Rest of Cardio
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Different types of heart failure
Left-sided failure
Systolic and Diastolic
Right-sided
Congestive
Systolic left sided
Reduced LV contractility → reduced ejection fraction
stroke volume/end diastolic volume
Diastolic left sided
Reduced LV compliance
reduced diastolic filling → lower end diastolic volume
same ejection fraction (both SV and EDV decreases)
Right sided
(left-sided causes right-sided)
Increased plasma volume
right side cannot pump back to pulmonary vein
blood backs up in the lungs (vena cava side)
consequence of left sided failure → less blood pumped systemically → backlog in pulmonary circulation
Congestive
Congestion in body tissues due to slow blood flow (hypotension or lack of contractility)
leads to oedema
Action of Atrial Naturetic Peptide
low pressure stretch receptors (volume receptors) in atria walls, detect high pressure
ANP and BNP released
stimulates glomerular afferent arteriole dilation
increased GFR
more excretion of Na+ and H20
decreased plasma volume (peeing more)
vasodilation (stimulation cGMP formation)
inhibits RAAS → decreases vasopressin (ADH) and aldosterone production
BNP generated in ventricular myocytes on heart failure
diagnostic marker
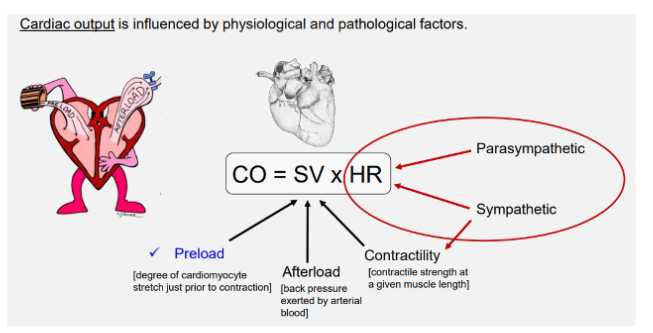
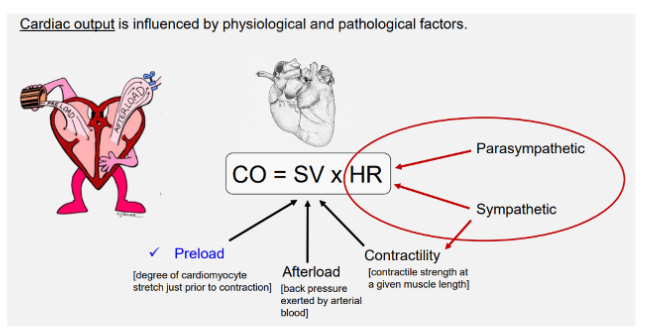
Major equations
CO = SV x HR
MAP = CO X TPR (total peripheral resistance)
CO = vol of blood pumped out LV per unit time (proportional to body metabolism
Venous return - blood volume RV per unit tume
ejection fraction = SV/EDV
Preload
venous return
circulating blood volume → impacted by haemorrhage
blood distribution btw central and peripheral veins
symp NS → peripheral venous tone
muscle pumps (gastrocnemius) → propels blood peripherally → centrally
thoracic pump
negative thoracic pressure and positive abdominal pressire propels blood centrally
degree of cadiomyocyte stretch prior to contraction
Influencers of ventricular filling [5]
VEDV → ventricular end diastolic volume = preload
circulating blood volume
venous tone
heart rate (reduced HR increases ventricular filling time)
myocardial compliance → preload (expansion when filling)
venous return → linked to circulating blood volume, blood distribution and venous tone
Heart rate
(Chronotropy)
beats per min (autonomic control)
Contractility (inotropy)
contractile strength at a given muscle length
Afterload
total force that opposes sarcomere minus the stretching that existed before contraction
pressure that the ventricles must overcome to eject blood (increasing systemic resistance increases afterload)
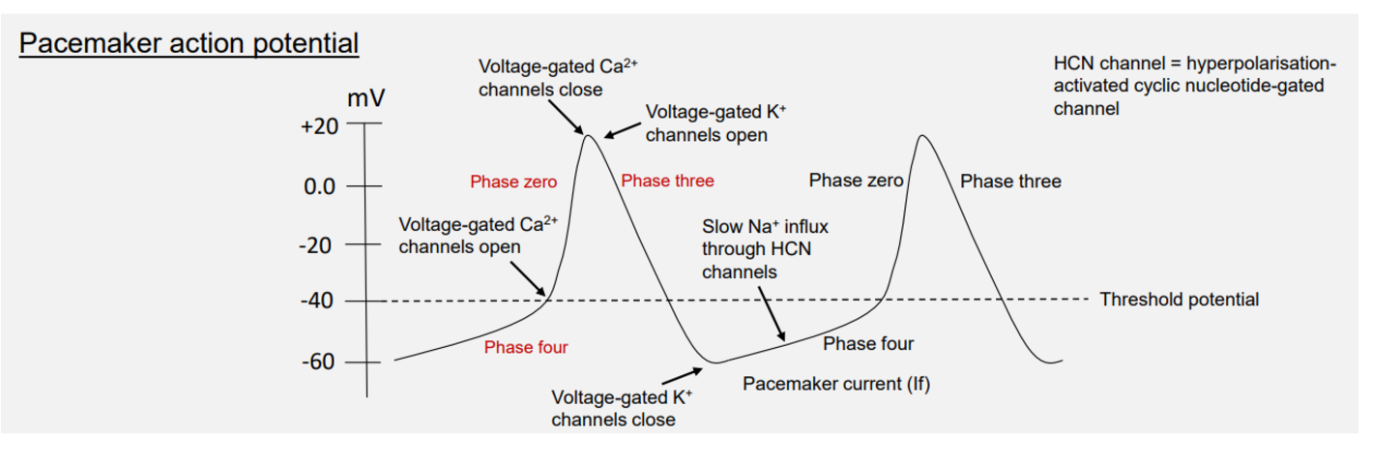
Pacemaker potential
4 → 0 → 3
phase 4 - funny current If - opening of slow Na+ ions channels
phase 0 - rapid depol → vgated Ca2+
phase 3 - vgK+ channels repolarisation
