ARH 314 FINAL
1/184
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
185 Terms
site
location
scale
the relationship between the portion of Earth being studied and Earth as a whole
approach/entry
What does the building look like as you approach and what does this communicate. How do you enter the building and what does this communicate. What is the end goal of your approach/how will you use the space
Profile/Massing
Perception in general shape and size of a building. Is it an oval, square, symmetrical?
circulation of movement
refers to the way people move throughout a building, and how they interact with the physical space around them
typology
building type that serves specific functions such as a temple, school, hospital, or prison. type of formal volumes, such as domes cubes parallelepipeds or bars
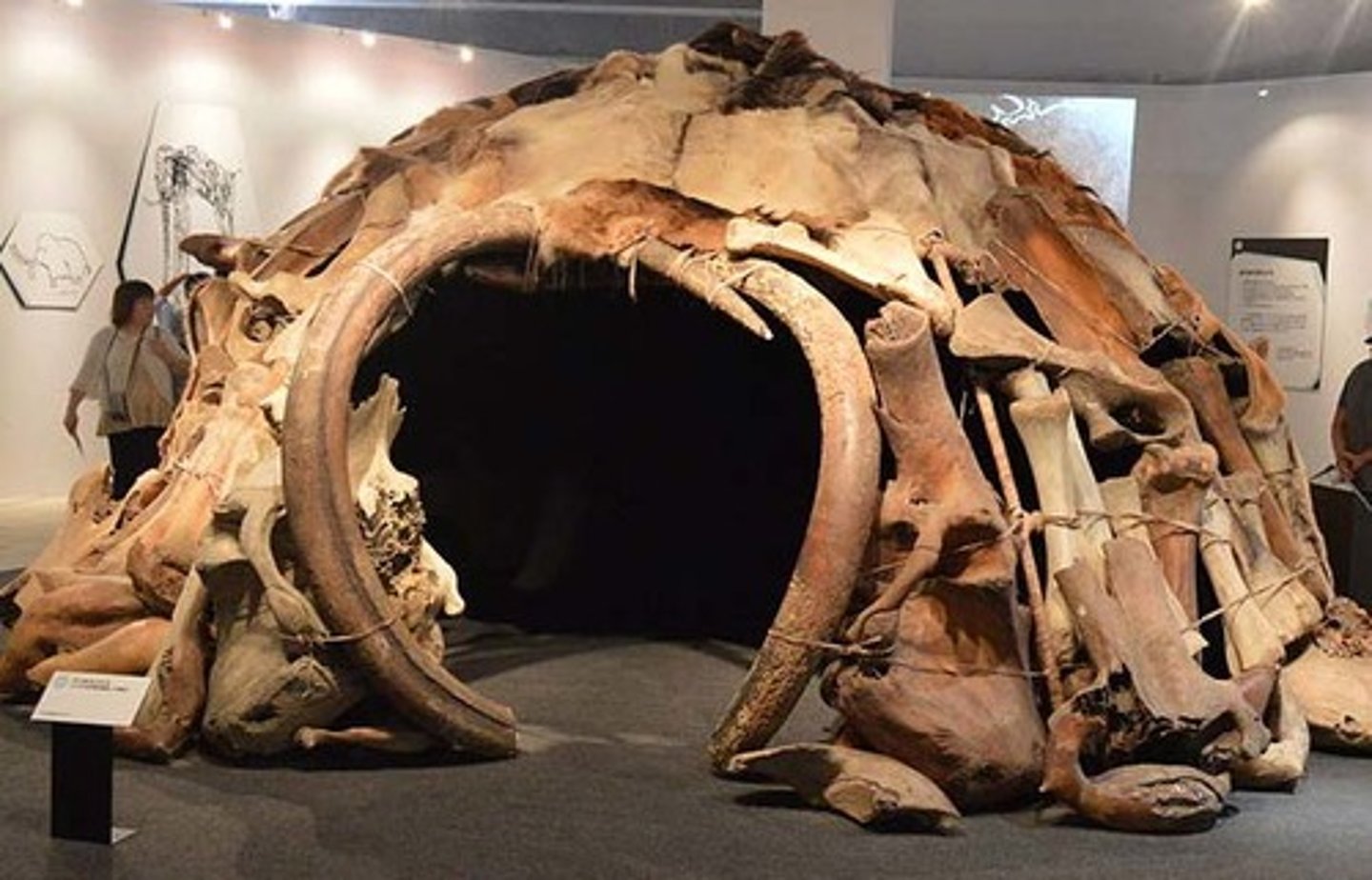
mammoth bone hut
15,000 BCE, Mezhirich, Ukraine. connection between function and material choice. curves tusks were used for entrances, bigger bones were on the bottom, smaller bones on top, skin used ontop

mud brick
Sumerian building material
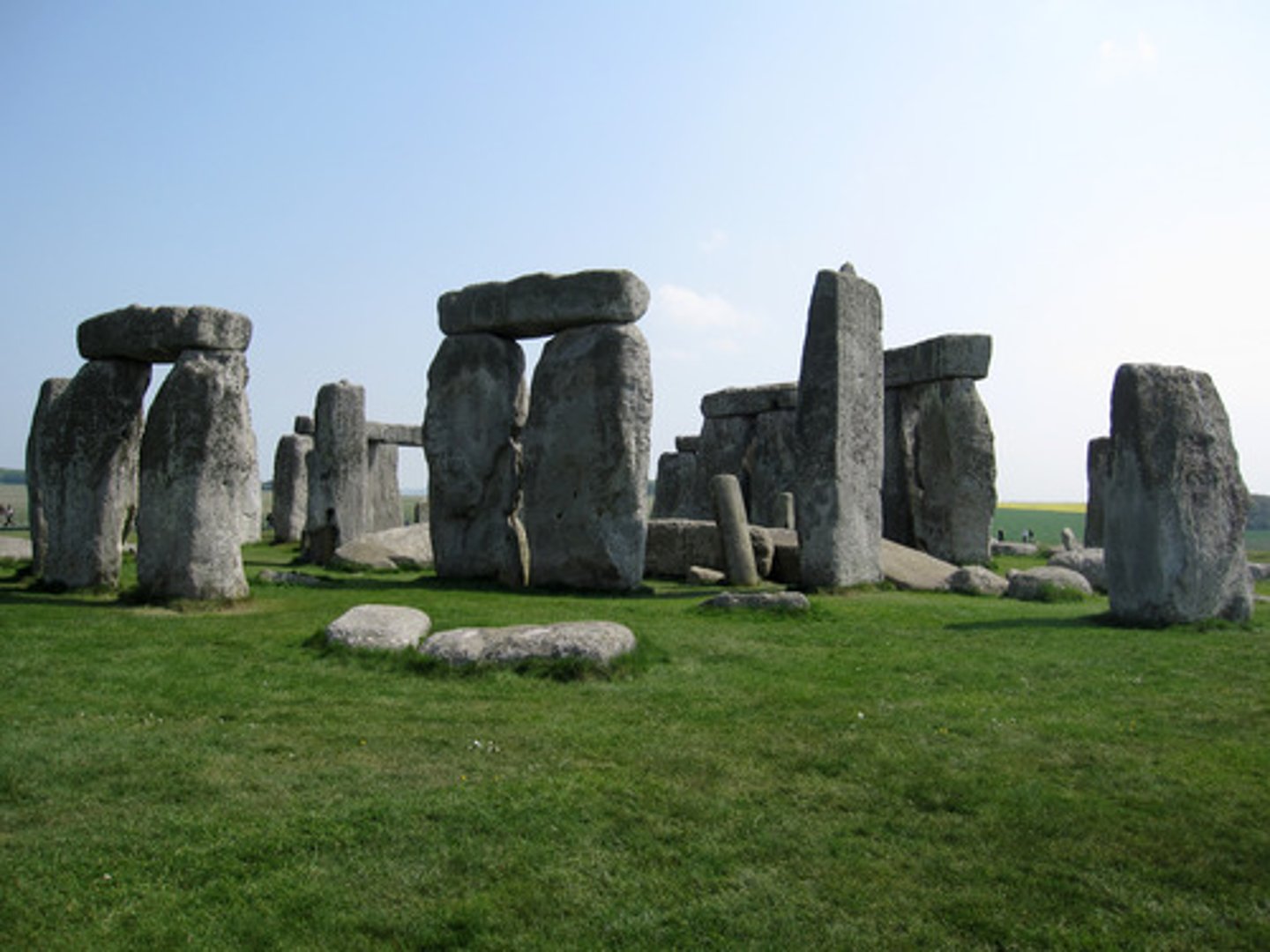
megalith
a huge irregular stone

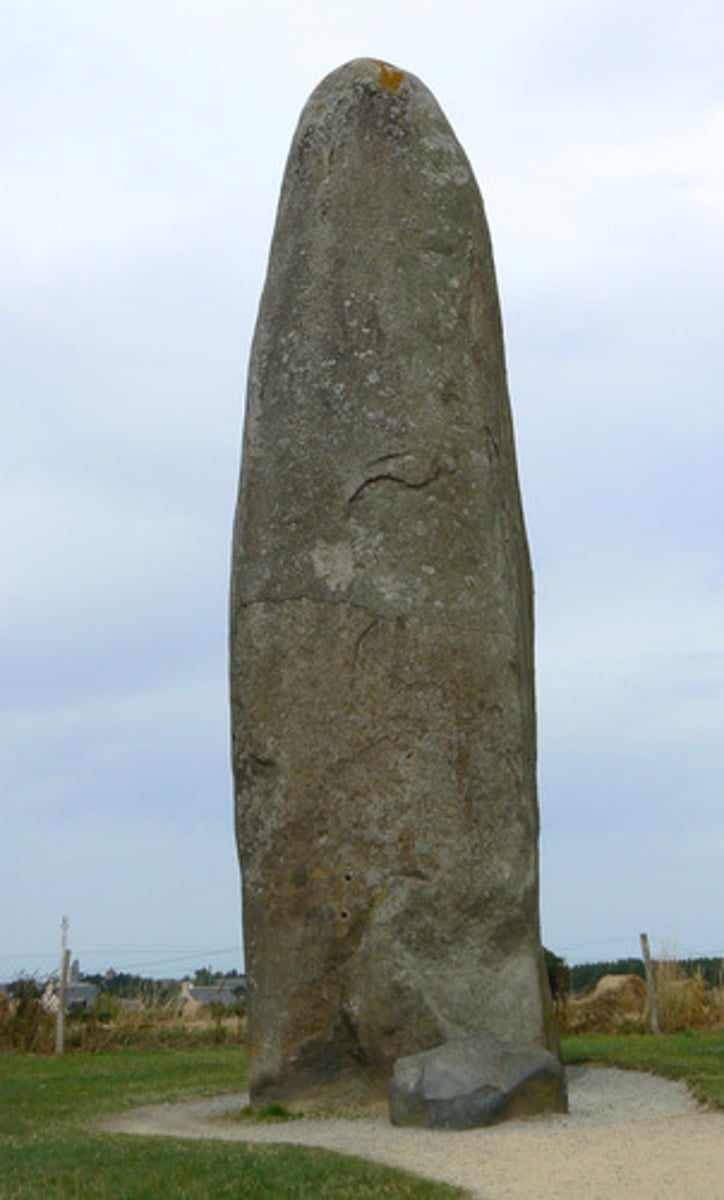
menhir
a prehistoric monument in the form of a large, upright stone

Trilithon
two upright monoliths supporting a lintel stone, similar to a dolmen
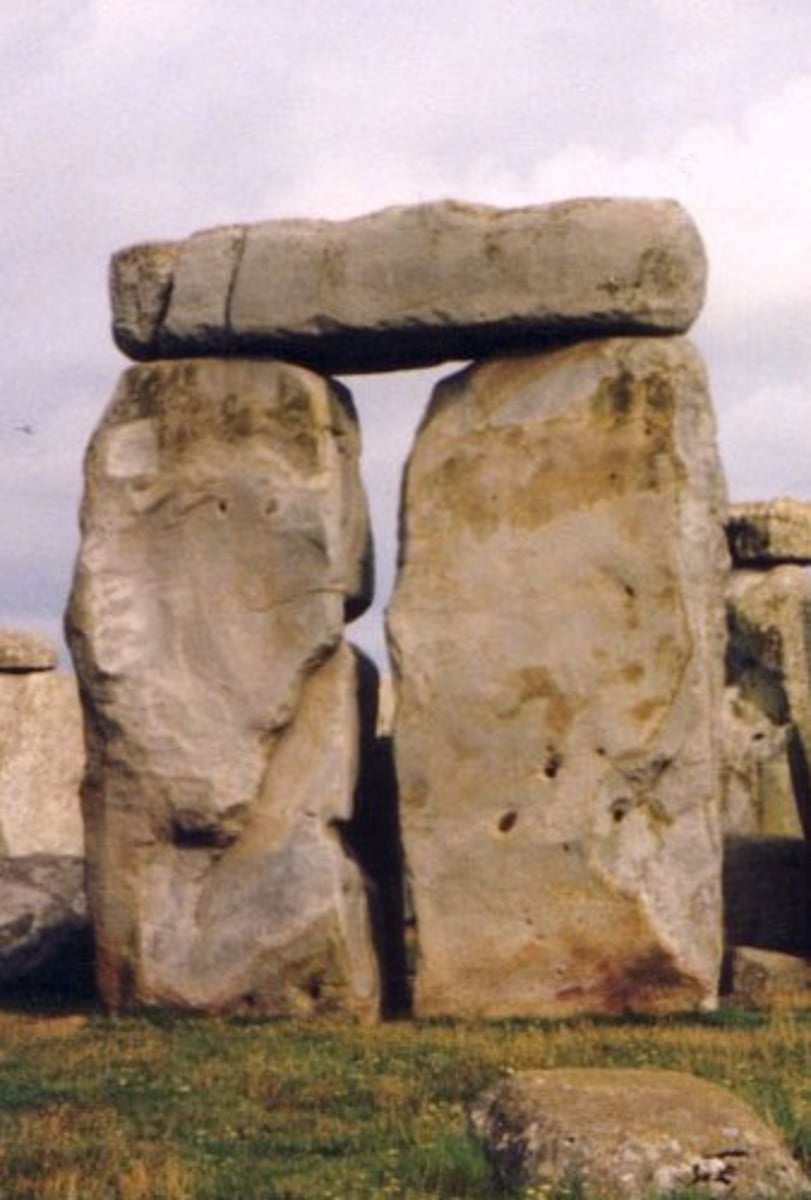

post and lintel
trabeation, a construction system using vertical supports (posts) spanned by horizontal beams (lintels)

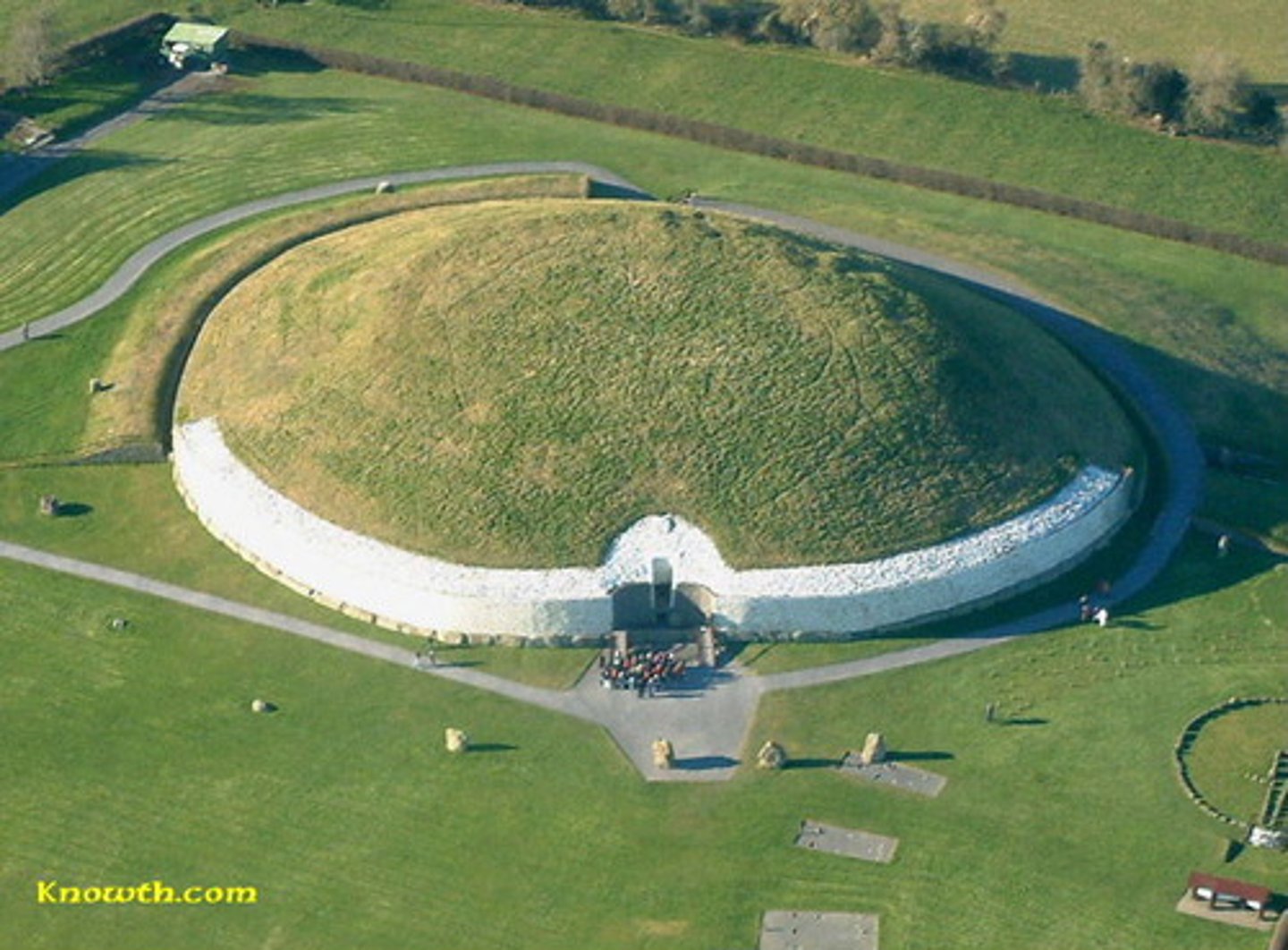
tumulus tomb
passage tomb, an earth or stone mound over a grave

