Midterm practice exam APHY II
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Oxygen is primarily transported through the body bound to the heme portion of hemoglobin.
True or False
True
Which of the following is a correct path of air through the respiratory tract?
Air travels into the nose, the pharynx, larynx, trachea, main bronchi, bronchioles, terminal bronchioles, respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and, finally, alveolar sacs.
Which of the statements correctly describes vital capacity?
Multiple Choice
The amount of air a person can exhale.
The total volume of air that is inside a person's lung.
All the air that can be inhaled on top of the normal breathing.
All the air that can be exhaled after a full inhalation.
All the air that can be exhaled after a full inhalation.
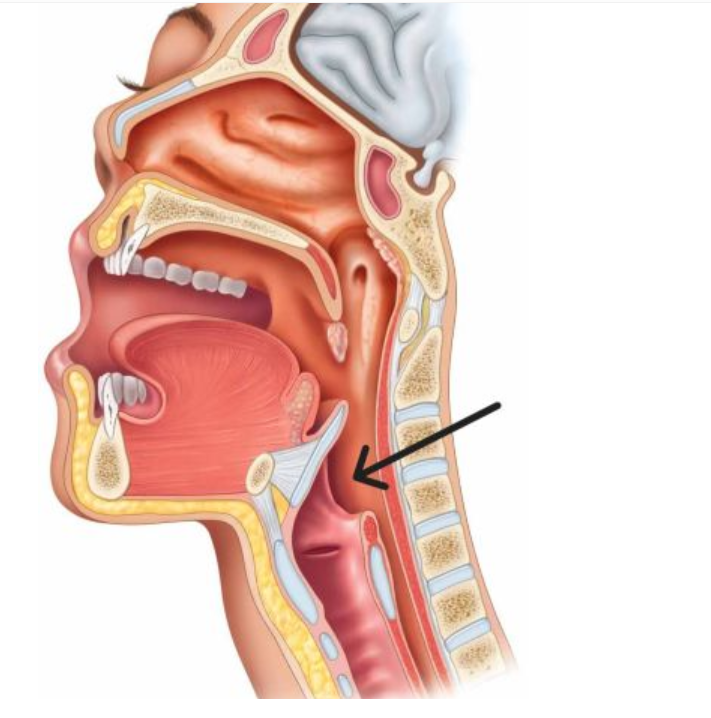
The highlighted structure is:
laryngopharynx
Boyle's Law states that
the pressure and volume of gases are directly proportional
the pressure and volume of gases are inversely proportional
the pressure and volume of gases are inversely proportional
The walls of alveoli are comprised of __________Blank epithelium.
stratified squamous
transitional
pseudostratified columnar
simple squamous
simple squamous
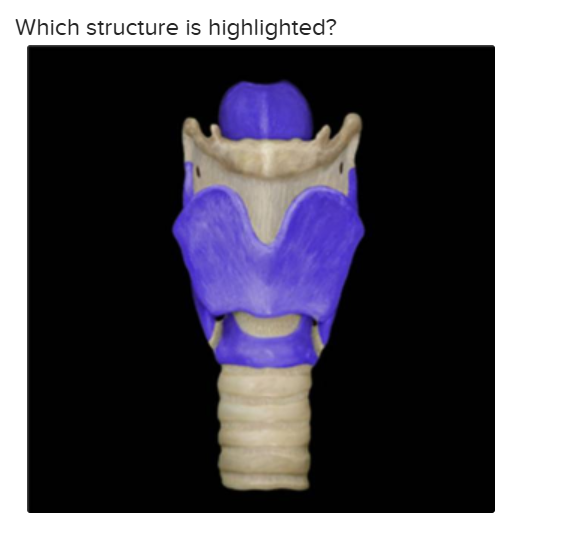
The highlighted structure is:
Laryngeal cartilage
The vestibular and vocal folds are found in the...
Larynx
Trachea
Pharynx
Nasal cavity
larynx
The pharynx is a shared region between which two body systems?