Ventricular Action Potential
4 → 0 → 1 → 2 → 3 → 4
ventricular - constant resting membrane potential = phase 4
when receives AP from AV node
phase 0 - vgated Na+ (fast) - rapid depol
phase 1 vg Na+ close → ito current
slow release K+ current
small drop in membrane channel triggers phase 1
phase 2 - plateau phase
Ca2+ influx balances K+ efflux
due to opening of vg L-type Ca2+ channels (slow)
phase 3 - repolarisation
Rapid delayed rectifier K+ channels open
slow Ca2+ channels close
phase 4 - resting potential reached again
EDV
Controlled by preload (filling time)
ESV
Controlled by force of blood ejection (contractility)
Resistance provided via vasoconstriction (MAP) → afterload
Frank Starling
Degree of stretch of muscle fibres dictates the energy for/strength of contractility
Higher fibre length → greater energy
Not linear
Overstretching impairs contractile function → optimum length for maximum contraction
Past this point → tension falls
Stroke volume
blood ejected per heart beat
Cardiac muscle ultrastructure
High mitochondria numbers → High energy dependency
Gap junctions within intercalated disk → electrically coupled
Desmosomes within intercalated disc → mechanical disk
Contractility regulation - independent of preload stretch (EDV)
Greater Ca2+ influx into cytoplasm (cytosol) → lower ESV
More blood pumped out → high SV
Ca2+ induced Ca2+ release
DHPR = voltage sensor
Ryanodine receptor → SER
Troponin C → exposure of myosin binding site
Troponin → 4 Ca2+ ion binding sites → cross bridges
Not usually saturated → higher relative force when more Ca2+ available
Power stroke → ATP bound myosin → mechanical force of contraction
Positive inotropism
Voltage gated Ca2+ channels conduct more Ca2+ → faster cardiomyocyte depolarisation
Ca2+ promotes faster cell depolarisation (increases conduction velocity)
Earlier activation of K+ currents (K+ RAPID delayed rectifier channels) → faster repol → increases heart rate
Ca2+ via calmodulin (activates kinase that →) enhances K+ current = faster repol
channels open earlier → If → reduced irregular heart beats
increased rate of contraction and relaxation
Sensitisation of troponin to Ca2+ → increase contractility at lower Ca2+ concentrations
Increased rate of Ca2+ uptake back into SER → faster muscle relaxation
Sympathetic stimulation → positive inotropic effect
Maximal contractile force increased
Rate of contraction increased
Rate of relaxation increased
Intrinsic vs Extrinsic inoptropy
Intrinsic → related to preload
Extrinisic → sympathetic stimulation, movement from one starling curve to another
contractility independent of stretch
increasing stroke work regardless of preload and afterload → (higher contractility)
How Ca2+ influences ventricular myocyte contraction
Action potential
faster plateau phase → 2 (shorter)
faster repol → 3 (shorter)
Sarcoplasm conc.