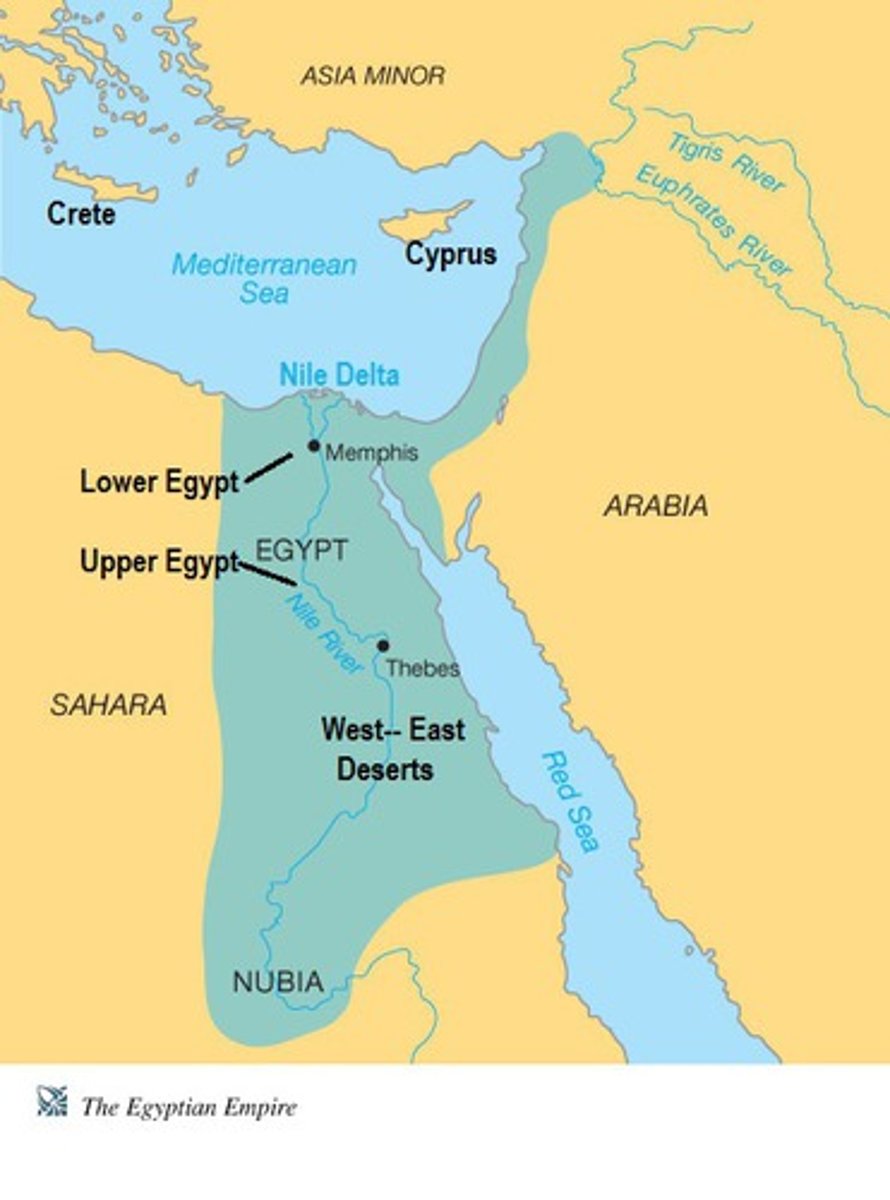
Upper and Lower Egypt
3150 BCE. the geographical and cultural divisions of egypt that occurred as the final stage of prehistoric egypt, and directly preceded the unification of the realm. upper egypt: more south, but was on the north portion of the nile
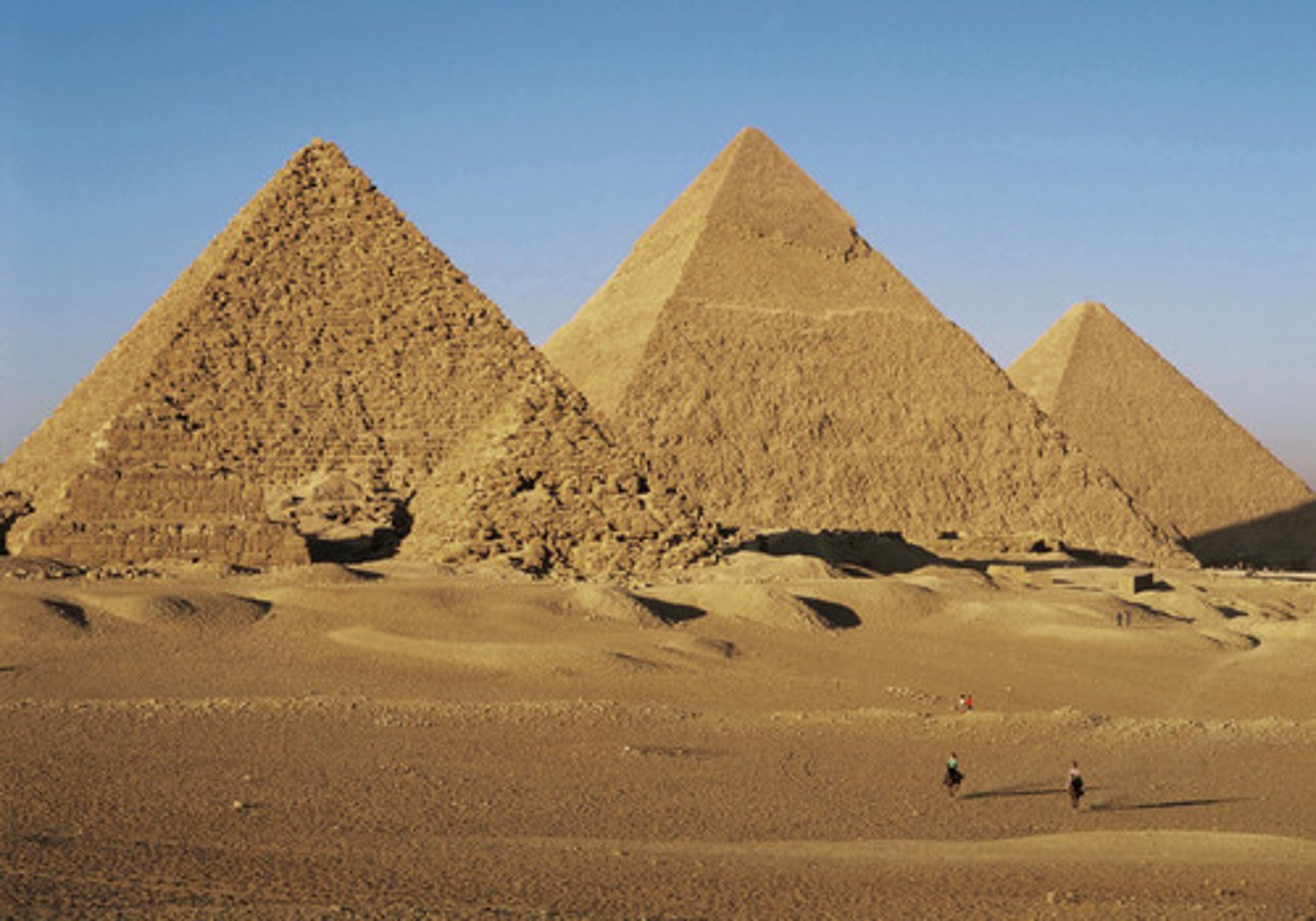
Old Kingdom
2700-2100 BCE. known as the "Age of Pyramids" as it includes the 4th dynasty when King Sneferu perfected the art of pyramids (including the pyramids of Giza). not many historical records of this period
New Kingdom
1550- 1100 BCE. most popular era in egyptian history, characterized by strong pharaohs who conquered an empire including Hatshepsut, Nefertiti, Tutankhamun
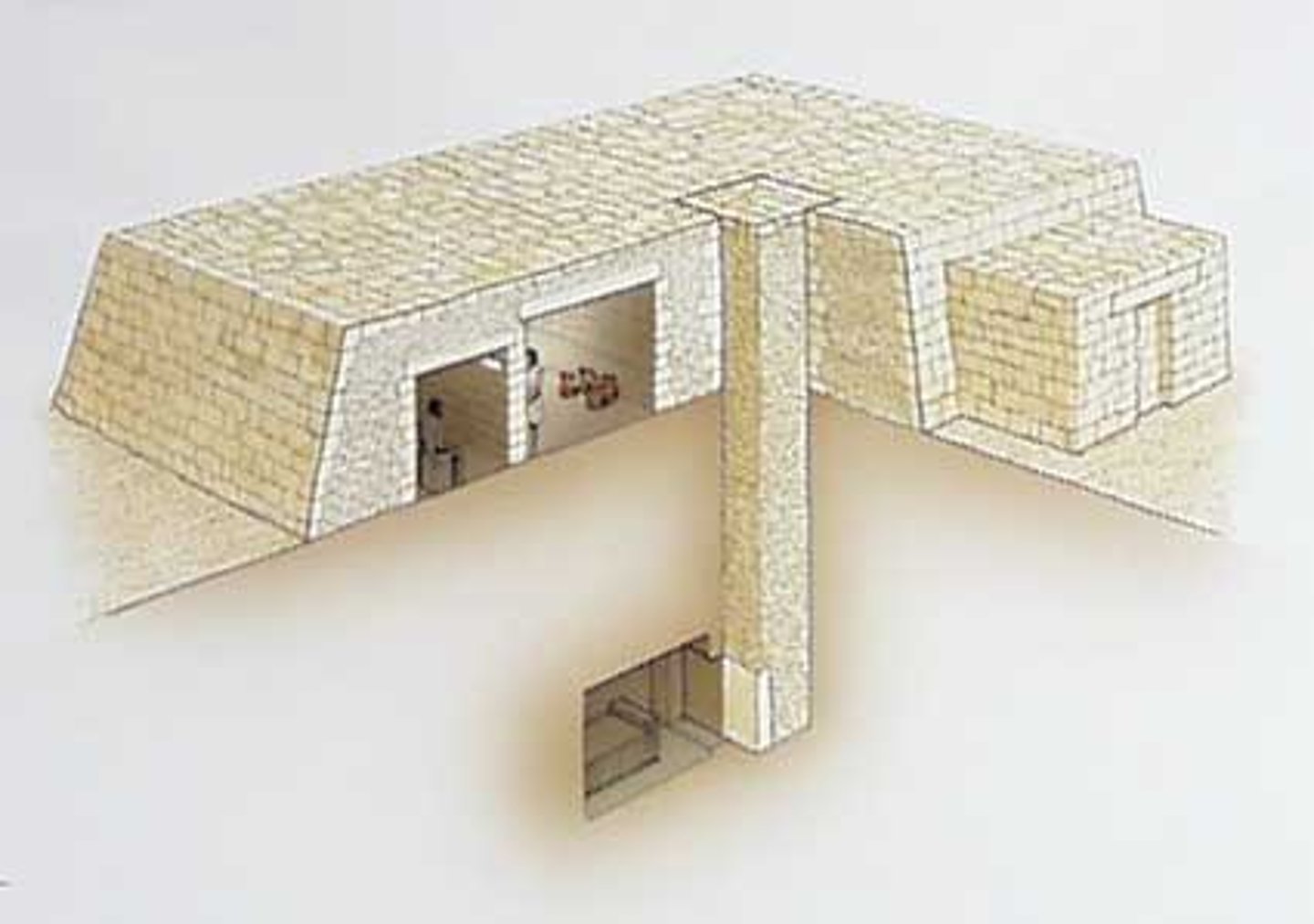
mastaba
2900 BCE. an arabic word for "bench" signifying the ancient egyptian flat-topped, rectangular tombs with sloping sides

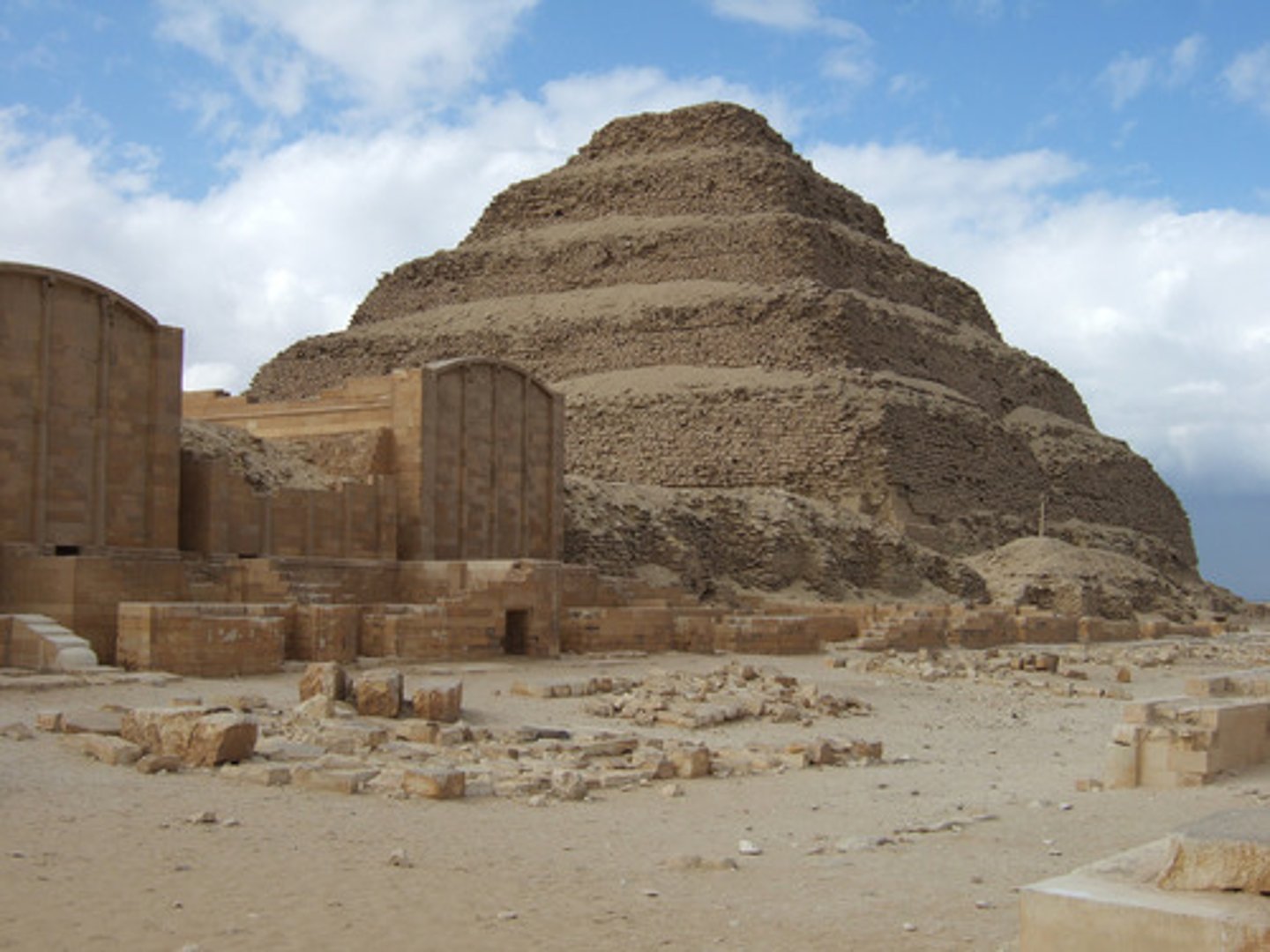
step pyramid
a pyramid whose sides rise in a series of giant steps
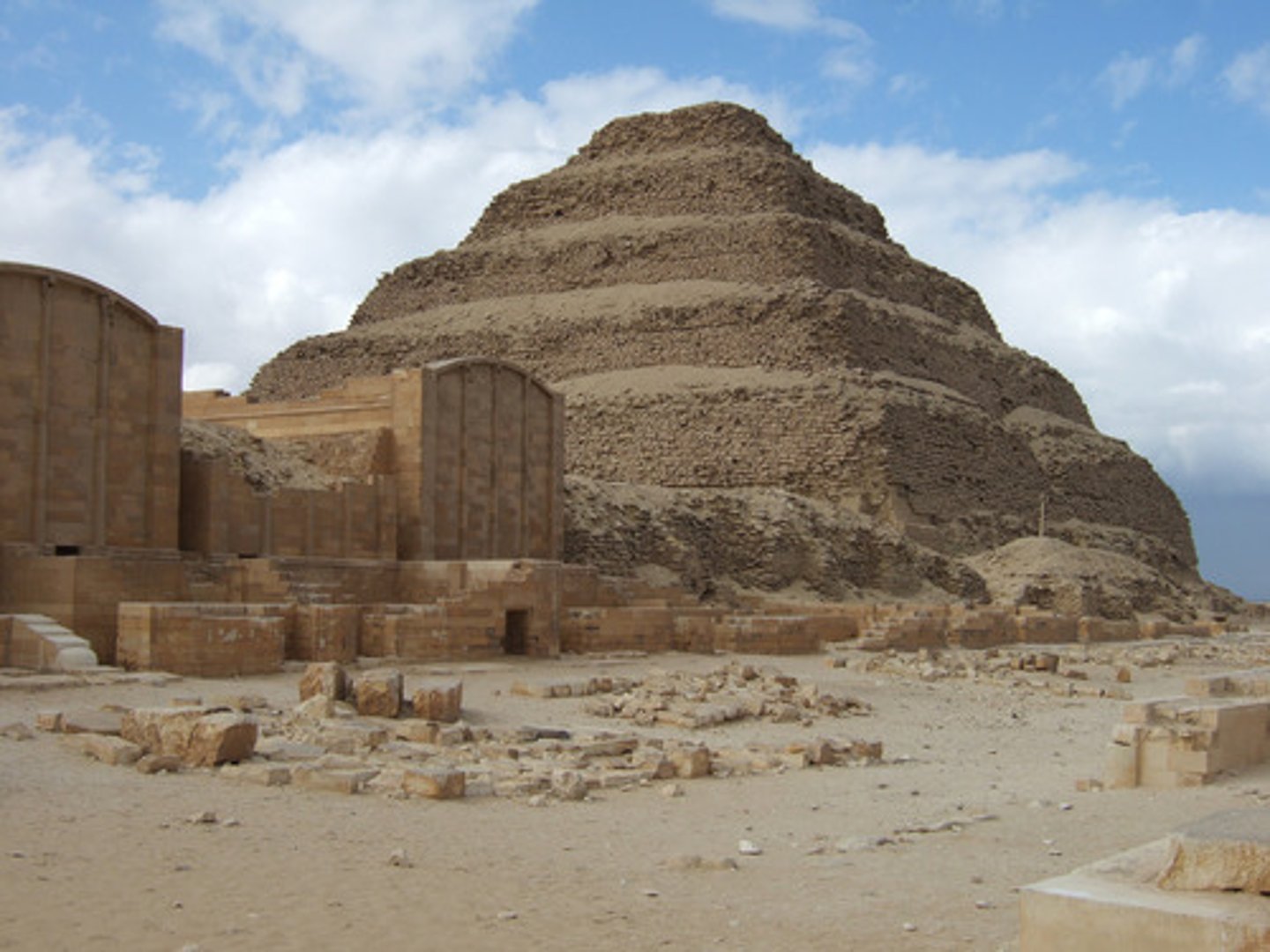

