***FINAL EXAM: Chapter 20 The Cardiovascular System - Blood単語カード | Quizlet
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
cardiovascular system and lymphatic system
The circulatory system is comprised of what two systems?
transport cells and dissolved materials, including nutrients, wastes, and respiratory gases throughout the body
What is the main function of the cardiovascular system?
blood
a specialized fluid connective tissue
- distributes nutrients, oxygen, and hormones
- carries metabolic waste to the kidneys
- transports white blood cells
- maintains homeostasis
- clotting factor / body temp redistribution
What are some functions of blood?
1. Plasma
2. Formed elements (rbcs, wbcs, and platelets)
Blood consists of 2 primary components
plasma
the liquid matrix of blood
contains dissolved proteins
formed elements
blood cells and fragments that are suspended in the plasma:
red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets (aids in clotting)
whole blood
mixture of both plasma and formed elements
5-6 liters
blood volume in males
4-5 liters
blood volume in females
7.35 - 7.45
What is the general pH range of blood?
plasma
accounts for 55% of blood volume
contains about 92% water
contains much more significant quantities of dissolved proteins compared to interstitual fluid
Because they are large and globular
Why are most plasma proteins unable to cross capillary walls?
- albumins
- globulins
- fibrinogen
What are the three classes of plasma proteins?
albumins
class of plasma protein
makes up 60% of plasma proteins
smallest in size
major contributor in osmotic pressure of plasma
plays a role in transport of fatty acids, steroid hormones, and other substances
globulins
class of plasma protein
makes up 35% of plasma proteins
- IMMUNOGLOBULINS (ANTIBODIES)
- TRANSPORT GLOBULINS - takes excretions to kidneys
Fibrinogen
class of plasma protein
makes up 4% of plasma proteins
largest in size
essential for CLOTTING
forms FIBRIN (found in SERUM fluid)
fibrin
fibers that provide the basic framework for a blood clot
serum
is the fluid that remains if fibrinogen is removed from plasma (the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin)
Lipoproteins
protein-lipid combinations that readily dissolve in plasma, which allows insoluble lipids to be delivered to peripheral tissues
the liver
What organ is the primary source of plasma proteins in which the organ synthesizes and releases more than 90% of such proteins?
RBCs and WBCs
What are the major cellular components of blood that are considered formed elements?
platelets
What are the minor cellular components of blood that are considered formed elements?
erthrocytes (RBC)
most numerous
biconcave discs - shape provides strength and flexibility and permits RAPID DIFFUSION
no nucleus, mitochondria or ribosomes
red due to hemoglobin
lifespan: 120 days
Rouleaux
Stacking of RBCs due to their biconcave shape, allowing them to pass easily through small vessels
hemoglobin
gives RBCs its red color
accounts for more than 95% of the proteins of RBCs
gives RBCs ability to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide
- transport oxygen from lungs to tissues
- transport carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs
What are the two functions of RBCs?
surface antigens on the plasma membrane of RBCs
Blood types are determined by the presence or absence of what specific components?
throughout the peripheral tissues
Where are leukocytes (WBCs) scattered?
- help defend body against pathogens
- remove toxins, wastes, and abnormal or damaged cells
What are the 2 functions of (Leukocytes) WBCs?
- contain nuclei of characteristic sizes and shapes
- they are as large as or larger than RBCs
What are the general characteristics of (Leukocytes) WBCs?
Granular leukocytes (granulocytes)
Agranular leukocytes (agranulocytes)
What are two classes of Leukocytes (WBCs)?
granular leukocytes (granulocytes)
a class of WBCs that have large granular inclusions in their cytoplasm
Agranular leukocytes (agranulocytes)
a class of WBCs that do not have visible cytoplasmic granules
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
What are granular leukocytes (granulocytes)?
monocytes and lymphocytes
What are the agranular leukocytes (agranulocytes)?
