Acidity, Lewis Acids and Bases, Nucleophiles, Electrophiles
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
pKa values
a value that indicates the relative strength of an acid.
High pKa = weak acid
Low pKa = strong acid
must know pKa values
NH4+: 9
H2O: 16
NH3: 33
CH4: greater than 40
resonance and pKa values
recall that resonance spreads the electrons over the entire molecule, which stabilizes the molecule and lowers its energy since the charge is spread over a larger area rather than confined to a smaller area.
When a conjugate base has resonance, it is more stable than a conjugate base that does not have resonance. When the conjugate base is more stable, the acid is stronger. Thus, resonance lowers pKa values since the acid is stronger.
Note— this is about the conjugate base having resonance and being more stable!! Which makes sense because how would the conjugate base be more stable if another molecule has the resonance structures!
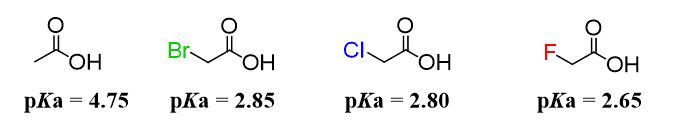
inductive effect and pKa values
the inductive effect is observed when a very electronegative atom is apart of a conjugate base. When there is a very electronegative atom in the molecule, it draws more of the electron density towards itself, which spreads out the electron density over the entire molecule. When this occurs in conjugate bases, it stabilizes the conjugate bases.
A more stable conjugate base yields a stronger acid, so an acid with a conjugate base that exhibits the inductive effect is stronger than an acid whose conjugate base does not have this property. So acids with a conjugate base with the inductive effect have smaller pKa values.
Note how this one also only involves the conjugate base.
acid-base equilibria favors…
the side with the weaker acid. So, if equilibrium favors the left, the acid on the left side of the equation is the weaker acid, and vice versa.
Keq is equal to…
10 ^ (pKaBH-pKaAH)
So 10 raised to the difference between the pKa of the acid in the products and the pKa of the acid in the reactants
Note: recall that H3O+ is the strongest acid in water, and all strong acids dissolve in water into H3O+. So, when doing calculations and you are using a strong acid as AH, make sure you use the pKa of H3O+, which is -1.8.
delta G is equal to…
-1.4 times delta pKa
acid-base reactions and solubility
acid-base reactions can be used to change the solubility of organic salts.
If you want to deprotanate a compound, you must combine it with a strong base.
If you want to go back and protonate the salt, you must combine it with a strong acid.
if pH is greater than pKa
A-H is basic and favors A-
if pH is smaller than pKa
A-H is acidic and favors A-H
Can use this to predict ionization states. If the pH is smaller than pKa, it is reasonable to predict that the acid will exist as A-H most of the time.
Henderson-Hasselbach equation
can be used to determine how much of an acid has dissociated. Can also be used to prove ionization state predictions.
If pH=pKa, then 50% of the acid has dissociated, and that 50% became its conjugate base.
Lewis Acid
an electron pair acceptor. Is also known as an electrophile.
Must have an empty orbital to accept electrons and/or not have a full octet. For example, can be sp2 hybridized and have an empty p orbital that it can accept electrons into.
Lewis Base
an electron pair donor. Is also known as a nucleophile.
Must have a lone pair or electrons in a sigma or pi bond that it can donate to the lewis acid.
electrophile
the atom or group that accepts the electrons. Has
'“electro” in the name. They also do not have a full octet and/or have an empty orbital.
nucleophile
the atom or group that donates the electrons. Must have a lone pair, or electrons in a sigma or pi bond that it can donate.
drawing lewis acid and base reactions
Draw the arrow from the lone pair/bond (of the nucleophile) to the space in the middle of the two molecules because technically those two electrons will be used to form a bond between the nucleophile and the electrophile.
The electrons from the nucleophile will become bonding electrons shared by the electrophile and nucleophile. This allows the electrophile to have a full octet while also preventing the nucleophile from having an incomplete octet.
identifying lewis acidic and basic sites
At first glance, you might be able to identify some lewis acidic and basic sites. However, you must make sure to draw out ALL resonance structures to make sure you identify all possible acidic and basic sites.
Lewis basic sites are usually lone pairs on an atom.
Lewis acidic sites are usually atoms without a full octet, or atoms with empty orbitals.
Some lewis acidic and basic sites can be missed if you do not draw out all of the resonance structures.
Most lewis acidic sites
sites that do not have a full octet most of the time/in most resonance structures
most basic sites
lone pairs that do not participate in resonance/pi bonding. These lone pairs stay on the atom, so they are more basic than lone pairs that participate in resonance and are in the pi circuit.
frontier molecular orbital theory and nucleophiles/electrophiles
recall the HOMO and LUMO, which is what frontier molecular orbital theory is about.
In Lewis acid and base reactions, the nucleophile has a HOMO, and the electrophile has a LUMO(it is accepting electrons, so it must have an empty, unoccupied orbital).
The HOMO is usually very high energy, and is usually occupied by a lone pair. The LUMO is usually low energy, and is usually an empty valence orbital.
The bond between the acid and base is created
HOMO of lewis bases
the nucleophile uses the electrons in its HOMO to form the covalent bond with the Lewis acid. This HOMO is usually a lone pair in a nonbonding orbital. This is because nonbonding orbitals are higher in energy than bonding orbitals and allow for the ideal reactivity (antibonding orbitals are too reactive, bonding orbitals are too stable). Then, the electrons in the nonbonding MO can easily get donated over electrons that are already in a bonding orbital.
LUMO of lewis acids
the LUMO of lewis acids is usually an antibonding orbital. So, when the nucleophile donates its electrons, these electrons will go into the LUMO to break the bond between two of the atoms so that a new bond can from with the nucleophile.
For example, if the new bond being formed is a sigma bond, the LUMO is probably a sigma antibonding orbital.
lewis acids usually have…
positive formal charges or positive charges in general since the lewis acids usually have incomplete octets and empty orbitals. So use positive charges an indicated that something is a lewis acid.
lewis bases usually have…
negative formal charges or negative charges over all because they usually have lone pairs. Additionally, they are usually unstable and want to donate those electrons, so the negative formal charge indicates that instability and willingness to donate electrons.