World History - S1 Exam
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Civilization
An advanced stage of human society marked by a well-organized government and high levels of culture, science, and industry
Cultural diffusion
The spread of ideas, customs, and technologies from one people to another
City-State
A political unit that includes a city and it surroundings and villages
Empire
A state containing several countries
Democracy
A form of government in which citizens hold political power
Martyr
A person who suffers or dies because of his or her beliefs
Pope
Head of the Roman Catholic Church; in ancient Rome, bishop of Rome who claimed authority over all other bishops
Secular
Having to do with worldly, rather than religious, matters; nonreligious
Papal Supremacy
The claim of medieval popes that they had authority over all secular rulers
Canon Law
Body of laws of a Church
Excommunication
Exclusion from the Roman Catholic Church as a penalty for refusing to obey Church law
Anti-Semitism
Prejudice against Jews
Schism
A split or divide
The Great Schism
The official split between the Roman Catholic and Byzantine churches that occurred in 1054
Crusades
A series of wars from the 1000s through 12000s in which Europe Christians tried to win control of the Holy Land from Muslims
Holy Land
Jerusalem and other places where Christians believe Jesus had lived and preached
Black Death
An epidemic of the bubonic plague that ravaged Europe in the 1300s
Epidemic
Outbreak of a rapidly spreading disease
Icon
Holy image of Christ, the Virgin Mary, or a saint venerated in the Eastern Orthodox Church
Citizen
Legal member of a country
Messiah
Savior sent by God
Humanism
An intellectual movement at the heart if the Renaissance that focused on education and the classics
Humanities
study of subjects such as grammar, rhetoric, poetry, and history that were taught in ancient Greece and Rome
Florence
A city in the Tuscany region of northern Italy that was the center of the Italian Renaissance
Perspective
Artistic technique used to give paintings and drawings a three-dimentional effect
Utopian
Idealistically or visionary, usually used to describe a perfect society
Indulgence
In the Roman Catholic Church, pardon for sins committed during a person’s lifetime
Wittenberg
A city in northern Germany, where Luther drew up his 95 theses
Diet
assembly or legislature
Predestination
Calvinist belief that God long ago determined who would gain salvation
Theocracy
Geneva
Swiss city-state that became Calvinist theocracy's in the 1500s; today a major city in Switzerland
Sect
A subgroup of a major religious group
Canonize
Recognize a person as a saint
Compromise
An agreement in which each side makes concessions, acceptable middle ground
Council of Trent
A group of Catholic leaders that met between 1545 and 1563 to respond to protestant challenges and direct the future of the Catholic Church
Heliocentric
Based on the belief that the sun in the center of the universe
Scientific Method
A careful, step by step process used to confirm findings and to prove or disprove a hypothesis
Hypothesis
An unproved theory accepted for the purposes of explaining certain facts or to provide a basis for further investigation
Calculus
A branch of mathematics in which calculations are made using special symbolic notations, developed by Isaac Newton
Gravity
Force that pulls objects in Earth’s sphere to the center of Earth
Middle Passage
The leg of the triangular trade route on which slaves were transported from Africa to the Americas.
Dutch East India Company
A trading company established with full sovereign powers by the Netherlands in 1602 to protect and expand its trade in Asia
Encomienda
The right, granted by Spanish monarchs to conquistadors, to demand labor or tribute from Native Americans in a particular area
Line of Demarcation
Line set by the Treaty of Tordesillas dividing the non-European world into two zones, one controlled by Spain and the other by Portugal
Missionary
Someone sent to do a religious work in a territory or foreign country
Viceroy
Representative of the king of Spain who ruled colonies in his name
Mercantilism
Policy by which a nation sought to export more than it imported in order to build its supply of gold and silver
Columbian Exchange
The global exchange of goods, ideas, planets, and animals, and disease with Columbus’s journey to the Americas
Sepoy
Indian soldier who served in an army set up by the French or English trading companies
Triangular Trade
Colonial trade routes among Europe and its colonies, the West Indies, and Africa in which goods were exchanged for enslaved people
Cartographer
A person who makes maps
Goa
A coastal city seized in 1510 that became the commercial and military base of Portugal’s India trade
Price Revolution
Period in European history when inflation rose rapidly
Circumnavigate
To travel completely around the world
Monopoly
Complete control of a product or business by one person or a group
Conquistador
“Conqueror“ in Spanish; a leader in the Spanish conquests of America, Mexico, and Peru in the sixteenth century
Treaty of Tordesillas
Treaty signed between Spain and Portugal in 1494, which divided the non-European world between them
French and Indian War
War between Britain and France in the Americas that happened from 1754 to 1763; it was a part of a global war called the Seven Years War
Outpost
A distant military station or remote settlement
Commercial Revolution
A period of European economic expansion, colonialism, and mercantilism which lasted from about the 1500s until the early 1700s. It included the growth of capitalism, banking, and investing
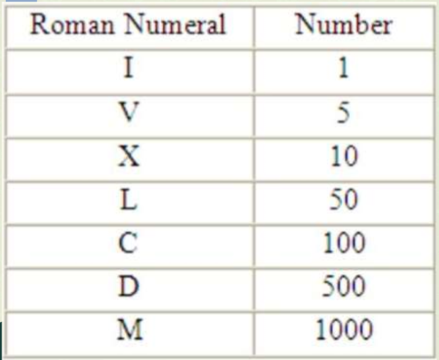
Roman Numerals
Roman Numerals are added from left to right
If there is a smaller number listed before a larger number, it means you subtract from the larger number
My Dear Children Like Xtra Vanilla Icecream
What does SPICE stand for?
