A+P II Chp 25 (pt 2): Urinary System
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What are 5 kidney functions?
1) removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, excess ions from blood
2) regulation of BV, chemicals, and pH
3) gluconeogenesis during fasting
4) endocrine functions: renin and erythropoietin
5) activation of vit D
How does each contribute to the endocrine function of the kidney?
a) renin
b) erythropoeitin
a) regulates BP
b) regulates RBC production
What does high resistance in afferent and efferent arterioles cause?
BP to decline from ~95 mmHg to ~8mmHg in kidneys
What is filtrate made up of?
blood plasma minus proteins
For urine,
a) how much of the total filtrate does it make up
b) what does it contain
a) <1%
b) metabolic wastes + unneeded substances
What are the 3 mechanisms of urine formation?
1) glomerular filtration: dumping everything
2) tubular reabsorption: removes stuff from urine (reclaiming in blood)
3) tubular secretion: adds stuff to urine
Glomerular filtration is a passive mechanical process driven by ____________________.
hydrostatic pressure
Why is the glomerulus a very efficient filter? (2 reasons)
1) its membrane is very permeable with a large SA
2) glomerular BP is higher than other capillaries
Molecules >5nm, like ______________, are not filtered and function to maintain ____________________ of the blood.
plasma proteins; colloid osmotic pressure
What is the net filtration pressure (NFP)?
the pressure responsible for filtrate formation (10 mmHg)
Which 3 forces determine NFP?
1) chief force: glomerular hydrostatic pressure (HPg)
2) opposing force: colloid osmotic pressure (OPg)
3) opposing force: capsular hydrostatic pressure (HPc)
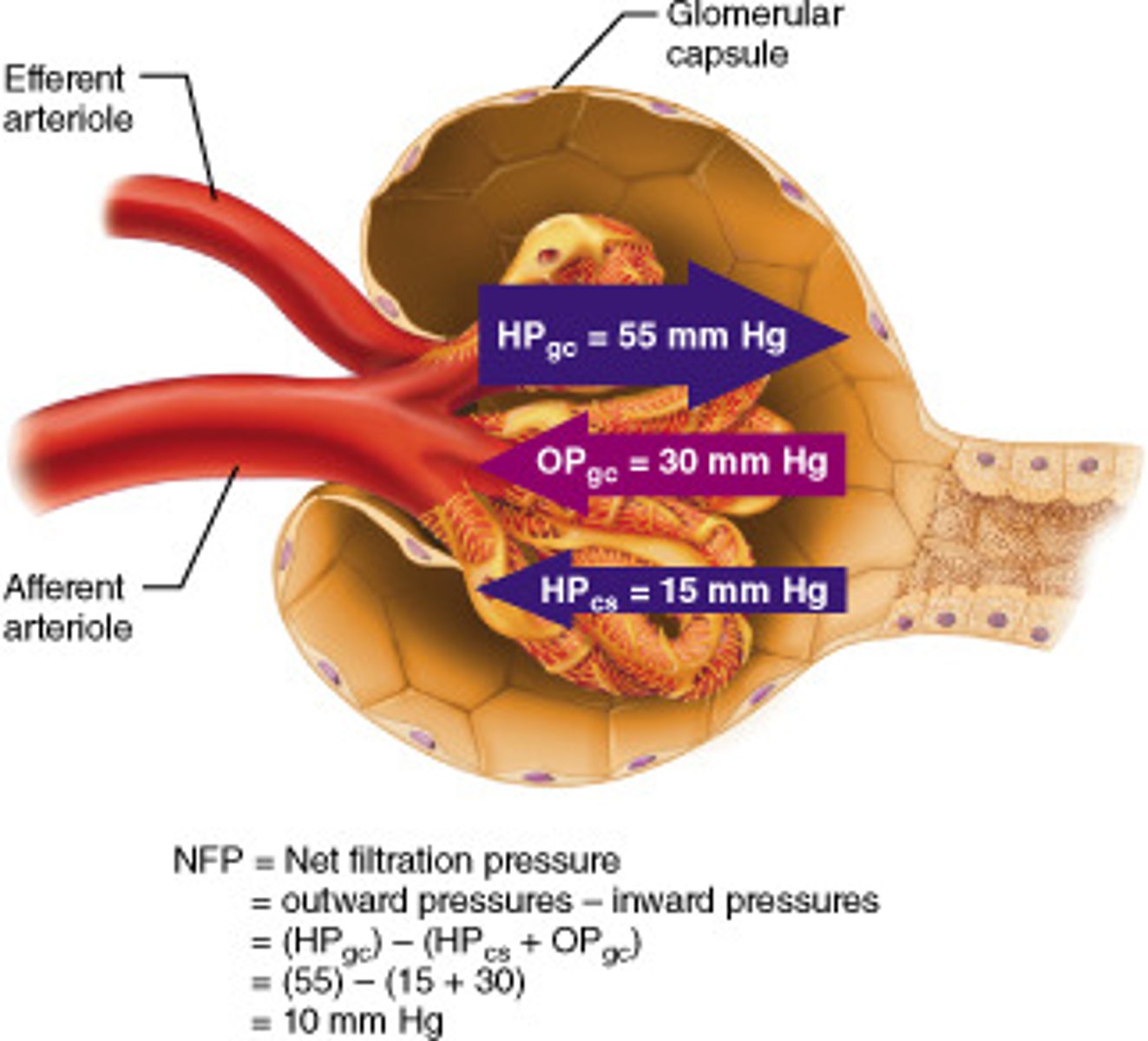
What is the pressure of each force?
