Lecture 3 - Aquatic Medicine
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
30
What percentage of fish lost are due to infectious diseases? In pet fish, this exact number is not known.
P=NV/R
What is the formula which is used to determine the probability of disease in fish? It uses P-probability, N-number of pathogens, V-virulence, and R-resistance.
Severity
As the number of pathogens present increases, what factor of disease will also increase?
Bacterial
What cause of disease in fish can appear as septicemia, hemorrhage, exopthalmia, dropsy/ascites, granulomatous inflammation, and external necrosis? Culture or pathogen-specific molecular tests are used to diagnose.
Lower
Should incubation of aquatic bacteria be done at higher or lower temperatures compared to in mammals?
Kidney, Spleen
What two organs, as well as in specific lesions, should be used for culturing bacteria in a sick/dead fish?
Secondary
Are most aquarium fish infections due to primary or secondary bacterial infections? They often lead to skin/gill lesions and progress to septicemia and most are gram - rods.
Aeromonads
What class of bacteria are the most problematic secondary infections in fish?
Flavobacterium
What genus of bacteria are an important primary pathogen in fish, include the species’ columnare and branchiophilum, and are yellow, filamentous, and found in freshwater fish?
Fresh
Are flavobacterium found in fresh or salt fish?
Columnare
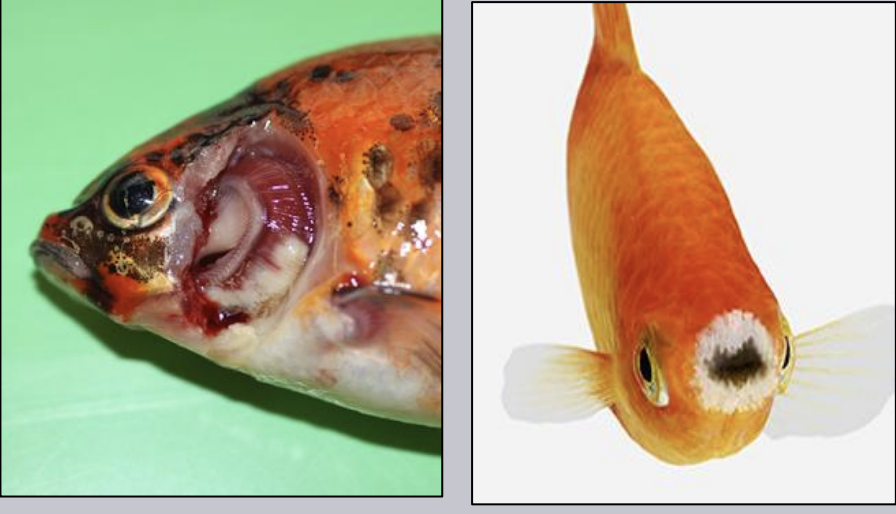
What species of Flavobacterium is also called columnaris disease, saddleback, or cotton/wool mouth? It is a warm water disease, and enters through the gills/skin causing septicemia. It is easy to diagnose using the haystack formation on microscopy and is treated with oral/injectable antibiotics. Tenacibaculum maritimum is the saltwater equivalent of it.
Branchiophilum
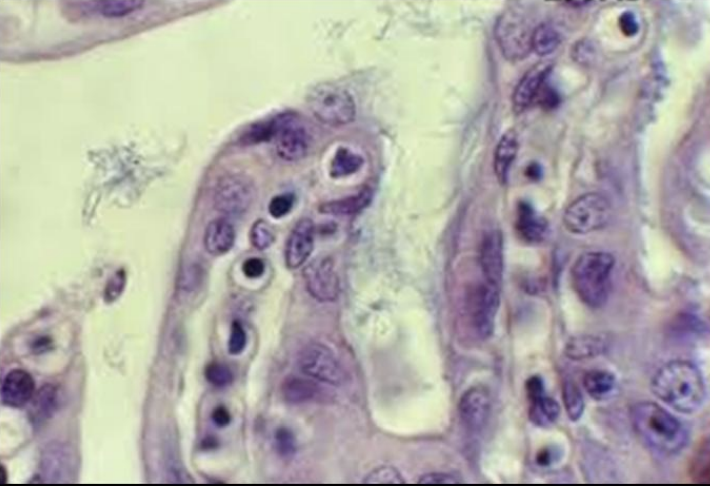
Which species of flavobacterium causes bacterial gill disease, makes a toxin, does not invade the gills themselves, and causes acute vasoconstriction? This leads to hypoxia/hyperplasia, is often seen after a stress event, and is treated with immersion in formalin or another medicine, often with instant recovery.
