CLEP MARKETING - ALL
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
Product
Anything that can be offered to satisfy a need or want
Service
Any service or benefit that can be offered, but doesn't result in the ownership of anything
Experiences
What buying the product/service will do for the costumer
Durable Products
Long lasting, generally expensive products
Nondurable Products
Products that don't last for a long time; usually is food
Consumer Products
Products purchased by the ultimate consumer
Industrial Products
products purchased for further processing or for use in conducting a business
Convenience Products
Bought with little time/effort
Shopping Products
Bought with more thought, and with an extensive comparison
Specialty Products
For consumers that have a strong brand preference
Unsought Products
Unknown/Undesired products to the consumer
Product Attributes
What benefits will it offer?
Branding
A name or symbol used to identify a product from a different manufacturers
Packaging
involves designing and producing the container or wrapper for a product & will often protect the product
Labeling
identifies the product or brand, supports the brand's positioning, adds personality to the brand, and also includes required information about the product.
Product Support Services
services that augment actual products such as installation, repairs, warranties, etc.
Product Line
A group of closely related product items
Brand Positioning
Attributes, benefits, beliefs and values
Brand Name Selection
Suggests product benefits - easy to pronounce and recognizable
Brand Sponsorship
Manufacturer's brand, private brand, licensing, co-branding
Line Extensions
Similar products offered under the same brand name
Brand Extension
Extending an existing brand name to new product categories
Product Development
Developing the product concept into a physical product
Test Marketing
The process of testing products among potential users
Commercialization
Introducing a new product into the market
Fad
Something that is very popular for a short time, then forgotten
BCG Matrix
a means of evaluating strategic business units on the basis of (1) their business growth rates and (2) their share of the market

BCG Matrix: Stars
High Market Share
High Growth
Can be Leader in the market which gives alot of added benefits
Growth in Market>Growth in Share
Increases in Share> Increase Margins
High Margin
Will eventually become a cash cow
BCG Matrix: Cow
low growth, high market share
BCG Matrix: Dogs
have low growth, low market share - should be gotten rid of
BCG Matrix: Question Marks
Risky new ventures- some will become stars, some dogs
brand
a name, term, symbol, design, or combination thereof that identifies a seller's products and differentiates them from competitors' products; the company's promise to deliver value