-penia
inadequate (deficiency)
-osis
excessive (much more than)
Diapedesis
the ability to move through vessel walls
- WBCs can move across the endothelial lining of capillaries by squeezing between adjacent endothelial cells
Chemotaxis
Attraction of cells to chemical stimuli
- WBCs are attracted to chemical signals of inflammation or infection - draws them to invading pathogens, damaged tissues and other WBCs that are already in the damaged tissue
NLMEB
From greatest to least, what is the order of the WBCs?e
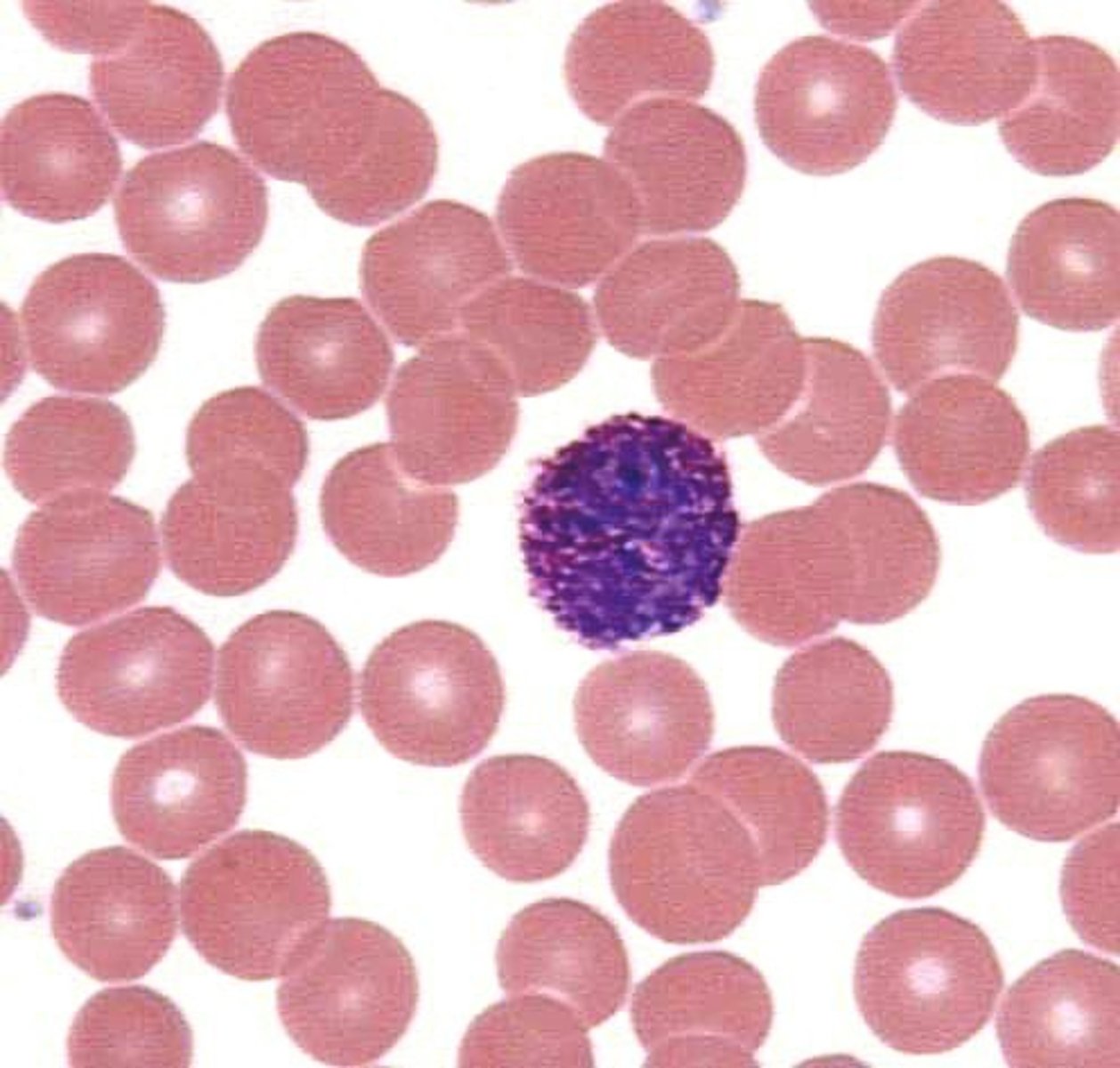
neutrophils
50-70% of WBCs - most common
contains lysosomal enzymes and bactericidal
pale, neutral-staining granules
nucleus resembles series of beads
first to appear at site of infection
highly mobile phagocytic cells
eosinophils
2-4% of all WBCs
stained with eosin (red-orange)
similar size to neutrophils
bilobed (two-lobed) nucleus
phagocytic cells
found more during allergic reactions or parasite infection

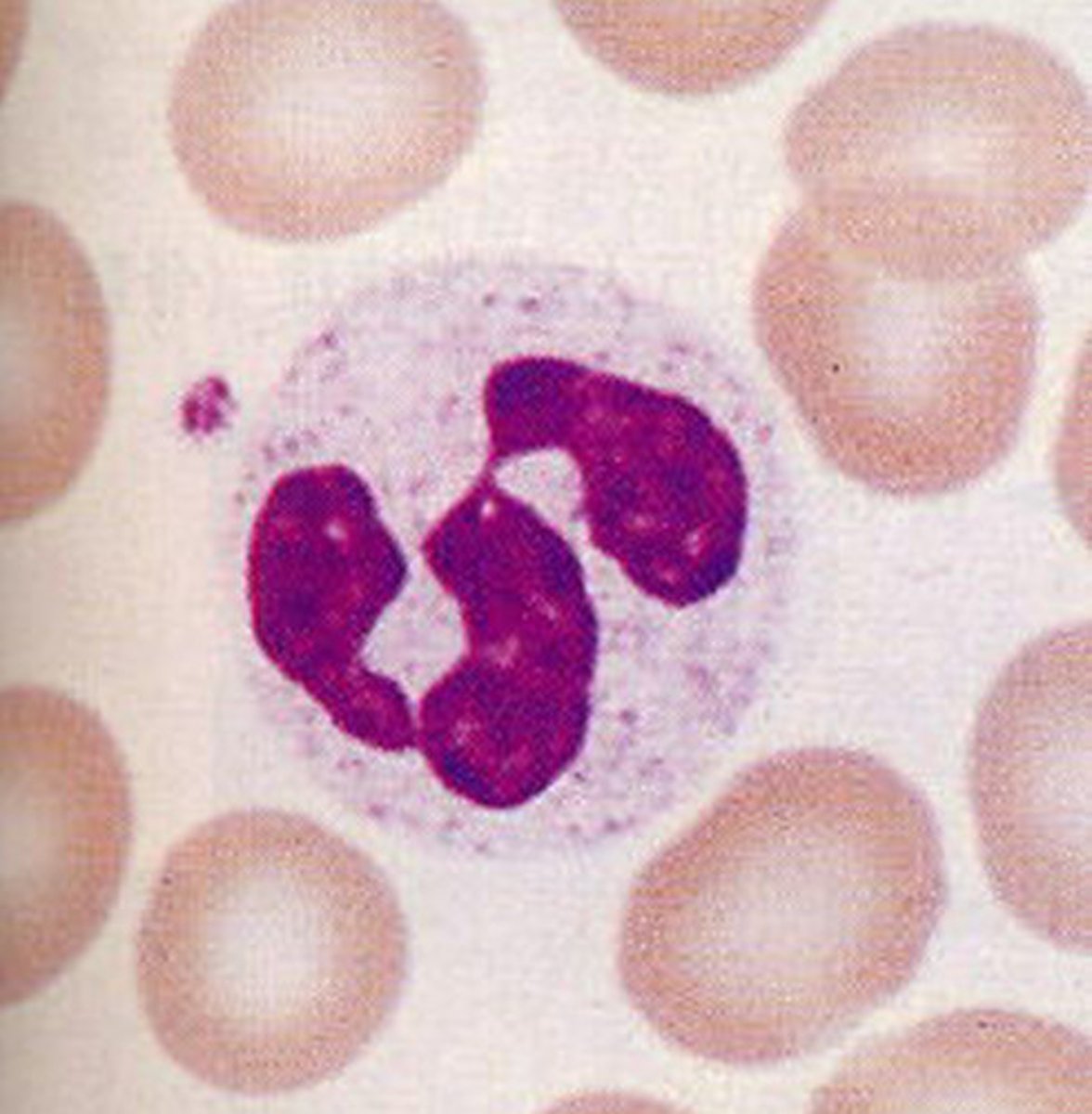
basophils
1% of WBCs - least common
stained with basic dye (dark purple)
enters damaged tissue and releases HISTAMINES and HEPARIN
- this increases capillary and venule permeability (resulting in increased inflammation response at injury site)
histamines
compound released by basophils that dilates blood vessels
heparin
compound released by basophils that prevents blood from clotting
monocytes
2-8% of WBCs
massive in size of all WBCs
spherical in shape (large oval or kidney bean-shaped nucleus)
free macrophages (highly mobile, phagocytic cells)

lymphocytes
20-30% of WBCs
very little cytoplasm
primary cells of the lymphoid system
responsible for SPECIFIC IMMUNITY
T-cells, B-cells, and NK cells (natural killer)
What are the 3 groups of lymphocytes?
T cells
type of lymphocyte that enters peripheral tissues and attack foreign cells directly
B cells
type of lymphocyte that differentiates into plasmocytes (plasma cells) that secretes antibodies that attack foreign cells
NK cells (natural killer cells)
type of lymphocyte that are responsible for immune surveillance, a process which destroys abnormal tissue cells
platelets
flattened, membrane-encolsed packets of cytoplasm (appears round or spindled shaped)
also called as THROMBOCYTES; not actually cells
continually replaced!!
lifespan: 10-12 days (remove phagocytes)
megakaryocyte
large platelet precursor cell found in the bone marrow
can produce around 4000 platelets
hemostasis
a process that prevents the loss of blood through the walls of damaged vessels
CLOTTING