Classic Ethical Theories
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
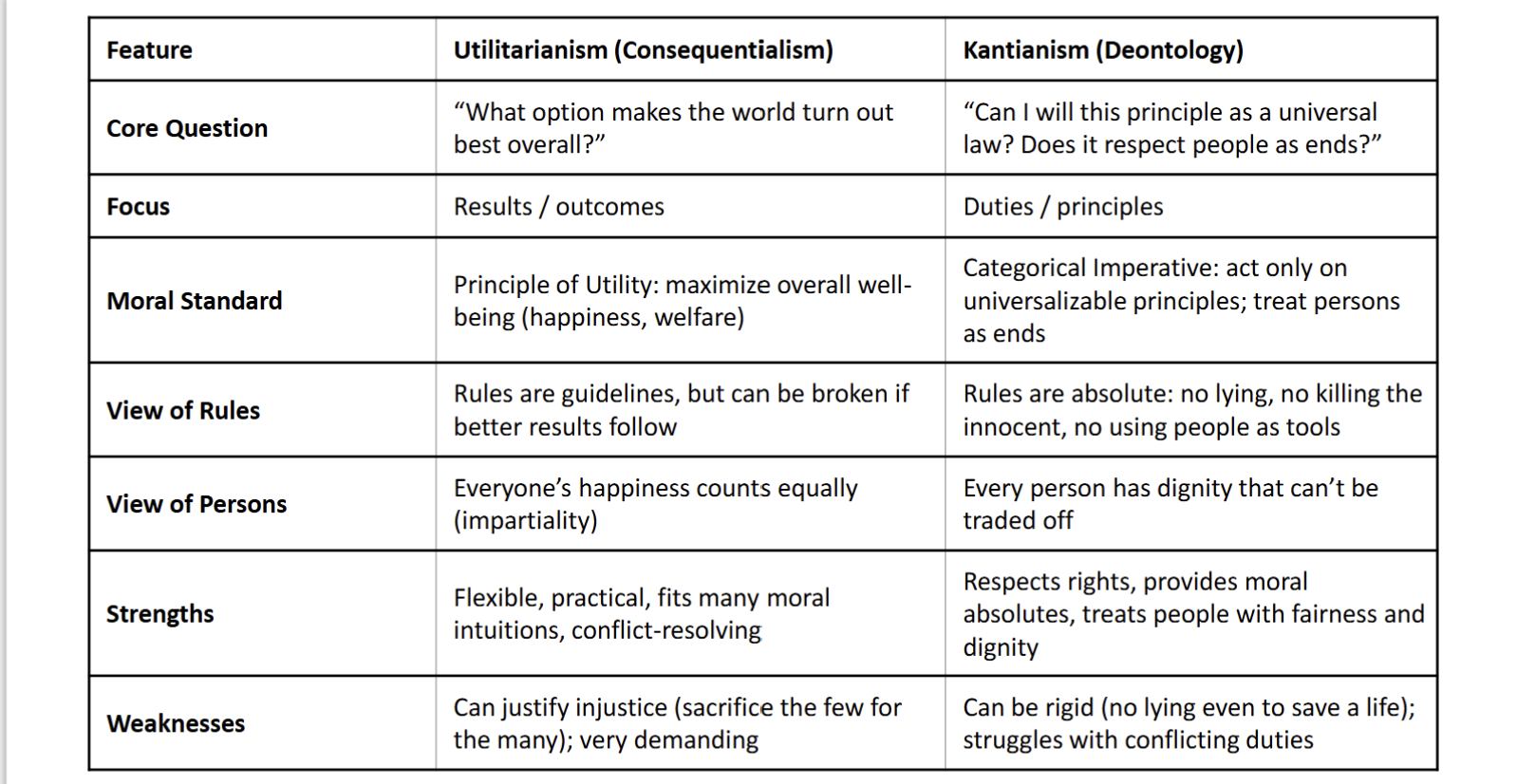
What does consequentialism focus on?
