Hematology Lab Practical #1
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Describe an adequately prepared peripheral blood smear.
The smear should:
Cover 2/3 of the slide
Feather shaped
Take the width of the slide w edges visible
How long can a blood smear be made from an EDTA tube at room temperature?
No more than 5 hours
What happens to blood in EDTA tubes if left at room temperature for more than 5 hours.
Red cells appear to be echinocytes
White cells can develop denatured or necrobiotic nuclei and vacuoles in the cytoplasm
Platelets can clump or agglutinate
How do you perform a WBC estimate?
Scan aprox 6-8 fields in good area of peripheral smear
Count WBCs and average based on #of fields.
At 10x multiply WBC seen by 200
If 40x multiply WBC seen by 2,000
Reported as WBC/uL
EX 10X: 34+31+33+37+32+35 = 202/6 = 33.67 X 200 = 6,733.33 WBC/uL
When performing a WBC estimate if examining the slide at 10x what do you multiply your avg # of fields by?
200x
When performing a WBC estimate if examining the slide at 40x what do you multiply your avg # of fields by?
2000x
How do you perform a Platelet Estimate?
Performed at 100X
Scan approx. 5-10 fields and count the number of Platelets
Multiple the average number of Platelets seen by 20,000
Reported as PLT/uL
Ex: Avg: 15+18+13+17+20= 83/5 = 17 x 20,000 = 340,000 platelets per uL
What power do you use for a PLT estimate? What do you multiply your count by?
100x
Multiply the average by 20,000
PLT/uL
What is the height and width of the hemacytometer?
3mm
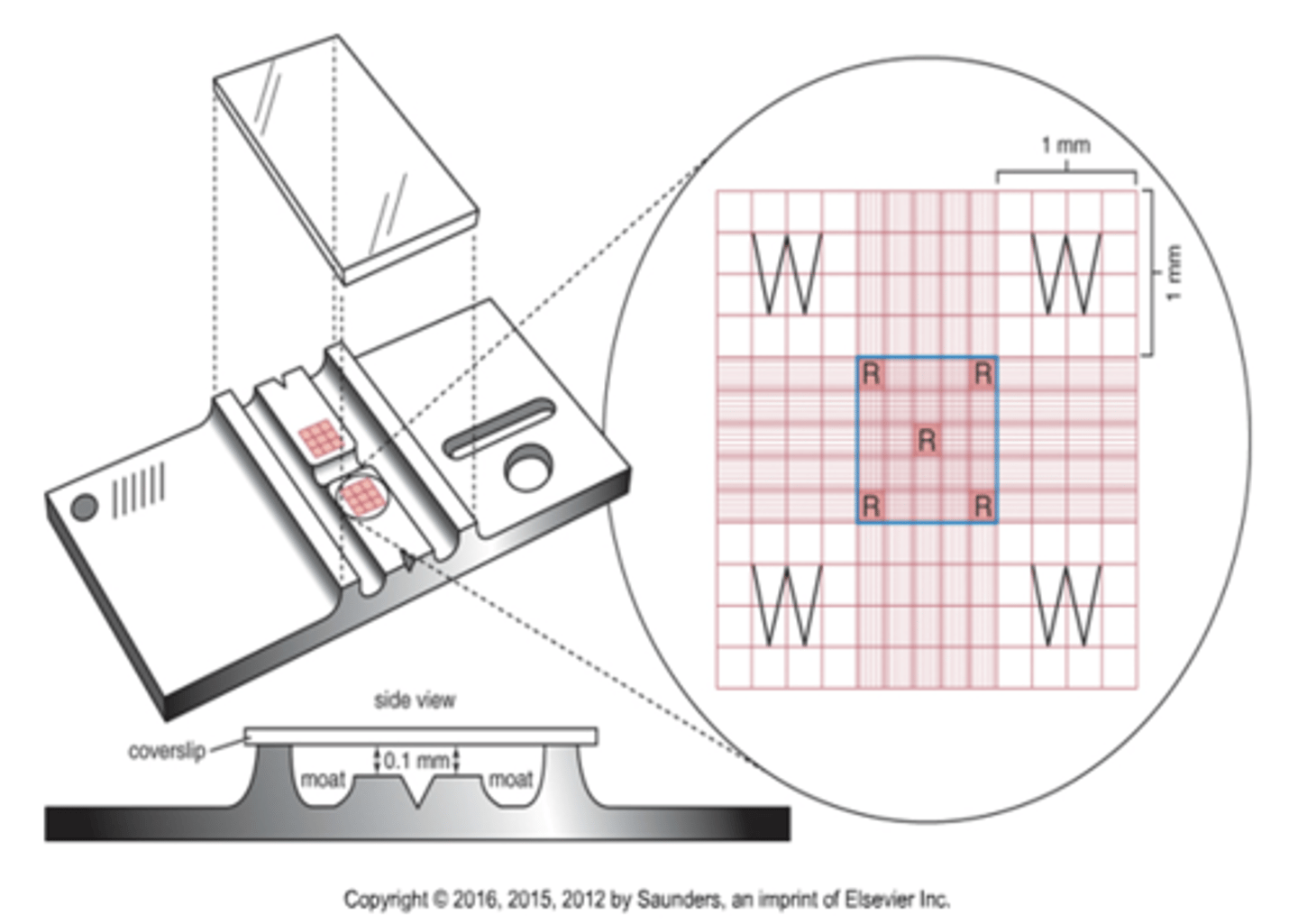
What is the size of the large squares on the hemacytomer?
1mm
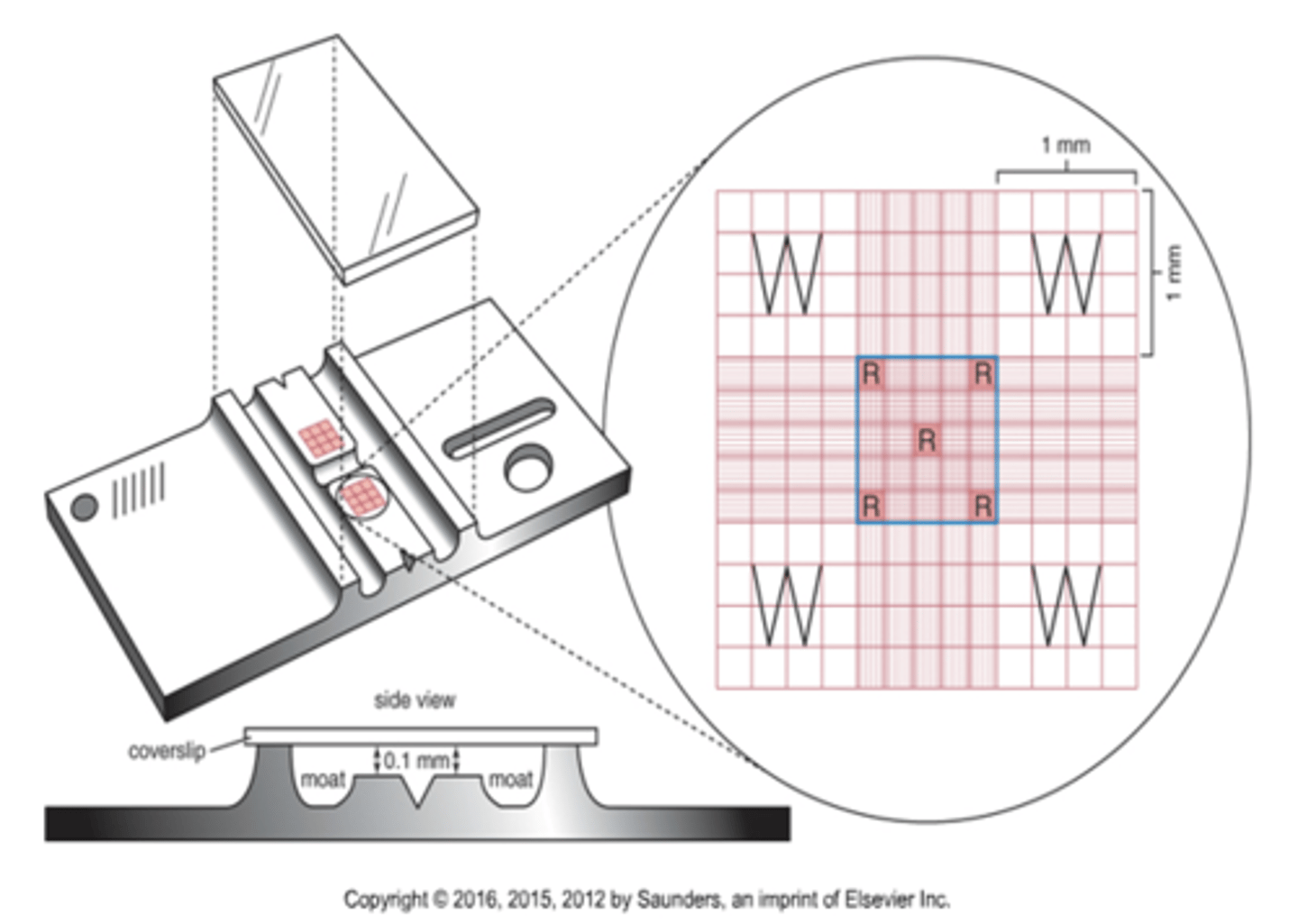
What is the depth of the hemacytometer?
0.1mm
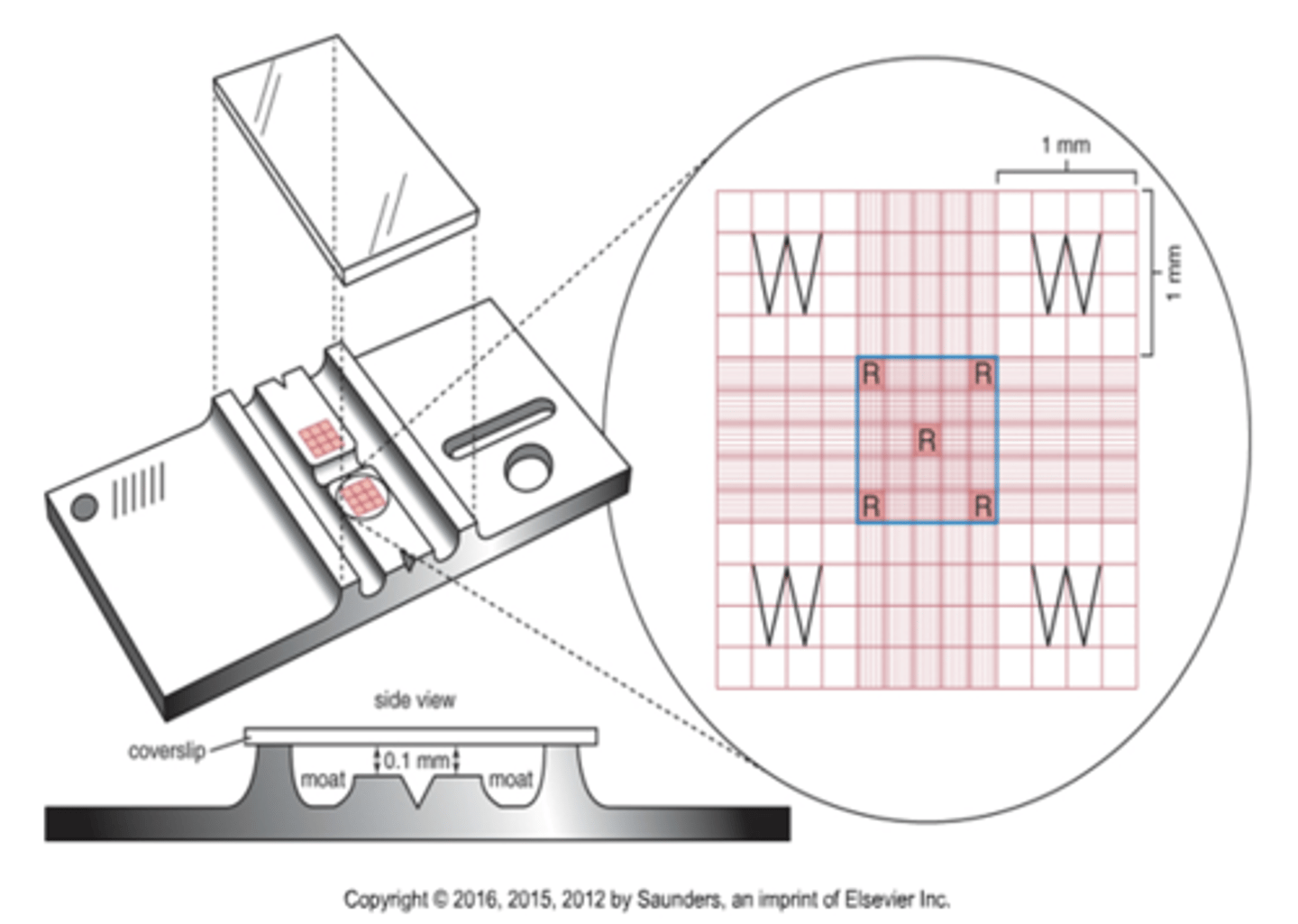
What is the total volume of the hemacytometer?