Imhotep
first acknowledged architect, best known for designing King Djoser's Step pyramid - later he is recognized as a god of science, wisdom, and architecture

column
a cylindrical, vertical support, usually tapering upward and made either in one piece (monolithic) or of shorter cylindrical sections, called drums. in classical architecture a column consists of a base, a shaft. and a capital
engaged column
a column embedded in a wall and partly projecting from the surface of the wall
pyramid
a massive memorial or temple rising from a square or rectangular base to an elevated altar or a point, with either a succession of steps or a smooth incline

mortuary complex/temple
place of worship of a deceased king and the depository for food and objects offered to the monarch

rock-cut tomb
a burial chamber that is cut into an existing and naturally occurring rock formation, carving out rather than building up
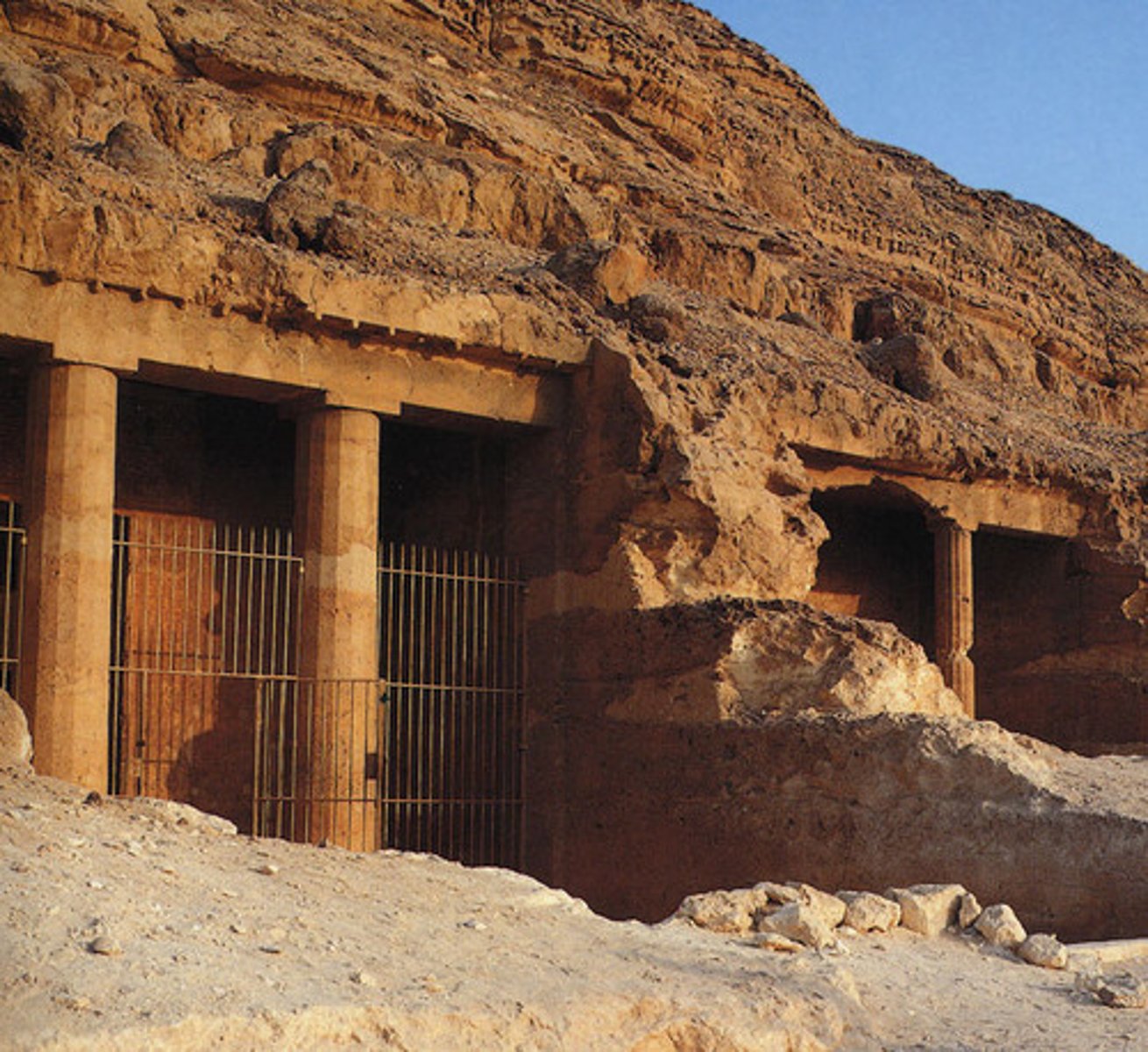

Hypostyle/Hypostyle Hall
a room with a roof supported by many columns

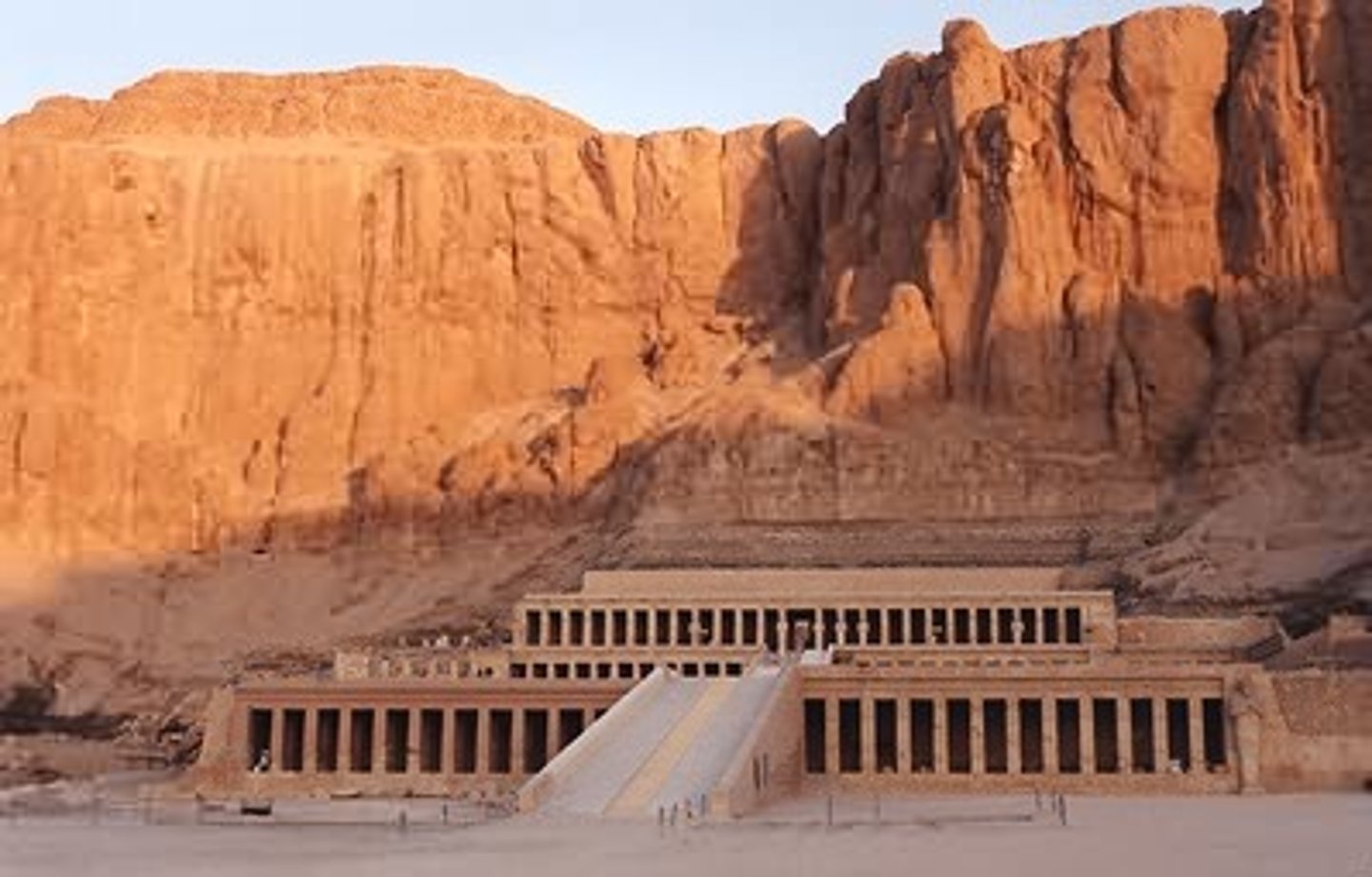
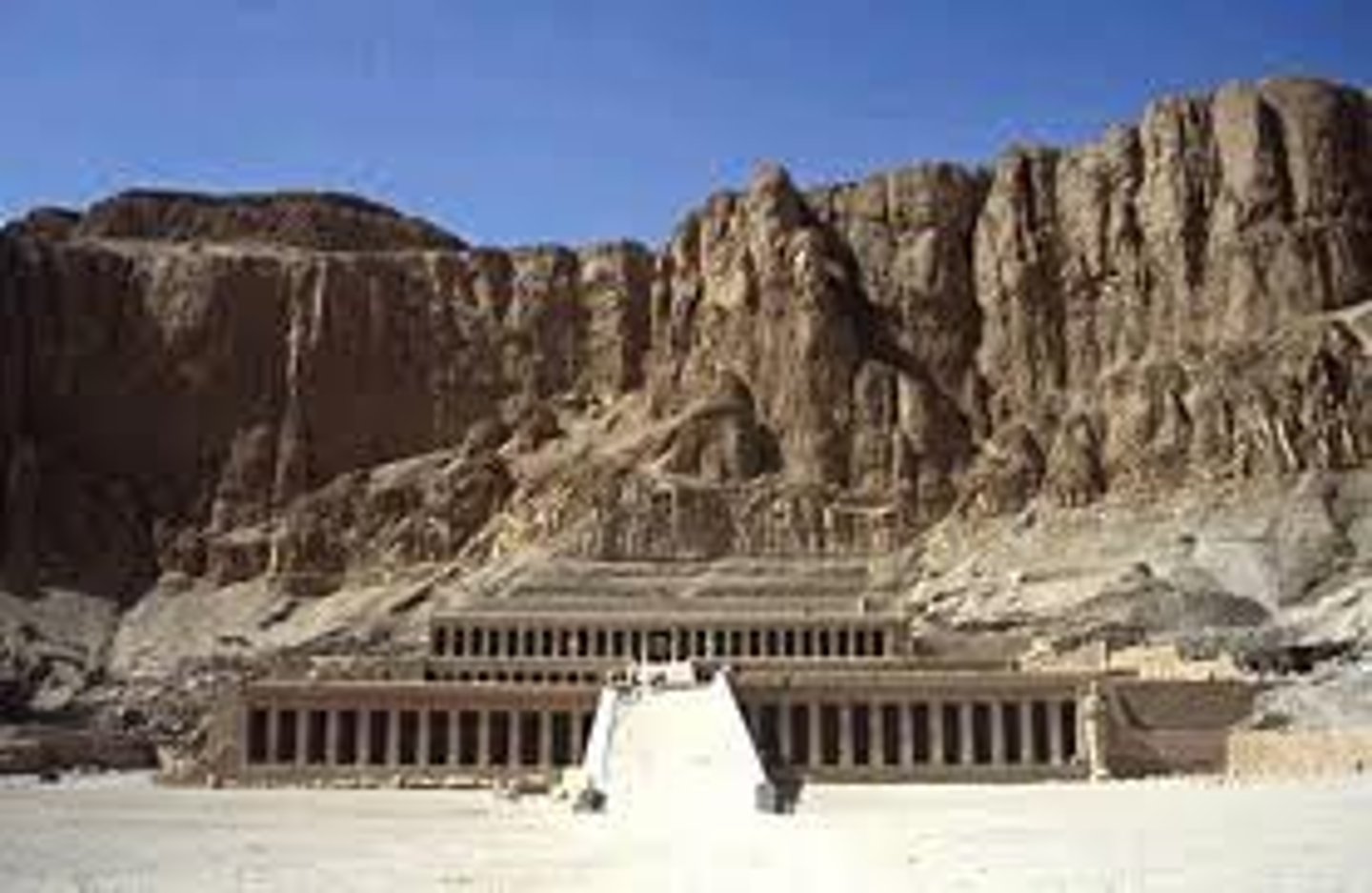
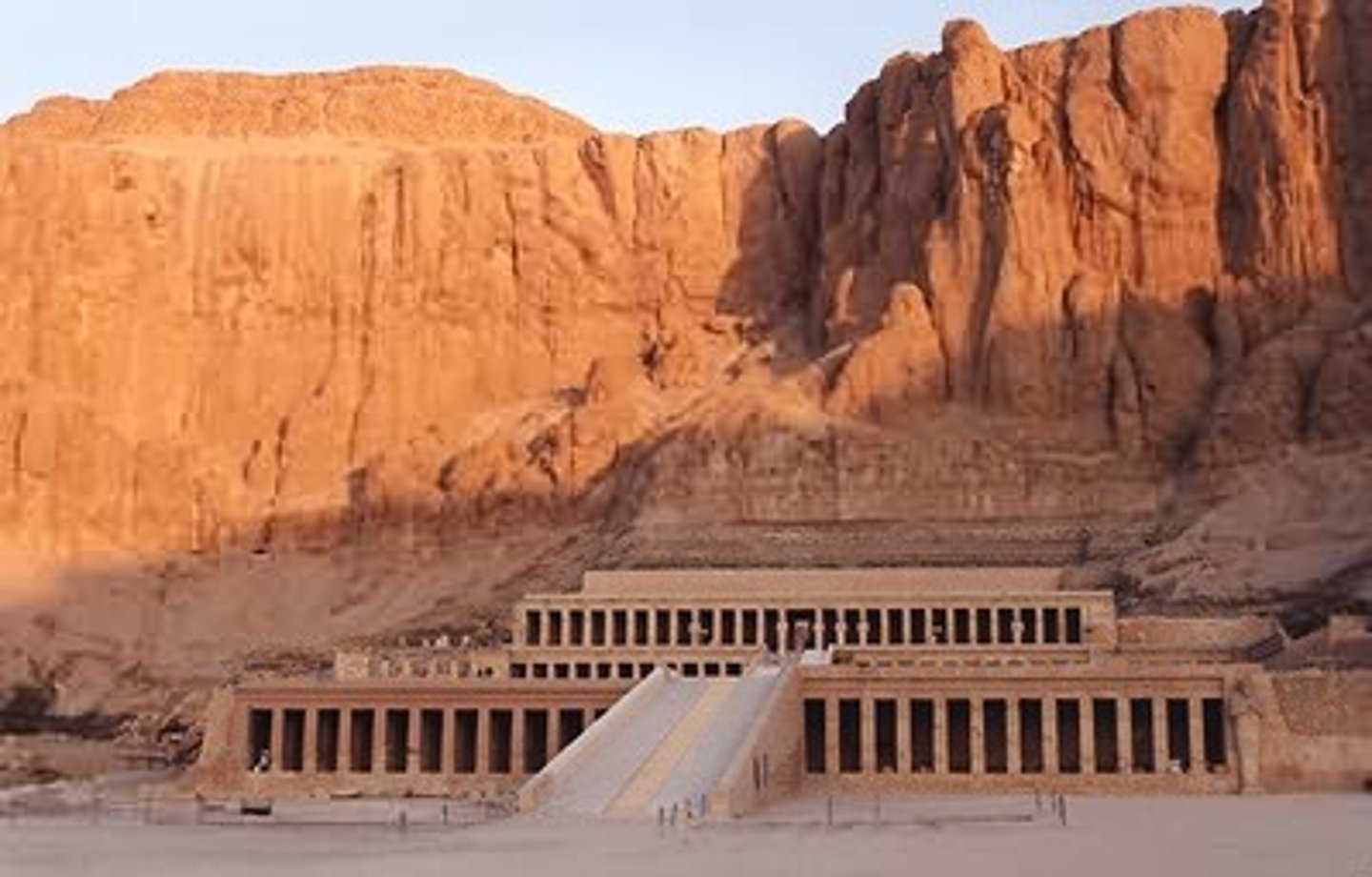
Hatshepsut
1479-1458 BCE. the female king of egypt, obtaining unprecedented power for a woman at the time