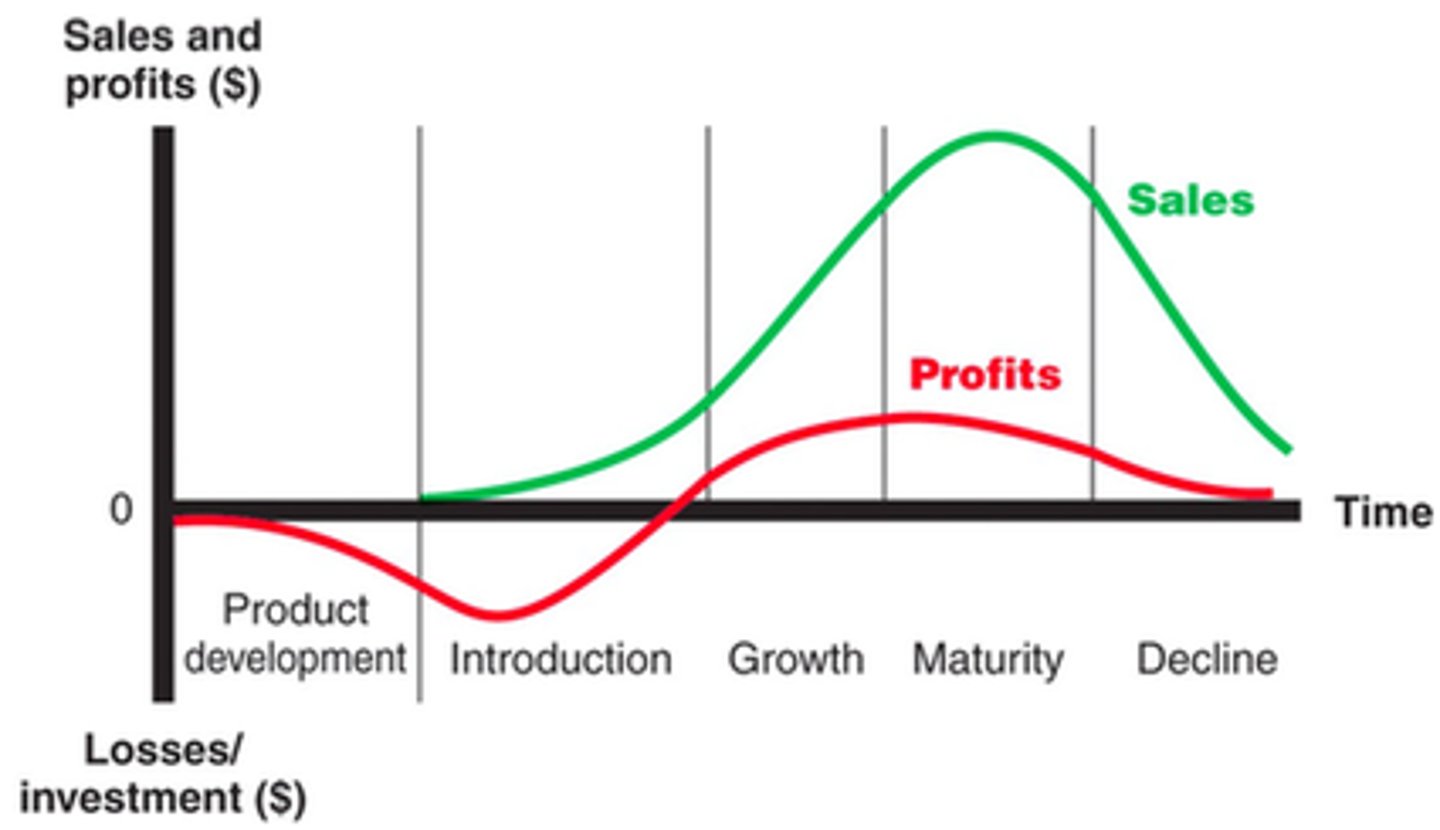
Product Life Cycle (PLC)
a concept that explains how products go through four distinct stages from birth to death: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline
market modification strategies
When a company tries to increase consumption of the current product
marketing mix modification strategy
When a company changes one or more of the marketing mix elements
product line pricing strategies
establishing and adjusting prices of multiple products within a product line
optional product pricing
takes into account optional or accessory products along with the main product
captive product pricing
setting a price for products that must be used along with a main product, such as blades for a razor and games for a video-game console
byproduct pricing
setting a price for by-products in order to make the main product's price more competitive
product bundle pricing
combining several products and offering the bundle at a reduced price
Rational Appeal (Logos)
Marketing appeals that are directed at the consumer's practical, functional need for the product or service.
emotional appeal (pathos)
aims to satisfy consumers' emotional desires rather than their utilitarian needs
informative advertising
communication used to create and build brand awareness, with the ultimate goal of moving the consumer through the buying cycle to a purchase
comparative advertising
a form of advertising that compares two or more specifically named or shown competing brands on one or more specific attributes
persuasive advertising
communication used to motivate consumers to take action
reminder advertising
communication used to remind consumers of a product or to prompt repurchases, especially for products that have gained market acceptance and are in the maturity stage of their life cycle
push strategy
directing the promotional mix to channel members to gain their cooperation in ordering and stocking the product
pull strategy
a marketing strategy that stimulates consumer demand to obtain product distribution
Evaluating Marketing
From an individual firm's perspective, success means to satisfy the needs/wants of customer
Exploitation
Taking advantage of a weaker group
Inefficiency
using resources in such a way as not to maximize the desired output from them
Ethics in Marketing
The standards of marketing practice have shifted from an emphasis on the products' interest to the consumers'. Codes of Ethics have been created to assist managers in following this shift
Code of Ethics
A formal statement of ethical principles and rules of conduct
Not-For-Profit Organizations
Groups that do not pursue profit as a goal; they engage in charitable, educational, humanitarian, cultural, professional, or other activities, often with a social purpose
pervasive advertisement
When companies promote so often, customers tire of it.