9mm2 x 0.1mm = 0.9mm3
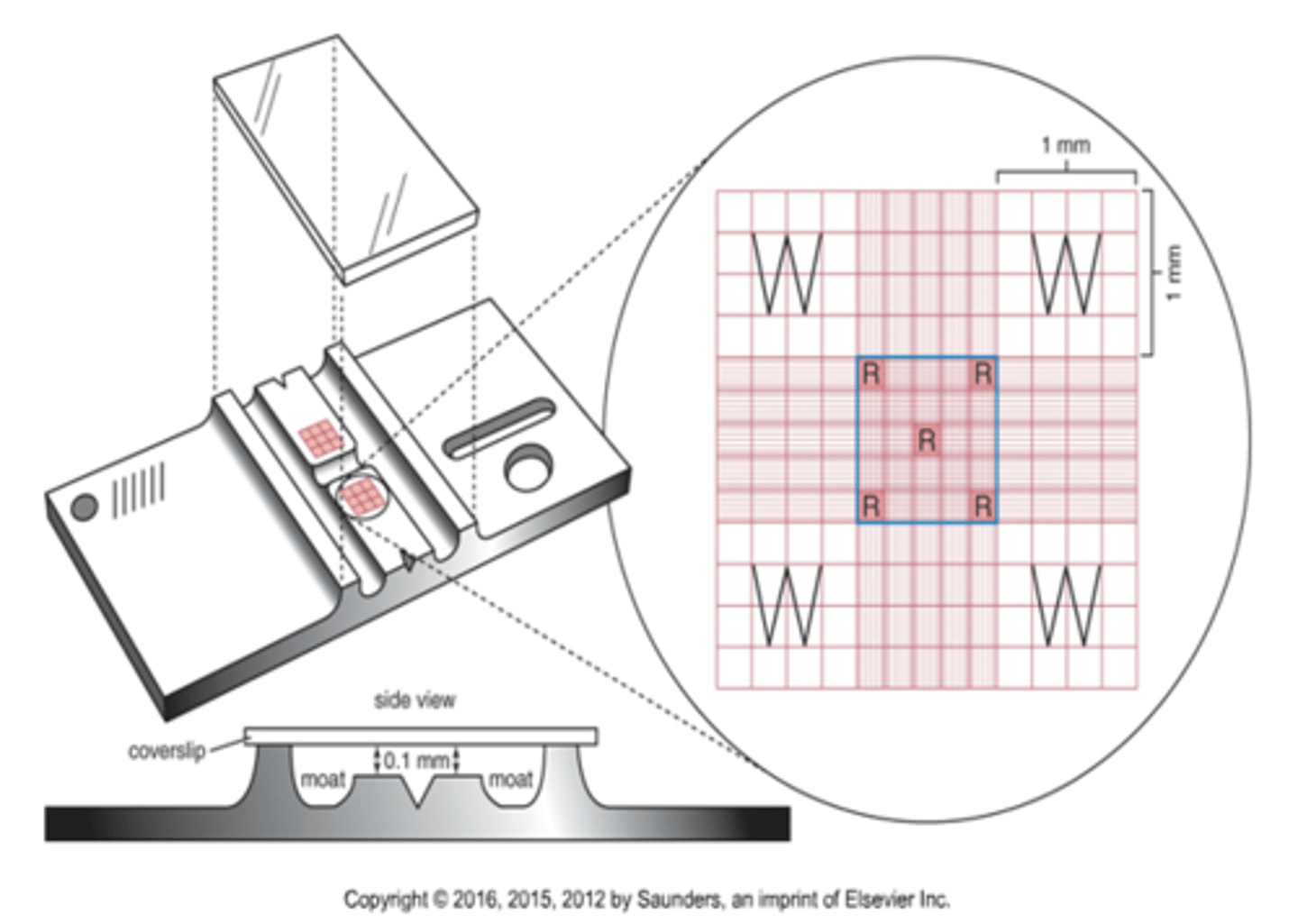
Where are the white cells counted on a hemacytometer?
What are the dimensions of this area?
The 4 white corners of the hemacytometer.
The dimensions are 1mm^2
Where are the platelets counted on a hemacytometer?
What are the dimensions of this area?
The center square (all 25 smaller squares)
1mm^2
Where are the red cells counted on a hemacytometer?
What are the dimensions of this area?
The center square (all 25 smaller squares)
1mm^2
What is the formula for a manual WBC cell count calculation?
#cells x dil factor x depth (10)
_________________
Areas counted
= WBC/uL
During a manual WBC cell count - how close should the counts be on each side of the chamber?
+/- 10%
If WBC counts are 14 or less does the +/- 10% rule apply?
No
Correction for presence of Nucleated RBC in WBC count formula
Corrected WBC = (uncorrected WBC x 100) / (# nRBC + 100)