RESULTS! The right action is the on that increases overall wellbeing.
Which ethical theory treats morality like a giant cost-benefit analysis?
Consequentialism
Think of a general summary of consequentialism and see if you miss anything.
—the moral act maximizes good and minimizes the bad
—no exception or loopholes, even if one must violate a rule to get the best results
—the end justifies the means (as long as the ends are good enough)
What is the structure/ steps to consequentialism?
Identify what’s intrinsically good.
Identify what’s intrinsically bad.
List your real options.
Predict the outcomes.
Balance the results. (Find out how which options have the most good with the least bad.)
Pick the optimific option.
How many morally right choices are there in Consequentialism?
Only one; the choice that maximizes overall benefit.
What is the most famous version of consequentialism?
Utilitarianism
Utilitarianism claims that the only intrinsic good is…
well being
With a utilitarianist view, an act is right only if it maximizes overall…
well-being
Which ethical theory uses the Principle of Utility?
Utilitarianism
What does the Principle of Utility say to do?
Produce the greatest net balance of happiness over suffering.
Which is broader, consequentialism or utilitarianism?
Consequentialism
Consequentialism is the general family of theories saying:
an action is only morally right if it produces the best overall results
The option that produces the best overall results is called the…
optimific option
How is consequentialism more broad than utilitariansim?
—It doesn’t specify what counts as “good results”
—different consequentialist theories may define “good” differently
—utilitarianism specifically weighs overall well-being (happiness or pleasure or satisfaction)
True or false: All utilitarian’s are consequentialists, but not all consequentialists are utilitarian.
True
True or False: All consequentialists are utilitarian, but not all utilitarians are consequentialists.
FALSE
What are the three attractions of Consequentialism?
Impartiality- Everyone’s well-being is valued the same.
Conflict-Resolution of Power- there is one clear rule to follow: pick the option that makes the world better overall.
Moral Flexibility- No rules are carved in stone. You can break rules to create an overall benefit. This gives a sense of realism and makes morality adaptable to circumstances.
What are the four critics of Consequentialism?
Measuring Well-Being is Hard- how can you add up things like happiness and freedom into a single number or variable? Different people value different things. Its asking for an impossible kind of moral math.
Too Demanding- requires people to always do the most possible good. Makes moral life feel like we’re constantly failing morality. Options that result in overall well-being range from the mundane to heroic and these are required not just admirable.
Impartiality Can Feel Inhuman- we naturally care more about the people nearer to us, and most people tend to think its ok to give those you care about more weight, but consequentialism does not allow this.
Moral Knowledge Problem- since morality depends on results, you can only know if you’ve made the right choice until after you’ve made it. you can’t always predict outcomes.
What ethical theory stresses that it is immoral to treat people as a means to an end?
Kantianism
What is another label for duty based ethics?
Deontological ethics
While Consequentialism is about results, Kantian ethics is about…
principles, rules, and respect for persons
Think of a summary for Kantianism.
—duty based
—not about results
—about principles, rules and respect for persons
—acting morally is acting from duty, not inclination or convenience
What rule does Kantianism use?
the Categorical Imperative
What are the two most famous versions of the Categorical Imperative?
The Universal Law Test
The Humanity Test
What is the Universal Law Test?
“Act only of maxims that you could will to become universal law” (only act in ways that could be justified universally.)
What is the Humanity Test?
“Always treat humanity, whether in yourself or others, never merely as a means, but always also as an end.”
(Never treat others as tools. respect people’s rationality and autonomy.)
Consequentialism is to Utilitarianism as Deontology is to…
Kantianism
What separates Consequentialism/Utilitarianism from Deontology/ Kantianism in simple terms?
Consequentialism/Utilitarianism: morality = results.
Deontology/Kantianism: morality = duty
QUIZ YOURSELF ON THIS NOW