Exam 2: Radiation Biology (168)
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
Extra: List the 6 Factors that affect treatment Dose
For: Fractionation
Our: O2 effect- OER
Little- LET
Royal Queen- RBE/QF
Stop The- Sensitivity of Tumors
DR- Dose Rate


Radiobiological measurements that relate dose and fractionation to cancer cell killed as graphs that show how different tissues are impacted differently by dose/fractionation:
Alpha-Beta Ratios
TFDs/ NSDs don’t take this into account
Extra: Explain

Extra: the dose required in the absence of O2 to produce the SAME effect as a dose in the presence of O2
OER
A typical OER would be:
Extra: What does OER stand for
2.5-3.0
Oxygen Enhancement Ratios
T/F: A dose of 750 cGy in one fraction would have the same biological effect as 75 cGy in 10 fractions (75cGy x 10 tx's).
750 cGy in 1 fraction would have a greater Biological Effect
(like taking 10 Tylenols at vs taking 1/ day for 10 days)
Which of the following best represents the Therapeutic Ratio formula:
TR = NTTD/ TLD
Therapeutic Ratio = Normal Tissue Tolerance Dose/ Tumor Lethal Dose
Extra: dose anoxic to produce an effect/dose aerobic for same effect
OER formula
A TR of 0.7 would best indicate a _____ tumor
A. Radiotreatable
B Radioresistant
C Radio-neutral
D well-oxygenated
B Radioresistant
FYI:
TR >1 radiotreatable
TR < 1 radioresistant
What, by far, is the most important radiosensitizer?
Oxygen
T/F b.i.d. treatment is synonymous with split-course treatment.
False: Synonymous with hyperfractionation
Extra: list all tx schedules
7 days/ week - treat every day
5 days/ week- (weekends off)
4 days/ week (wed. & weekends off)
split-course (treat a few weeks, take a week+ break, finish treating)
hyperfractionation (BID)- more than 1 tx/ day
The unit of measurement RET was developed by:
Ellis
Extra: QF stands for
Quality factor
Extra: QF chart for different energies
electons also 1
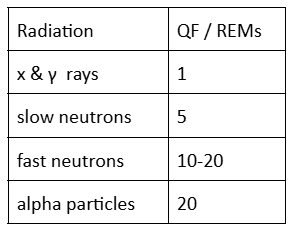
Typical quality factor for electron beams:
1
The differences in the mitotic rates of different cells is characterized by a difference in the length of what phase of the cell cycle?
G1
if it takes 3000 cGy to kill an anoxic tumor, what dose, in cGy, is required to kill an aerobic tumor?
1000 cGy
FYI:
1/3 rule of oxygen sensitization
3000 cGy/ 3 = 1000 cGy
The 4 R’s of radiation biology
↑ Repair (Recovery) = ↓ Kill
↑ Reoxygenation = ↑ Kill
↑ Redistribution = ↑ Kill
↑ Repopulation (Regeneration) = ↓ Kill
extra: acute radiation syndromes aka
manifest syndromes
Extra: What are the 3 acute radiation syndromes & causes of death
Hematologic : massive infection (WBC)
GI: fluid & electrolyte loss (NV & Diarrhea)
CNS: death within a few hours due to intracranial pressure
Extra: Dose Ranges for the 3 manifest syndromes
Hematologic
GI syndrome
CNS syndrome
Hematologic: 100- 1000 cGy
GI syndrome: 1000-5000 cGy
CNS syndrome: >5000 cGy
Death from the Hematologic syndrome would usually be from:
acute infection
Extra: Acute radiation syndromes can further be broken down by their ___& ___ periods
Prodromal syndrome
Latent Period
The immediate radiation sickness following a high whole body exposure" best defines what term:
prodromal
extra: the period FOLLOWING the prodromal syndrome during which there is NO sign of sickness
Latent Period
Extra: In your own words, describe the following
1. threshold effect:
2. non-threshold effect;
3. stochastic effect;
4. non-stochastic effect
1. threshold effect: X effect can happen after reaching X dose
2. non-threshold effect: effect can happen at any dose
3. stochastic effect: have no threshold dose (Carcinogenesis & genetic mutations)
4. non-stochastic effect: somatic effects that ↑ dose = ↑ severity
Erythema is an example of:
1. threshold effect:
2. non-threshold effect;
3. stochastic effect;
4. non-stochastic effect
1, 4
Extra.