When does a corrected WBC count need to be preformed?
When there are 5 or more NRBCs on the differential regardless of age
What is the normal amount of nucleated red blood cells in an adult? In a newborn?
Adult: 0
Newborn: <25 per 100
Normal WBC Count
3.6-10.6 x 10^3 / uL
Normal RBC count for adults male/femal
Male: 4.2-6 x 10^6 / uL
Female: 3.8-5.2 x 10^6 / uL
Normal Platelet Count
150,000-450,000 / uL
Normal HGB for adult male/female
Male: 13.5-18 g/dL
Female: 12-15 g/dL
Normal HCT for adult male/female
Male: 40-54%
Female: 35-49%
Normal MCV range
80-100 fL
Normal MCH
26-34 pg
Normal MCHC
32-38 %
Relative % of Neutrophil bands and segs in WBC differential
Bands 0-5%
Segs 50-70%
Relative % of Lymphocytes in WBC differential
18-42%
Relative % of Monocytes in WBC differential
2-11%
Relative % of Eosinophils in WBC differential
1-3%
Relative % of Basophils in WBC differential
0-2%
Calculation of absolute values
WBC x % cell line = cells/uL
Ex: WBC count of 2.0 x 10^3 / uL
80 neutrophils
absolute 2,000 x .80 = 1,600 neutrophils / uL
How is Neutrophenia / Neutrophilia or Lymphopenia / Lymphophilia determined?
Using the calculation of abosolute values.
In the previous example the PT has relative neutrophilia because of the relatively high percentage of neutrophils.
However, the absolute count is below reference range so the PT has absolute neutrophilia
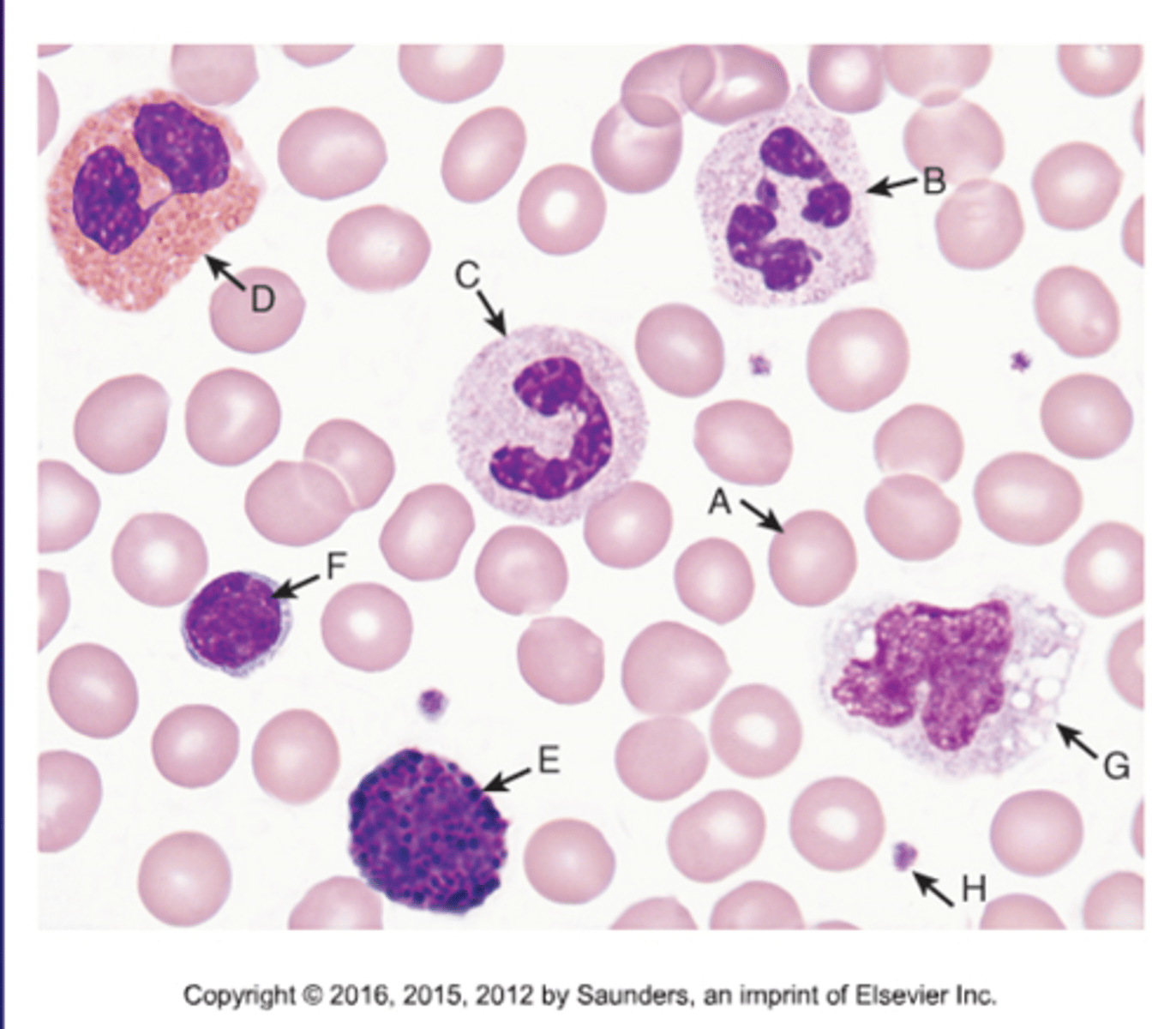
Normal WBC Identification
A.Normal RBC
B.Segmented Neutrophil
C.Banded Neutrophil
D.Eosinophil
E.Basophil
F.Lymphocyte
G.Monocyte
H.Platelet
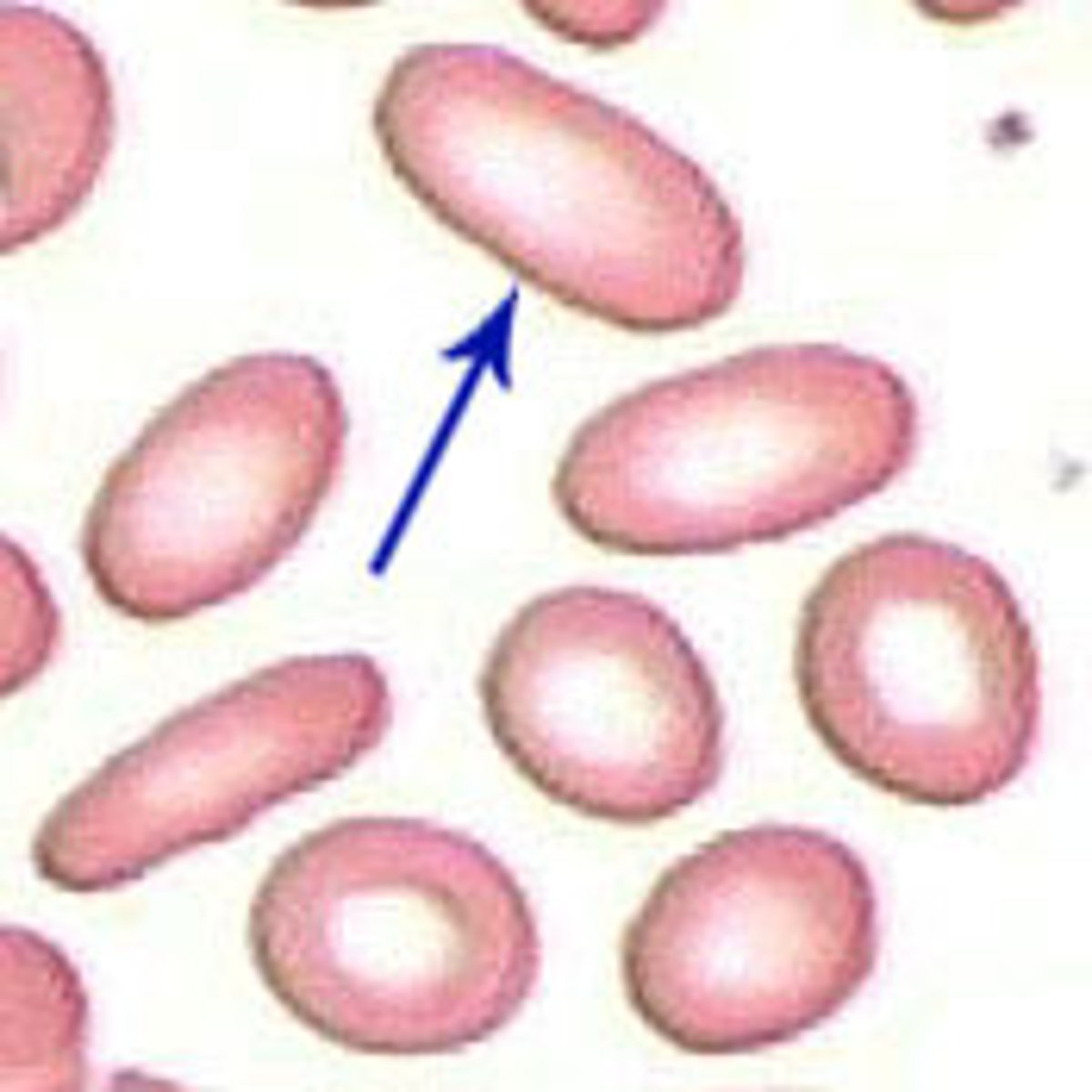
Ovalocyte + cause
altered membrane
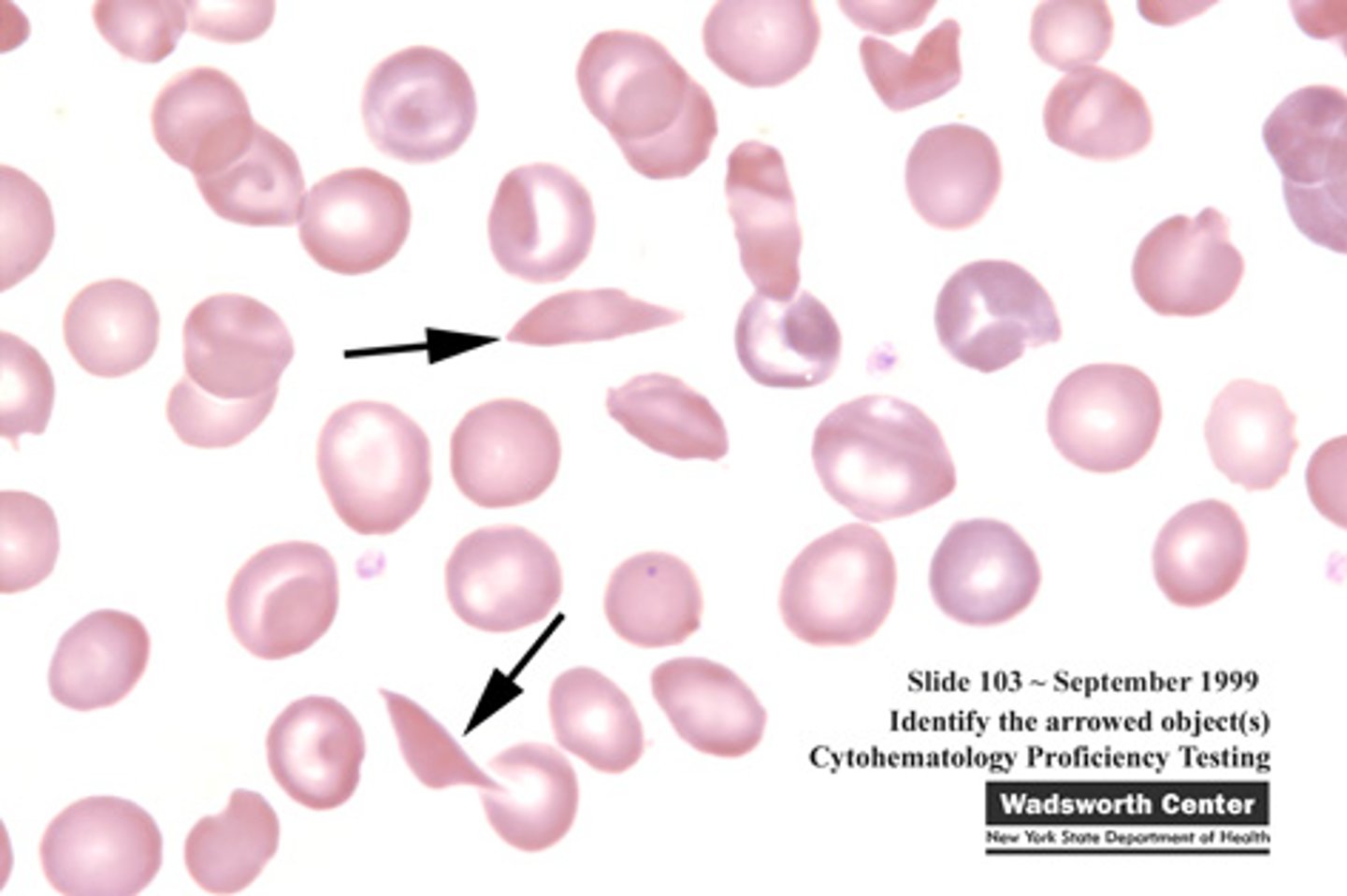
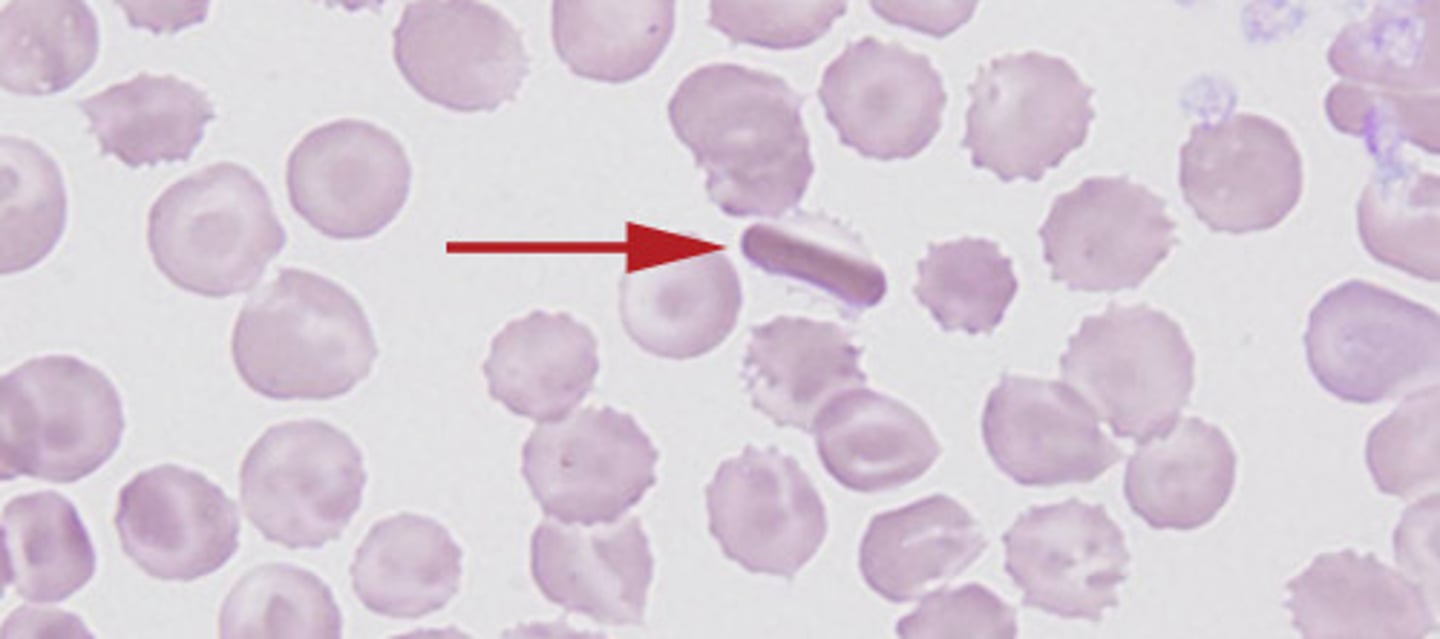
Sickle Cell + cause
Abnormal globin chain structure caused by 1 single amino acid rearrangement