Multiple Choice
Circulatory and respiratory
Digestive and nervous
Lymphatic and circulatory
Respiratory and digestive
respiratory and digestive

The structure highlighted is:
external naris
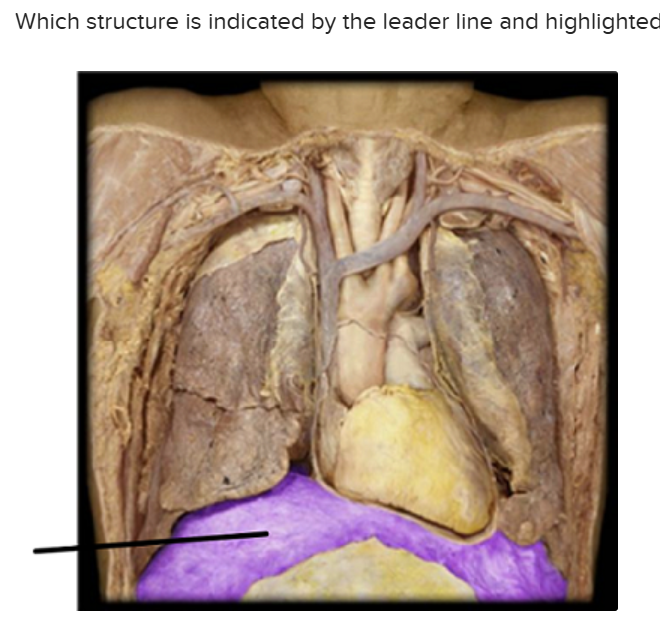
The structure highlighted is:
Diaphragm
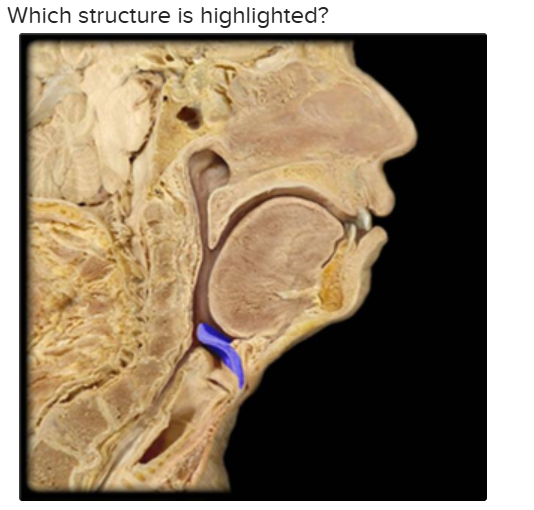
The structure highlighted is:
epiglottis
Select the structures that are a part of the lower respiratory tract.
Check All That Apply
trachea
nasal cavity
pharynx
bronchus
Trachea, Bronchus
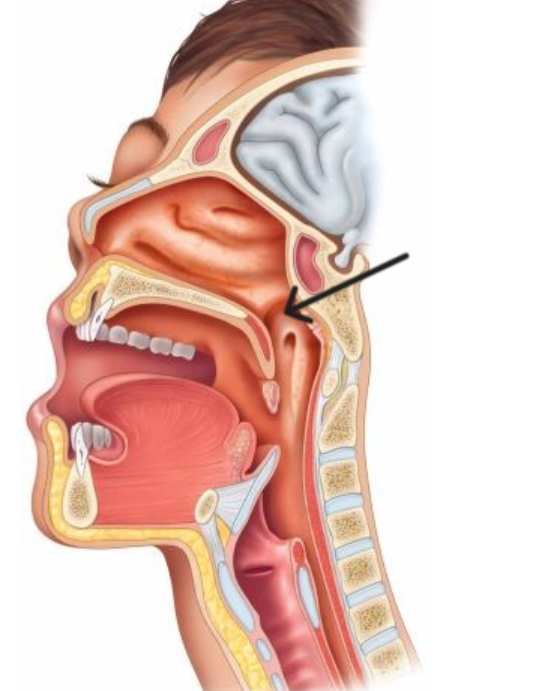
The structure highlighted is
Nasopharynx
The amount of air in excess of tidal volume that can be inhaled with maximum effort is the
Multiple Choice
expiratory reserve volume.
vital capacity.
inspiratory reserve volume.
residual volume.
inspiratory capacity.
inspiratory reserve volume
Select the structures that are a part of the upper respiratory tract.