LD 50/30 means
aka
the lethal dose to 50% of the population within 30 days
LD 50
The dose for LD 50/30 (for whole body) is typically about cGy
400 cGy
FYI: avg. 300-500 for whole body
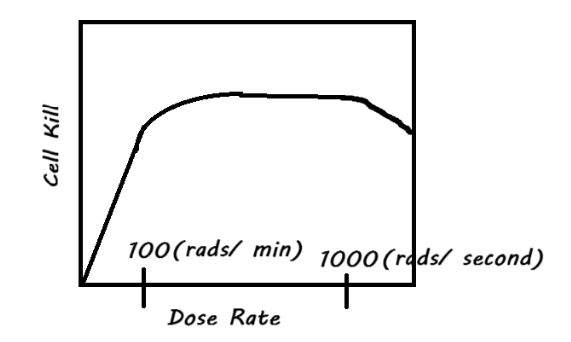
Extra: Draw a graph of how dose rate would impact cell kill
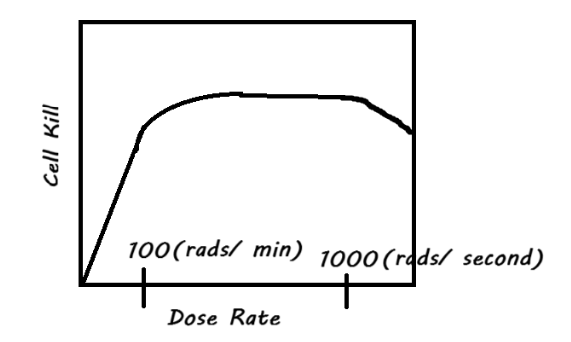
The "law" or principle that states that, for example, eating too much of something results in a decreased appreciation for that thing as more and more is ingested describes The Law of___
Diminishing Returns
FYI: Anything over 100 rads/ min (or 100 MU/ min) doesn’t increase cell kill due to Law of Diminishing Returns
The Acute Whole body radiation syndrome with the shortest latent period would be:
CNS
FYI:
Short prodromal period
Very short latent period if there even is one
The "most important" radiation induced malignancy:
Leukemia
The only "Acute Whole Body Radiation Syndrome" that has a chance for survivability:
hematologic
FYI:
Dose range for hematologic : 100-1000cGy
Avg. LD50/30 whole body = 400
Highest whole body dose survive: 850 cGy
What is the most important chemical radiosensitizer?
Oxygen
What dose represents the LD 50/30 for humans?
400 cGy
FYI: for whole body
Longer times between cell divisions are caused by an increased length of what phase of the cell cycle?
