Biology II chapter 1
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MOLECULAR GENETICS academy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
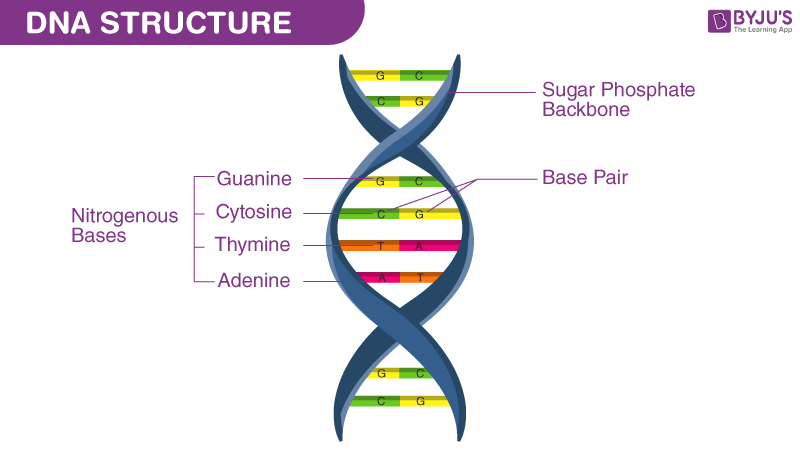
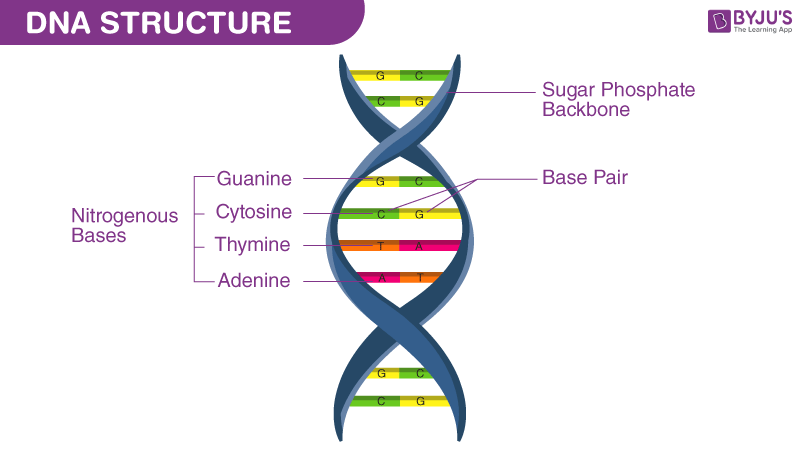
Structure of nucleotide
Three main components: a pentose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
The sugar and phosphate groups form the backbone of each strand, alternating with each other.
The specific pairing of the nitrogenous bases adenine with thymine (in RNA, uracil - U) and cytosine with guanine holds the strands together by hydrogen bonds.
The specific sequence of these base pairs along the DNA strand carries the genetic information.
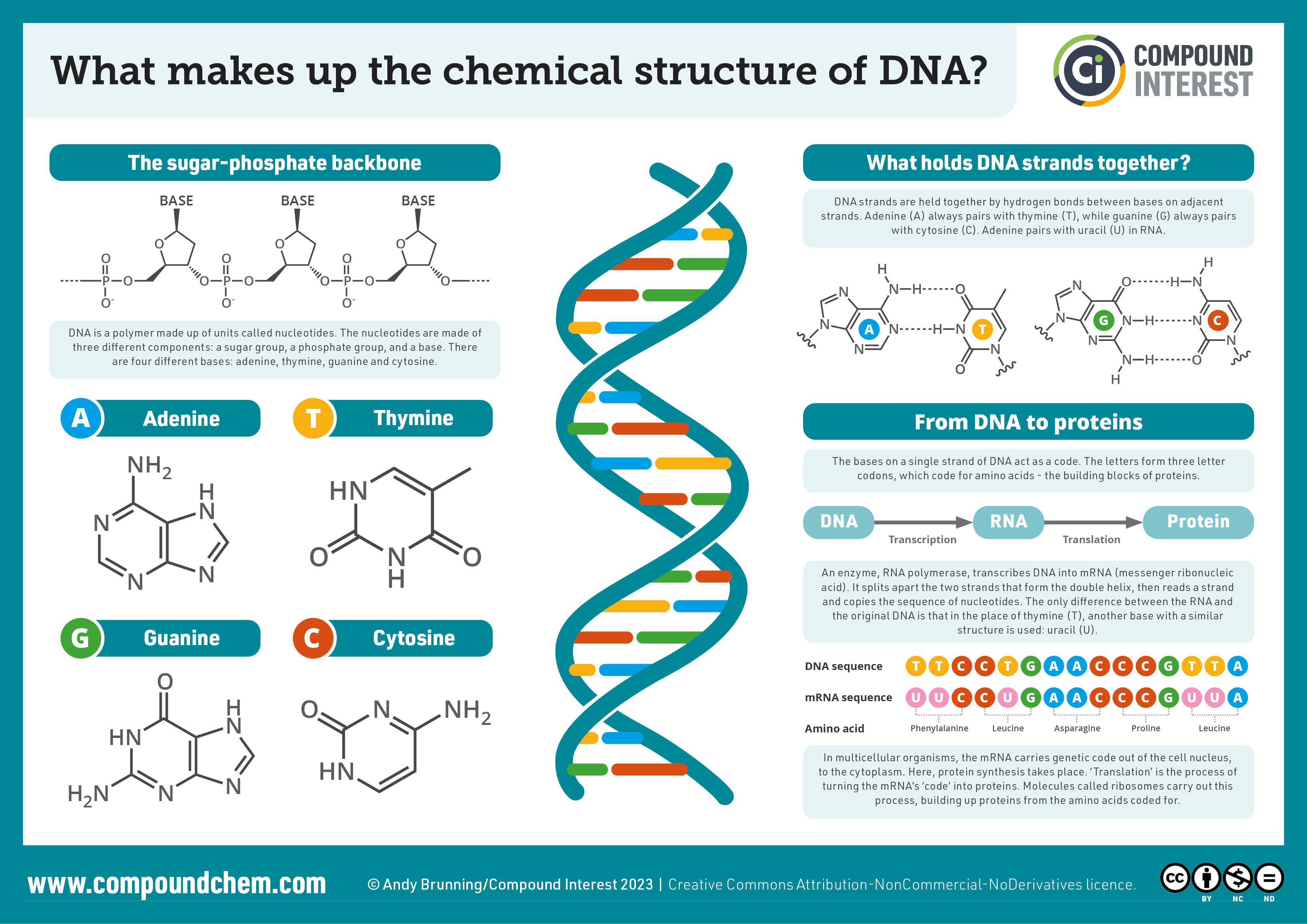
Structure of DNA?
a double helix structure, resembling a twisted ladder
form from: nucleotides
DNA (the long molecule that stores all genetic information) → gene (a specific segment of DNA that carries instructions, often to make a protein) → allele (An alternative version of a gene)
