and write
Student-teacher ratio - # of students per teacher
What demographic indicators are part of HDI?
Life Expectancy - Average # of years a newborn can expect to live at current mortality rate.
10.2 Notes ( answer with “10.2” )
10.2
What is the Inequality-Adjusted HDI?
A modified version of the HDI to account for inequality within a country.
If the IHDI is less than the HDI, inequality exists.
A greater gap shows inequality.
Where are the lowest and highest scores located?
Lowest - ( HIGHEST INEQUALITY ) Sub-Saharan Africa & South Asia
Highest - ( LOWESTED INEQUALITY ) MDCs.
Who is Immanuel Wallerstein?
- American sociologist, and historical social scientist
- Created the World System Theory.
What is the World Systems Theory?
A theory that suggests the interdependency of LDCs and MDCs as a world system.
- Core nations typically being former colonial powers.
- Periphery nations are typically former colonies.
- Core nations use their privileged position to maintain inequality.
Which are Core Countries closely related to, LDCs or MDCs?
MDCs
Describe the Economy, Infrastructure, Workforce, Labor Compensation, and Job Sectors of Core Countries.
CORE COUNTRIES
Economy - Household consumption based economy.
Infrastructure - Sophisticated transportation, communication, and energy.
Workforce - Highly educated/skilled labor.
Labor Compensation - High wages, salaries, and benefits.
Job Sectors - Majority of jobs in tertiary sector.
Describe the Economy, Infrastructure, Workforce, Labor Compensation, and Job Sectors of Semi-Periphery Countries.
SEMI-PERIPHERY COUNTRIES (BRIC+)
Economy - Traditional manufacturing; some household consumption
Infrastructure - Sophisticated transportation and energy limited to cities
Workforce - Highly educated/skilled, AND low skilled labor
Compensation - Uneven; highly skilled labor paid less than in MDCs
Job Sectors - All job sectors are found in abundance
Describe the Economy, Infrastructure, Workforce, Labor Compensation, and Job Sectors of Periphery Countries.
PERIPHERY COUNTRIES
Economy - Commodity markets and resource extraction
Infrastructure - Rudimentary and/or limited transportation and energy
Workforce - Low skilled labor, many subsistence farmers
Compensation - Poorly compensated with few or zero benefits.
Job Sectors - Majority of jobs in primary and secondary sectors.
What is the GDI?
Gender Development Index
Measures the difference in development between men and women.
If the GDI score is less than 1.0, what does it imply?
Males score higher on HDI than females.
If the GDI score is more than 1.0, what does it imply?
Females score higher on HDI than males.
If the GDI score is 1.0, what does it imply?
Perfect equality between men and women..
In MDCs and LDCs, do women or men score higher on the GDI?
Males score higher in both MDCs and LDCs.
What is the GII?
Gender Inequality Index
Measures gap in reproductive health, empowerment and the labor market.
If the GII is zero, what does it imply?
Perfect equality between men and women.
If the GII is one, what does it imply?
Women fare as poorly as possible on all measures.
In what countries is the GII zero?
None. There are no countries in the world where women fare as well as men.
What statistics are used in the calculation of the GII?
Women in government - % of seats in legislatures held by women.
Women in labor market - % of adult women with a job
Secondary Schooling for Women - % of women who have completed some high school.
Adolescent Fertility Rate - Live births per 1,000 women aged 15-19.
Maternal Mortality Rate - Deaths while giving birth per 100,000 live births.
What is the percentage of women in government in LDCs and MDCs?
MDCs : 25 - 40%
LDCs : Less than 25%
What is the percentage of women in the labor market in LDCs and MDCs?
MDCs : Non-predictive
LDCs : Non-predictive
What is the global percentage of secondary schooling for women?
62% ( 71% for men )
Regarding reproductive health, are the effects of reproduction more significant for males or females?
Females.
What is the AFR in MDCs and LDCs?
MDCs - 19/1000
LDCs - 53/1000
What is the Adolescent Fertility Rate in the U.S? How does this compare to other MDCs?
21/1000. The AFR is twice as high compared to other MDCs.
How has the MMR changed in the U.S since 1990?
It has increased since 1990. ( It is one of 13 countries where it has increased. )
10.3.1 Notes ( answer with “10.3.1” )
10.3.1
Developing countries generally adapt one of two paths of development, which are they?
self-sufficiency & international trade
In the Self-Sufficiency Model, what do countries invest in?
They invest equally between all sectors/industries.
In the International Trade Model, what do countries invest in?
Limited number of industries
What happens in the Self-Sufficiency model?
Countries produce everything they need.