Mentuhotep I
Egyptian pharaoh who founded the Middle Kingdom by REUNITING Upper and Lower Egypt in 2134 BCE.
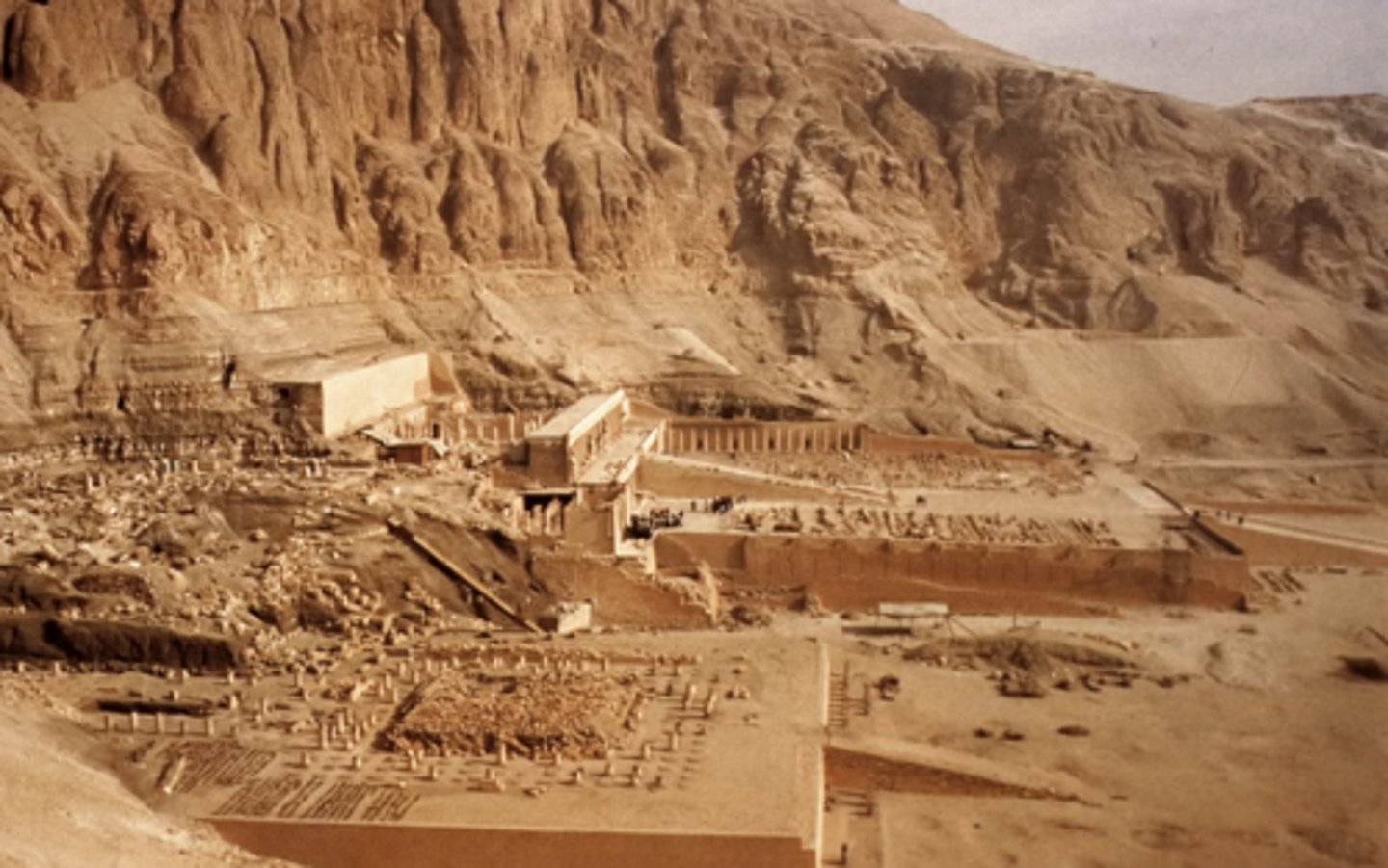

senemut
Chief architect and advisor of Hatshepsut. made the Temple of Hatshepsut

Bronze Age Aegean
3000-1200 BCE, cyclopean masonry
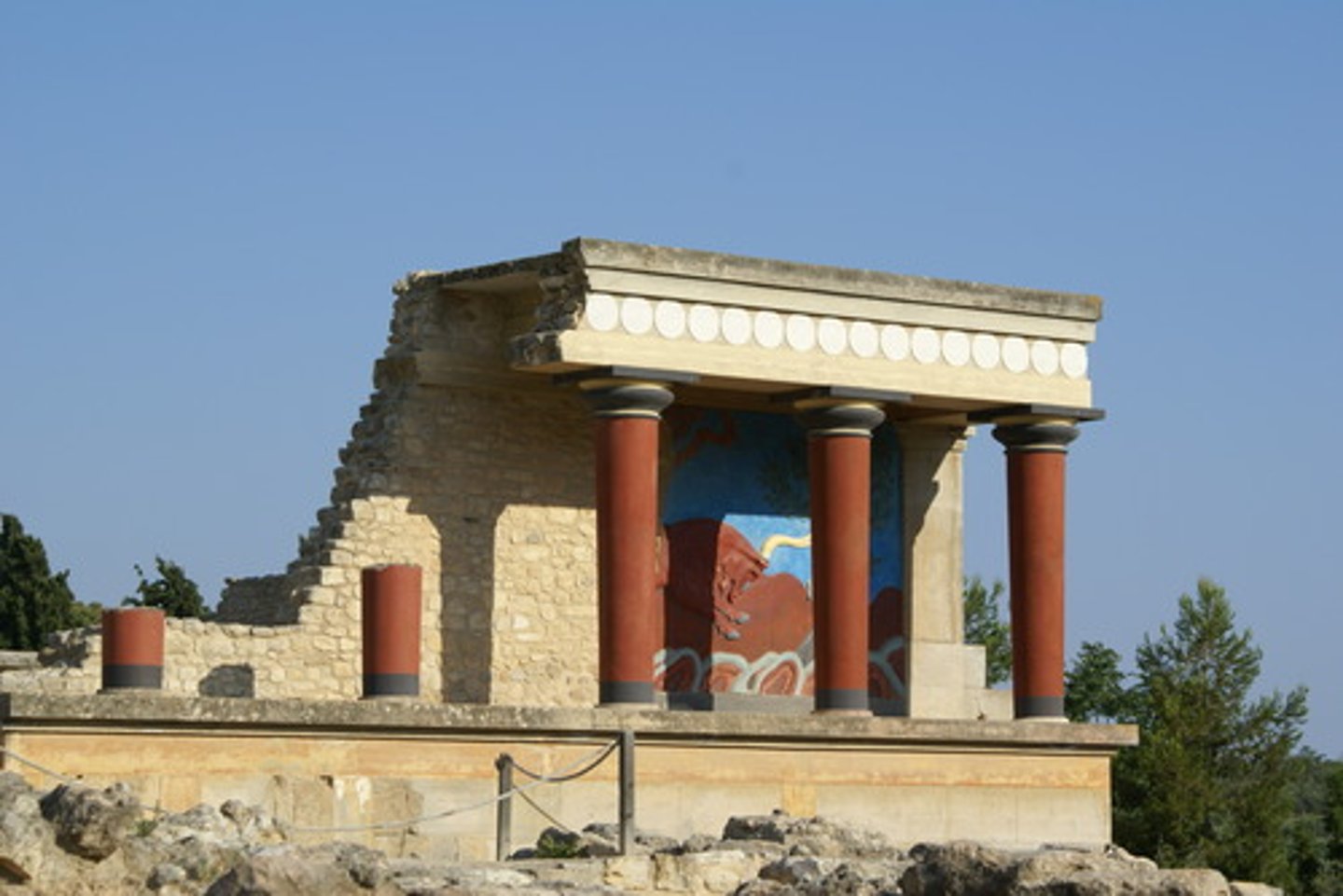
crete
A Greek island in the Mediterranean Sea, southeast of Greece. flourished in the bronze age
Minoans
1900-1600 BCE. The Mediterranean society that formed on the island of Crete and who were a big maritime society.

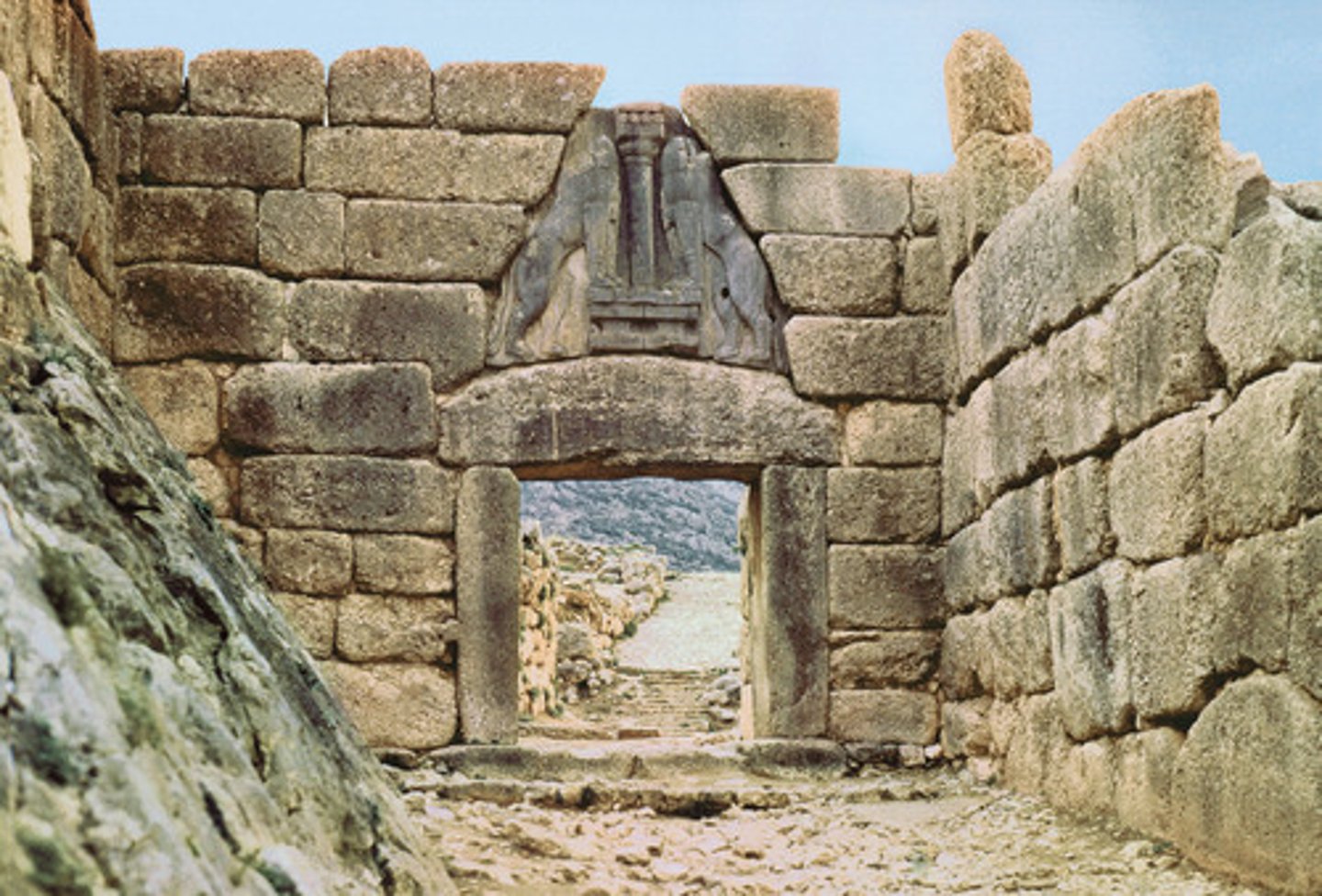
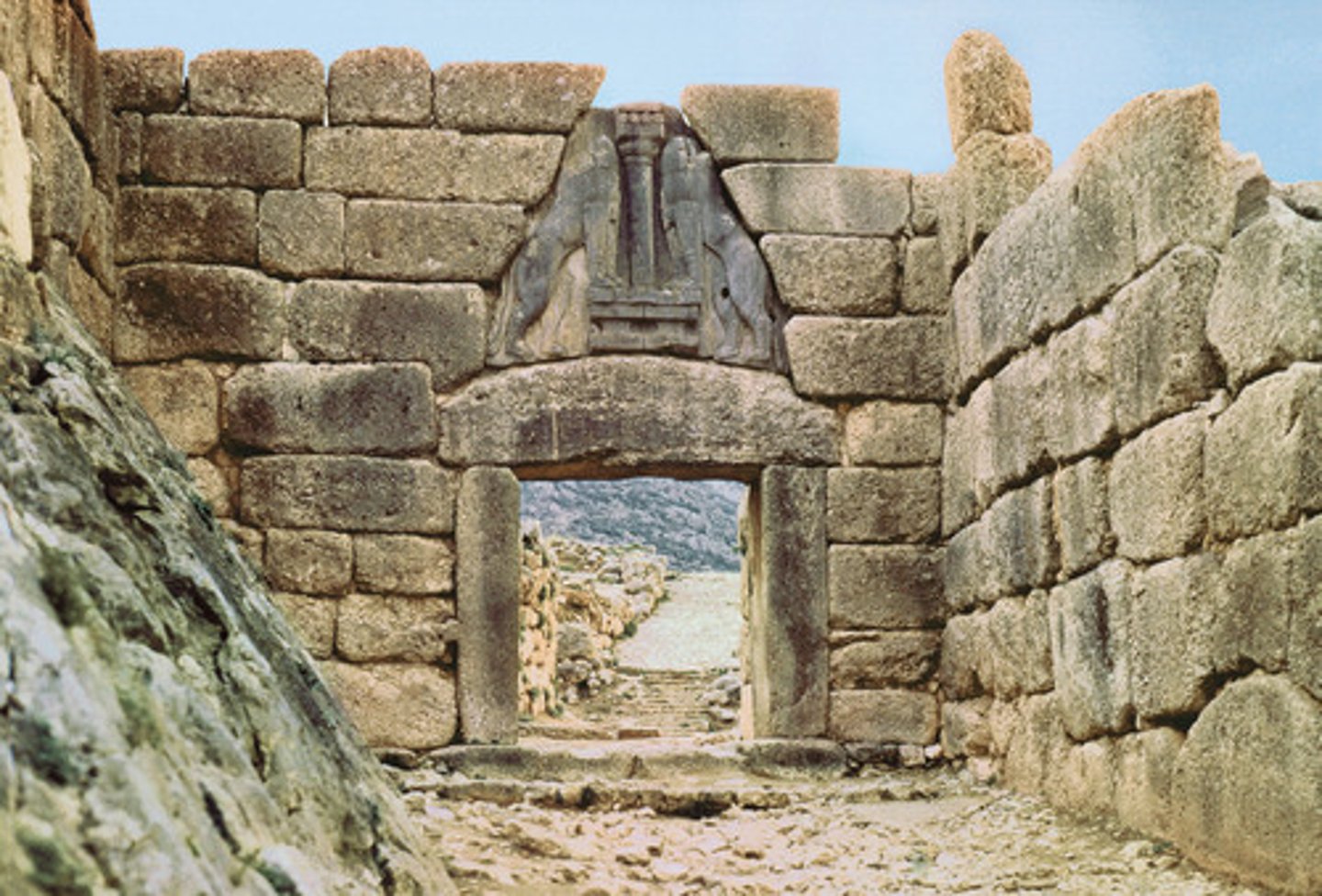
Mycenae/Mycenaean
was the last phase of the Bronze Age in ancient Greece/they largely overpowered Minoan society/it represented the first advanced civilization in mainland Greece w/ urban organizations, works of art and writing system. mycenaeans overthrew minoans. added lions gate

tapered column
Typical of Minoan architecture. column that gets skinnier or wider at the base.
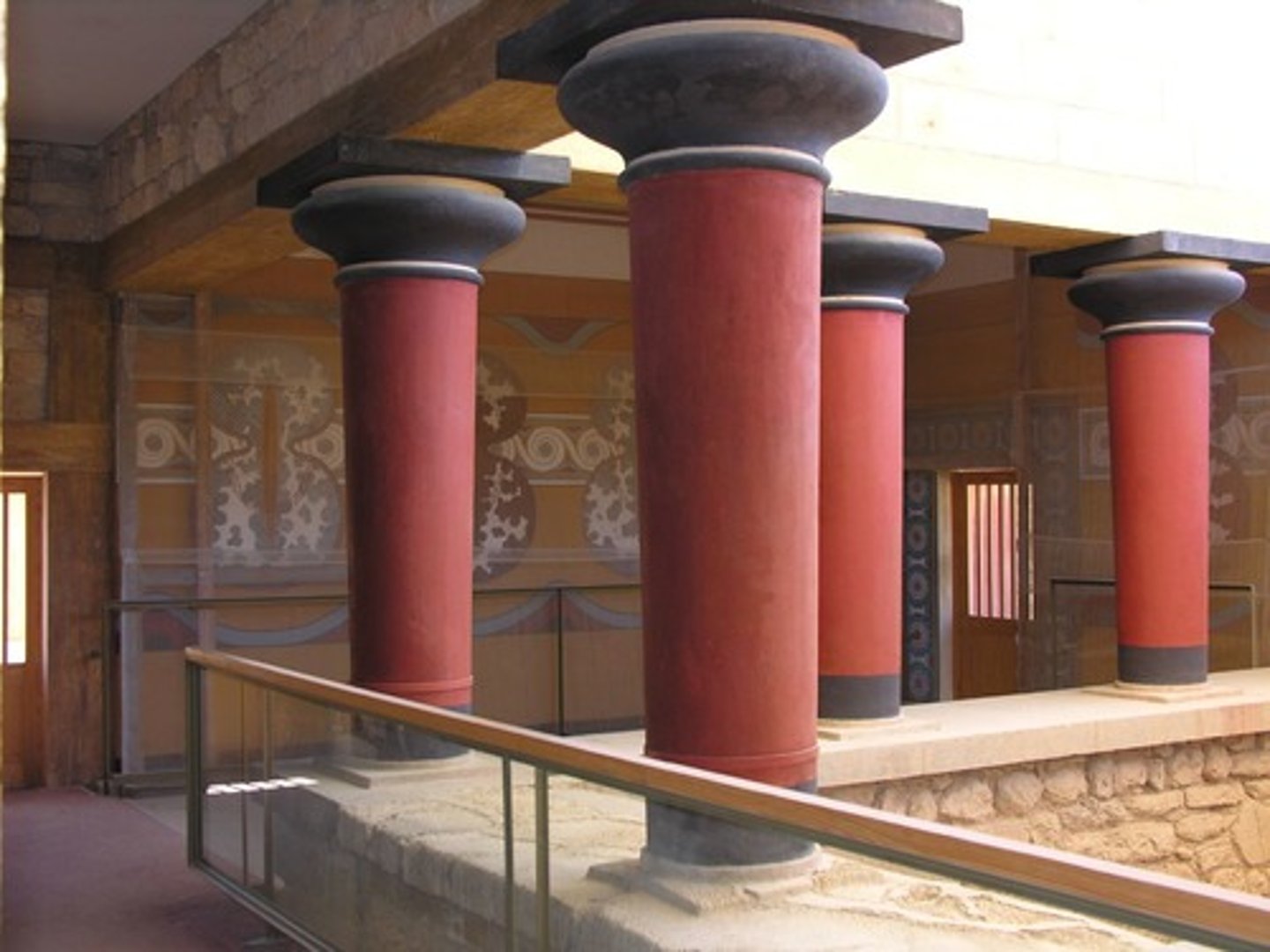

fresco
a wall painting made on wet plaster with water-based colors
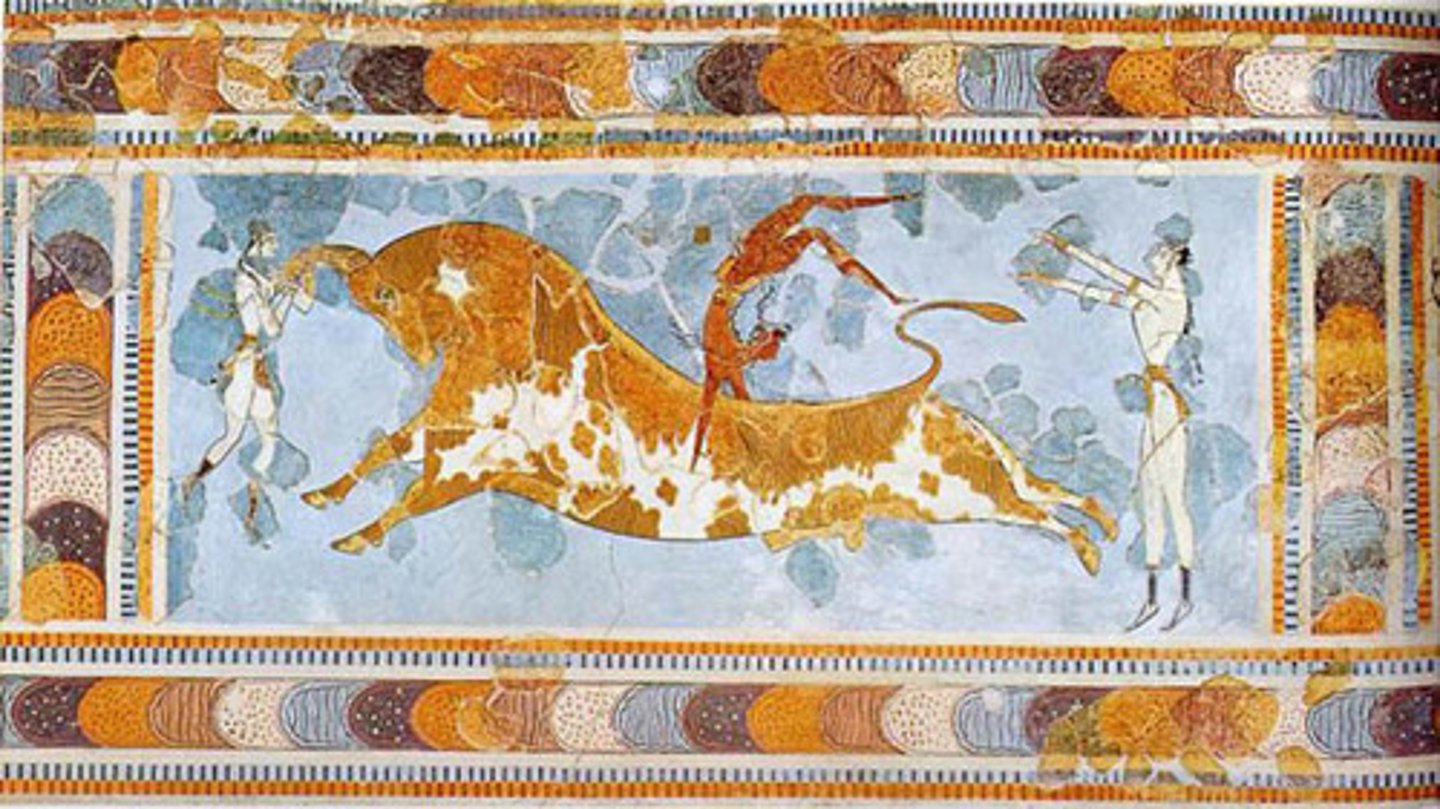