G1
The majority of the biological effects from radiation exposure results from the: (direct/indirect) effects
indirect
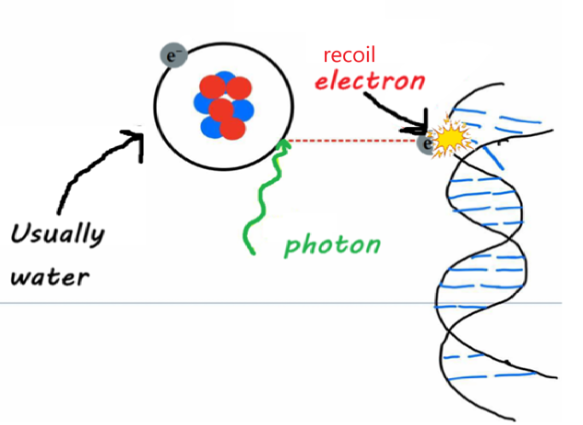
Extra: Direct EFFECTS of RTT on DNA
photon ionizes an atom (usually H2O), ejecting an electron
the recoil electron causes a break in the DNA molecule
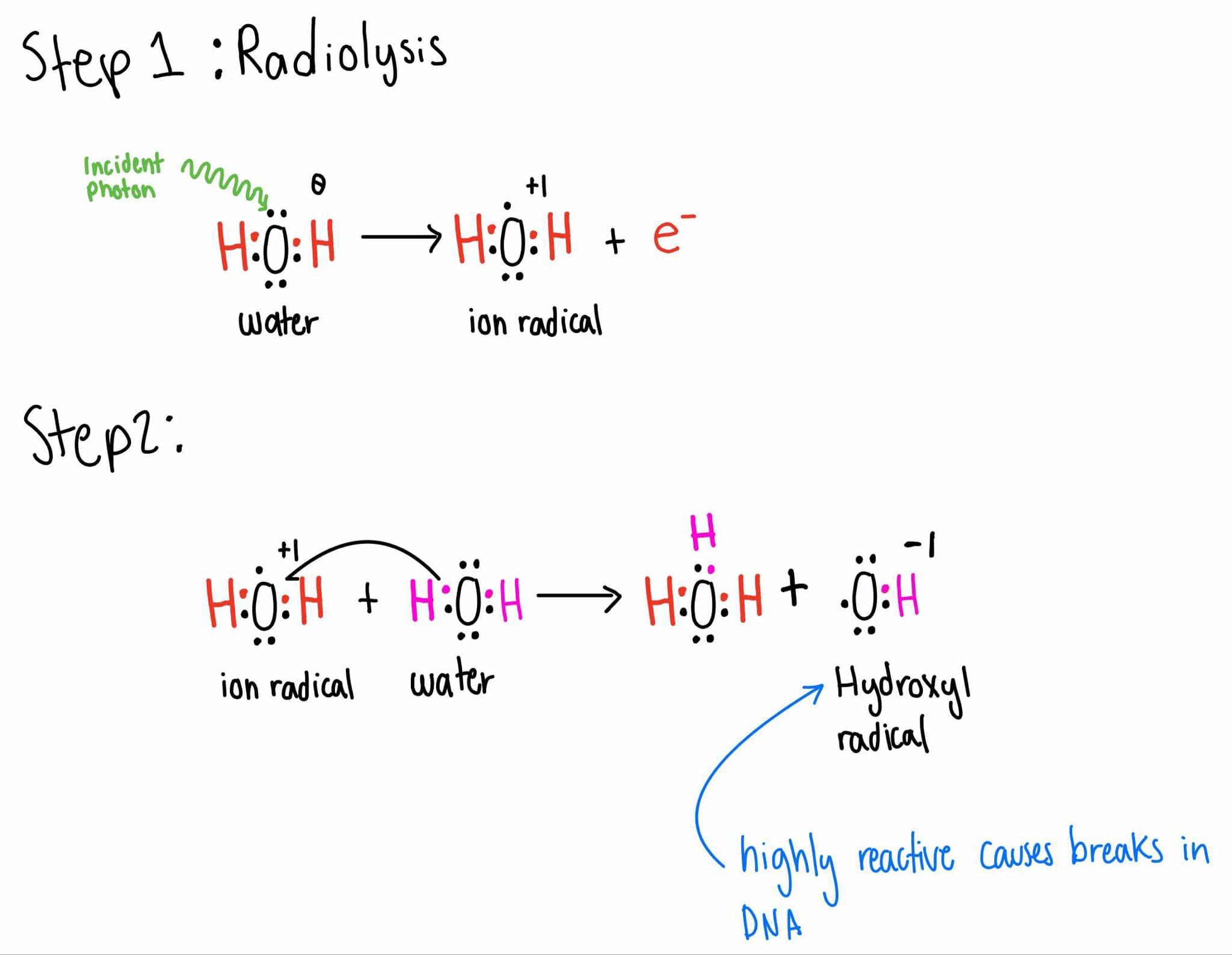
Extra: Indirect Effect of RTT on DNA
Step 1: Radiolysis
The incident photon ionizes a water molecule producing H2O+, an ion radical, & an electron
H2O+ combines with a normal H2O molecule producing H3O+ & OH*. a hydroxyl free radical, which is HIGHLY reactive and readily causes breaks in the DNA molecule
What molecule most commonly undergoes the process of radiolysis when exposed to ionizing radiation in mammals?
H2O
Electromagnetic (EM) radiations:
1. travel at light speed;
2. travel in waves;
3. tend to interact with matter more easily than particulate radiations
1, 2
The “most important” radiation induced malignancy (late carcinogensis) is:
Leukemias
Which of the following best represents the chemical symbol for the most reactive free radical that is presumed to cause most of the damage to cells upon irradiation?
OH*
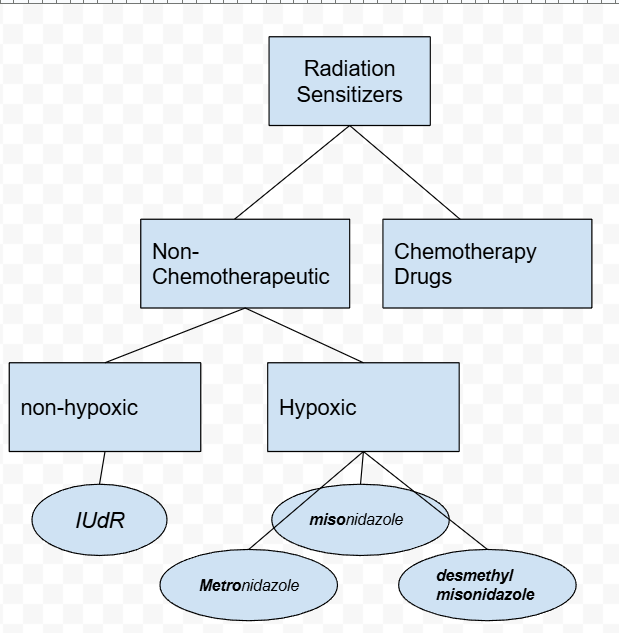
Which of the following is an example of a non-hypoxic radiosensitizer?
