Psychology: Quiz #4 Study Guide
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Trait
a disposition to behave consistently in a particular way; the major force behind personality
Personality
uniqueness and relatively enduring set of behaviors, feelings, thoughts, and motives thay characterize an individual
Behavioral Threshold
the points at which a person moves from not having a particular response to having one
Psychoanalytic
one personality resides in the unconscious, and early childhood experiences by the foundation for adult personality (include different types of consciousness, ID, Ego, Superego)
Unconscious
contains all the drives, urges, or instincts that are outside awareness but nonetheless motivate most of our speech, thoughts, feelings, or action
Conscious
being aware of at any given moment in time
Preconscious
below the surface of awareness; latent parts of the brain that are readily available to the conscious mind
ID
identification; the seat of impulse and desire; the part of our personality that we don't yet own; it owns or control us at birth
Ego
a sense of self; the only part of the mind that is in direct contact with the outside world; operates on the "reality principle"
Superego
the part of the self that monitors and controls behavior, "stand over us" and evaluates action in terms of right and wrong; our conscience; impulse control
Humanistic-Positive
we have a natural interest in becoming the best person possible; the strives toward growth and fulfillment (Maslow and Roger)
Social Cognitive
a person's behavior changes in different situations; behavior results from the interaction of the cognitive and emotional qualities of the person and the particular situations they are in (Mischel)
Five-Factor Model For Trait
Openness to experiences, conscientiousness (planned, organized, controlled), extraversion (sociable, talkative, outgoing), agreeableness (warm, trusting, generous), neuroticism (anxious, worrying, tense) [O.C.E.A.N.]
Cortical Arousal
the brain's level of authority at a resting state and its sensitivity to stimulation
Sensory Threshold
refers to how much a stimulus is required for it to be perceived
Human Evolutionary Heritage
why people work to preserve group membership and they modify their behavior when in the presence of others
Conformity
the tendency of people to adjust their behavior to what others are doing or to adhere to the norms of their culture
Fundamental Attribution Error
the tendency to explain other's behavior in dispositional rather than situational terms
Stereotypes
schemas of how people are likely to behave based simply on groups to which they belong; they are oversimplified perspectives of people based solely on their group membership
Informational Social Influence
conformity to the behavior of others because one views them as a source of knowledge about what one is supposed to do (Ex. Where everyone's eating lunch)
Normative Social Influence
conformity to the behavior of others in order to be accepted by them (Ex. Not to eat at CR because that's where the nerds go)
Groupthink
a situation in which the thinking of the group takes over, so much so that group members forget logic or critical analysis in the service of reading a decision
Implicit Association Test
Identify two types of things with left-handed responses; two opposites types with right-handed response
Mere Exposure
our tendency to develop preferences fro things simply since we are familiar with them; repeated presentation with a stimulus eventually engenders a preference (nurture)