increase influx and efflux → faster contraction
Contraction
rapid and more powerful contraction → 2
rapid relaxtion
3 ways altering contractility
preload stretch
troponin sensitisation
change of free Ca2+ conc in cytosol/sarcoplasm
Acetylcholine - weak negative ionotrope
acts only on atria
reduces cAMP → less PKA → less Ca2+ release → less contraction
Other factors that decrease contractility
parasympathetic drive (weak)
heart failure
myocardial infarction
hypoxia
negative inotropic drugs
beta-blockers (less PKA action)
calcium channel blockers
Na+ blockers → increase Na+/Ca2+ exchange → more Ca2+ pumped out
Increasing cardiac work reduces cardiac efficiency
little anaerobic capacity
Coronary artery 4-5% of cardiac output
smaller blood supply relative to other organs
Cause of eccentric hypertrophy
high preload
thinning chamber
overwork → fibrosis
Cause of concentric hypertrophy
high afterload
thickening chamber
overwork → fibrosis
worse fibrosis
Chronic stress → fibroblast activation → collagen deposition
preserved ejection fraction
Increased afterload
inverse relationship btw afterload and stroke volume
increased cardiac work
stroke volume decreases → must increase contractility (positive ionotropic effect)
high pressure (hypertension) → aortic valve stenosis (narrowing of outflow tract)
mean arterial pressure
MAP = DAP + (SAP-DAP)/3
Pulse pressure
SAP - DAP
SAP - peak pressure → blood ejection
DAP - residual pressure → ventricular filling
Factors influencing peripheral resistance
vessel diameter
vessel length
blood viscolsity
Carotid sinus and Carotid body
Carotid sinus is a dilated area (occipital-internal carotid trunk) at the base of the internal carotid artery, right after the bifurcation of the common carotid artery.
body = chemical
sinus = baroreceptors → IN tunical media elastic tissue
detects stretch not pressure
stretch activates → nerve fibres
Tunica adventitia (externa)→ thickened → accomodates afferent nerve endings
Aortic sensors
Aortic bodies and baroreceptor zone
in aortic arch
Supplied → carotid sinus nerve of glossopharyngeal never (CNIX)
Other sensor locations
right subclavian artery and R&L pulmonary artery ROOTS
Baroreceptor firing
Signal to raise pressure = increased firing
sympathetic outflow
Signal to lower pressure = Gap in firing
depressor/pressor reflex (parasympathetic outflow dominant)
TPR control
arteriole diameter.radius
hypertension → increases resistance (higher pressure)
lower flow
Factors affecting arteriolar radius
Central → neurohumonal (sympathetic, baro, RAAS)
alpha (constriction) vs beta2 (dilation)
peripheral
tissue factors
metabolites → oxygen = main controlling factor → low = vasodilation
functional hyperaemia → increase bloodflow to meet metabolic demand (skeletal muscle)
K+ ions (opposite of calcium)
low = constriction
high = dilation → hyperpolarising current
lactate
others: pCO2, phosphate, osmality
vascular factors
NO and PG → vasodilators
+ histamine, bradykinine, ANP
constrictors
vasopressin
(N)Ad
5-hydroxytryptamine
seratonon
angiotensin II
endothelin
TxA2 (thromboxin AII)
ADP and ATP
vascular anatomy → number of perfused vessels + mechanical stimuli
Lymph formation
interstial fluid formation → excess drained as lymph
hyrdostatic > colloid (oncotic) pressure
net movement of fluid out of capillary
arterial end - dominant hydrostatic
venous end - dominant oncotic
sinus rhythm
SA nose acting as pacemaker
(healthy ECG)
Sinus arrhythmia
normal ECG but RR interval varrues
commonly related to respiration
Sinus tachycardia
normal response to exercise
hyperthyroidism
fever
reflex to low arterial pressure (real or perceived decrease in CO)
Sinus bradycardia
abnormal but indicative of fit intervals
thershold potential
-40MV
Na+ slow influx → funny current
btw -60 → -40MV
when Vg K+ channels open
+30MV
Conduction system → noncontractile cardiomyoctes
fewer myofibrils
no intercalataed disks - but sill connected by gap junctions and desmosomes
more glycogen and mitochondria
Key facts about depol and repol of the heart
SA fastest + dominant
depolarisation: endo→epi (in→out)
repol: out → in (epi→ endocardium)
Moderator band → quick connection to papillary muscle to right ventricle
Extends from the interventricular septum to the anterior papillary muscle of the right ventricle.
It’s only in the right ventricle –
coordinated contraction of both ventricles
Moderator band
Septomarginal trabecula
Trabecula septomarginalis