(just list all the radiosensitizers instead)
Place the following events in the order they occur with respect to free radical production by ionizing the radiation:
1. Photon interacts with water molecule;
2. Radiolysis occurs;
3. H2O+ combines with H2O;
4. Free radical are produced
1, 2, 3, 4
Free radicals can recombine to form water again, react with nearby macromolecules causing damage to the molecule or produce a toxic substance harmful to the cells called:
Hydrogen Peroxide
It is estimated that about ____% of x-ray damage to cells is due to the production of free radicals.
95
Which of the following does NOT constitute particulate radiation?
A. Gamma
B. Alpha
C. Neutrons
D. Electrons
E. More than 1 is correct
A. Gamma- EM radiation (e.g. cobalt)
What molecule is considered to be the "target" molecule?
DNA
Chemical breaks in macromolecules can:
A. result in no harm
B. cause reproductive death
C. Cause mutations
D. A and B only
E. All can occur
E. all can occur
Extra: Chemical breaks in macromolecules can:
3 things
Restitution- DNA repairs itself
Failure to Rejoin (of rungs in ladder)
Mutation
How many doubling times does it generally take for a tumor to be clinically noticeable (about 1 cm in diameter)?
30
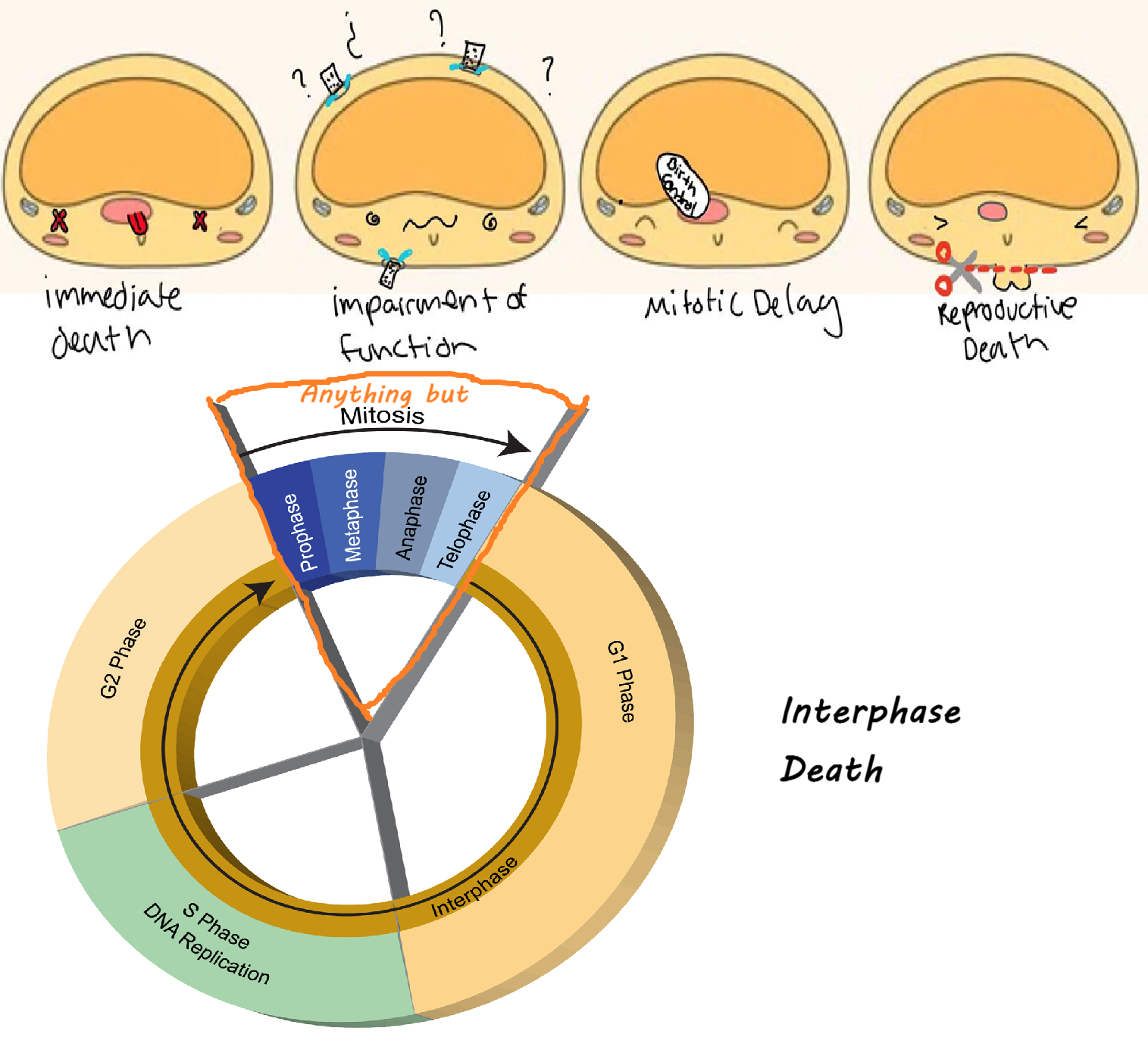
When slow reproducing cells such as muscle and cartilage die as a result of mechanisms that are poorly understood (probably relating to DNA breaking down resulting in destruction of the nucleus) this type of effect of radiation on a cell is called:
Interphase Death
(cells die before mitosis)
Which cells have the best repair abilities?