🧬 DNA Replication Mechanism
semi-conservative mean 1 original strand, 1 newly made strand
steps:
Initiation: begin at origins → helicase enzyme unwinds the DNA by breaking H2 bonds → Single-strand binding proteins stabilize the unwound strands & prevent them from rejoining → Topoisomerase acts ahead of helicase, relieve supercoiling preventing knots/tangles.
Elongation: Primase lays down RNA primers → DNA polymerase adds nucleotides in 5′ - 3′ direction → Leading strand synthesized continuously → Lagging strand synthesized discontinuously as Okazaki fragments → DNA polymerase replaces RNA primers with DNA → DNA ligase seals gaps.
Termination: Replication forks (Y-shaped region) meet or reach end → RNA primers removed & replaced with DNA → DNA ligase seals backbone → Two identical DNA molecules (semi-conservative).
Structure of gene?
prokaryotes:
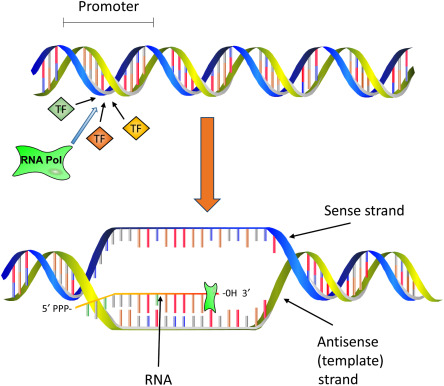
Promoter: DNA sequence where RNA polymerase and transcription factors bind to start transcription.