Cyclopean Stones/Construction
mycenean architecture. large, unrendered stones, to create structures that looked as if they had been formed by natural processes. the greeks of the next millennium though such works had been built by giants

Corbeled arch/vault
arch or vault made up of inwardly projecting courses of stone
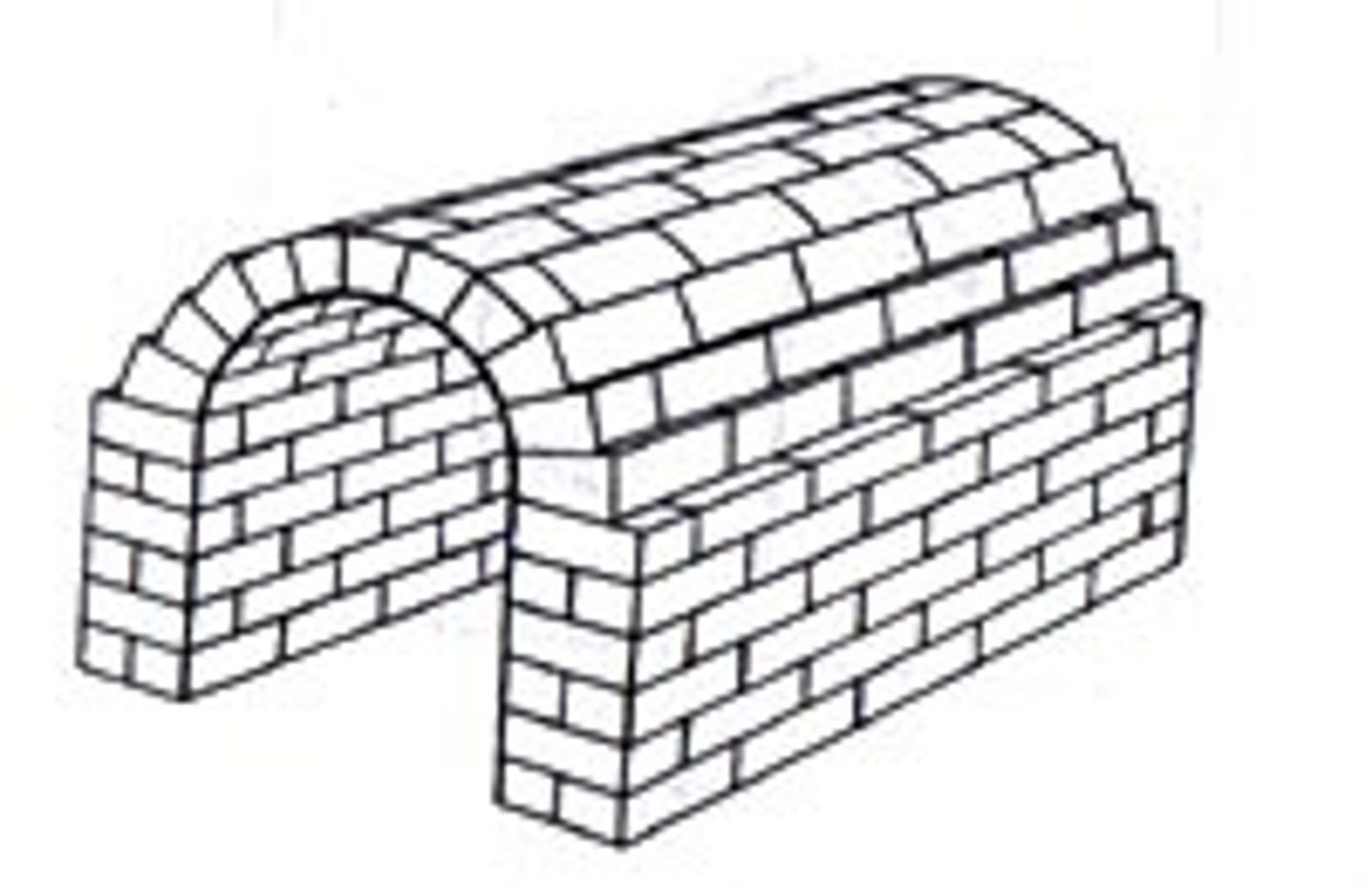
vault
an arched ceiling or roof
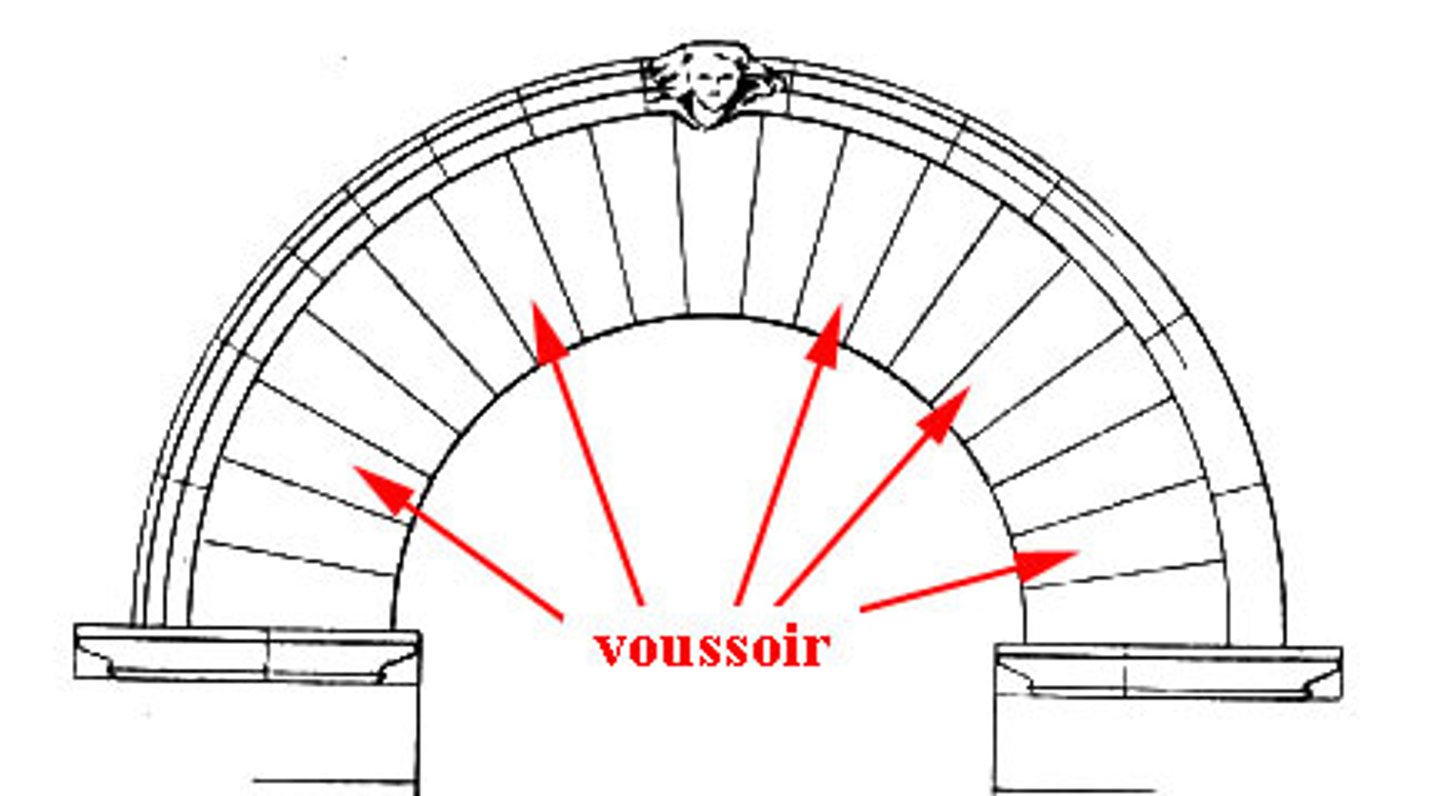
true arch
a curved structure, usually made of wedge-shaped stones (voussoirs), that spans an opening
relieving arch
an arch which redistributes weight above a lintel
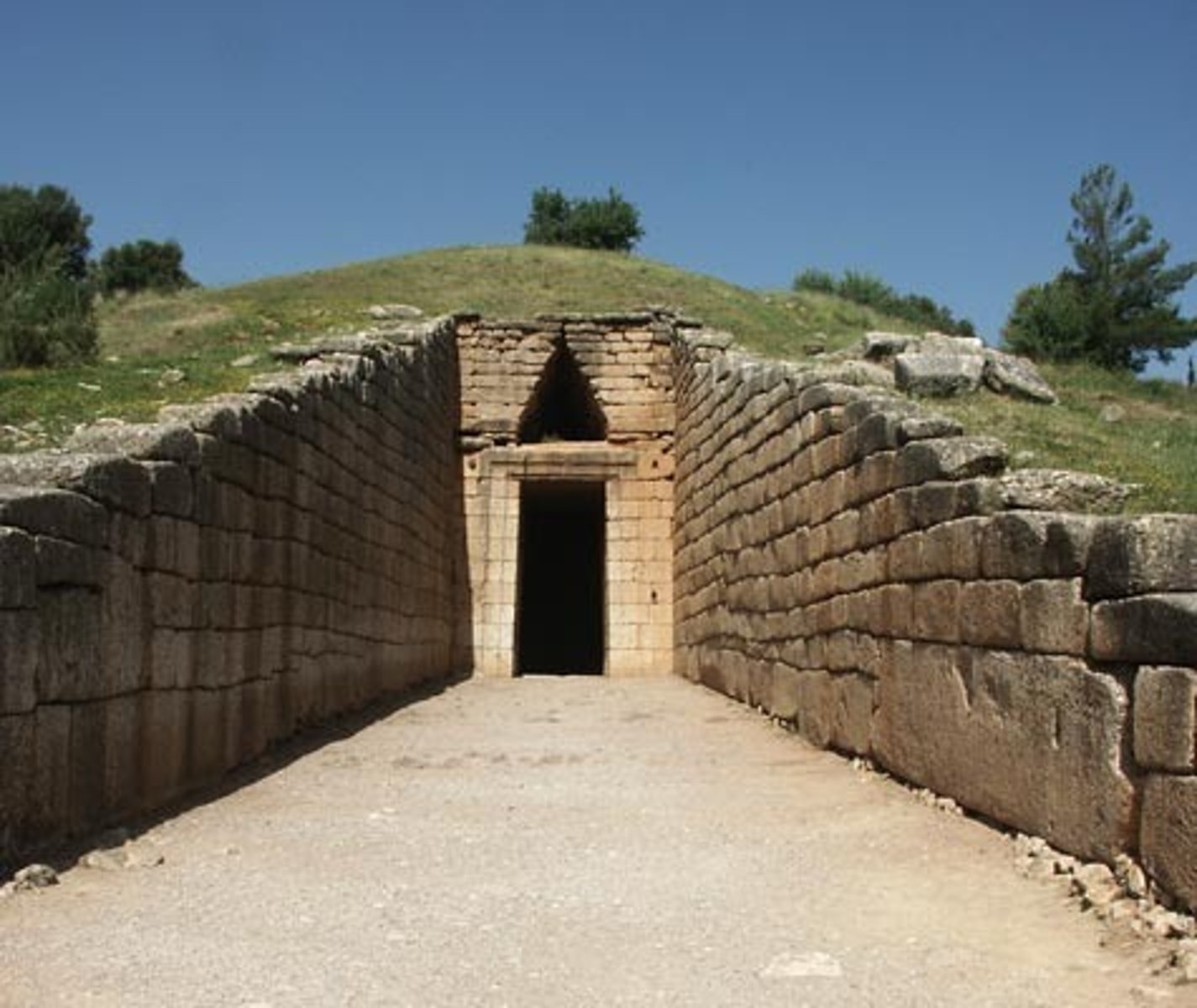