1. normal cells;
2. cancer cells;
3. poorly differentiated cells;
4. well differentiated cells
1, 4
Law of Bergonie & Trinodeau
Normal cells= normal reproducing & well differentiated
Cancer cells= fast reproducing & poorly differentiated
When side effects return, as might happen when a patient receives radiation treatments and-6 months later-has a re-appearance of those side effects while undergoing chemotherapy, this effect is called:
Radiation Recall
Which of the following tissues would be most sensitive to the effects of radiation?
A. Blood forming tissues
B connective tissues
C muscle tissues
D nervous tissues
A. blood forming cells
Extra:
Very sensitive cells
LESO
Lymphocytes
Erythroblasts
Spermatogonia
Oogonia
Extra:
Moderately Sensitive Cells
Glandular Epithelium
Basal Cells of skin (& it’s appendages)
Lens of the eye
Cells of Small Intestine Crypts
Liver Cells
Good Boys Love Selling Liver
Extra: Not sensitive cells
Glial
Nerve
Muscle
Osteocytes
Connective tissue cells
GMO? No C
Extra:
Which structure is the most radiosensitive?
And what mature cell type is the most radiosensitive?
lens of the eye
lymphocytes
Which of the following is not a direct effect at the cellular level?
(list direct effects instead)
Extra: List indirect effects on a cellular level
Loss of blood supply causes local cell death
Damaged cells fall victim to antibodies
The theoretical dose of radiation at which a biologic response is noted to occur is termed the:
threshold dose
Which of the following has the greatest probability of interacting with matter?
A. Neutrons
B. x-rays
C. Beta particles
D. Alpha particles
D Alpha particles
FYI:
Particle = interacts with matter more
Bigger particle = more interaction so Alpha, Neutrons, Beta
x-ray is EM so less interaction
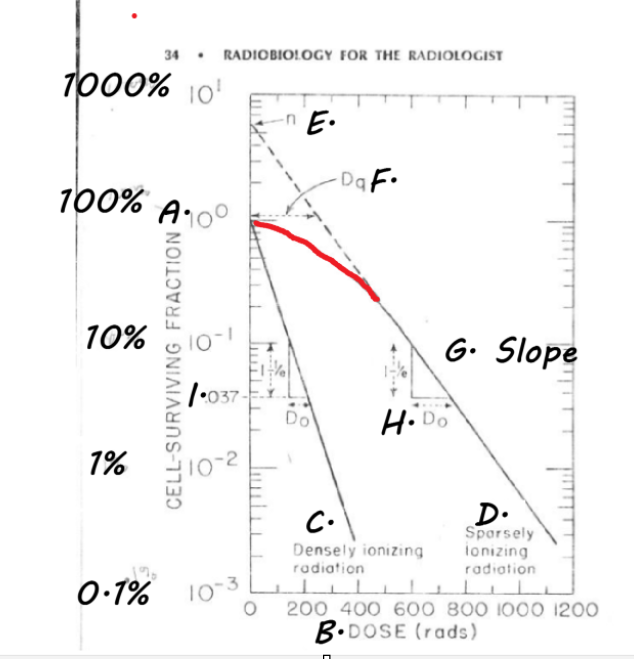
What is the part in red called?