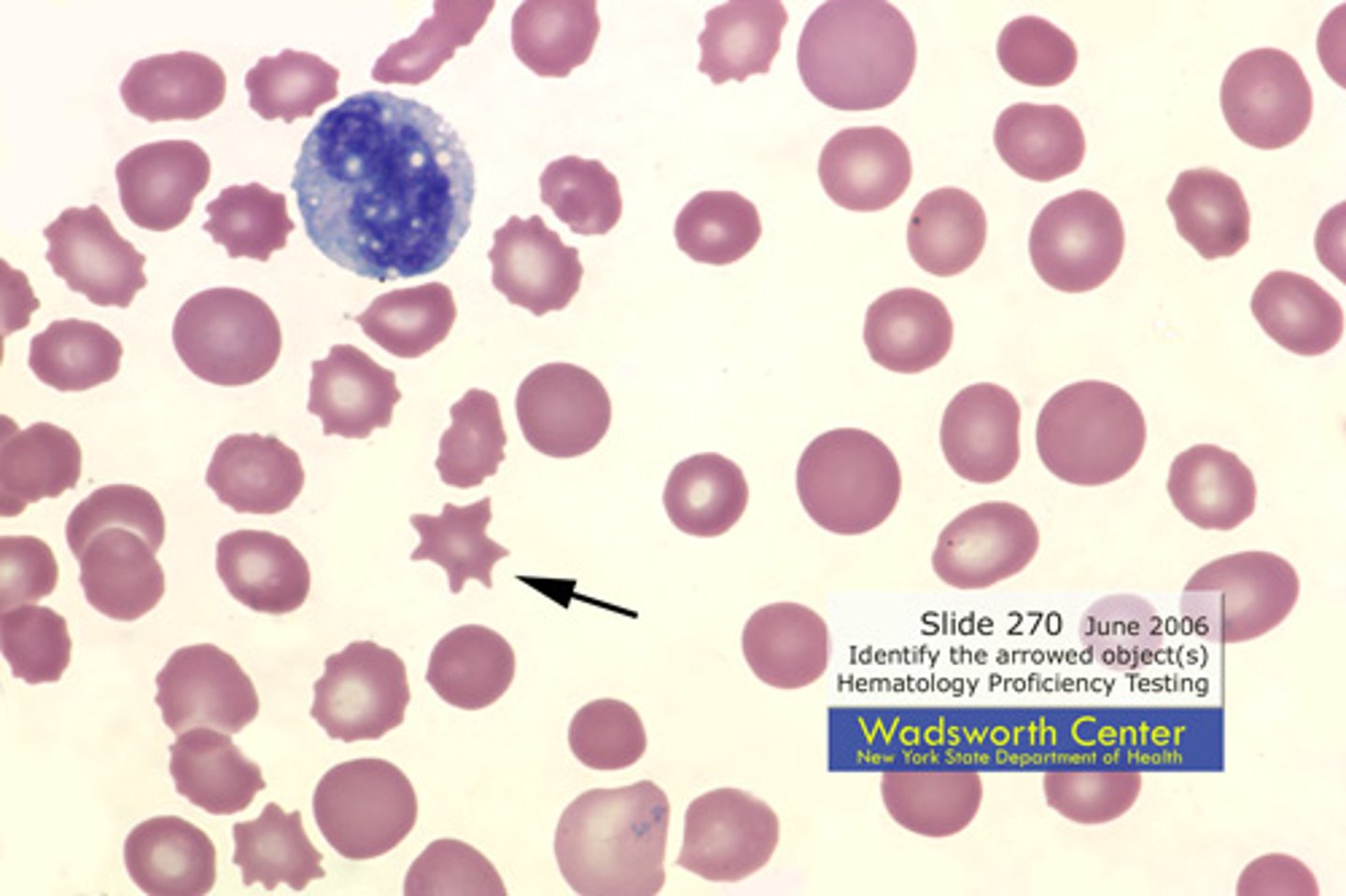
Acanthocyte + cause
Increased cholesterol
alphabetical less spikey
Echinocyte + cause
cation imbalance, change in toxicity
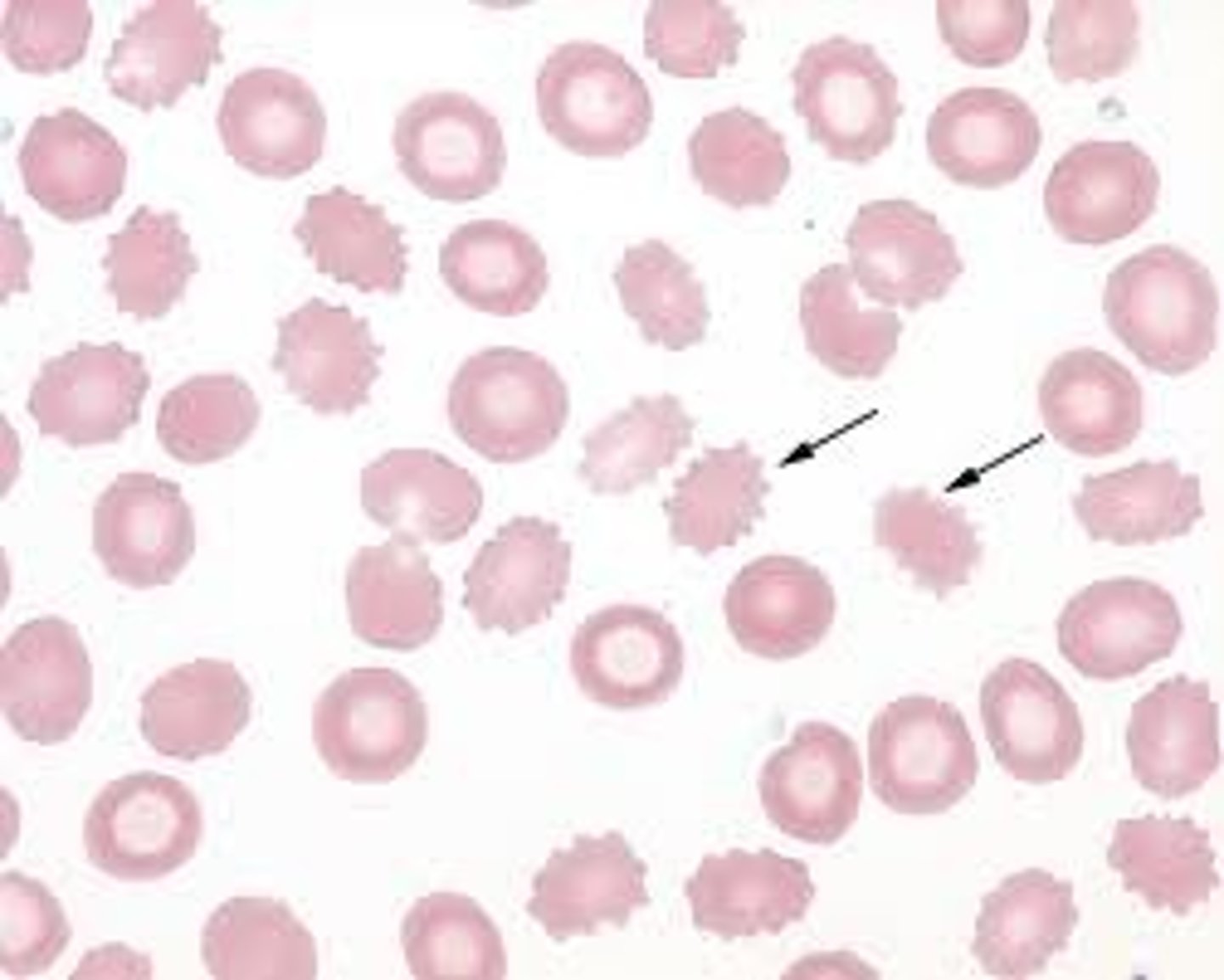
Schistocyte + cause
fragmented by fibrin
shistocyte! its the devil! fragmented by fibrin
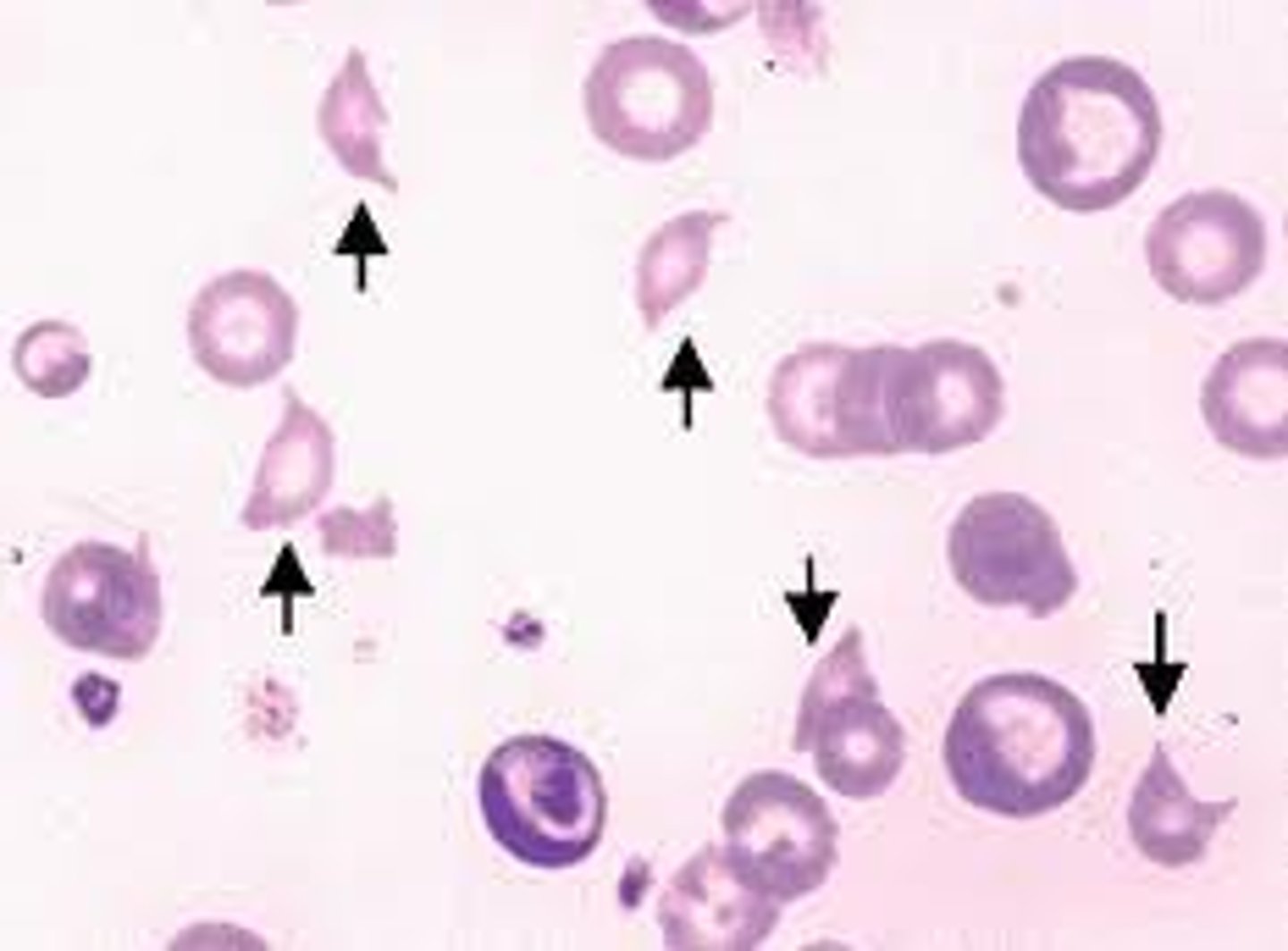
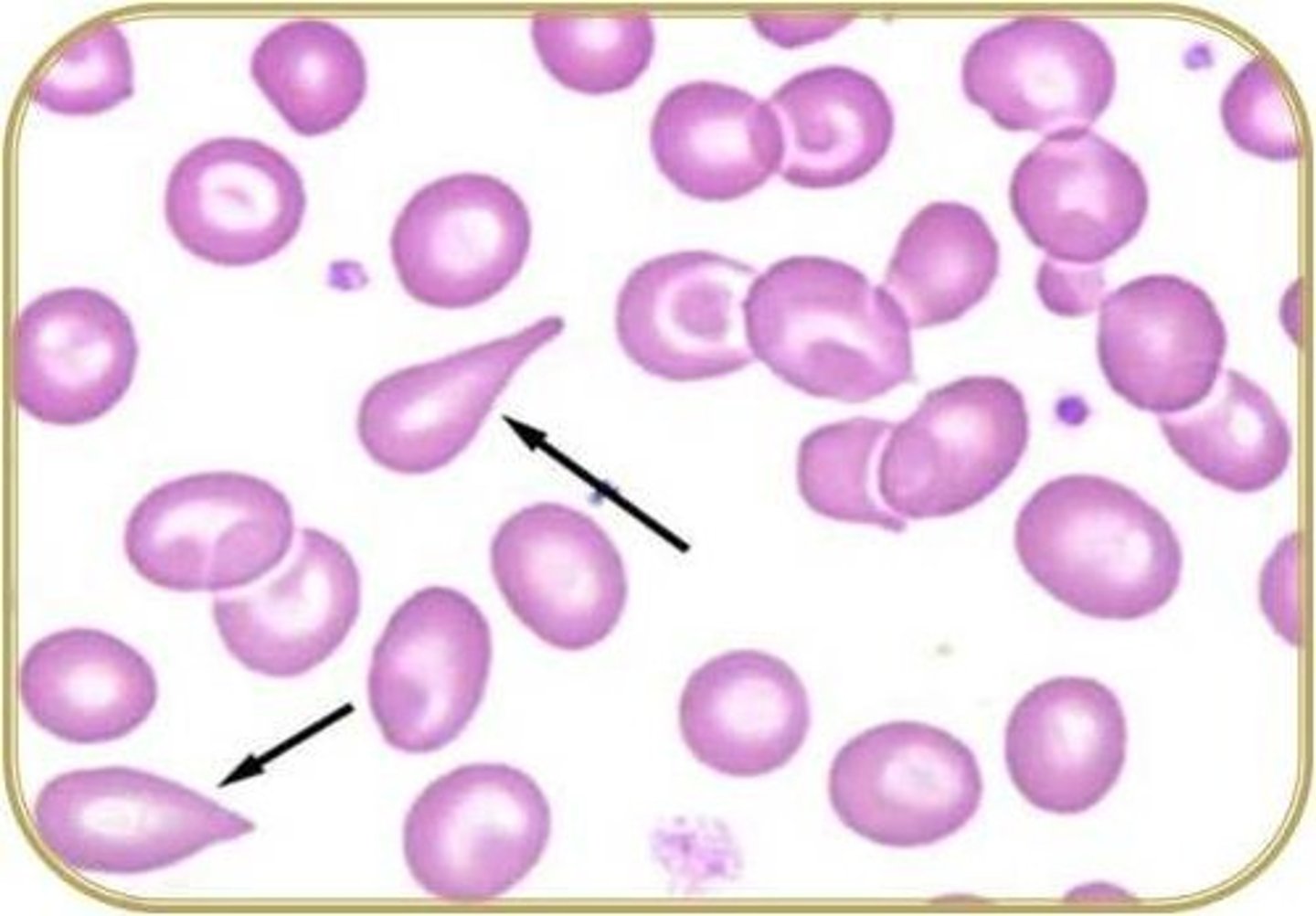
Dacrocyte/teardrop cell + cause
Englarged spleen
dont cry about your enlarged spleen
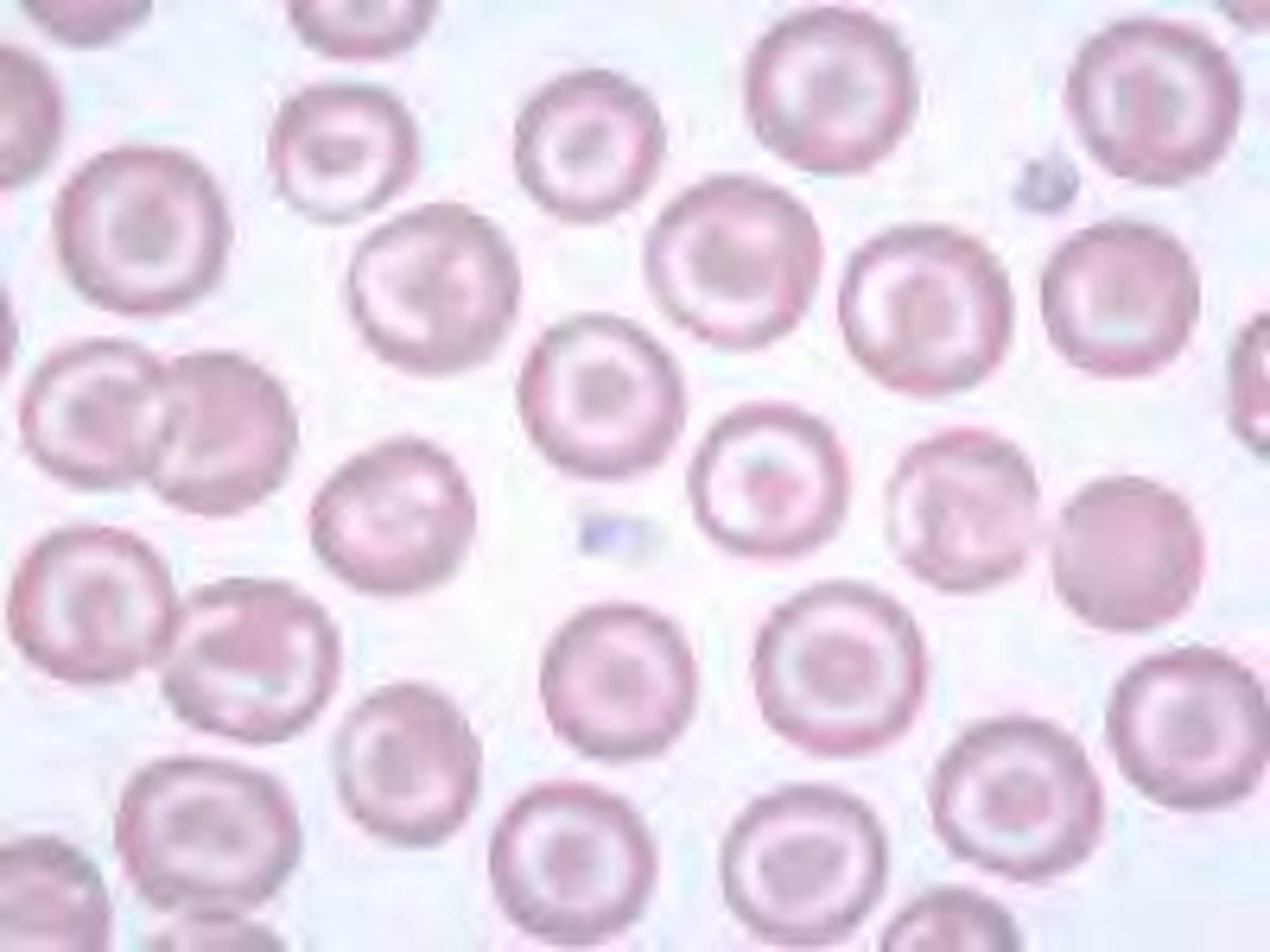
Codocyte + cause
Liver disease
Howell-Jolly body + content + conditions
DNA
Seen post-splenectomy, megaloblastic anemias, hemolytic anemias
HOLLY JOLLY CHRISTMAS W/O UR ****IN SPLEEN
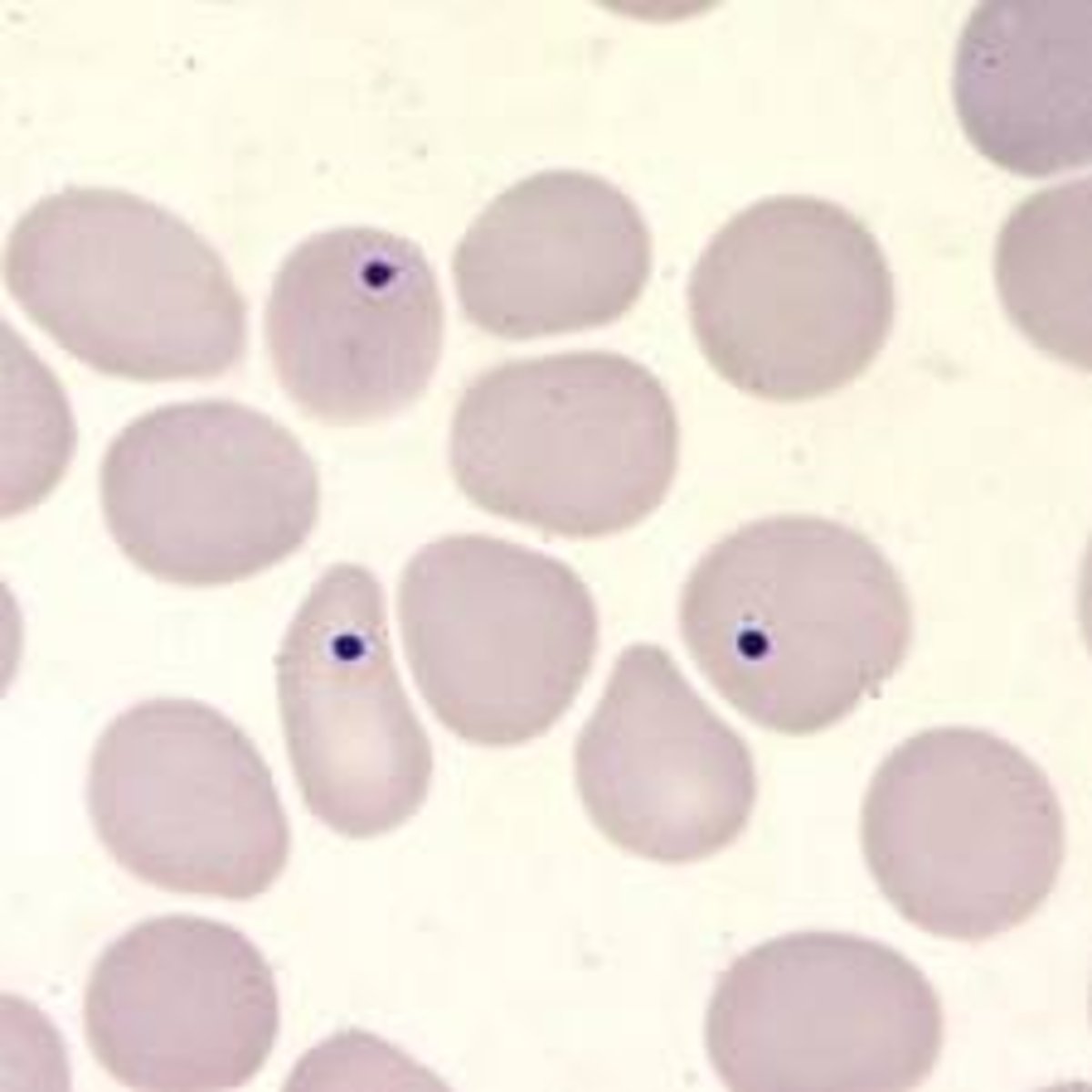
Reticulocyte
RNA (R for RNA)
associated w decreased RBC survival/hemorrage, erythroid hyperplastic marrow
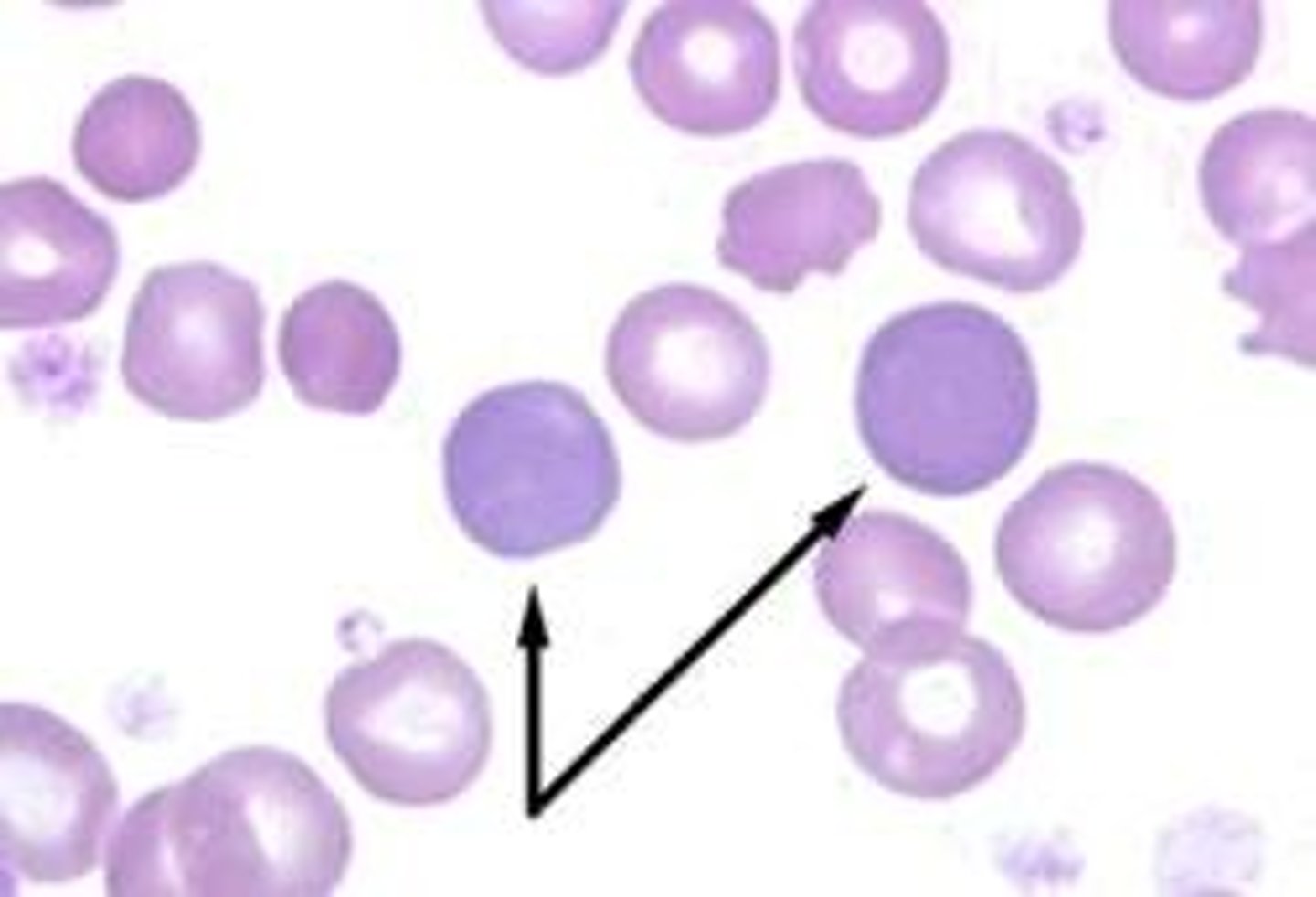