Check All That Apply
tracheatrachea
nasal cavitynasal cavity
pharynxpharynx
bronchusbronchus
nasal cavity, pharynx
The _______ is the amount of air remaining in the lungs after a forced expiration.
residual volume
The volume of air exchanged during normal breathing is called the_______.
tidal volume
After a normal inspiration, the amount of air that can then be inspired forcefully is called the ________.
inspiratory reserve volume
The total lung capacity minus the residual volume equals the_______.
vital capacity
The vital capacity minus the_______equals the inspiratory capacity.
expiratory reserve volume
The effects of_______such as asthma or emphysema, may be determined by measuring rapid exhalation with a spirometer.
obstructive diseases
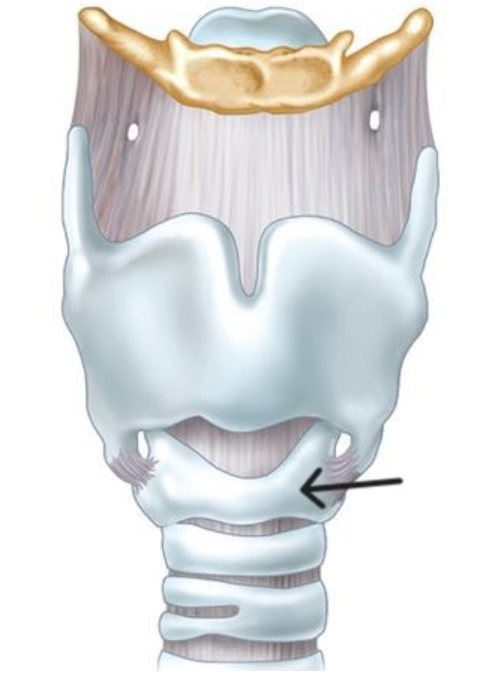
The arrow points to the:
Cricoid cartilage
The total amount of air a person can exhale after filling the lungs completely is called ________.
vital capacity
It is the sum of three respiratory______.
volumes
_______. which is the amount of air inhaled and exhaled in one cycle during quiet breathing
tidal volume
_________ which is the amount of air in excess of a normal breath that can be inhaled with maximum effort
inspiratory reserve volume
______. which is the amount of air in excess of a normal breath that can be exhaled with maximum effort.
expiratory reserve volume
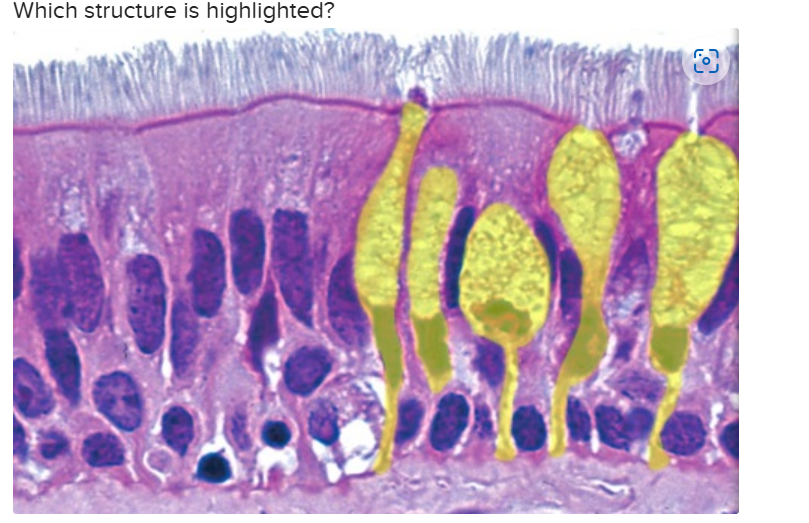
goblet cells of respiratory epithelium
Gas exchange between alveolar air and blood
external respiration
Gas exchange between blood and tissue
internal respiration
Movement of air into and out of lungs
ventilation
Use of oxygen for metabolic reactions within cells
cellular respiration
What is the name of the volume of air moved in or out of the lungs during a quiet respiratory cycle?
Multiple Choice
residual volume
vital capacity
inspiratory reserve volume
tidal volume
tidal volume
As the volume in the alveoli increases, the pressure decreases.
True or False
true
Which structure houses the vocal cords and consists of a framework of muscles and cartilages?
Multiple Choice
oropharynx
nasopharynx
trachea
larynx
larynx
Entry point for airflow during inspiration
nose
Voice production
larynx
Branching structures carrying air to alveoli
bronchial tree
Warms, filters, and moistens air as it enters respiratory tract
nasal cavity
Respiratory organs; comprised of airways and air sacs
lungs
Reduces weight of skull; voice modulation
paranasal sinuses
Conveys air from larynx to bronchial tree
trachea
Conveys air from nasal cavity to larynx
pharynx