Illusory Truth
repeated representation with a falsehood eventually engenders a beliefs
In-Group/Out-Group Bias
tendency to show positive feelings toward people who belong to the same group as we do, and negative feelings toward those in other groups
Implicit Bias
indirect, perhaps unconscious
Explicit Bias
plainly state
Dispositional
internal attributions for our successes
Situational
external attributions for our failures
Psychological Disorder
conditions characterized by abnormal thoughts, feelings, two behaviors
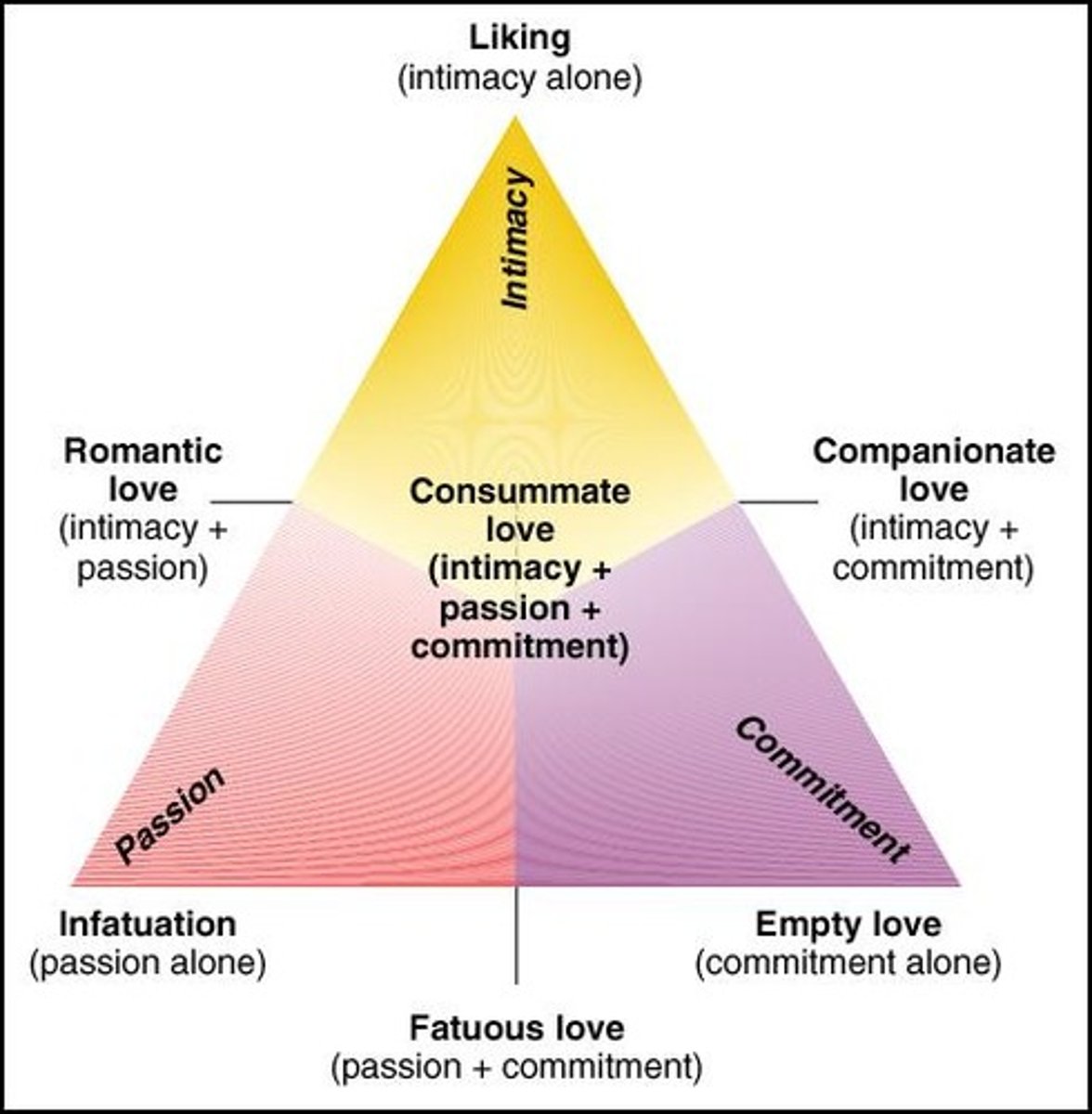
Sternberg's Triangle of Love
passion, intimacy, commitment
Syndrome
a group, or cluster of related symptoms that are characteristic of a disorder
Four "D"s Syndrome
Disturbance (of thought, emotion, or behavior), dysfunction (of biological or developmental processes), distress (or disability) (in everyday life especially relationships or work), deviant (thought, emotion, or behavior, but only if also dysfunctional)
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
inattention (careless mistakes, not listening), hyperactivity, impulsivity (blurts, interrupts, can't wait turn)
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
impaired social interaction, impaired communication, repetitive/stereotypic behaviors (hand flapping, inflexible routine)
Joint Attention
the ability to make eye contact with others and to look in the same direction that someone else is looking
Schizophrenia
a psychotic disorder characterized by significant disturbances in thought and emotion, specifically problems with perceptions, including hallucinations
Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia
nonresponsiveness emotional flatness, immobility, catatonia, problems with speech, and inability to complete tasks
Cognitive Symptoms of Schizophrenia
working memory, attention, verbal learning and memory, reasoning and problem solving, processing and speech
Word Salad
the speech of people with schizophrenia, which may follow grammatical rules but be nonsensical in terms of content
Dopamine Hypothesis
states the people with schizophrenia have an excess of dopamine activity in certain areas of the brain
Major Depressive Disorder
a mood disorder characterized by persuasive low mood, lack of motivation, low energy, and feelings of worthlessness and guilt that last for at least two conservative weeks
Bipolar Disorder
a mood disorder characterized by substanial mood fluctuations, cycling between very low (depressive) and very high (manic) moods
Symptoms of Manic
Distractibility, indiscretion, grandiosity, flight in ideas, activity increased, sleep (decreased need for), talkativeness (at least once a week) [DIGFAST]
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
an anixety disorder in which uncontrollable thoughts lead to repeated, unwanted behaviors
Obsession
an unwanted thought, word, phrase, or image that persistently and repeatedly comes into a person's mind and causes distress
Compulsion
a repetitive behavior performed in response to uncontrollable urges or according to a ritualistic set of rules
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
a type of trauma- and stressor-related disorder that involves intrusive and persistent cognitive, emotional, and physiological symptoms triggered by catastrophic or horrifying events
Dissociative Disorders
psychological disorders characterized by extreme splits or gaps in memory, identity, or consciousness
Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID)