Shoulder- sub-lethal damage (cells are able to repair themselves)
↑ shoulder = better repair abilities = ↑ radioresistant
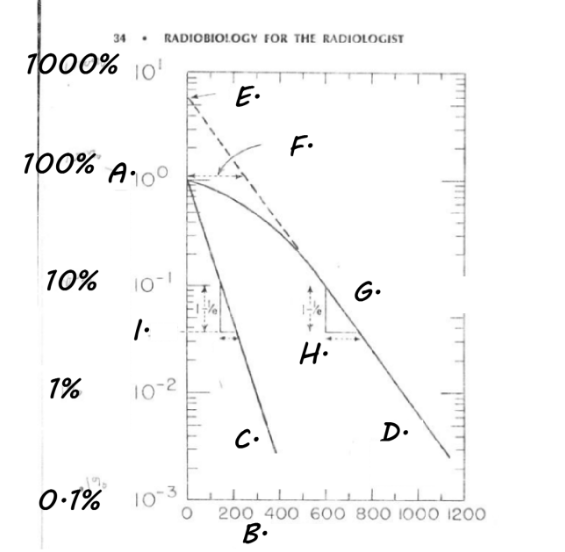
Extra: Label the Cell Survival Curve
E. n= extrapolation number, where curve would be if there was no shoulder, indirect way to measure width of shoulder
F. Dq= Threshold / Quasi-Threshold dose= another way to measure repair ability
G. Slope- line straight down from shoulder; depicts liner cell kill
H. Do/ D37 / Mean Lethal dose
I. .037
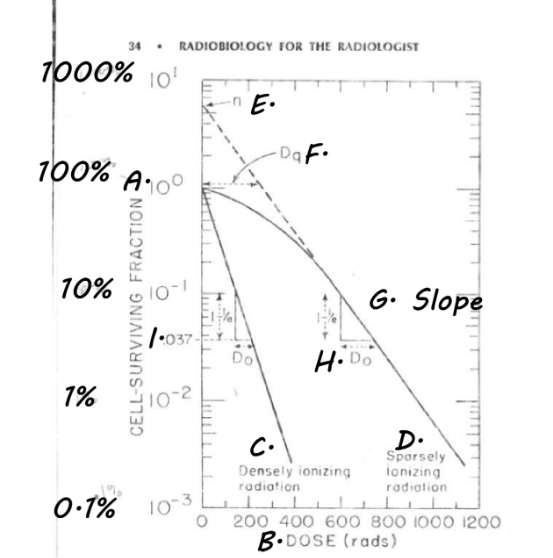
extra: Define Do/ D37/ Mean Lethal Dose
the dose required to REDUCE the # of surviving cells to 37% of their original #
the dose required to AVERAGE one inactivating event (hit) per cell
What portion of a cell survival curve is also known as the threshold dose?
Dq
FYI: Threshold dose or Quasi-threshold dose
In radiation biology terms, a "hit" is:
A. a song selling more than a million copies
B An inactivating ionization in the target molecule, an ionizing event
C The dose sufficient to kill all the cells in a group
D the dose slightly higher than the threshold dose
B
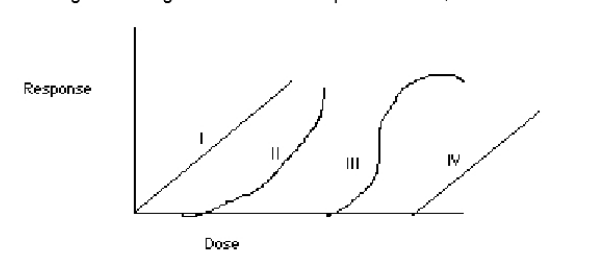
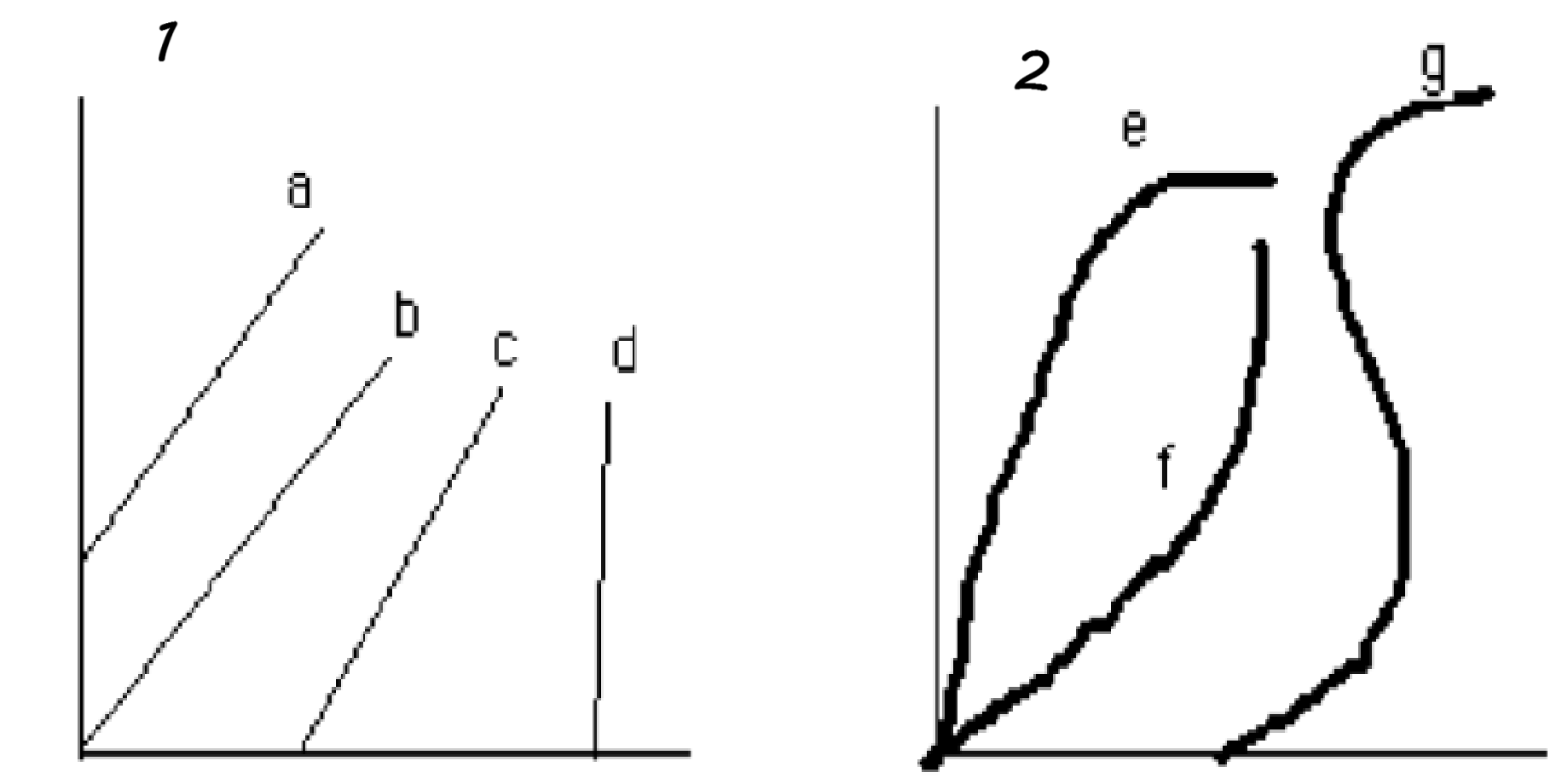
In the diagram, the linear, threshold dose-response curve is represented by the number:
(describe the other lines)
IV
FYI:
I. Linear & non-Threshold
II. & III. non-linear &-threshold
Which of the following tumors would not be considered resistant to the effects of radiation ?
H&N
Skin ca
glioblastoma
bladder ca
B. skin
Extra:
List Sensitive Tumors (Low Dose TX)
Moderately Sensitive Tumors
Resistant (High Dose Tx)
NOTE: No need to know the dose, just the order
List Sensitive Tumors (Low Dose TX)
stay-at-Home Lover (SHL)
3000- 4000 rad: Seminoma