Pappenheimer bodies
Iron
seen in sideroblastic anemia, thalassemia
prussian blue stain
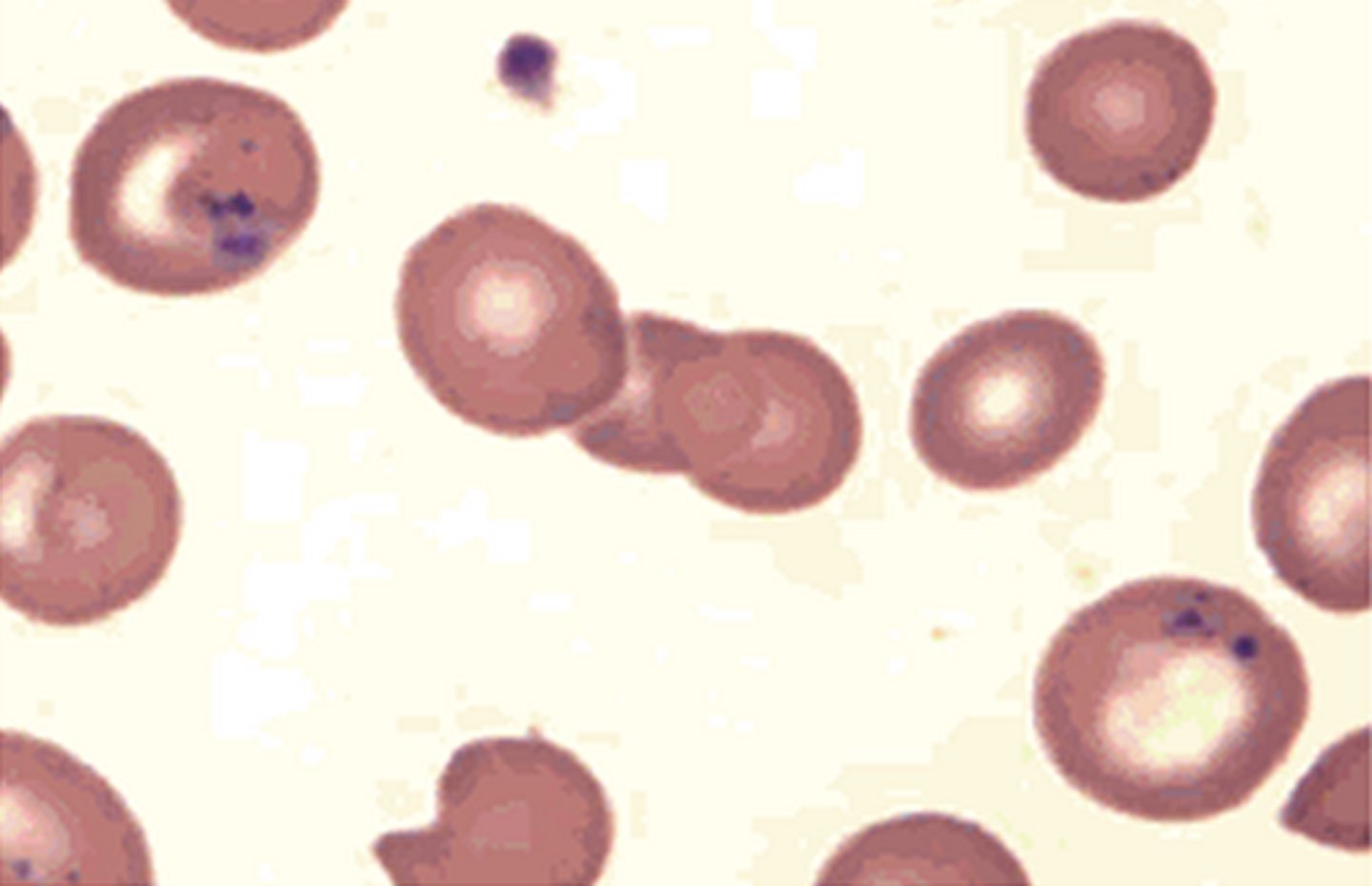
Heinz Body + content + conditions
Precipitated hemoglobin (H for hemoglobin)
Seen in G6PD deficiency
Only seen w supravital state
Ketchup is wright = cant see them w wright stain need supravital stain
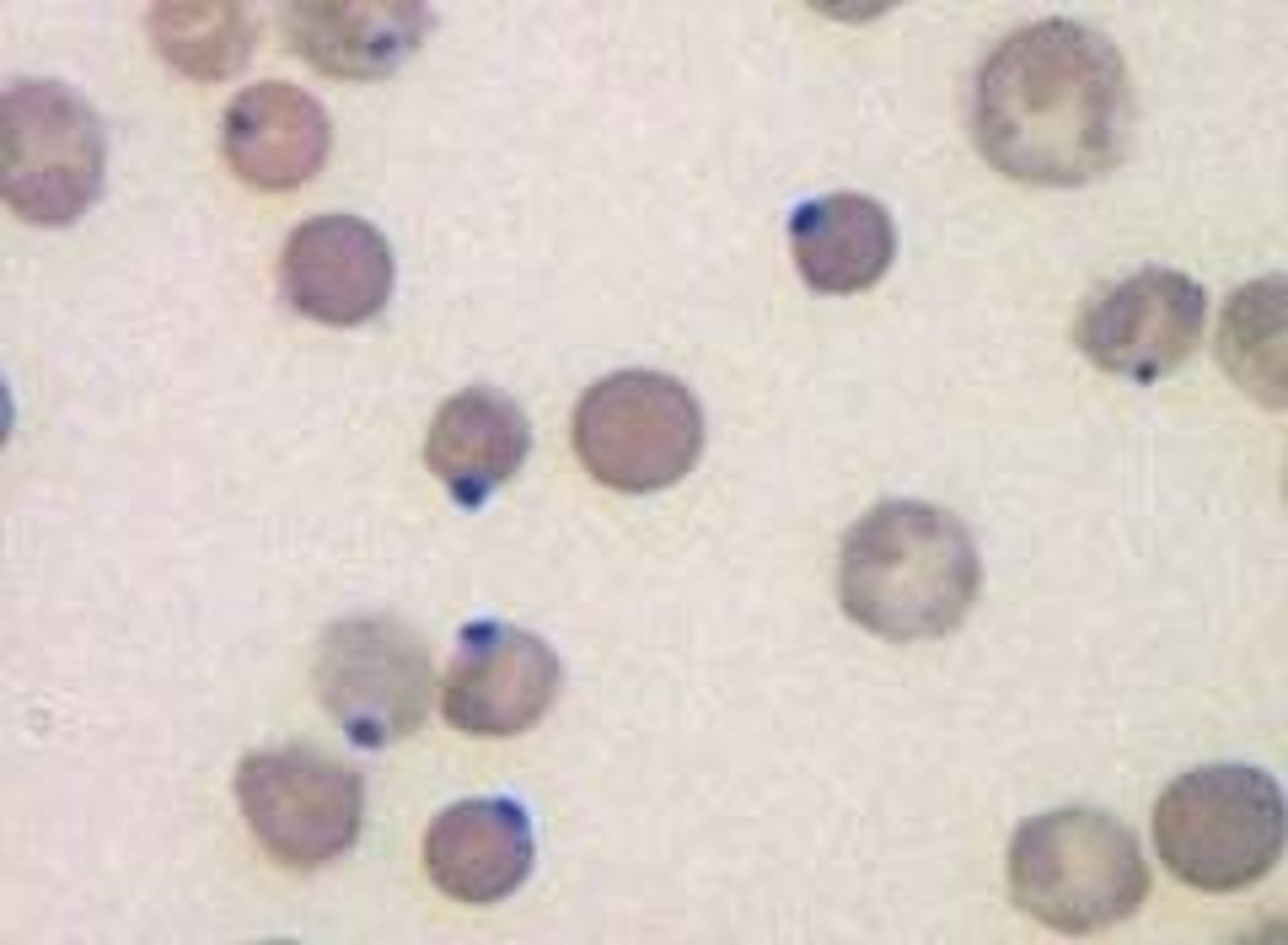
Hemoglobin C crystals
Crystalized Hgb C
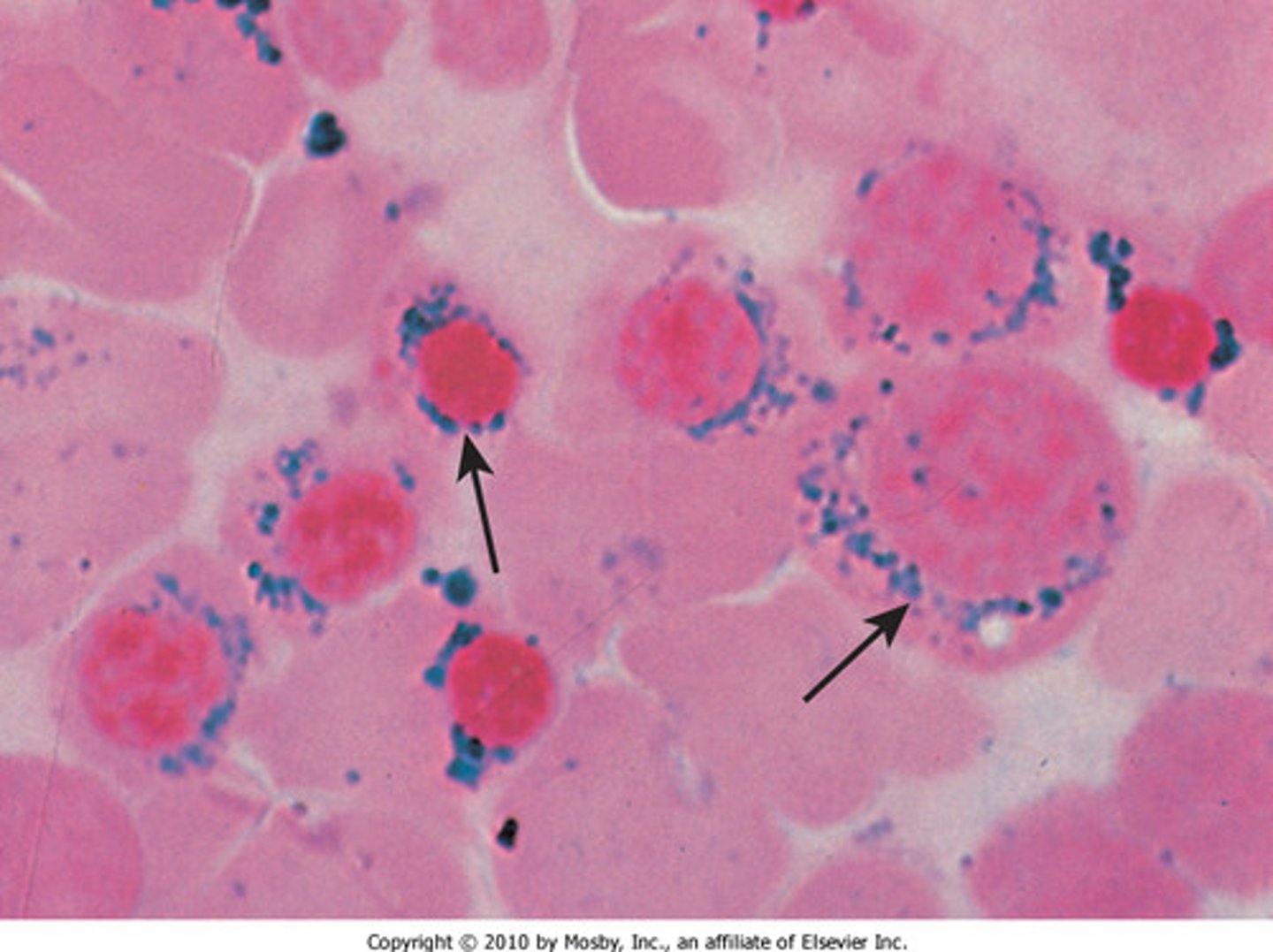
Ringed Sideroblasts
Iron
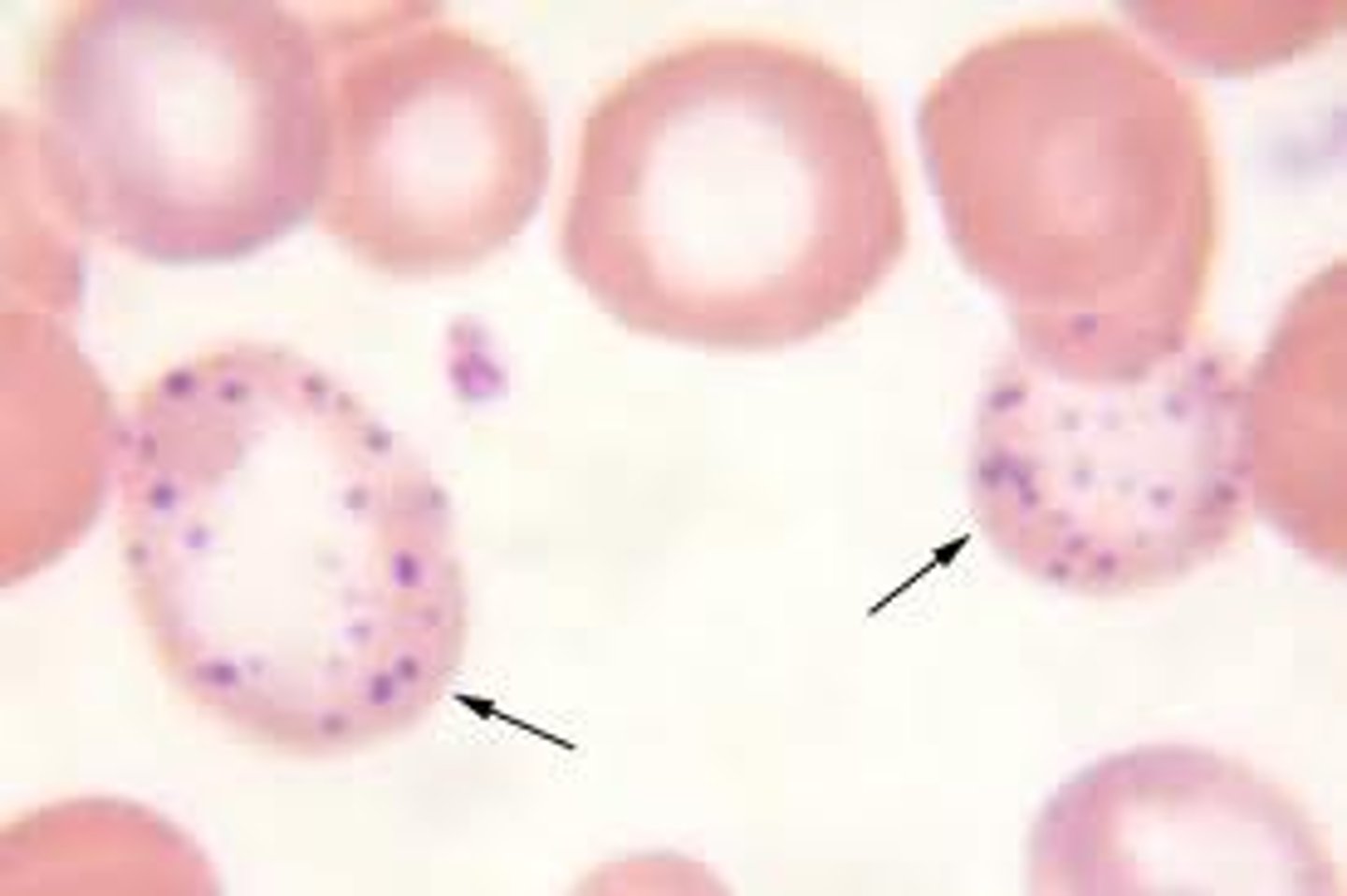
Basophilic Stippling
RNA aggregates
Thalassemia and lead poisoning
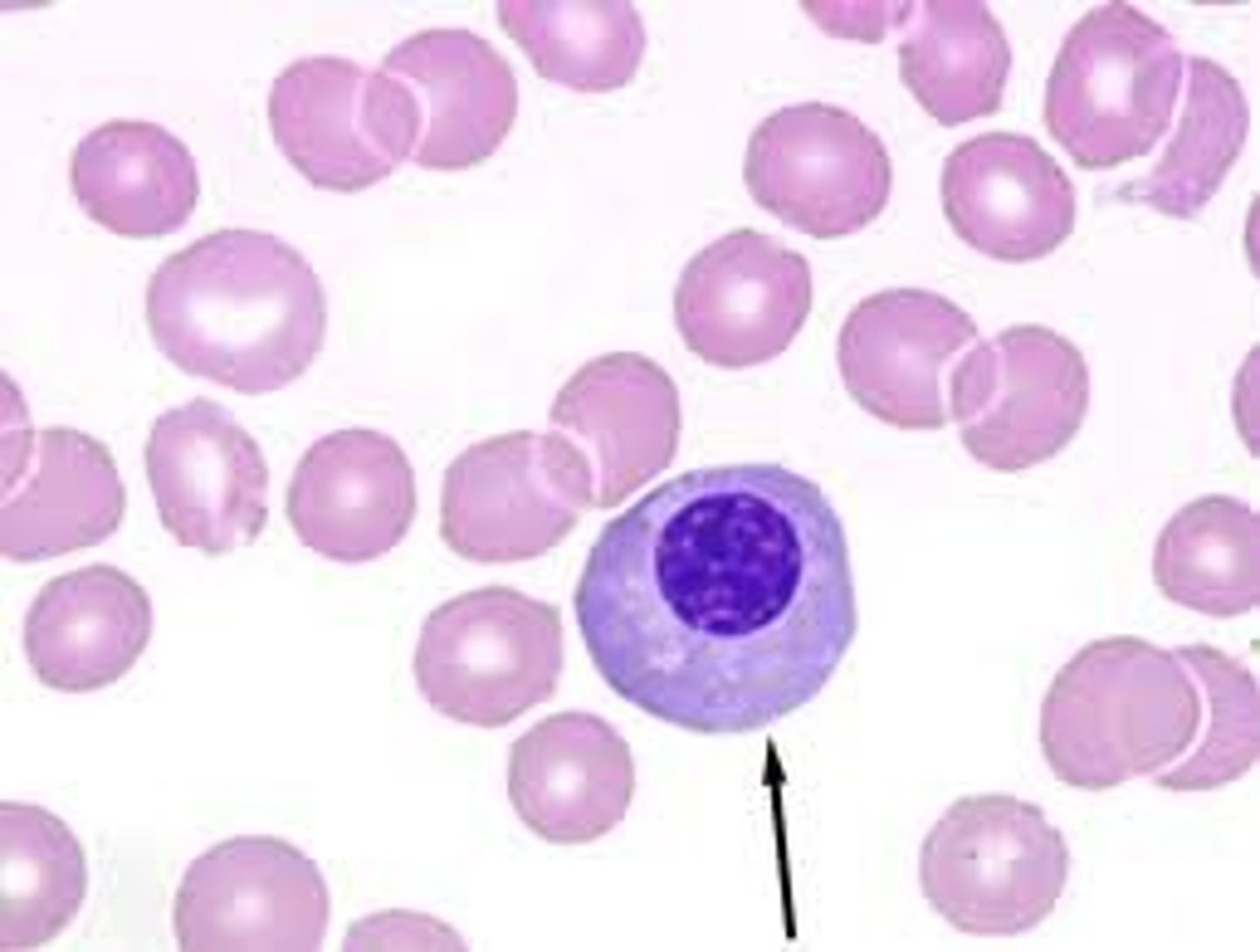
Nucleated RBC
DNA
Calculation of MCV
MCV = Hct/RBC x 10
Calculation of MCH
HGB/RBC x 10
Calculation of MCHC
HGB/HCT x 100
HCT calculation fix
Hct = MCV x RBC
Anemia Classification MCV < 80 fL
Microcytic Anemia
Anemia Classification MCV > 100 fL
Macrocytic Anemia