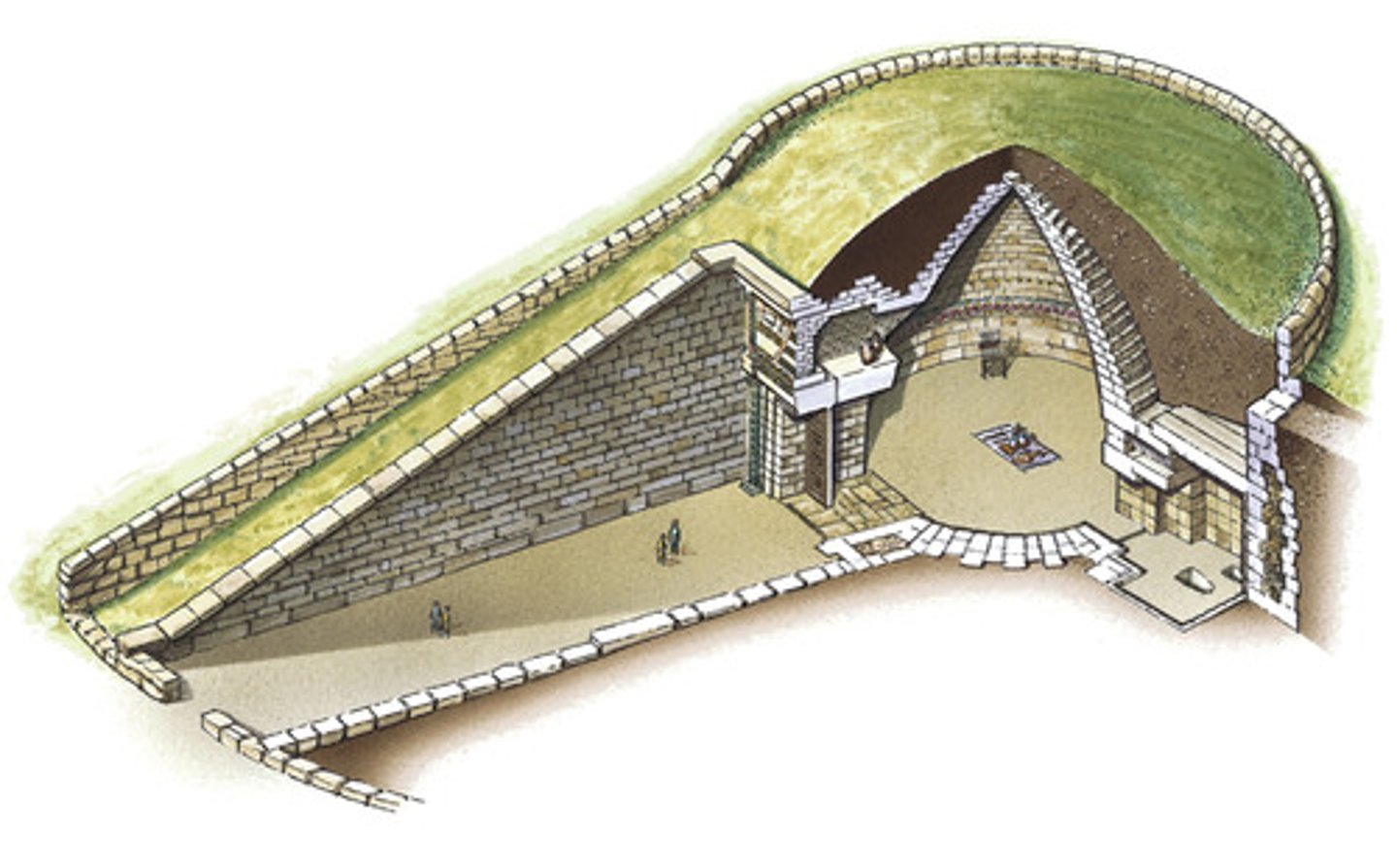
tholos tomb
an ancient Mycenaean circular tomb in a beehive shape
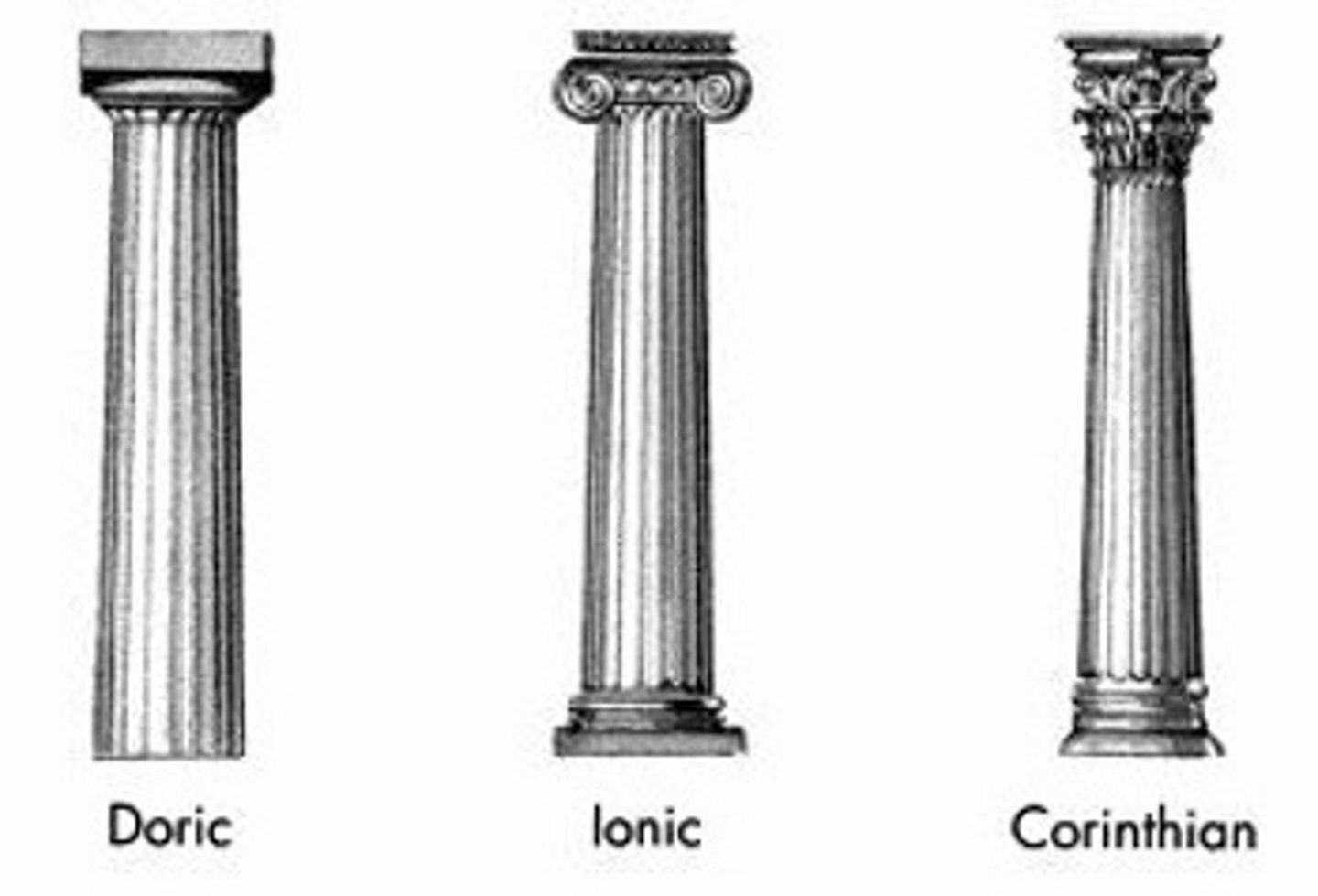
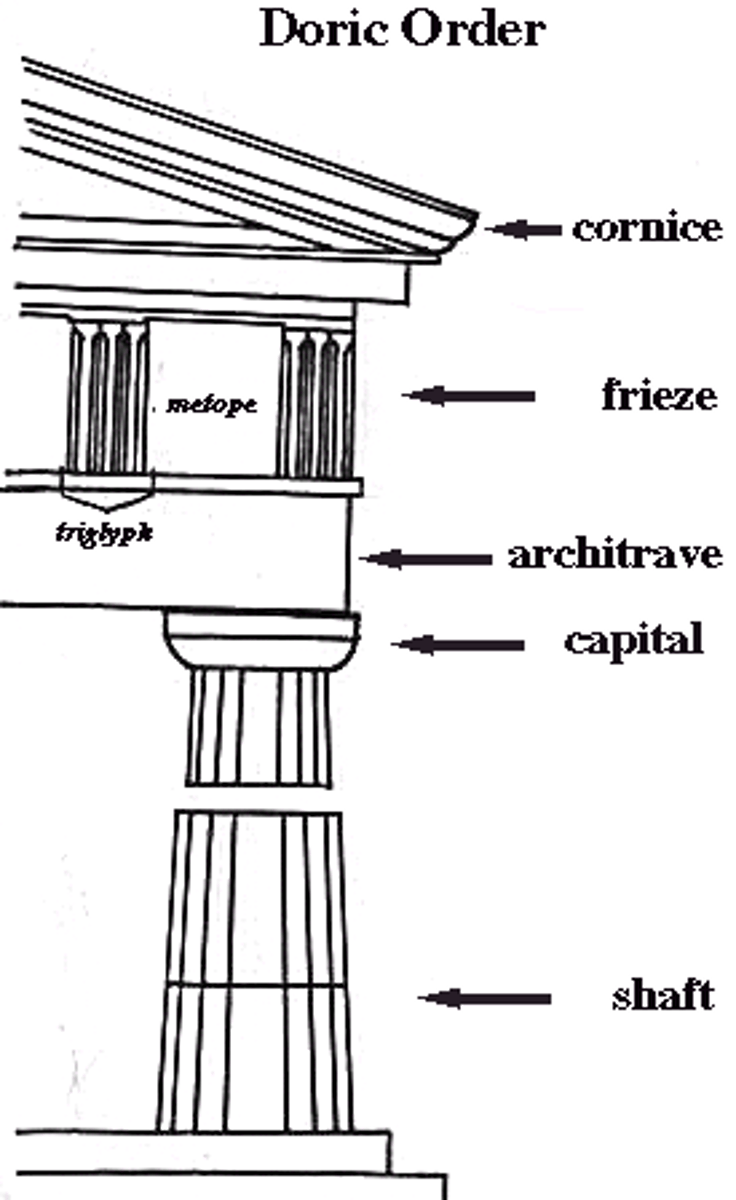
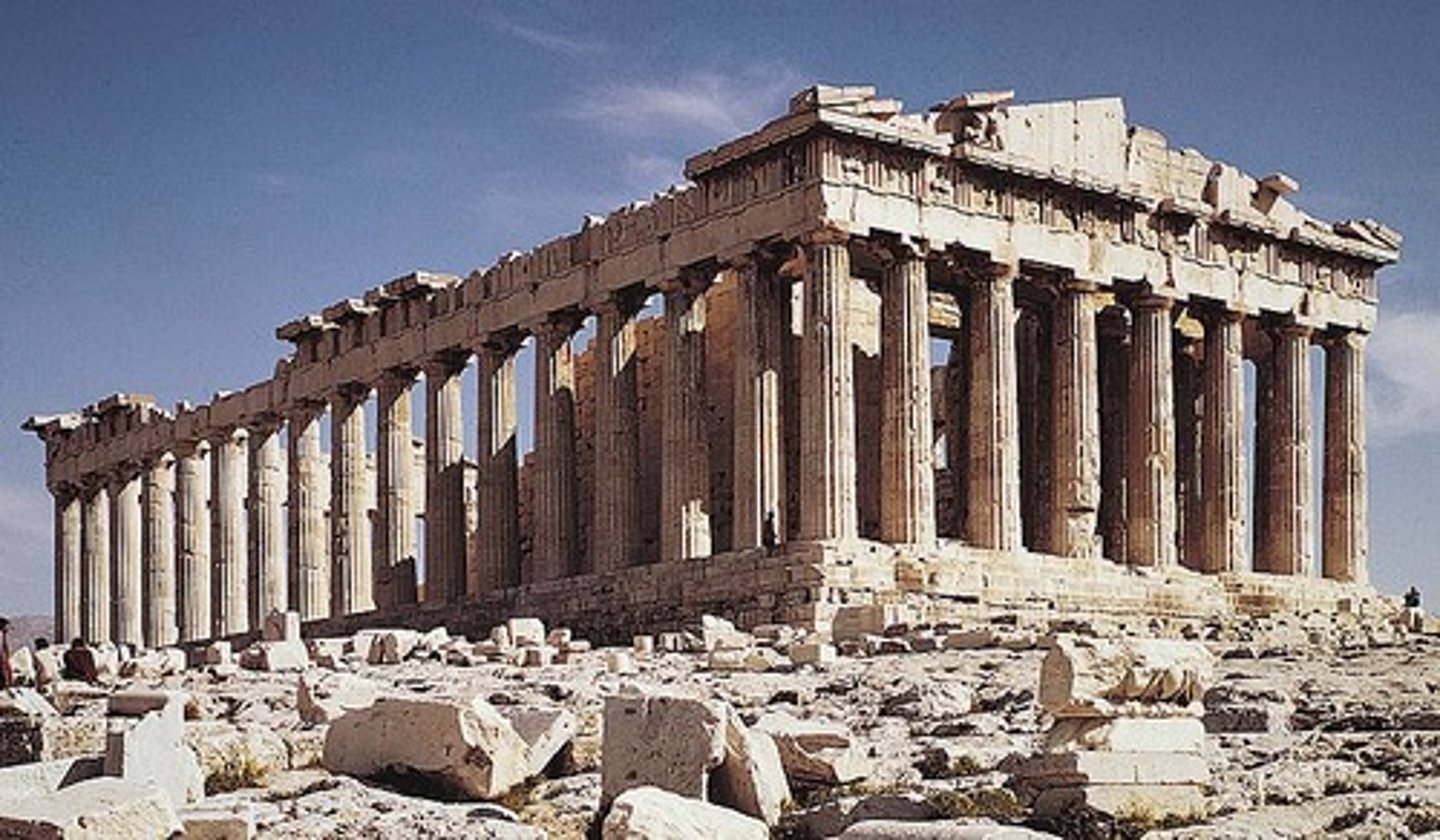
Doric Order
the simplest of the classical Greek architectural styles, featuring unadorned columns with no base. has metopes and triglyphs
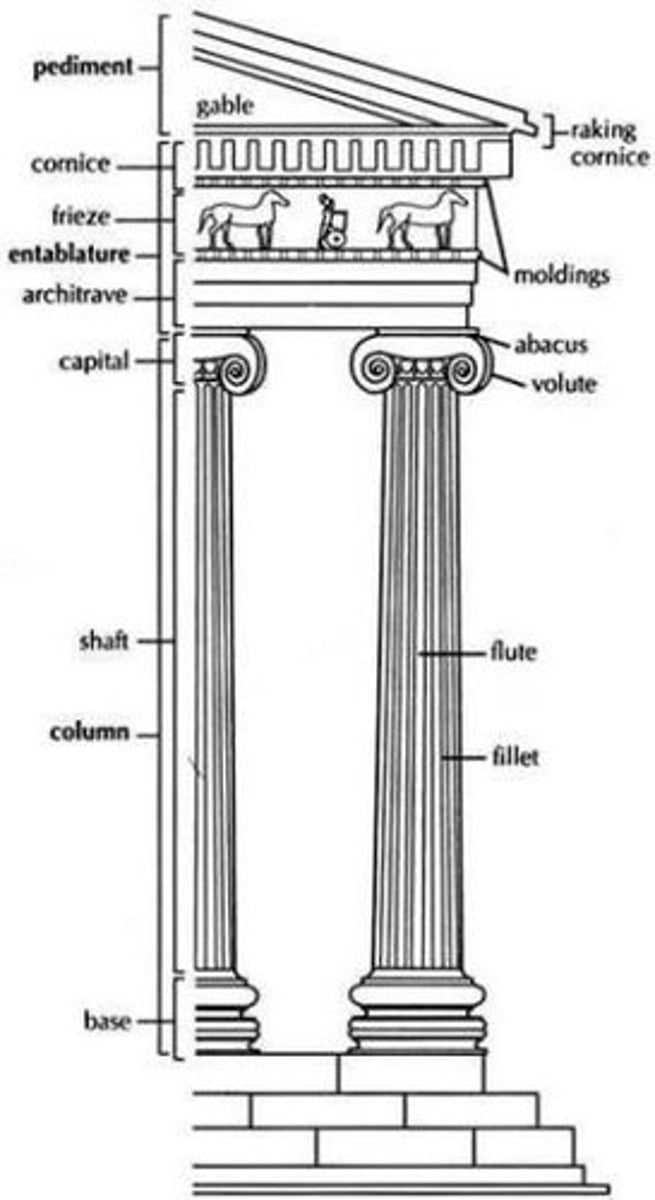
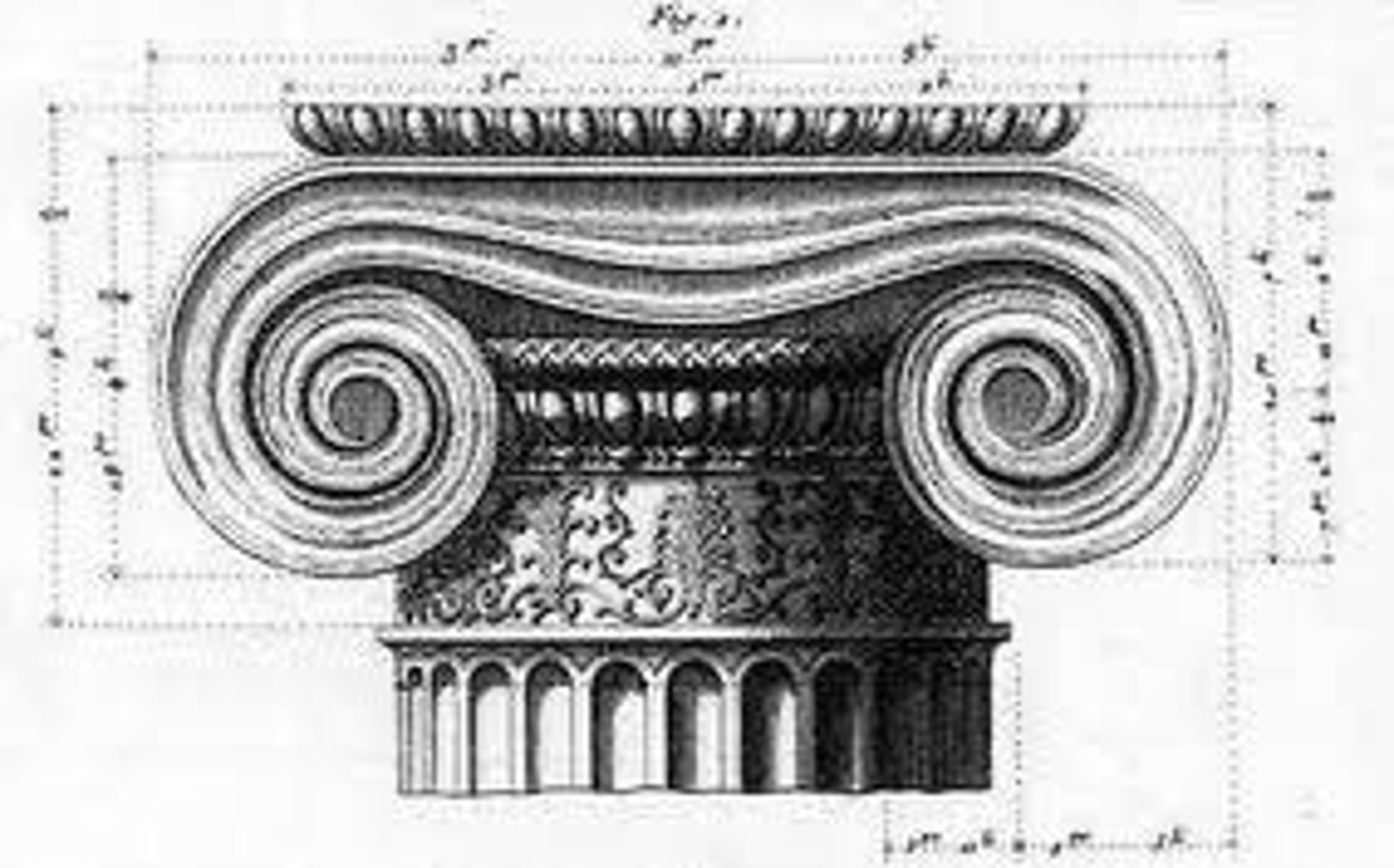
Ionic Order
classical Greek architectural style that features a fluted column shaft, capitals with volutes (spiral scroll-like ornaments) and a large base
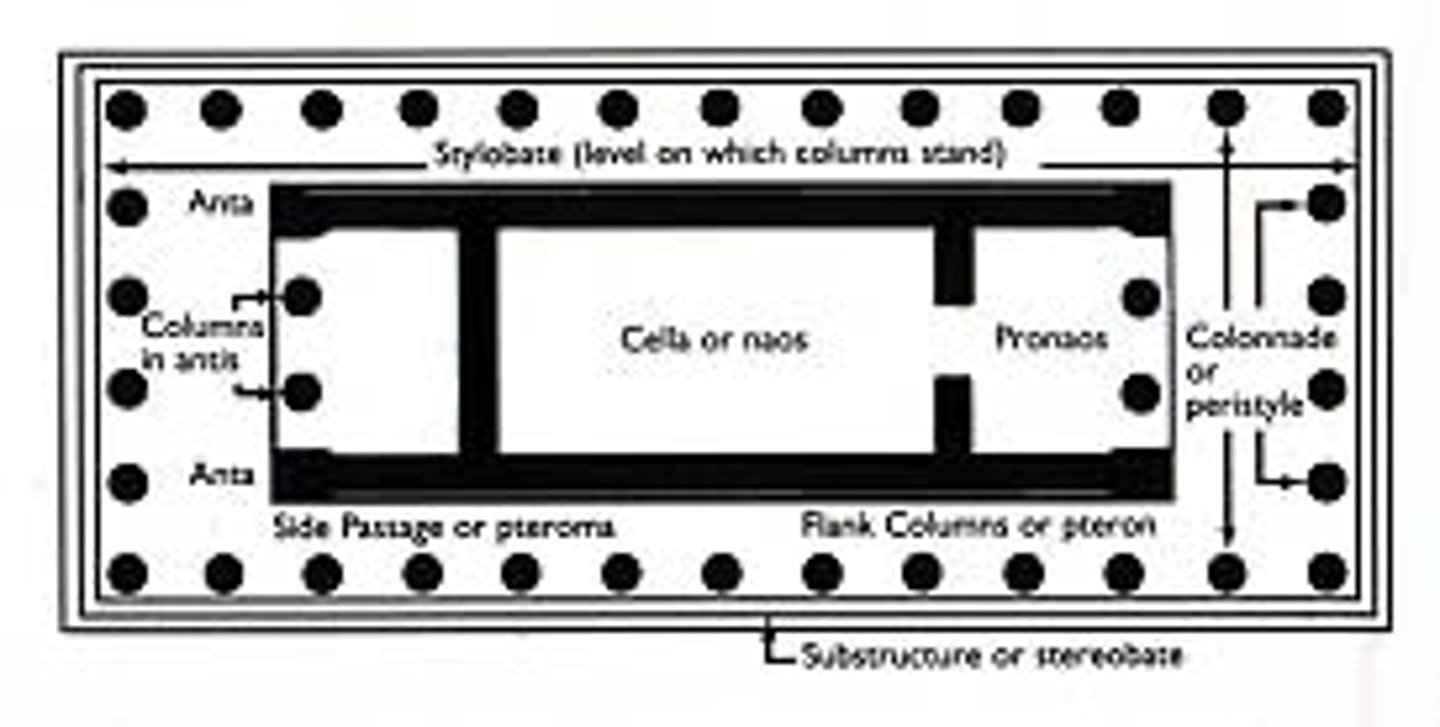
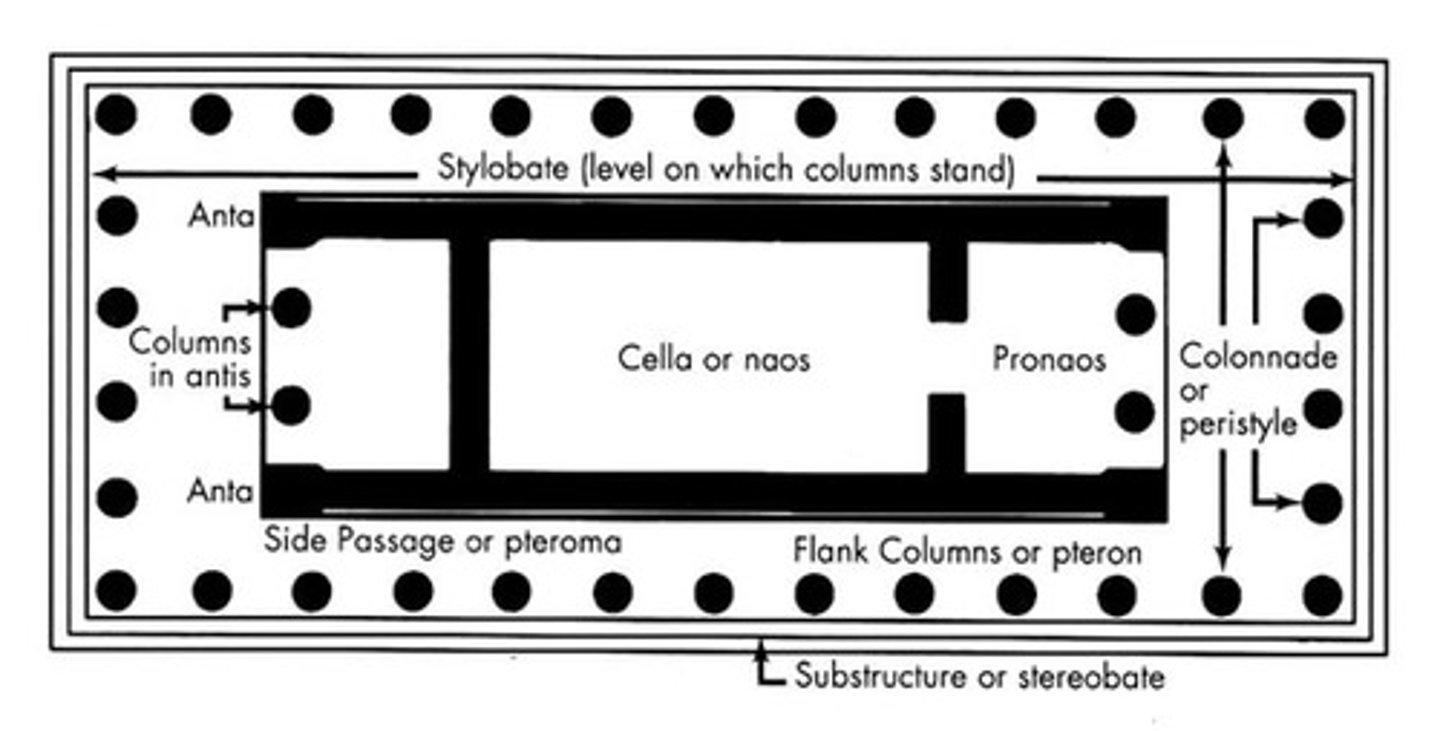
peristyle
a roofed, columned porch or colonnade surrounding a building or courtyard