Francisella noatunensis
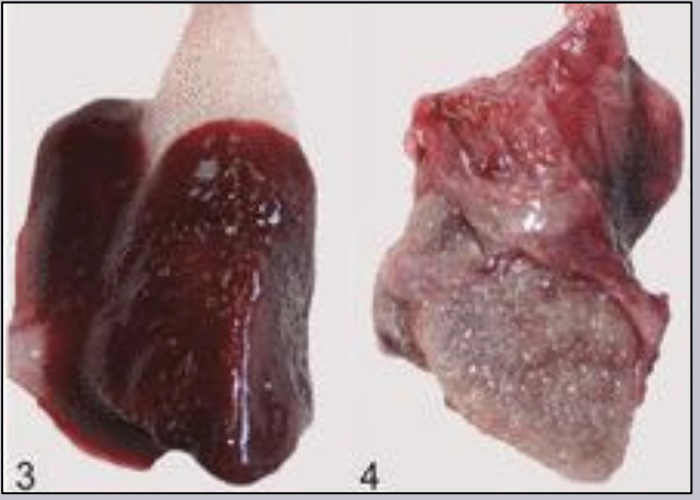
What bacteria (two names) is a primary pathogen of fish not in the flavobacterium genus? It is an emerging disease in wild/cultured fish, has the subspecies orientalis and noatunensis, is very virulent, is a facultative intracellular pathogen, forms granulomas, and difficult to treat with antibiotics.

Streptococcus
What genus of bacteria is a common primary pathogen in fish, includes the species agalactiae, iniae, dysgalactiae, and faecalis, is epizootic in wild and captive fish, is found in fresh and saltwater fish, and causes septicemia with fibrinous lesions? There will be increased bacteria loads in the brain and they are zoonotic. A wide variety of reef fish can be affected due to rainwater or temperature changes.
Vibrio
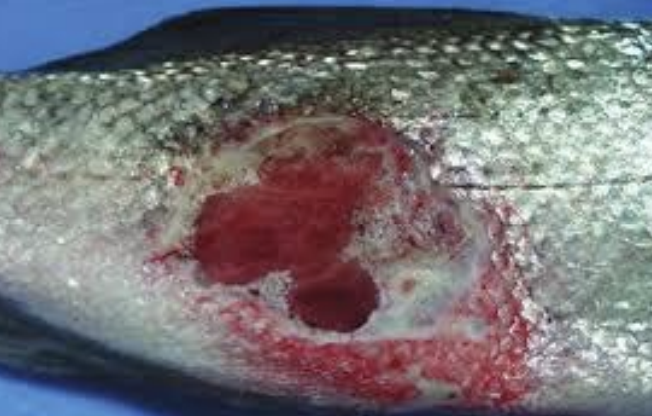
What bacteria genus is a common primary pathogen of fish, is found in saltwater fish, causes skin lesions and sepsis, is epizootic, zoonotic, and is most often seen in stressed fish?
Salt
Is vibrio found in fresh or salt fish?
Mycobacteria
What genus of bacteria is a common primary pathogen of fish, is also called fish tuberculosis, and most species of it cause chronic wasting disease? Prominent granulomas appear in individual fish and it is not usually an epizootic. Incidence is high in aquarium/lab fish and it is very difficult to remove from aquarium systems. It is also called fish handler’s disease, is zoonotic, and is removed by depopulating the tank and cleaning it.
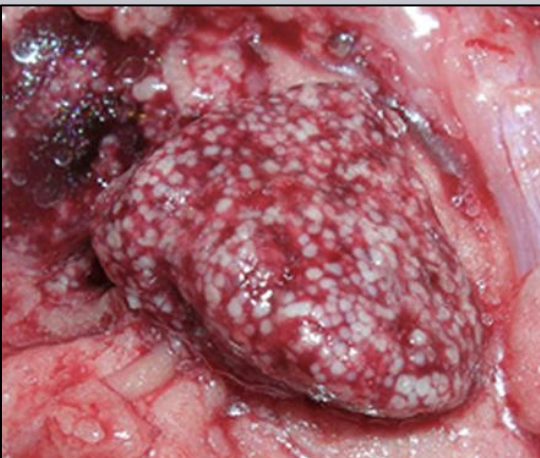
Immersion
By what method are chloramine-T and formalin used to treat fish?
Feed
By what route are florfenicol, oxytetracycline, and sulfadimethoxine used to treat fish?
30-60
About how many days (range) should new fish be quarantined before added to an aquarium?
Chloramine-T
Which drug is given by immersion to freshwater food fish for Flavobacterium in gills?
Hydrogen peroxide
Which drug is given immersion to freshwater salmonid food fish with F. branchiophilum and to cool and warm water freshwater fin foodfish for F. columnare?
Florfenicol
Which drug is given in feed to catfish for E. ictaluri, to freshwater salmonid foodfish for F. psychophilum and A. salmonicida, and to freshwater fin foodfish for F. columnare or S. iniae?
Oxytetracycline
Which drug is given in feed to freshwater salmonids foodfish with F. psychrophilum and rainbow trout foodfish for flavobacterium columnare?
Sulfa
Which drugs are given in feed to salmonid foodfish for Aeromonas salmonicida and catfish with E. ictaluri?
Broad
Are oxytetracyclines, quinolones, nitrofurans, and sulfa drugs given to fish for broad, negative, or positive bacteria?
Negative
Are aminoglycosides and cephalosporins given to fish for gram negative, positive, or broad bacteria?
Positive
Are erythromycin and penicillin given to fish for gram positive (strep), gram negative, or broad bacteria?
Opportunistic
Are aeromonas hydrophila, A. sobria, A. caviae, Pseudomonas, and Plesiomonas shigelloides primary or opportunistic pathogens?
Warm
In what type of water temperature is F. columnare mainly found?