S - Social
P - Political
I - Interactions between humans and the enviorment
C - Cultural
E - Economic
Social
How were social structures created, maintained, and transformed?
Political
how systems (government, hierarchies, etc.) are created/constructed and maintained?
State forms - how do you organize your people?
Interactions between human and the environment
geography
how does geography affect a civilization?
what happens when human utilize the environment?
Culture
religion, beliefs, philosophies, ideologies, etc.
how are ideas adopted?
What happens when two cultures meet?
Economics
How do you make money? How do you use it?
How do you distribute resources?
How do you handle scarcity?
What is an era?
Long and distant period of history with a particular feature or characteristic
What are the five major eras?
Prehistoric
Ancient History
Medieval History
Pre-Modern Age
Contemporary Age
Timelines
Helps organize information into a chronological event
Will help show recurring events, key events, cause and effect
Basic features of civilizations
CITIES
Larger and more complex than villages
Support the other features of civilization
GOVERNMENTS
Coordinate public-works projects such as bridge and dam construction
Establish laws and organize defense
COMPLEX RELIGIONS
Belief in one or more Gods or Goddesses
Institution of rituals
JOB SPECIALIZATION
Different types of jobs that lead workers to specialize on one task
SOCIAL CLASSES
Ranked groups based on job or status
ARTS AND ARCHITECTURE
Artwork that expresses a society’s talents, beliefs, and values
PUBLIC WORKS
Large-scale projects for the benefit of a city and its people
WRITING
Structured writing system initially used by governments and merchants to record important information
Monarchy
Hereditary power (king, queen) holds central power
Examples: England (1558-1603), France (1643-1715), Russia (1762-1796), Oman, Saudi Arabia
Aristocracy
Hereditary landholding upper class rules
Examples: England (1688-1832), France (1700s before French Revolution)
Oligarchy
Small wealthy elite exercises power
Examples: Renaissance Florence, South Africa under apartheid, former Soviet Union
Charlemagne
1) unified the empire as a Christian Empire and anyone that was conquered had to convert to Christianity
2) returned to Latin teachings (bible, laws, etc. in Latin)
3) moved the central power out of Rome to present day Germany
Chivalry
1) be brave
2) be loyal
3) be true to your word
4) fight fair
Effects of the Crusades
Growth of a money economy
Changes for monarchs and the church
Europeans gain a wider view of the world
impact of the middle east and byzantine empire
Causes and Effects of the Hundred Years’ War
CAUSES:
Long-standing English and French rivalry over lands in France
Edward III of England claims the French throne
Edward III’s armies invade France
EFFECTS:
English monarchy is weakened; French monarchy is strengthened
Knights displaced as main fighting force; replaced with soldiers for hire
Weapons become more technologically advanced
Catholicism
salvation is achieved through faith and good works
priests perform seven sacraments, or rituals - baptism, confirmation, marriage, ordination, communion, anointing of the sick, and penance
Pope is the head of Church
Bible is one source of truth; Church tradition is another
Priests interpret the Bible and Church teachings for the people
Lutheranism
Salvation is achieved through faith alone
accepts some sacraments, but rejects others because rituals cannot erase sin- only God can
The head is the elected councils
Bible alone is source of truth
People read and interpret the bible for themselves
Calvinism
God alone predetermines who will be saved
accepts some of the sacraments, but rejects others because rituals cannot erase sin- only God can
the head is the council of elders
bible alone is the source of truth
People read and interpret the Bible for themselves
Jamestown
the first permanent British settlement in Virginia
The impact of Justinian’s code
In the Byzantine Empire:
His code simplifies and organizes laws, thus helping to unify the Byzantine empire’s vast territories.
During the Middle Ages:
European monarchs use Code’s principles to strengthen and centralize their power.
Up to the present:
Through England’s common law tradition, the code influences American laws.