Phonology Flashcards
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for Phonology review, focusing on vocabulary from the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Phonemic Analysis
Phonemic system
Phonotactic rules
Allophonic Rules
Allophonic Rules
phonological processes that change how sounds are pronounced, often making the spoken form of a word different from its mental form.
Example: In English, the /t/ in "top" is pronounced with a puff of air (aspirated) [tʰ], but in "stop" it's unaspirated [t]. Both are allophones of the same phoneme /t/.
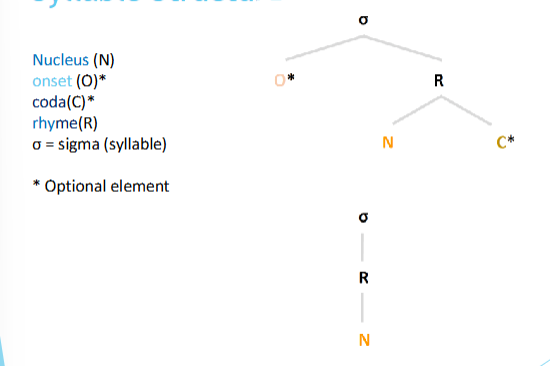
Syllable
A unit of pronunciation consisting of a nucleus (vowel) and optional onset and coda (consonants).
Syllabic Structure
onset
nucleus
coda.( no coda→ opensyllsble; coda→ closed syllable)
rhyme(R)= nucleus+ coda
σ = sigma (syllable)
Syllabification
The division of words into syllables.
Structuring Phonological rule
input
output
condition
/ p t k / → [p*h t*h k*h] / .___V[+stress]
Environment element
/___ A = before a given context
/A ___ = after a given context
/A ___ B = between two given contexts
Phonotactic Rules
define the distribution of speech sound
based on posiition within a word (mainly consonants)(word initial/medial/final..)
based on the structure of a sylable (onset, nuclear, coda)
word combination
Phonological facts
phonological rule
It shows how a phonemic form (input) changes into a phonetic form (output) in a specific environment or context.
input
output
condition
/ p t k / → [p*h t*h k*h] / .___V[+stress]
Allophonic Processes + 4 types
Phonemes are realized in specific ways (allophones) depending on the environment/phonetic context
Aspiration
Assimiliation
Elision
Insertion
Aspiration
Increased air release
voiceless plosives are aspirated in word-initial position in stressed syllables before a vowel
/ p t k / →[p h t h k h ] / #___ V [+stress]
but the /t/ in attire is also aspirated
/ p t k / → [p h t h k h ] / .___V[+stress]
Assimilation(allophonic process)
sound changes to become more like a nearby sound.
e.g. Alveolar plosive /t/ becomes more like palatal [j] by becoming postalveolar
affricate [ʧ]
Careful speech [doʊnt.ju]
Casual speech [doʊn.ʧju]
Elision
The deletion or removal of a sound segment
e.g. [æskt] →[æst]
[sǝˈpoʊz] →[spoʊz]
Insertion
Including an additional segment in a sound sequence,
dreamt [dɹɛmpt]
liaison
insertion of linking sound (mostly in non-rhotic accents)
linking [ɹ] or Intrusive [ɹ]
far vs. far away
law[ɹ] and order
Segmental Phonology
Focuses on (individual and collection of) phones of a given language
E.g. analyzing consonants and vowels, their distinct features
Suprasegmental Phonology
Studies the phonological properties of units above individual segments,
e.g. (syllables,) stress, words and intonation phrases
Rhythm
The pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables in a language
E.g.Stress-Timed Rhythm

syllable marker
a low dot
technical → tech.ni.cal
Stress
The emphasis given to a syllable within a word.
Multiple factors contribute
Length
Loudness
Pitch
quality
light syllable
rejects stress (stress goes to penultimate syllable)
heavy syllable
accepts stress
Pitch
Relative Highness/Lowness of a tone in speech
Intonation
The variation in pitch used to convey meaning in speech.
e.g. Rise-Fall, Fall-Rise, Monotone
consonants can serve as the nucleus of a syllable
Only nasals and liquids (sonorant consonants)
e.g.
[n̩] | Syllabic nasal /n/ | button, kitten, garden | /ˈbʌtn̩/, /ˈkɪtn̩/ |
[l̩] | Syllabic lateral /l/ | bottle, little, middle | /ˈbɒtl̩/, /ˈlɪtl̩/ |
[m̩] | Syllabic nasal /m/ | rhythm (less common) | /ˈrɪðm̩/ |
[r̩] | Syllabic rhotic /r/ (in rhotic accents like Scottish English) | butter, letter (rhotic accents) | /ˈbʌtər̩/ |
Function of Intonation
Attitudinal
Accentual
Grammarical
Attitudinal (Function of Intonation)
Convery a particular emotion in context
No way I would never say that!
Accentual (Function of Intonation)
Used for contrastive stress (emphasize a concept)
I want a big ice cream
Grammatical (Function of Intonation)
Provides informative
Those who work slowly get to the top.
Phonotactic Rules
Restrictions on the distribution and sequencing of sounds in a language.
Distribution of Speech Sound
Distribution of speech sounds based on their position within a word.
Light Syllables
Syllables with short vowels or syllabic consonants
(sorry, enter in non-rhotic)
Heavy Syllables
Syllables with long vowels/diphthongs or vowels followed by coda consonant.
exclude, undo, redye