Anemia Classification MCV 80-100 fL
Normocytic Anemia
GO OVER ANEMIA SLIDE MOAR
Osmotic Fragility Test normal values!
Normal Cells begin lysis at 0.45-0.55% NaCL
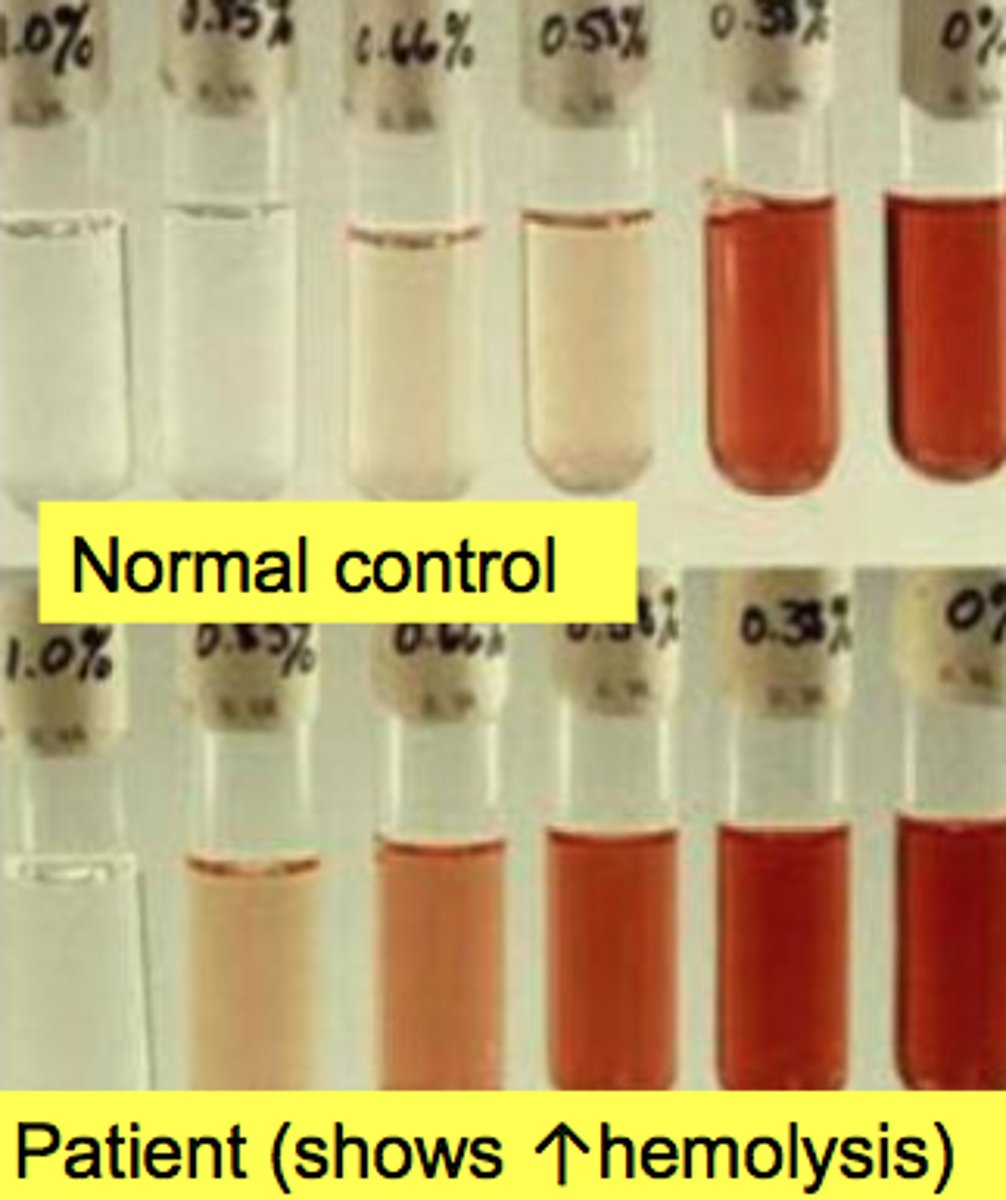
Osmotic Fragility
Has an increased osmotic fragility test
Lysis begins at >0.5% NaCL
Spherocytes have decreased surface to volume ratio. Cannot stand intake of excess water. Will lyse at higher concentrations of NaCL than normal RBC.
Target cells have increased surface area to volume ratio. Handles larger influx of water. Lysis occurs at lower NaCl concentration. Seen in hemoglobinopathies
Hemoglobin solubility test
Good screening tool
Deoxygenated Hgb S has decreased solubility when added to reducing agent
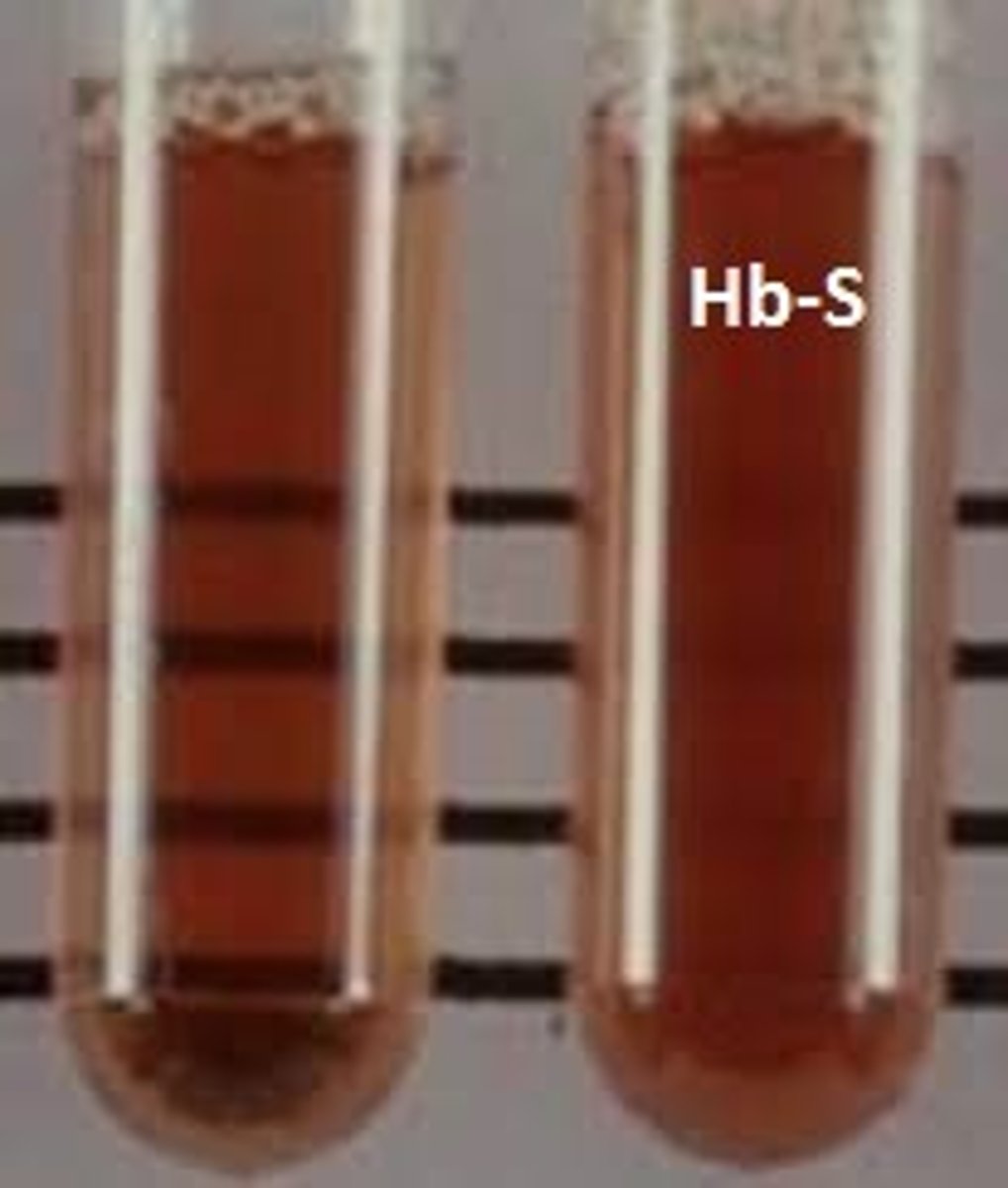

If Hgb solubility test is positive then?
Hemoglobin Electrophoresis
What is the screening tool in Hgb solubility test? What does it do?