Customer Buying Behavior
Behavior exhibited by buyers as they consider, select, and purchase goods and services
Consumer Market
consumers who purchase goods and services for personal use
Cultural Influences
Meanings that are shared by most people in a social group
Subcultures
subgroups within the larger, or national, culture with unique values, ideas, and attitudes
Social Factors
Influences purchase decisions and behavior
Norms
rules and expectations by which a society guides the behavior of its members
Status
the relative position an individual holds in social or organizational settings
reference group
a social group that serves as a point of reference in making evaluations and decisions
Brand Personality
set of traits people attribute to a product as if it were a person
Motivation
the reason or reasons one has for acting or behaving in a particular way.
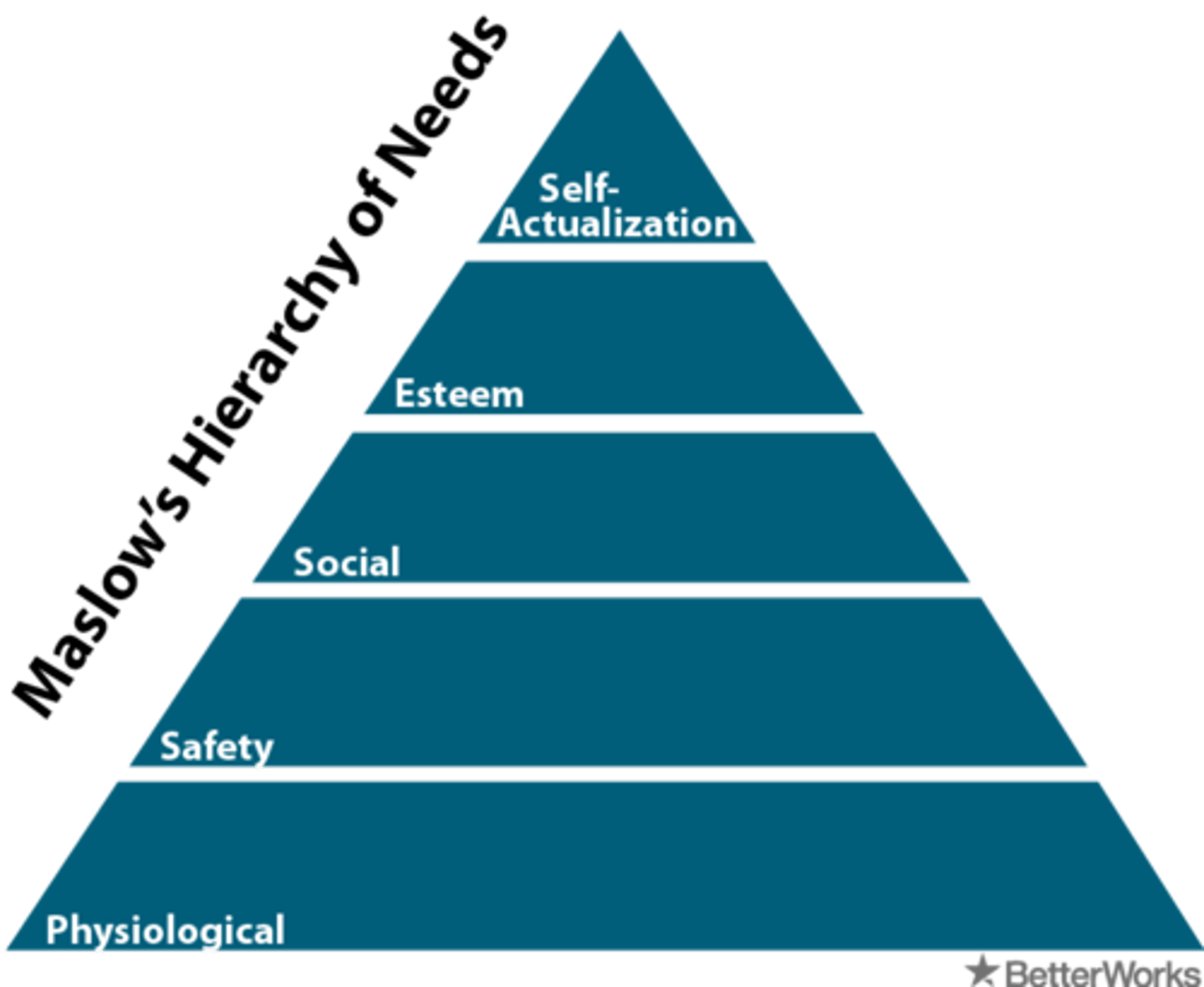
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
physiological, safety, love/belonging, esteem, self-actualization
Perception
the process of organizing and interpreting sensory information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events
Selective attention
the focusing of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus
selective distortion
process by which consumers interpret information in ways that are biased by their previously held beliefs
selective retention
a process whereby a consumer remembers only that information that supports his or her personal beliefs
Buyer Decision Making Process
1. Need recognition
2. Information search
3. Evaluation of alternatives
4. Purchase decision (Product Choice)
5. Post-purchase behavior (Outcomes)
Information Search
the stage of the buyer decision process in which the consumer is motivated to search for more information
external search
An information search in which buyers seek information from sources other than their memories
brand belief
a thought about a specific property or quality of the brand
Evaluation Process
Combining beliefs to form attitudes and preferences
postpurchase behavior
The stage of the buyer decision process in which consumers take further action after purchase, based on their satisfaction or dissatisfaction