a dissociative disorder in which a person develops at least two distinct personalities, each with its own memories, thoughts, behaviors, and emotions; some psychiatrists question the legitimacy of the disorder
Personality Disorders
patterns of cognition, emotion, and behavior that develop in late childhood or adolescence and are maladaptive and inflexible; they are more stable than clinical disorders
Cluster A of Personality Disorders - Odd-Eccentric
Schizoid: Lack of interest in social relationships, inappropriate of flat emotion, thought, and coldness; Schizotypal: Isolated, odd, and bizarre thoughts and beliefs; Paranoid: Extreme, unwarranted and maladaptive suspicion
Cluster B of Personality Disorders -Dramatic-Emotional
Histrionic: Wild, exaggerated behaviors, extreme need for attention, suicidal, seductive, unstable relationships, shifting moods; Borderline: Shifting moods, dramatic, impulsive, self-injury (Ex. cutting); Narcissistic: Grandiose thoughts and sense of one's importance, exploitative, arrogant, lack of concern for others; Antisocial: Impulsive, violent, deceptive, and criminal behavior; no respect for social norms, ruthless
Cluster C of Personality Disorder - Anxious-Fearful
Avoidant: Anxious and worrying, sense of inadequacy, fear of being criticized, nervousness, avoids social interaction; Dependent: Pervasive selflessness, need to cared fro, fear of rejection, total dependence on and submission to others; Obsessive-compulsive: Extreme perfectionism and anxiety over minor disruption of routine, very rigid activities and relationships, pervades most aspects of everyday life
Causes For Psychological Disorders
a combination of genetic and environmental factors
Phenothiazines
drugs used to treat schizophrenia; they help diminish hallucinations, confusion, agitation, and paranoia but also have adverse side effects
Traditional Antipsychotics
1st medications used to manage psychotic symptoms
Tardive Diskinesia
repetitive, involuntary movements of jaw, tongue, face, and mouth resulting from the extended use of traditional antipsychotic drugs
Atypical Antipsychotics
Newer antipsychotic drugs that do not create tardive dyskinesia
Class of Drug Treatment For Schizophrenia
chlorpromazine, haloperidol, clozapine
Class of Drug Treatment For Anxiety
risperidone, SSRIs, benzodiazepines, barbiturates
Class of Drug Treatment For Depression
MAO inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, SSRIs, bupropion
Class of Drug Treatment For Bipolar Disorder
Lithium
Class of Drug Treatment For Anxiety and Depression
SNRI and SSRIs
Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) Inhbitors
a class of drugs used to treat depression; they slow the breakdown of monoamine neurotransmitters in the brain
Tricyclic Antidepressants
drugs used for treating depression as well as chronic pain and ADHD
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
drugs prescribed primarily fro depression and some anxiety disroders that work by making more serotonin available in the synapse
Serotonin-Nonrepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
antidepressant and anti-anxiety drugs that boost levels of serotonin and nonrepinephrine
Benzodiazepines
a class of anxiety-reducing drugs that can be addictive but are less dangerous than barbiturates
Barbiturates
a class of anxiety-reducing sedatives that can additive and carry a risk of overdose
Lithium
a salt that is prescribed fro its ability to stabilize the mani associated with bipolar disorder
Side Effect of Chlorpromazine
Fatigue, visual impairment, tardive dyskinesia
Side Effects of Haloperidol