How would they encourage the domestic production of goods in the Self-Sufficiency model?
By implementing tariffs & protecting local businesses.
What are the two problems with the Self-Sufficiency model?
They might protect unproductive businesses. This means there is little incentive to improve quality or quantity of the produced goods.
Requires complex bureaucracy. ( which allows for increased potential for abuse and corruption, and resources being used to implement and monitor policies. )
What happens in the International Trade model?
They develop limited industries and trade for all other needs.
Who promotes and enforces international trade?
WTO ( World Trade Organization )
What does the WTO do?
Works to eliminate trade barriers between countries.
Enforces trade agreements and protects rights.
Why is the WTO criticized?
For ignoring the poor
Threatening state sovereignty
Destroying the government
What are the three problems with the International Trade model?
Reliance on a single resource/commodity
Global price fluctuations affect the entire country.
Some resources/commodities are more profitable than others.
Increasing dependence on MDCs
Lack of local businesses causes reliance on MDC imports, which are expensive.
Effects of changing in global markets
Foreign competition and market decline.
What are the Four Asian dragons?
Hong Kong, Taiwan, Singapore, South Korea
Did the Four Asian Dragons use Self Sufficiency or International Trade?
International Trade
How did the Four Asian Dragons become successful?
By first exporting cheap goods like plastic toys and progressing to goods like computer parts.
What countries are in the Arabian Peninsula?
Saudi Arabia, UAE (United Arab Emirates), Kuwait, Bahrain, Oman
How did the Arabian Peninsula become successful?
Exporting petroleum (oil).
What is likely the most Self-Sufficient country in the world?
North Korea
10.3.2 Notes ( answer with “10.3.2” )
10.3.2
What did W.W. Rostow propose?
A five stage development model of the International Trade path.
Identify and describe the stages of Rostow’s Model.
Traditional Society
Primary sector income, low income
Preconditions for Takeoff
Investments made in technology and infrastructure (energy, transportation, communications)
Takeoff
Rapid growth in a number of specialized industries.
Drive to Maturity
Increased income promotes growth in other industries.
Workers become more skilled.
Age of Mass Consumption
Shift towards manufacturing consumer goods and high-tech products.
What four things have happened as more nations choose International Trade?
Trade grew more rapidly than wealth in late 20th century
# of MDCs grew
Self-sufficiency has proven impractical in global economy.
Ex. India
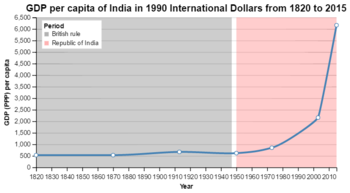
What are the THREE primary sources of financing economic development?
Foreign Direct Investment
Microfinance
Loans from International Organizations
What is Foreign Direct Investment?
Investment by a transnational corporation into a foreign economy.
A majority of FDI goes from which of the following?
A. MDC → LDC
B. LDC → MDC
C. LDC → LDC
D. MDC → MDC
D.
Where does a third of FDI to LDCs go?
China
( NOTE - Another third goes to High Development Countries. Also this is a third of LDC FDI, not all FDI. )
Where are 344/500 of the largest transnational corporations headquartered?
MDCs.
What is Microfinance?
Small loans and other financial services to those in LDCs unable to obtain loans from commercial banks.
Microfinance are a common path for _____-owned businesses in LDCs
women
What is the World Bank and International Monetary Fund?
The World Bank and International Monetary Fund is used to…
Fund government programs
Develop financial institution
Build infrastructure
Where does the money from the World Bank and International Monetary Fund come from?
Sales of bonds and government contributions.
What does the International Monetary Fund (IMF) do?
Loans to countries experiencing “balance-of-payments” problems.
Used to help indebted nations stabilized their economies
Who funds the IMF?
Funding of the IMF is donated by MDC governments.
What are the four reasons development programs may fail?
Faulty engineering
Funds are stolen or squandered
No new investment attracted
Economic Downturns (Recessions)
What is Stimulus & Austerity?
The names of the two approaches to fighting economic recessions.
Describe the Stimulus Strategy.
Government should spend to stimulate economic growth.
Describe the Austerity Strategy
Governments should reduce taxes & cut programs so the private sector can spend savings to stimulate economic growth.
Why may LDCs not have a choice between Stimulus & Austerity?
The condition of loans.
This may/will lead to…
Cuts in health, education, and social services that benefit the poor.
Elimination of jobs in government.
Less support for those in need, such as poor pregnant women, nursing mothers, young children, & elderly people.
10.4 Notes ( answer with “10.4” )
10.4