Coding region: sequence that is transcribed into RNA and often translated into protein.
Terminator: sequence signaling the end of transcription.
eukaryotes = regulatory sequences (promoter, enhancers/silencers) + coding sequences (exons, introns) + UTRs + terminator
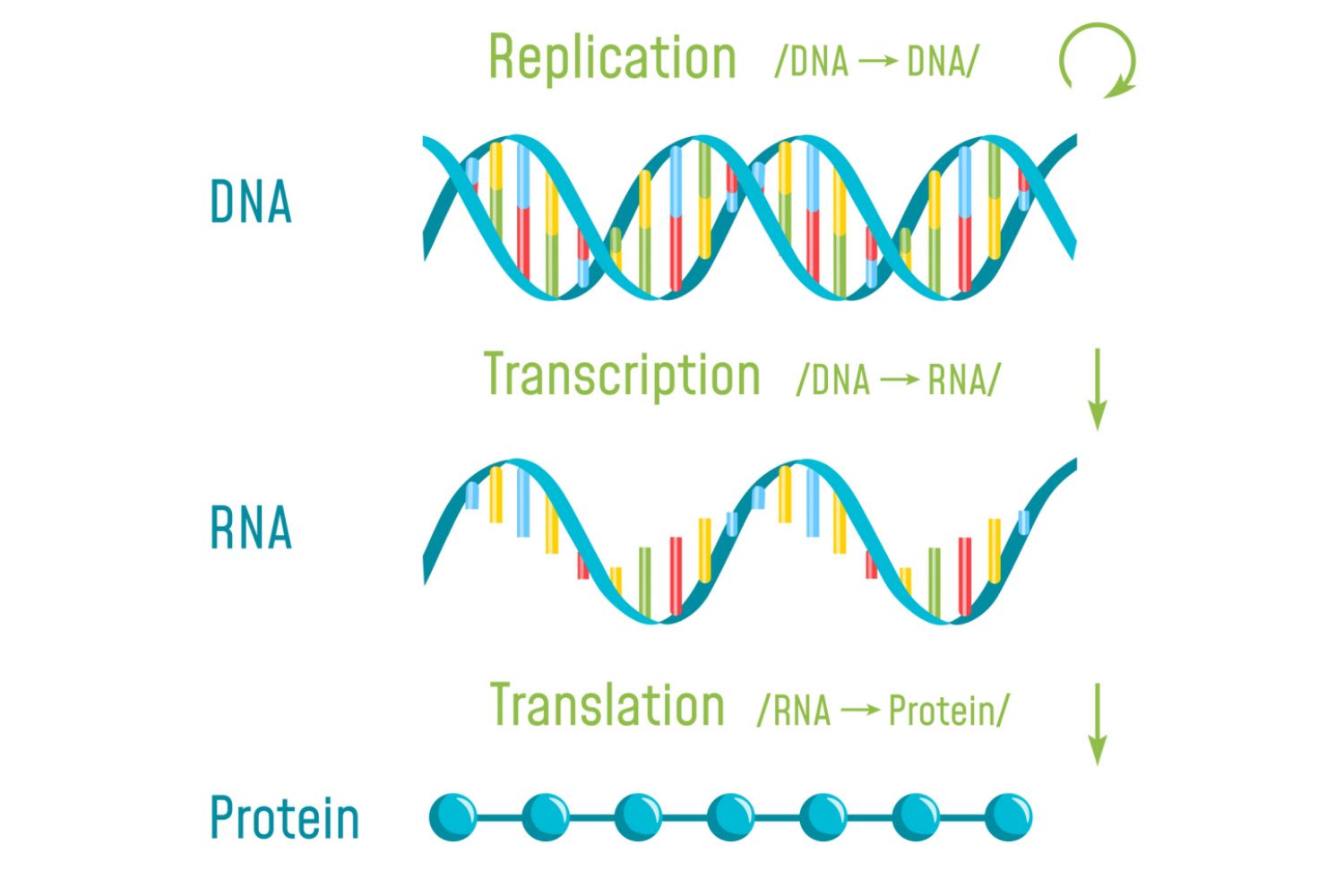
Transcription (from gene)
Definition: The process of copying a gene’s DNA sequence into RNA.
