Mycobacterium
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What are the key characteristics of the genus Mycobacterium?
Strictly aerobic, non-spore forming, curved or straight
Gram (+) rods (acid fast organism)
Forms___________that break into ______ or_____i when
disturbed
Filaments, rods, and cocci
How does the high lipid content (60% of dry weight) in the cell wall of Mycobacterium affect its properties and growth?
It makes Mycobacterium hydrophobic, slows its growth, and increases resistance to acids, disinfectants, antibiotics, and desiccation
It categorizes nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) based on their growth rate and pigment production.
Runyon’s Classification
What are the four classification under Runyon’s Classification
Group I – Photochromogenic strains
Group 2 – Scotochromogenic strains
Group 3 – Non-chromogenic strains (No pigment production)
Group 4 - rapid grower
Which group in Runyon’s classification grows slowly, produces a yellow pigment when exposed to light, and causes skin ulcers and pulmonary diseases in humans?
Group I – Photochromogenic strains
Which group in Runyon’s classification grows slowly, forms an orange-yellow pigment in both light and dark, and is usually considered saprophytic?
Group 2 – Scotochromogenic strains
Which group in Runyon’s classification grows slowly, does not produce pigments, forms smooth colonies resistant to isoniazid, is highly pleomorphic with filamentous forms resembling Nocardia, and causes pulmonary diseases in humans?
Group 3 – Non-chromogenic strains
Which group in Runyon’s classification consists of rapid growers that mature in less than one week at 25 to 37°C?
Group 4 – Rapid growers
Which Mycobacterium species is pathogenic for humans and is found in meat and milk?
Mycobacterium bovis
Which Mycobacterium species causes Johne’s disease in cattle?
Mycobacterium paratuberculosis
Which Mycobacterium species is commonly found in eggs and meat?
Mycobacterium avium
Which Mycobacterium species causes bovine farcy in tropical countries?
Mycobacterium farcinogenes
Which Mycobacterium species affects humans, primates, dogs, pigs, and cattle?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Most frequently used media in Mycobacterium?
Dorset’s, Stonebrink’s w/ egg yolk
How many week does Mycobacterium spp does needed?
Usually 6-8 weeks, depends on the species
What is the appearances of colonies Mycobacterium in media?
Colonies appear minute dull flakes, progressing into dry irregular masses
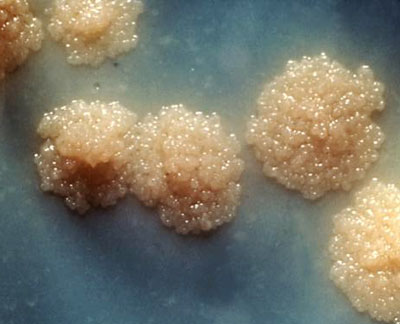
Mycobacterium color changes from light yellow to ______/____ upon light exposure
deep yellow/brick red
In fluid medium, we used _____ to separate the organism?
Tween 80
Which part of the bacteria does antigens found in mycobacterium?
Cell wall, which composed of 3 lipids
What are the three lipids found in the cell wall of mycobacterium?
mycosides (glycolipids), waxes D (mycolic acid), cord factor (trehalose 6,6 dimycolate)
Which component released into the medium by Mycobacterium tuberculosis is used for diagnostic testing?
Tubercuoprotein/Tuberculin
What are the principal modes of transmission for Mycobacterium infections?
Aerogenous (Airborne)
Milkborne
Congenital (Primary complex in young animals)/sexually transmitted
What is the natural primary host of the Mycobacterium?
Cattle
What is unique about Mycobacterium tuberculosis in terms of toxin production and extracellular virulence factors?
It produces no toxins or extracellular virulence factors.
How does Mycobacterium evade intracellular digestion by immune cells?
It prevents lysosome-phagosome fusion, inhibiting intracellular digestion (antifusion effect).
How does Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection progress in the body?
Tubercles (aggregates of macrophages, lymphocytes, and leukocytes) form at the primary infection site, then spread to lymph nodes and metastasized sites.
What are the common sites of Mycobacterium lesions in swine?
Lymph nodes of the head, neck, and abdomen
What are the common sites of Mycobacterium lesions in horses?
Pharyngeal region, mesentery, lungs, liver, and spleen
What are the common sites of Mycobacterium lesions in sheep and goats?
Mainly pulmonary, progressive in young kids
What are the common sites of Mycobacterium lesions in cats?
Abdominal organs and lungs
How are macrophages activated in response to Mycobacterium infection?
lymphokines from T-lymphocytes
Does immunity completely eliminate Mycobacterium from the body?
No, some organisms remain
How long do T-lymphocytes remain sensitized after infection?
For life
What staining method we used to identify the capsule of Mycobacterium?
Ziehl-Neelsen staining, which is a acid fast staining
What are the characteristic lesions found at necropsy in Mycobacterium infections?
Primary lesions in the lungs
This test was used to “identify the species of Mycobacterium” using animals?
Animal inoculation
What are the three animals that we used in animal inculcation?
Guinea pig, Rabbit, and chicken
Result from animal inoculation (Guinea pig (+), Rabbit (+/-), Chicken (0) which species of mycobacterium is most likely is involved?
M. tuberculosis
Result from animal inoculation (Guinea pig (+), Rabbit (+), Chicken (0) which species of mycobacterium is most likely is involved?
M. bovis
Result from animal inoculation Guinea pig (+/-), Rabbit (+), Chicken (+) which species of mycobacterium is most likely is involved?
M. avium
Which test we used for mycobacterium to test the potency of bacteria?
Tuberculin test
Where are the site of injection for Tuberculin test?
Caudal fold, lip of vulva, side of the neck
Among the three site of injection (Caudal fold, lip of vulva, side of the neck)? which one is more sensitive?
side of the neck
What is the comparative test used to differentiate between avian and mammalian Mycobacterium?
Comparative tuberculin test
What does BCG stand for in Mycobacterium diagnostics?
Bacillus of Calmette and Guérin
What are some diagnostic tests used for Mycobacterium infections?
Ophthalmic test, thermal test, and Stormont test
What is the procedure for the Stormont test?
Two injections, examined 7 days later
Which Runyon’s classification does M. avium belong?
Runyon’s Group 3
What are the colony characteristics of Mycobacterium avium?
Soft, moist, yellow, turning pinkish with age and light exposure
What are the morphological characteristics of Mycobacterium avium?
Highly variable, strongly acid-fast, and alcohol-fast
What serotype is present in M. avium especially in chicken ?
Serotype 1 & 2
How many serotypes are included in the Mycobacterium intracellulare complex?
Serotypes 1-21
What is the natural host of Mycobacterium avium?
Birds
Which serotypes of Mycobacterium avium are virulent for chickens?
Serotypes 1, 2, and 3
How does avian tuberculosis progress in birds?
Slow progression, rare in birds younger than 1 year
What are the characteristic lesions of avian tuberculosis?
Caseous lesions in the intestines, liver, and spleen
What is the impact of Mycobacterium avium on cattle?
Minimal lesions but sensitizes to avian/mammalian tuberculin
How does Mycobacterium avium affect swine?
Lesions in mandibular and mesenteric lymph nodes
What types of immunity are involved in Mycobacterium avium infections?
Both cell-mediated and humoral immunity
What are the diagnostic methods for Mycobacterium avium?
Ziehl-Neelsen staining