peripteral
surrounded on all sides by a single row of columns
Intercolumniation
spacing between adjacent columns
pediment
the triangular gable end of an ancient Greek or Roman temple
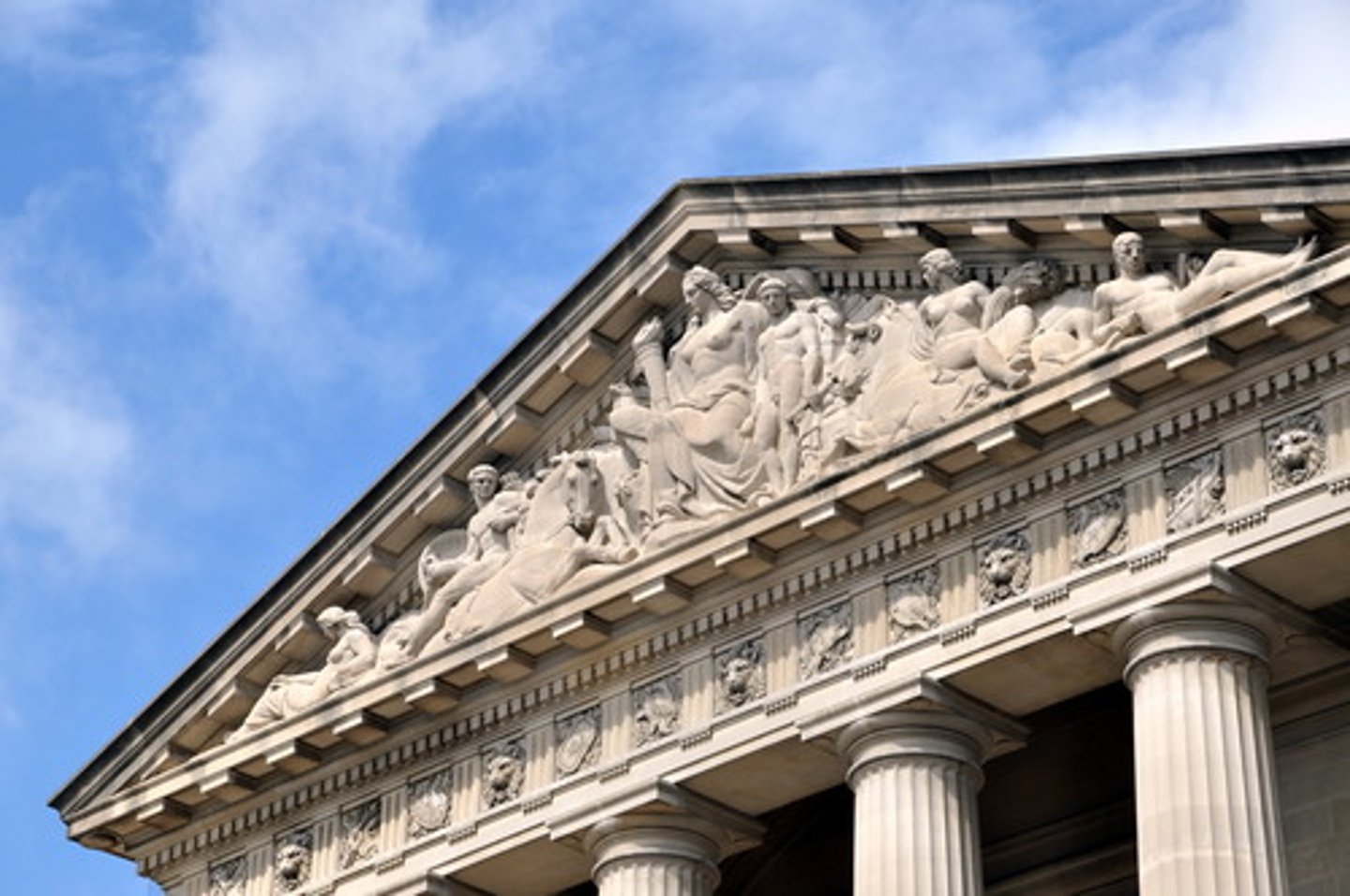

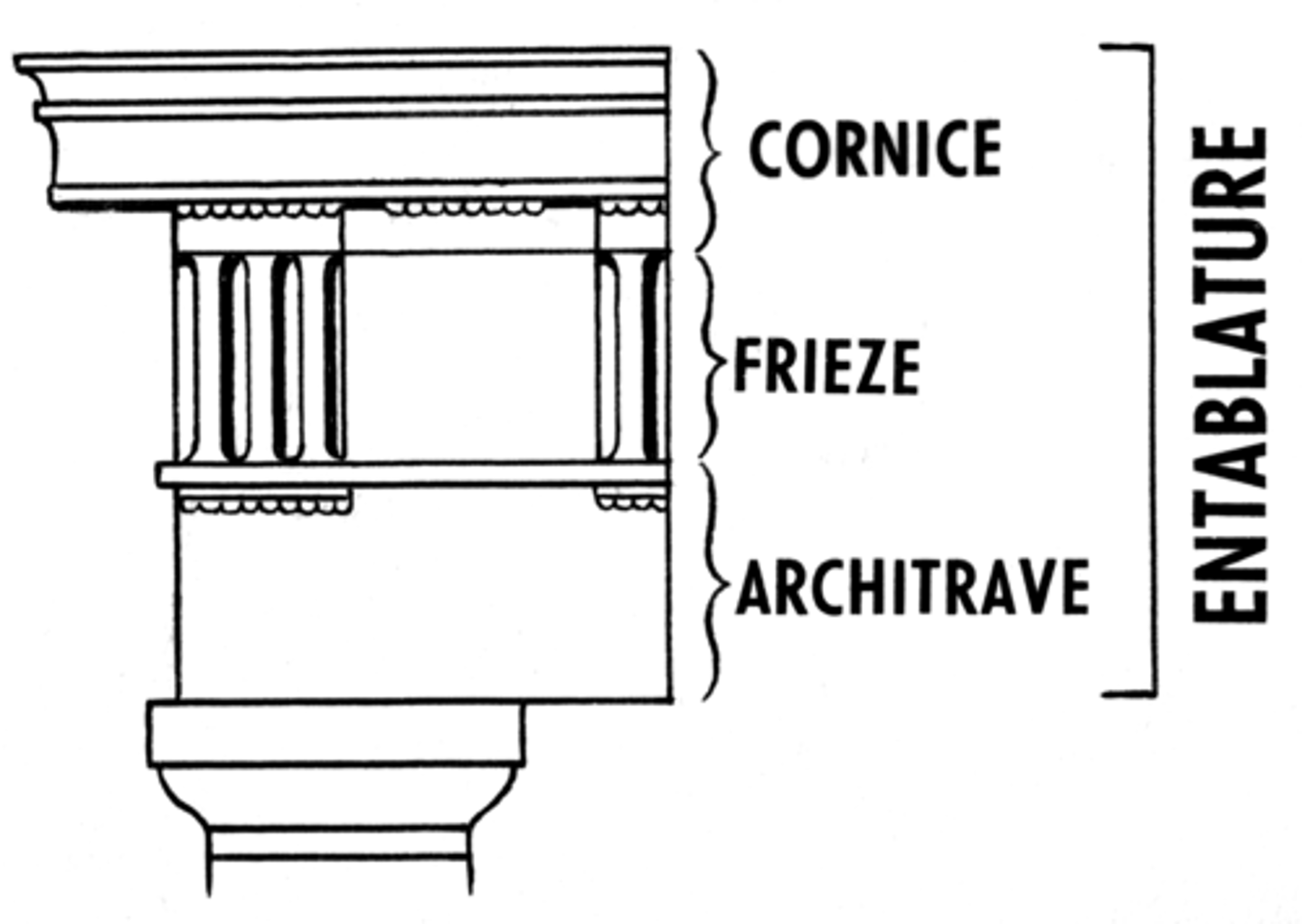
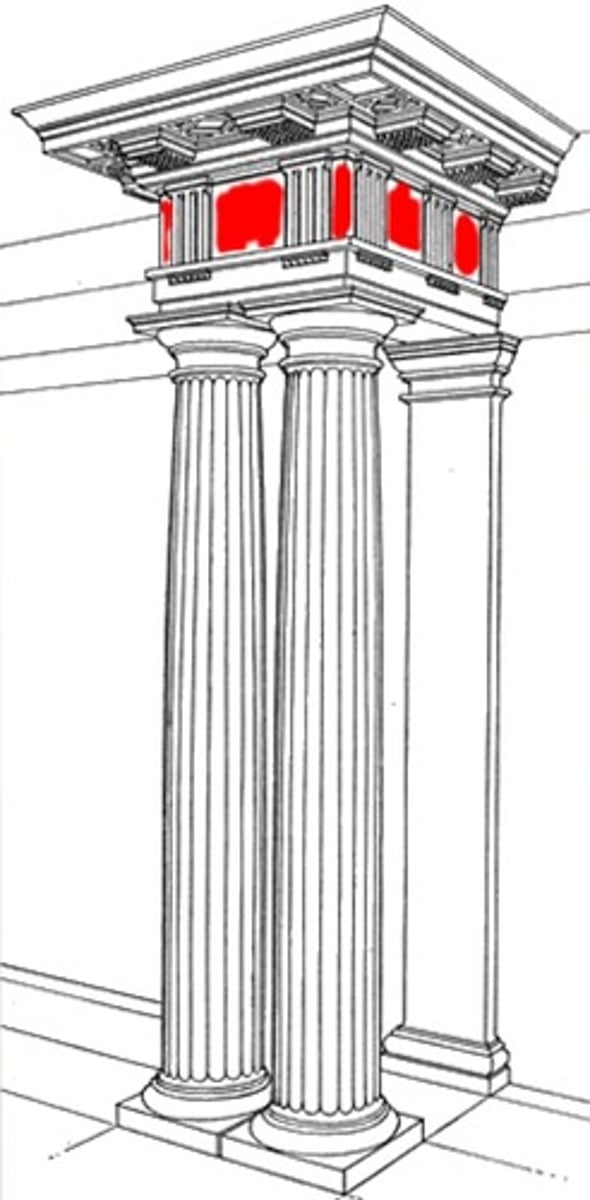
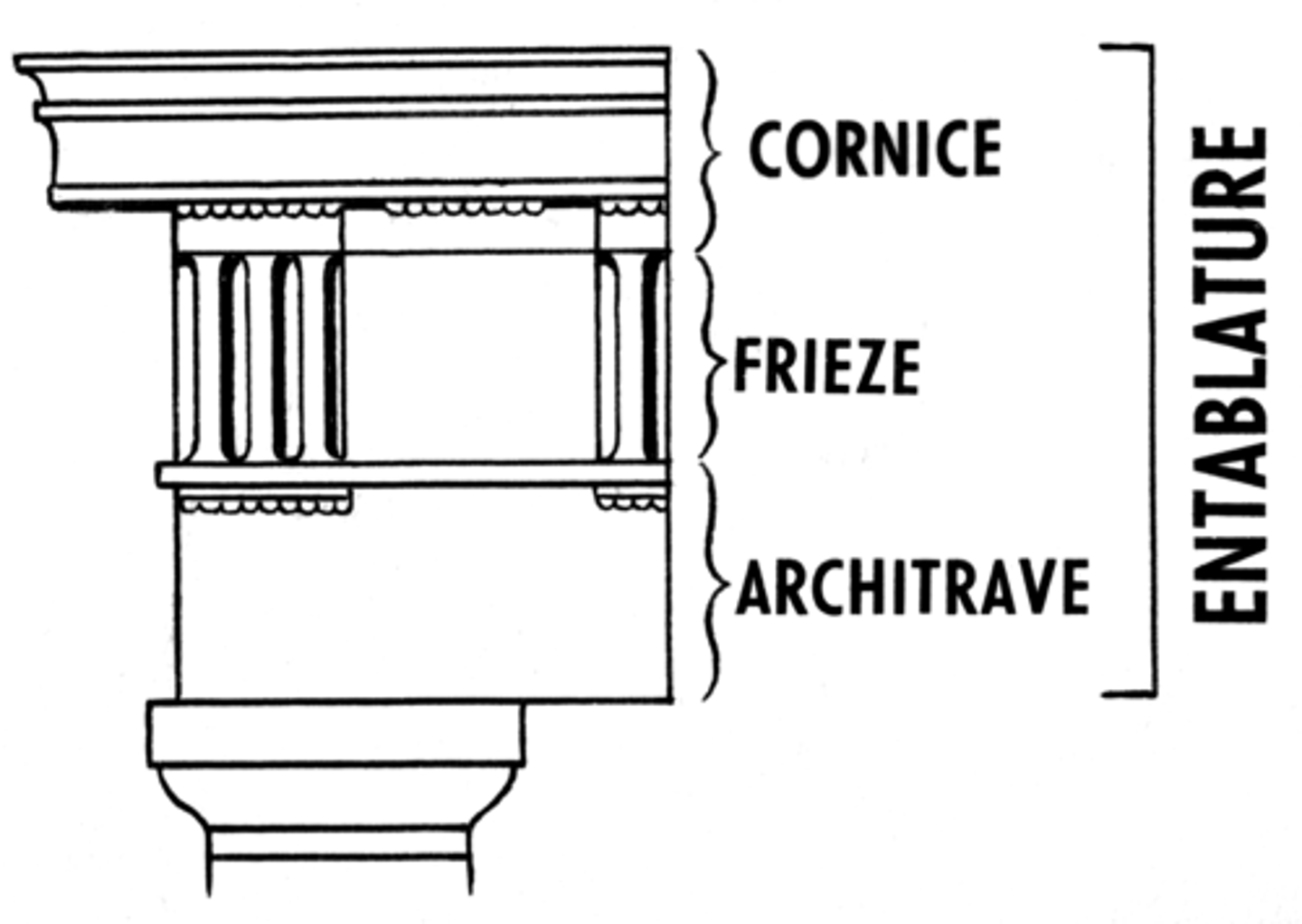
Entablature
the horizontal spanning element of a classical order divided into the architrave (bottom), frieze, and cornice (top)
triglyph
a triple projecting, grooved member of a Doric frieze that alternates with metopes
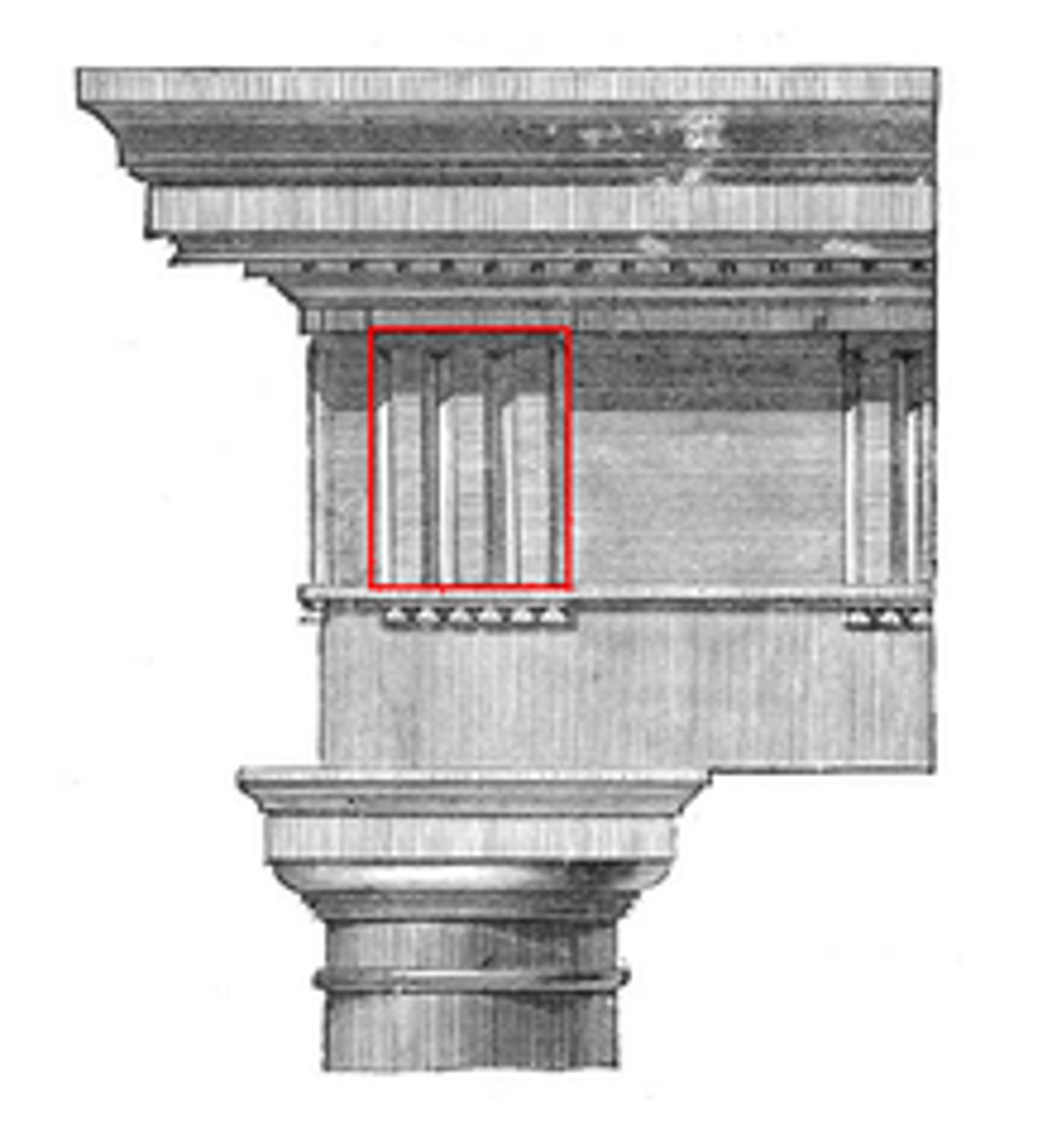
Metope
panel between the triglyphs in a Doric frieze, often sculpted in relief
Architrave
The beam that spans a pair of columns
capital
the upper element of a column above the shaft