cognitive dissonance
a state of anxiety caused by the difficulty of choosing between different products
Segmentation
dividing a market into distinct groups of consumers who share common tastes and requirements
Market Segmentation
the process of dividing a market into meaningful, relatively similar, and identifiable segments or groups
Target Marketing
Marketing directed toward those groups (market segments) an organization decides it can serve profitably.
market positioning
involves the process of defining the marketing mix variables so that target customers have a clear, distinctive, desirable understanding of what the product does or represents in comparison with competing products
positioning strategy
The key themes or concepts an organization features for communicating the distinctiveness of its product or service to the target segment.
marketing strategy
the activities of selecting and describing one or more target markets and developing and maintaining a marketing mix that will produce mutually satisfying exchanges with target markets
geographic segmentation
the grouping of consumers on the basis of where they live
Undifferentiated marketing
plan wherein the same basic product is offered to all customers
differentiated marketing
a market-coverage strategy in which a firm decides to target several market segments and designs separate offers for each
Concentrated (niche) marketing
firm goes after a large share of one or a few segments or niches
Micromarketing
tailoring products and marketing programs to the needs and wants of specific individuals and local customer segments; it includes local marketing and individual marketing
product position
the way a product is defined by consumers on important attributes- the place the product occupies in consumers' minds relative to competing products
demographic segmentation
segmenting markets by age, gender, income, ethnic background, and family life cycle
psychographic segmentation
segmenting markets on the basis of personality, motives, lifestyles, and geodemographics
Behavioral Segmentation
A segmentation method that divides customers into groups based on how they use the product or service. Some common behavioral measures include occasion and loyalty.