a) HPg
b) OPg
c) HPc
a) 55mmHg
b) 30mmHg
c) 15mmHg
What is the equation to determine NFP (and solve it)?
1) NFP = HPg - (OPg + HPc)
2) NFP = 55 - (30 + 15)
3) NFP = 10mmHg
What would happen if the glomerular hydrostatic pressure (HPg) were less than 55 mmHG?
the glomerulus would have trouble pushing blood/fluids (or can't push fluids at all if less than 45mmHg)
What is the glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
volume of filtrate formed per minute by the kidneys
What 3 things is the GFR governed by (and directly proportional to - meaning if it's greater, then GFR is greater)?
1) total SA available for filtration
2) filtration membrane permeability
3) NFP
GFR is tightly controlled by which 2 types of mechanisms?
1) intrinsic controls (renal autoregulation): within the kidney
2) extrinsic controls: nervous and endocrine mechanisms
Intrinsic controls maintain a nearly constant GFR. What are the 2 types of renal autoregulation?
1) myogenic mechanism: regulated by muscles in blood vessels
2) tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism: senses changes in the JGA
Regarding the myogenic mechanism, what happens when...
a) BP increases
b) BP decreases
a) afferent arterioles constrict --> less blood flow --> lower GFR/NFP to normal
b) afferent arteriole dilate --> more blood flow --> raise GFR/NFP to normal
What happens in tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism?
macula densa senses the NaCl concentration of the filtrate + regulates the vasodilation/constriction of afferent arteriole
Regarding the tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism, what happens when...
a) NaCl conc is high
b) NaCl conc is low
a) more salt --> high GFR --> macula densa constricts afferent arteriole
b) less salt --> low GFR --> macula densa dilates afferent arteriole
What are the 2 mechanisms of extrinsic control?
1) neural mechanism: sympathetic control
2) hormonal mechanism: renin-angiotensin mechanism
Which mechanism (intrinsic or extrinsic) is GFR controlled by in each situation?
a) sympathetic NS is at rest
b) sympathetic NS is active/under stress
a) intrinsic controls: blood vessels dilated
b) extrinsic controls: blood vessels constrict
Under stress,
a) which 2 hormones are released
b) what do afferent arterioles do
a) norepinephrine + epinephrine (from adrenal medulla)
b) constrict and inhibit filtration
What happens if someone is under too much stress (such as having a surgery)?
too much constriction --> kidneys shut down --> dialysis needed to keep person alive until they're stable
What are the steps of the renin-angiotensin mechanism?
1) JG cells release renin
2) renin: angiotensinogen to angiotensin I
3) angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE): angiotensin I to angiotensin II
What 2 things does angiotensin II do?
1) causes systemic and glomerular hydrostatic pressure to rise
2) releases aldosterone
What are 3 methods of tubular reabsorption?
1) ATP: primary and secondary
2) passive transport: diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis
3) water + ion reabsorption: controlled by hormones
What are the 2 routes of tubular reabsorption? (from lumen into blood)
1) transcellular: across cell
2) paracellular: between cells
What is the transcellular route? (4 steps)
1) apical membrane of tubule cells
2) cytosol of tubule cells
3) basolateral membrane of tubule cells
4) endothelium of peritubular capillaries
What is the paracellular route?
What are some molecules that take this route?