4000-4500 rad: Hodgkin’s Disease & Lymphosarcoma
Moderately Sensitive Tumors 5000-6000 rad
miguel BOSE
Breast
Ovarian
Skin Ca: Basal & Squamous
Ewing’s Sarcoma (connective tissue CA)
Resistant (High Dose Tx)
BLew m Necked
7000-7500 rad
Head & Neck CA
Bladder CA
Cervix CA
Lung CA
8000 rad +
Best S-H-Bf ,that M
Head & Neck CA (advanced)
Brain CA
Bone CA
Melanoma
Soft Tissue Sarcoma
My Stay at Home Lover is miguel BOSE, he BLew m + Necked m, he is the Best Stay-at-Home Boyfriend, that Man
In general, RBE increases with an increase in the:
A. Quality Factor
B. Linear Energy Transfer
C. Oxygen Enhancement Ratio
D. Both A and B
D. both A and B
FYI:
RBE = Damage
A. ↑ QF = ↑ Damage
B. ↑ LET = ↑ concentrated = ↑ Damage
C. ↑ OER means you need ↑ dose = ↓ damage
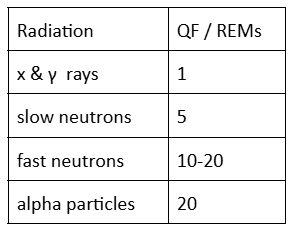
Energy unleashed per micron of medium by an ionizing particle is called:
LET
Which of the following tumors would not be considered sensitive to the effects of radiation?
A. Seminoma
B. Wilms
C. HD
D. Astocytoma (brain tumor)
D
Which of the following are listed in order of increasing sensitivity?]
A lymphocytes, cells of the lens of the eye, osteocytes
B muscle cells, erythroblasts, connective tissue cells
C nerve cells, cells of the lens of the eye, lymphocytes
D spermatogonia, osteocytes, liver cells
C
Which of the following groups of cells is most radioresistant?
A nerve cells, connective tissue, muscle cells
B liver cells myeloblasts, basal cells
C lymphocytes, erythroblasts, spermatogonia
D cartilage cells, cells of the small intestine, cells of the lens of the eye
A
Cells are most resistant to radiation during what phase of the cell cycle?
late S phase
Cells are least resistant to radiation during what phase of the cell cycle?
M
Which machine has the greatest LET?