Sodium dithionite - converts ferrous iron to ferric iron. Oxygen molecule becomes deoxygenated - polymerization
Causing turbidity
Hemoglobin electrophoresis
memorize order? know??? from video
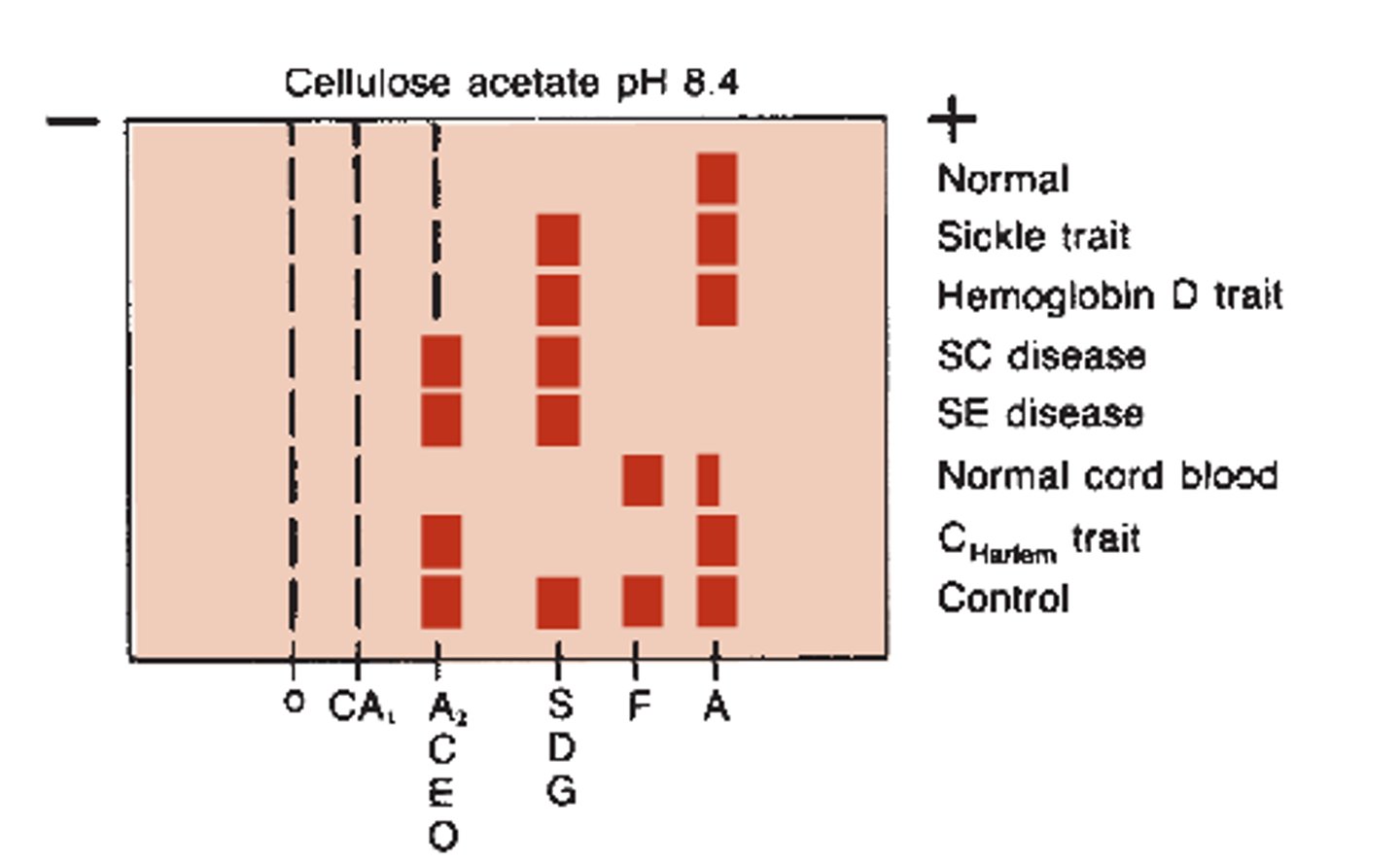
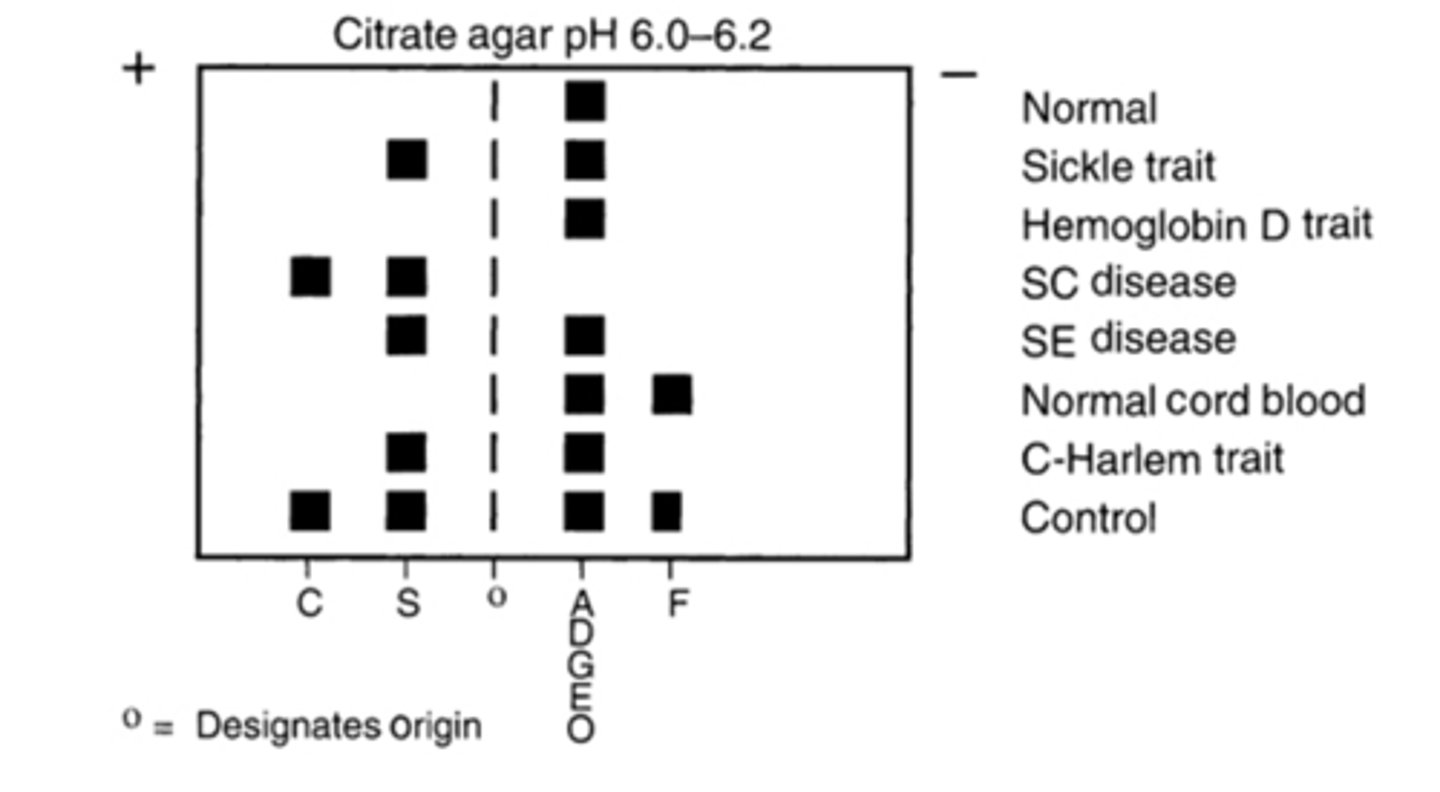
Hemoglobin Electrophoresis Citrate agar
Separates C from E and S from DGE
Kleihaur-betke
Adult HGB elutes from RBC due to citrate acid buffer.
HGB F resists eluation and remains.
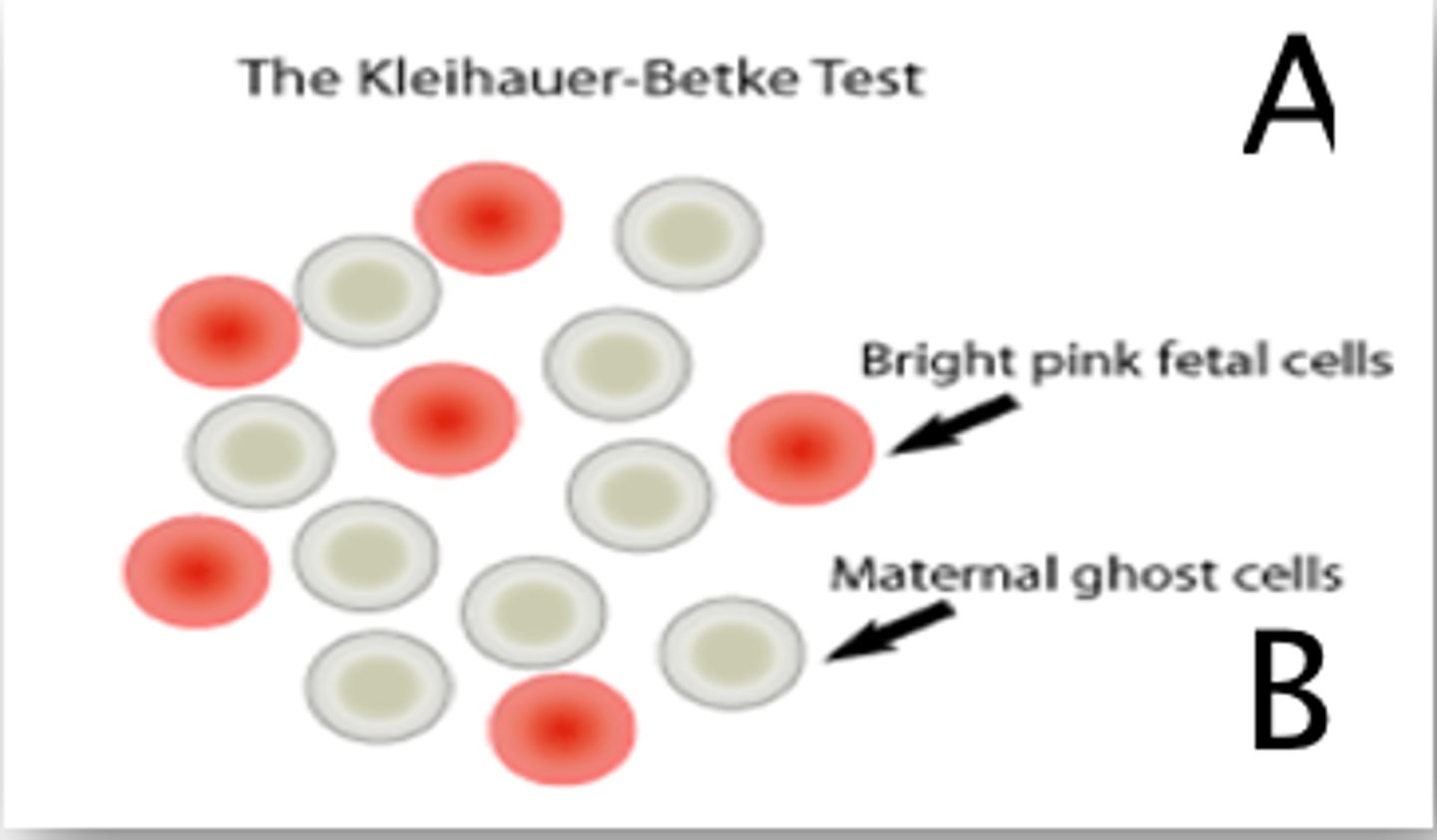
Kleihauer Betke Test
Calculation
% Hgb F = (total # of fetal cells/500) x 100
When are increased Hgb F values seen?
Hereditary persistence of hemoglobin F
Thalassemia major (40-90% Hgb F)
Thalassemia Minor (5-10% Hgb F)
Sickle Cell Anemia
Normal Hemoglobin F Levels
At birth
12 Weeks
4-5 Months
2y-adult
Birth: 60-90%
12 Wks: 7%
4-5M: 1.1-5.3%
2y-adult: 1-2%
Reticulocyte Count
# of retics counted x 100 = % reticulocytes
generally 10 fields which would be 100 RBCs per field
Normal Retic range
0.5-2.5%
Absolute retic count
Actual number of reticulocytes in 1 liter or 1 uL of blood
(% retics x rbc count)/100 retics/uL
Expected retic count value in each anemia
??
Retics
Low value before treatment
Higher value after treatment
Corrected retic counts
In specimens with a low Hct, the percentage of reticulocytes may be falsely elevated because the whole blood contains fewer red blood cells. A correction factor is used with the nromal Hct is considered 45%
Correctted retic count
% retic X (patient Hct / 45 = corrected retic count
Reference interval Retic
Patients w Hct of 35% should have elevated retic of 2-3%
Hct is >25% 3-5%
Corrected retic count is dependent on the degree of the anemia and determines how well the bone marrow is compensating for the anemia