- between cells
- limited by tight junctions, but leaky in proximal nephron
- water and some ions get reabsorbed in the PCT
What are 3 things that get reabsorbed?
1) all nutrients: glucose + amino acids
2) ions
3) water
_____ is the most abundant cation in filtrate.
Na+
How is Na+ transported across the...
a) apical membrane
b) basolateral membrane
a) secondary active transport
b) primary transport via Na+-K+ ATPase pump: maintains sodium gradient
How are glucose, amino acids, ions, and vitamins reabsorbed by the kidneys? (4 steps)
1) sodium gradient created
2) low intracellular Na+
3) nutrients cotransported with Na+ into cell (secondary active transport)
4) facilitated diffusion out of cell to peritubular capillaries
How is water reabsorbed by the kidneys? (3 steps)
1) movement of Na+/other solutes creates osmotic gradient
2) goes through aquaporins: water-filled pores
3) water is reabsorped passively to peritubular capillaries
What are the 2 types of passive tubular water reabsorption and where does each occur?
1) obligatory water reabsorption: PCT
2) facultative water reabsorption: collecting ducts
Are aquaporins present in the...
a) PCT
b) collecting duct
a) always present
b) absent; inserted only when ADH is present (ex: during dehydration)
How are solutes reabsorbed by kidneys? (3 steps)
1) as water is reabsorbed, solute conc in filtrate increases
2) a concentration gradient is created for solutes
3) osmotic/solute drive: passive reabsorption to peritubular capillaries
How are other substances - such as fat-soluble substances, urea, lipid-soluble drugs - reabsorbed by the kidneys?
- passively
- they go down concentration gradients + follow water into peritubular capillaries
What is the transport maximum (Tm)? What is this due to?
- when no more of a particular substance can be reabsorbed
- transcellular proteins are specific and limited
When carriers (transport proteins) are saturated...
a) where does the excess go
b) give an example
a) urine
b) hyperglycemia: too much glucose in blood, so glucose remains in urine (no more can be reabsorbed)
The ______ is the site of most absorption in the nephron.
PCT
What are 4 things the PCT reabsorbs?
1) all nutrients: glucose and amino acids
2) 65% of Na+ and H2O
3) many ions
4) uric acid and urea
What are the reabsorptive capabilities of the...
a) descending limb
b) ascending limb
a) H2O leaves (reabsorbed), solutes stay
b) H2O stays, solutes leave (reabsorbed)
What does each segment of the ascending limb have?
a) thin segment
b) thick segment
a) passive Na+ movement
b) Na+-K+-Cl- symporter and Na+-H+ antiporter
The reabsorption of the DCT and collecting duct are ____________ regulated.
hormonally
Which 3 hormones regulate the DCT and collecting duct and what does each regulate?
1) antidiuretic hormone (ADH): water
2) aldosterone: sodium (therefore water)
3) PTH: calcium
Regarding the antidiuretic hormone (ADH),
a) what gland is it released by
b) what does it cause
c) what happens as ADH levels rise
a) posterior pituitary gland
b) principal cells of collecting ducts insert aquaporins in apical membranes: facultative water reabsorption
c) increased water reabsorption
Regarding aldosterone,
a) which parts of the nephron does it target
b) what does it promote
c) what are some of its functions
a) principal cells of collecting ducts + DCT
b) synthesis of apical sodium channels + basolateral Na+/K+ ATPases: Na+ and water reabsorption
c) increase Na+ and water, decrease K+
Regarding the atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP),
a) what releases it
b) what does it cause
a) cardiac atrial cells due to high BV/BP
b) less blood Na+: decreased BV/BP
The parathyroid hormone acts on _________ to increase __________ reabsorption.
DCT; Ca2+
Almost all tubular secretion occurs in the ___________.
PCT
What are some selected substances that are secreted?
K+, H+, NH4+, creatine, organic acids and bases
What is the pathway of tubular secretion? (3 steps)
1) peritubular capillaries
2) tubule cells: can synthesize substances like HCO3-
3) filtrate
What are 4 important functions of tubular secretion?
1) disposing drugs and metabolites
2) eliminating urea and uric acid
3) getting rid of excess K+
4) controlling blood pH
How does the nephron get rid of excess K+? (2 steps)
1) reabsorbed in PCT
2) secreted by aldosterone in DCT and collecting duct
What does the nephron do if...
a) pH decreases
b) pH increases
a) secrete H+ and reabsorb HCO3-
b) reabsorb H+ and secrete HCO3-