A 250 KV x-ray unit
B Cobalt 60
C 4MEV x-ray unit
D 25 MEV betatron (x-ray) unit
A. 250 KV
Higher Energy = Lower LET
Particulate = Higher LET
EM = Lower LET
Which of the following factors does not change the radiosensitivity of a cell?
O2
Chemotherapeutic drugs
Cell Cycle
All of the above
4
What dose range represents the Do for mammalian cells?
Context Do aka D37 aka Mean Lethal dose
100-200 cGy
(i.e. if you give 100-200 cGy each day you are average to 1 hit / cell)
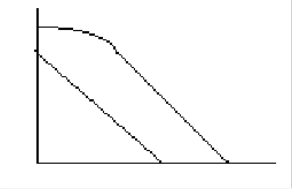
Which curve best represents a cell survival curve for particulate radiation? Note on the following illustration: the upper curve is curve A, the lower (straighter) curve is curve B
A
B
both A & B
neither A or B
B
Particulate radiation - linear
EM radiation - curvilinear
According to the cell survival curve, as dose increases, survival generally:
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C.. Stays the same
D Unable to determine
B. Decreases
Cuz the higher the dose = the more cells you kill, duh
Which of the following cell types are listed in order of decreasing radiosensitivity?
A lymphoid, skin, nervous
B bone marrow, lymphoid, skin
C skin, muscle, lymphoid
D skin, lymphoid, nervous
A
The Ellis formula:
A is used to determine RBE
B is used in determining TDF schemes
C is used to determine the effect of mitotic rate on cell sensitivity
D is used to calculate lethal cellular damage for cell survival curves
B
Which type of radiation is least effected by oxygen?
A. Alpha
B. Beta
C. Neutrons
D Oxygen affects all particulate radiations the same
C. Neutrons
If it took 300 rads to kill an aerobic tumor with x-rays, about how many rads would it typically take to kill an anoxic tumor with x-rays?
A 100
B 600
C 900
D unknown, not enough info is given
E None of these is correct
C. 900
1/3 rule of oxygen sensitization
Anaerobic dose = 3x Aerobic Dose
Aerobic Dose = 3 × 300 rads = 900 rads
Which of the following statements is NOT true?
A as LET increases, RBE increases
B as OER increases, RBE increases
C as LET increases, OER increases
D all of the above are true
C
FYI
A ↑LET = Radiation deposits most of their dose at one point = ↑ RBE (damage)
C not true cuz Higher LET (particulate radiation) = OER matters less (even if cells are hypoxic it doesnt matter)
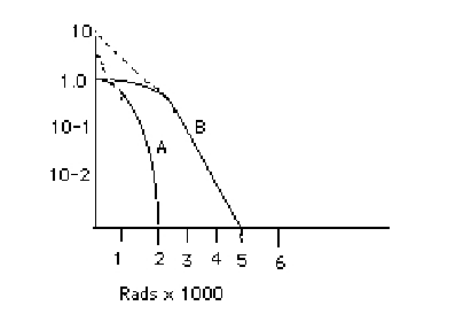
If curve "A" on the following diagram represents an aerated tumor and curve "B" represents the same tumor with low oxygen content, what is the OER for this tumor?
5/2 = 2.5
Which of the following dose fractionation schemes would have the highest biological effect?
A1000 rads X 1 tx
B 500 X 2
C 200 X 5
D all would have the same effect since the total dose is the same
A. Cuz its like taking 10 Tylenols at once vs taking 1/ day for 10 days
The initial radiation sickness after a large whole body exposure:
Prodromal
Which of the following fractionation schemes would have the highest biological effect using the same total dose and same daily dose?
A 5/wk
B 7/wk
C 4/wk
D split course
B.
If a dose response relationship is described as being linear/threshold, which of the following can be said about it?
1. as dose increases, response increases;
2. as dose increases, response decreases;
3. regardless of the dose, the desired effect could take place;
4. a minimum specific dose is needed for the desired effect to take place
1,4
An increased or improved blood supply would most likely effect:
A LET
B OER
C TDF
D NSD
B OER
What is the most important definition of cell death following irradiation?
A. The cell can no longer perform metabolic functions
B. The cell has undergone lysis
C. the cell has lost its capacity to proliferate indefinitely
D. the cell can no longer synthesize RNA
C. Reproductive Death: the cell has lost its capacity to proliferate indefinitely
FYI:
A is loss of function
B is Immediate cell death
D idk
Which of the following statements regarding the oxygen effect is least correct?
A oxygen is a potent radiosensitizer for gamma and x-rays
B The dose required to produce the same biologic effect is generally three times greater under hypoxic conditions than under oxic(aerobic) conditions for gamma and x-rays
C Oxygen must be present during irradiation to be effective
D oxygen is a potent sensitizer for all particulate radiations
FYI:
A. True, less so for particulate
B. True 1/3 rule of oxygen sensitization
C. True
D. False, doesn’t matter for particulate