6.4 Regulation of Sleep-Wake Patterns by Internal Biological Mechanisms
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
biological rhythms
natural, repeating cycles in the body and brain
controls physical functions and behaviours
biological clocks
internal timers that regulate rhythms
found in nearly every cell
“Master Clock”
located in the brain and coordinates all the body’s clock to keep them in sync
Circadian Rhythms
approx. 24 hours
endogenous but influenced by exogeneous cues like light, clocks, meals
e.g. sleep wake cycle, body temprature, cortisol levels
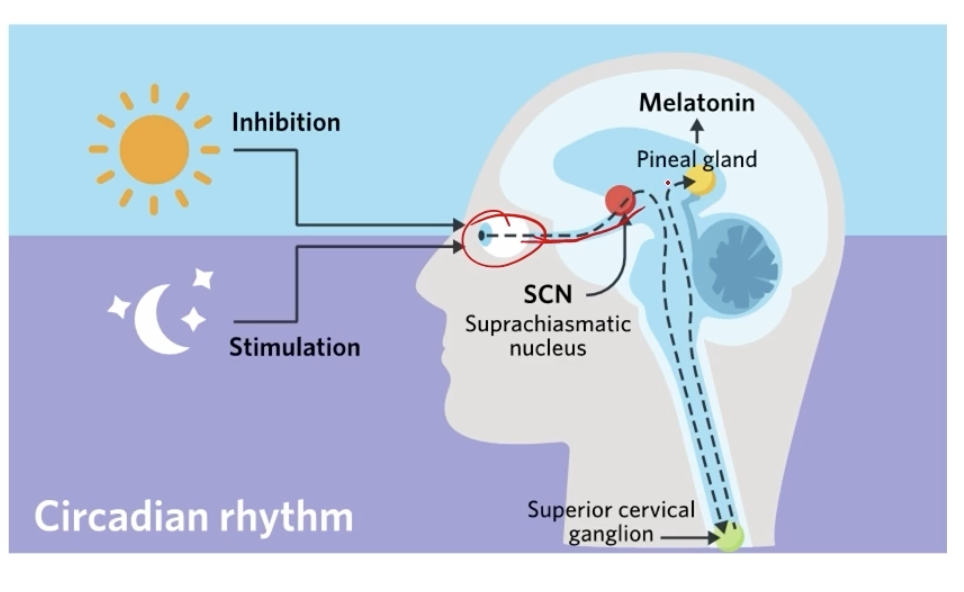
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN)
strcutre in hypothalamus that regulates an individual’s sleep-wake pattern and helps to release melatonin
controls circadian rhythm
pineal gland
responsible for the production and release of melatonin
Ultradian Rhythms
less than 24 hours
e.g heart rate, breathing, eating pattenrs, hormone bursts
sleep cycle is a key rhythm
Sleep as an ultradian rhythm
one cycle is about 90 mins
repeates 4-6 times a night
alternates between REM and NREM sleep
Suprachiasmatic Nucleaus Features
located in hypothalamus
master biological clock
recieves light info from optic nerves
sends signals to the pineal glands to control melatonin production
How does the SCN help to regulate sleep-wake cycle
light is detected by the eyes
stimulates the SCN in the brain
SCN sends signald to the pineal gland
melatonin hormone is released to the brain
Meltonin
hormone that make the brain feel sleepy
produced by the pienal gland, regulated by the SCN
more meltonin= more drowsy
less light= more melatonin
morning light= melatonin drops= wakefulnes
often referred to as “dracula of hormones”- only come out in the dark