Fatigue, visual impairment, tardive dyskinesia
Side Effects of Clozapine
Weight gain, increased risk of diabetes, reduction of white blood cells
Side Effects of Risperidone
Weight gain, increased risk of diabetes, reduction of white blood cells
Side Effects of SSRIs
Agitation, insomnia, nausea, difficulty achieving orgasm; rare cases of increased risk for suicide
Side Effects of Benzodiazepines
Can be addictive
Side Effects of Barbiturates
Slows breathing and hear rate; can lead to overdose
Side Effects of MAO Inhibitors
Dangerous increases in blood pressure
Side Effects of Tricyclic Antidepressants
Dry mouth, weight gain, irritability, confusion, constipation
Side Effects of SSRIs
Agitation, insomnia, nausea, difficulty achieving orgasm; rare cases of increased risk for suicide
Side Effects of Bupropion
Weight loss, dry mouth, headaches
Side Effects of Lithium
Diarrhea, nausea, tremors, kidney failure, cognitive effects, adverse cardiac effects
Side Effects of SNRI
Sleep disturbance, dizziness, sexual dysfunction, suicidal thoughts
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
the treatment of last resort for severe depression that involves passing an electrical current through a person's brain in order to induce a seizure
Psychotherapy
the use of psychological techniques to modify maladaptive behaviors or thought patterns, or both, and to help patients develop insight into their own behavior
Psychoanalytic Therapy
Based on Freud's ideas, a therapeutic approach oriented toward major personality change with a focus on uncovering conscious motives, especially through dream interpetation
Psychodynamic Therapy
the modern offshoot of Freud's psychoanalysis and a form of talk therapy that confronts unconscious impulses, ideas, and wishes
Client-centered Therapy
a form of humanistic therapy in which the therapist shows unconditional positive regard for the patient
Cognitive Therapy
any type of psychotherapy that works to restructure irrational thought patterns
Cognitive-behavioral Therapy (CBT)
an approach to treating psychological disorders that combines techniques for restructuring irrational thoughts with operant and classical conditioning techniques to shape desirable behaviors
Group Therapy
a therapeutic setting in which several people who share a common problem all meet regularly with a therapist to help themselves and one another
Support Groups
meetings of people who share a common situation, be it a disorder, a disease, or caring for an ill family member
Evidence-Based Therapy
treatment choices based on empirical evidences that they produce the desired outcome
Technology-Based Therapies
therapies that make use of technology or the Internet to complement current therapies or to make psychotherapeutic techniques available to more people
Virtual Reality Therapies
therapies that use virtual (digital simulation) environments to create therapeutic situations that would be hard to create otherwise
Integrative Therapy
an eclectic approach in which the therapist draws on different treatment approaches and uses those that seem most appropriate for the situation
Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT)
an approach that combines element of CBT with mindfulness meditation to help people with depression learn to recognize and restructure negative thought patterns
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
treatment that integrates elements of CBT with exercise aimed at developing mindfulness without meditation and is used to treat borderline personality disorders