Key points:
Occurs in the nucleus (in eukaryotes).
RNA polymerase binds to the promoter, unwinds DNA, and synthesizes pre-mRNA (complementary to the DNA template strand).
In eukaryotes, pre-mRNA is processed: introns are removed, exons are spliced together, a 5′ cap and 3′ poly-A tail are added → mature mRNA.
Purpose: to create an RNA copy of the gene that can leave the nucleus for protein synthesis.
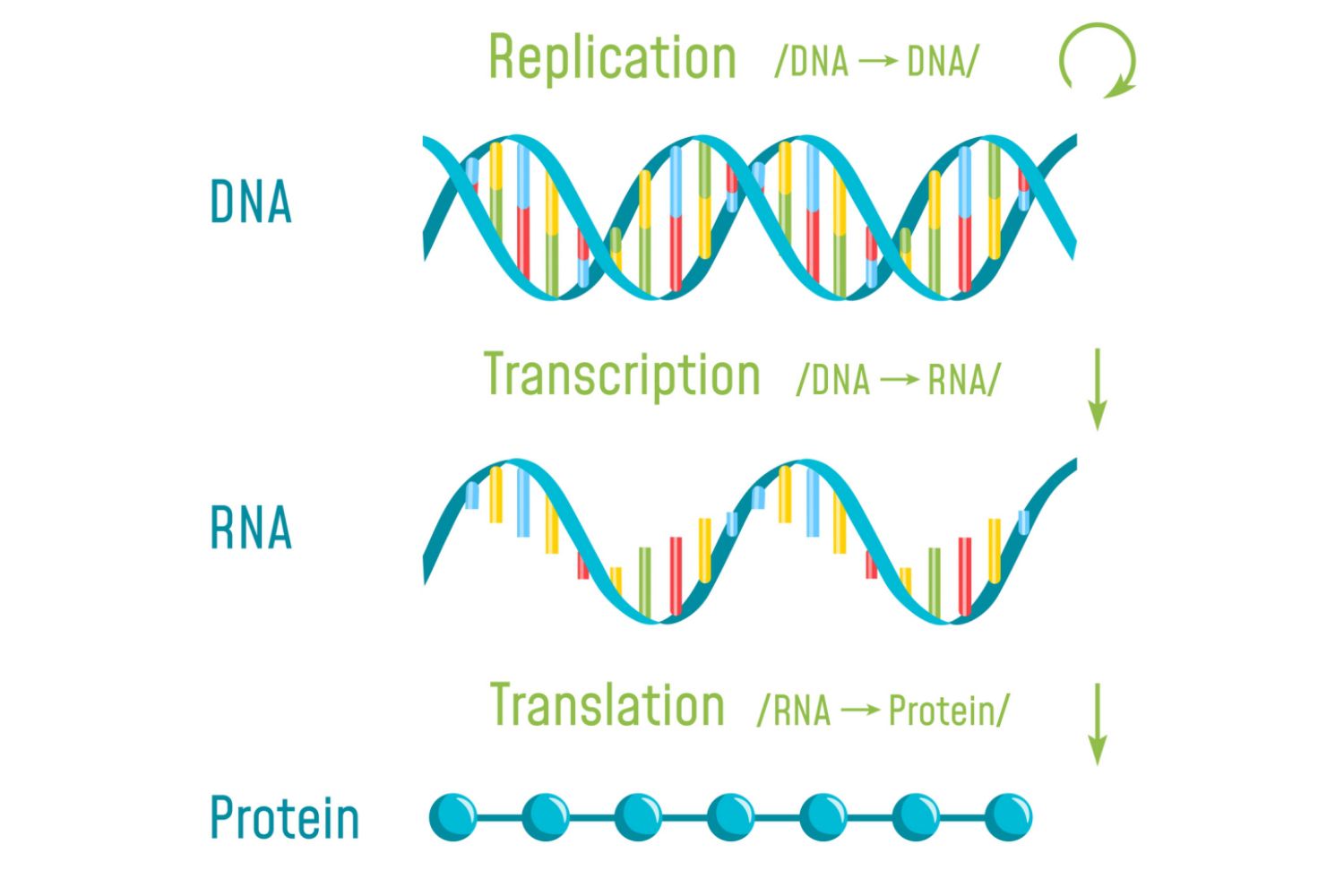
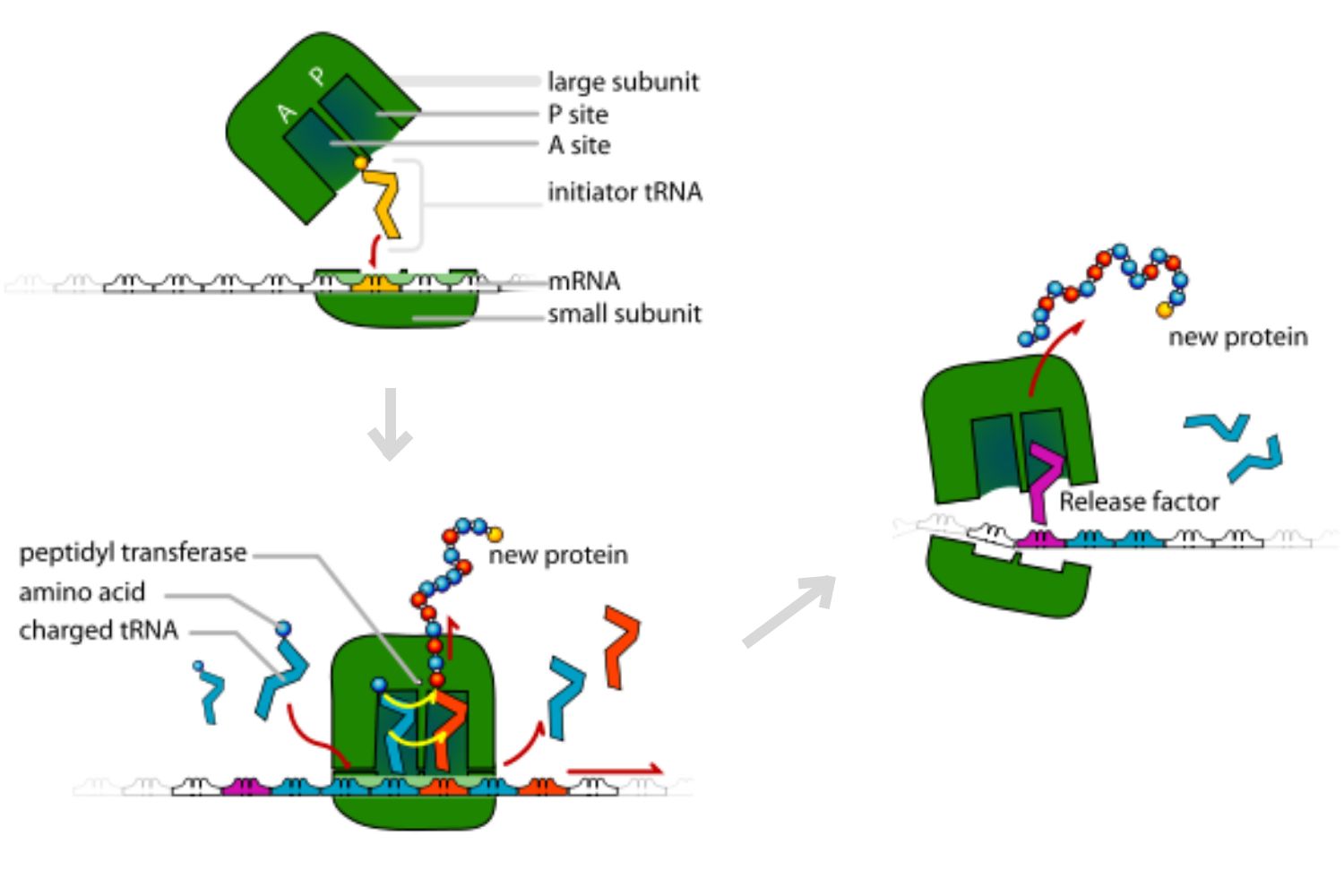
Translation (form RNA)
Definition: The process of synthesizing a protein from the mRNA sequence.
Key points:
Occurs in the cytoplasm, on ribosomes.
mRNA is read in codons (three-nucleotide sequences).
tRNA molecules bring the correct amino acids according to the codon sequence.
Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds, forming a polypeptide chain → folds into a functional protein.
Purpose: to convert genetic information in mRNA into a functional protein.