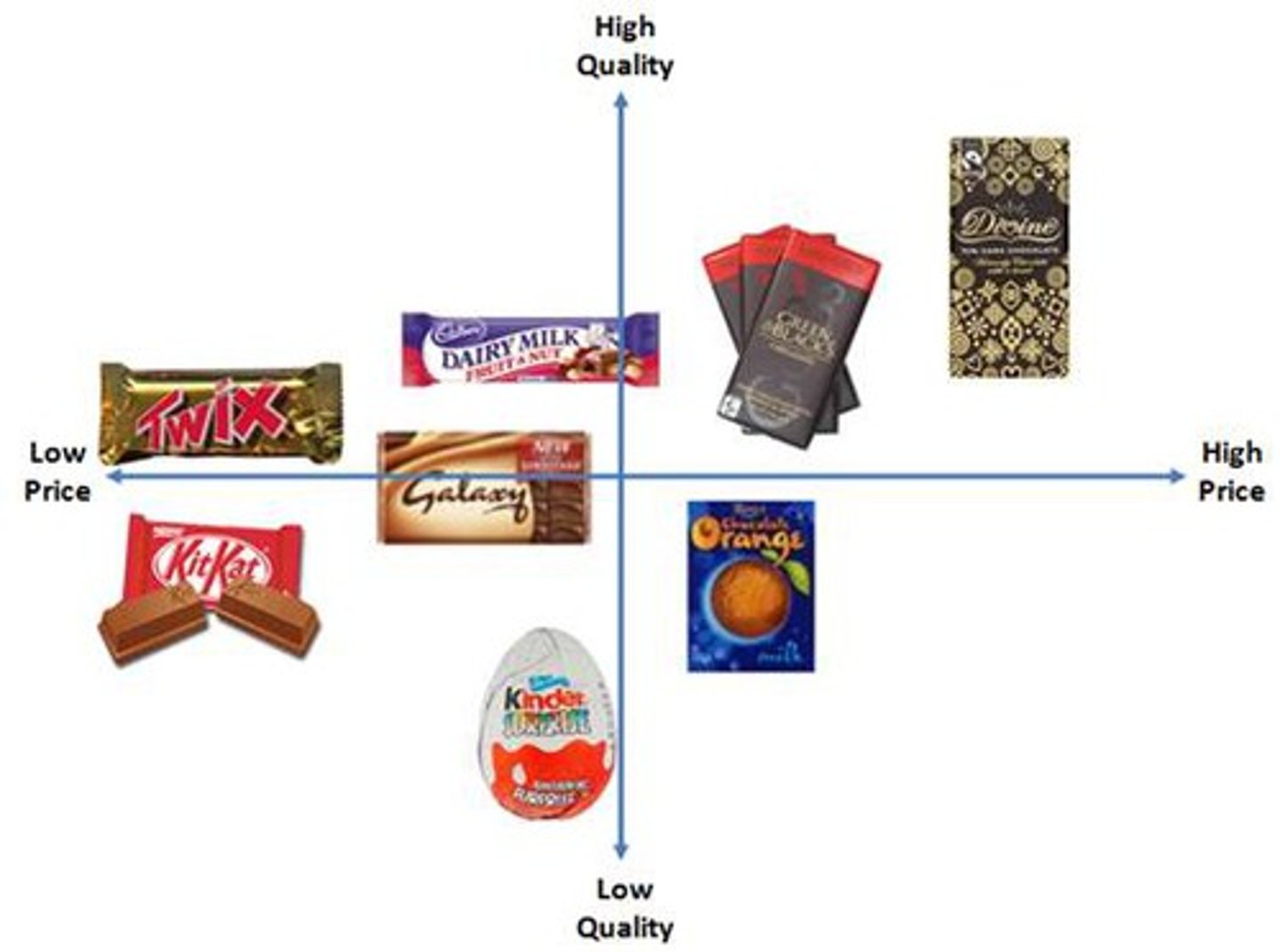
positioning map
A diagram of how consumers in a segment perceive brands based on specific elements they consider important
competitive advantage
a set of unique features of a company and its products that are perceived by the target market as significant and superior to those of the competition
Repositioning
changing consumers' perceptions of a brand in relation to competing brands (rebranding)
Business Buying
Purchased goods/services used in production of other products/services that are sold, rented, or supplied to others
Buying Center Roles
users, influencers, buyers, deciders, gatekeepers
buying center roles: Users
- People who will actually use the purchased good or service
- Influence on purchase decision can be extensive or neglible
buying center roles: influencers
Affect the purchasing decision by providing information for the evaluation of alternatives or by setting buying specifications
buying center roles: deciders
- Make the decision on which products to buy
- The size and importance of the decision dictate who performs the role