Frieze/Continuous Frieze
in a classical order, middle horizontal division of an entablature, usually decorated with sculpture
ionic order has a continuous frieze
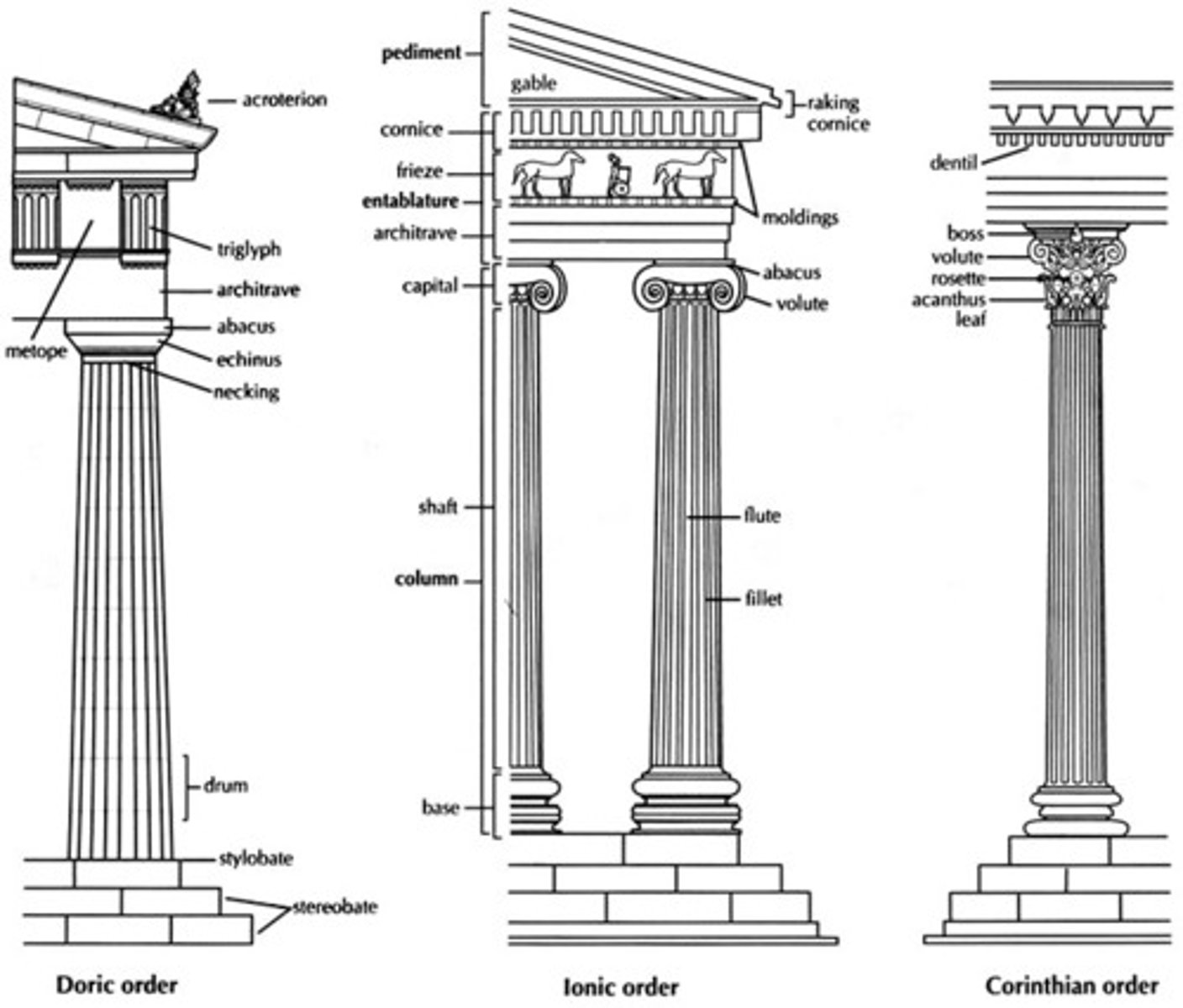
volute
A spiral, scroll-like form characteristic of the ancient Greek Ionic and the Roman Composite capital.
cella
the main room in a classical greek or roman temple, housing the cult statue
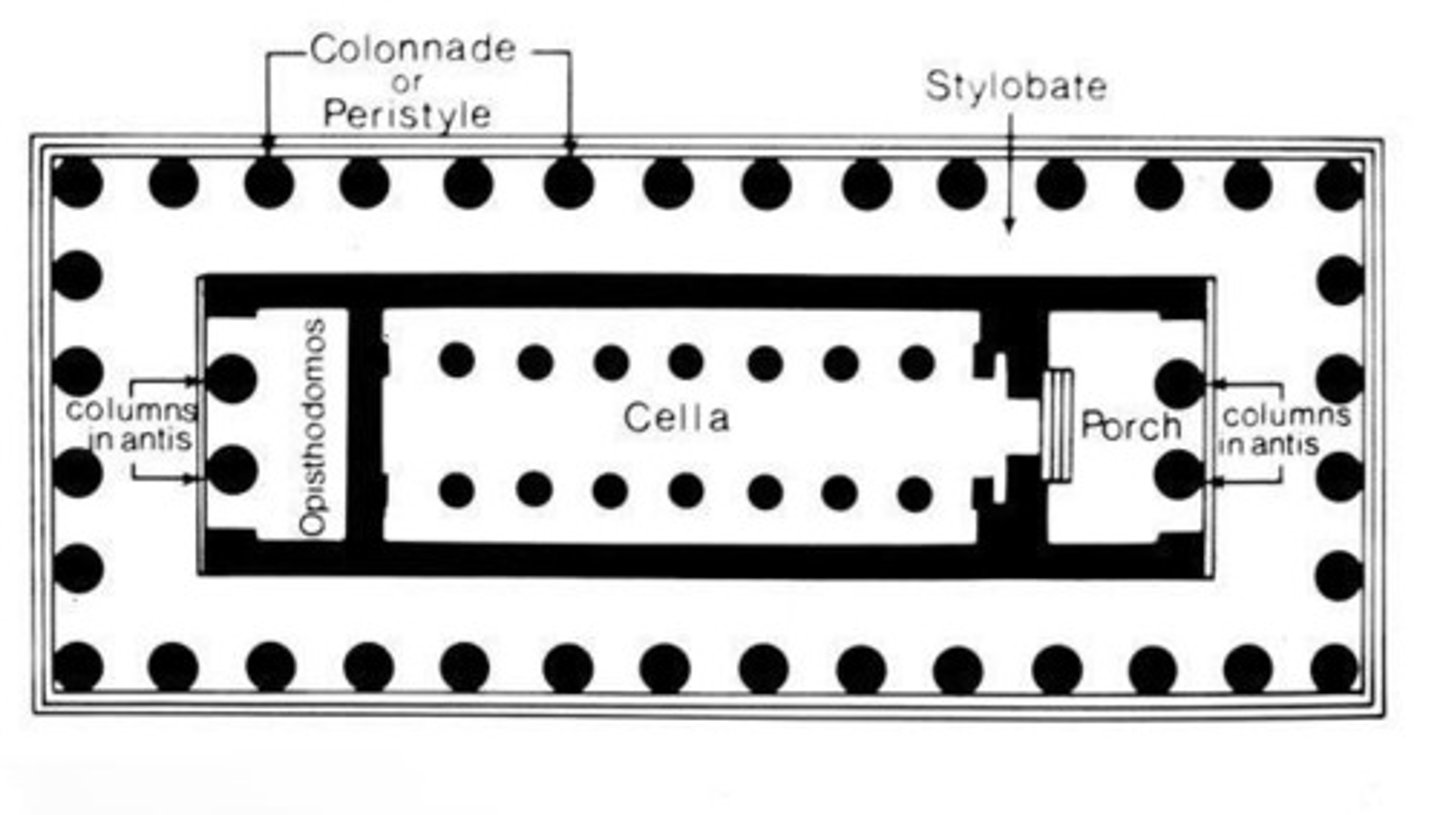
greek temple
usually sited in remote, nonurban settings as landmarks associated with the legends of their gods, conformed to one of the three styles: doric, ionic, or corinthian.
built to house statues of gods
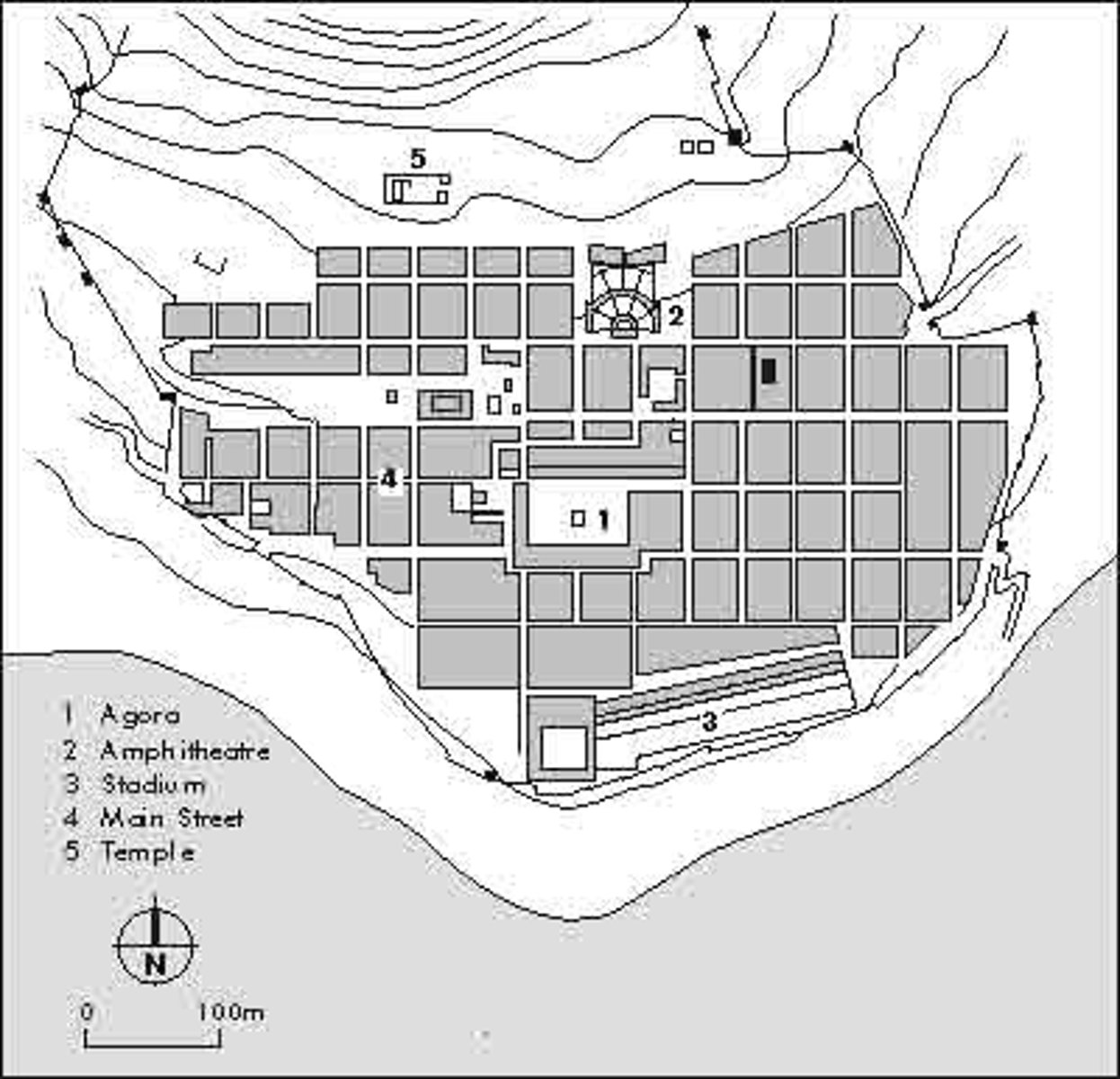
orthogonal grid plan
an urban plan consisting of a series of broad, straight streets, cutting one another at right angles
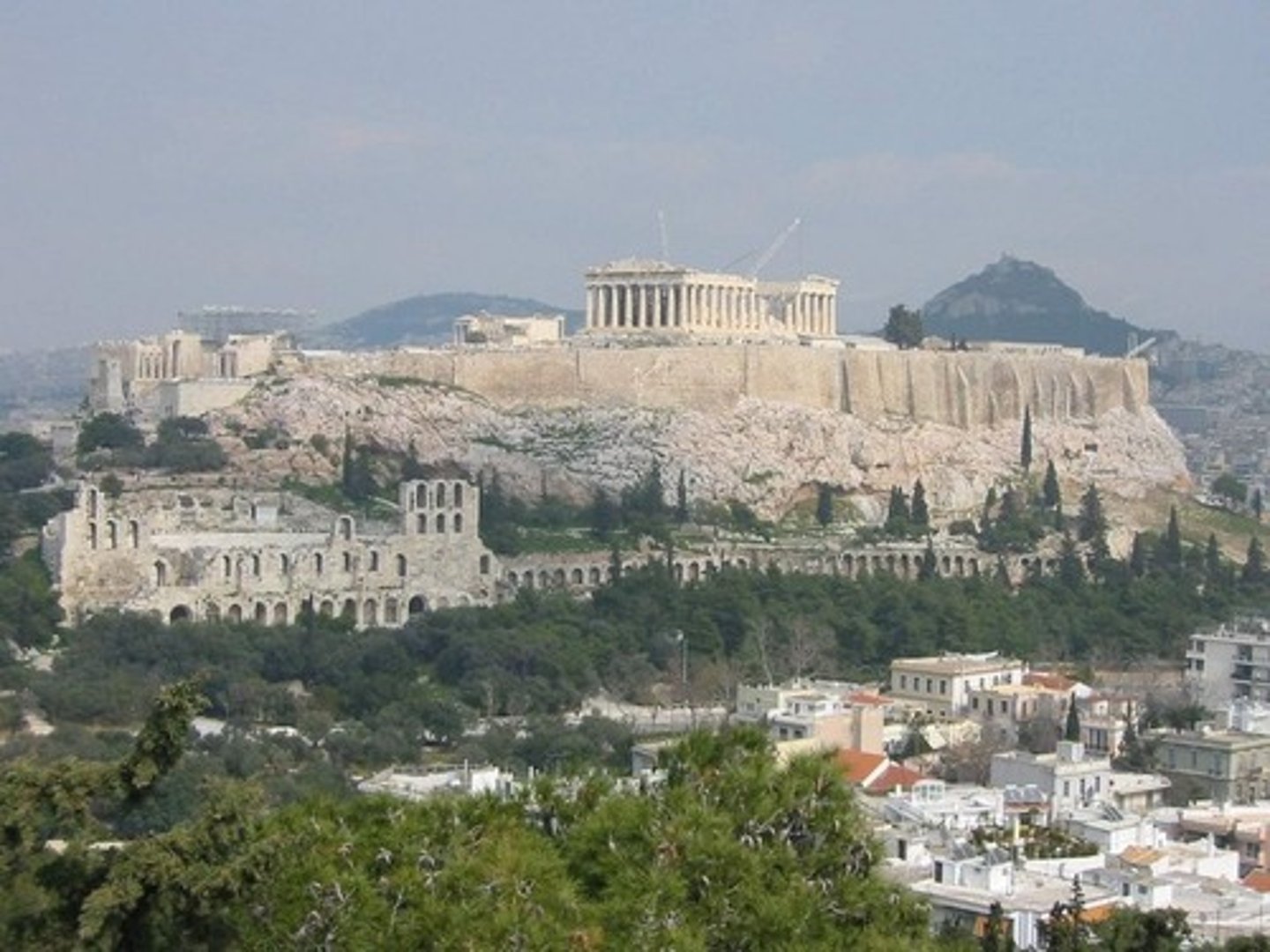
Pericles
460 BCE. Athenian leader noted for advancing democracy in Athens and for ordering the construction of the Parthenon.

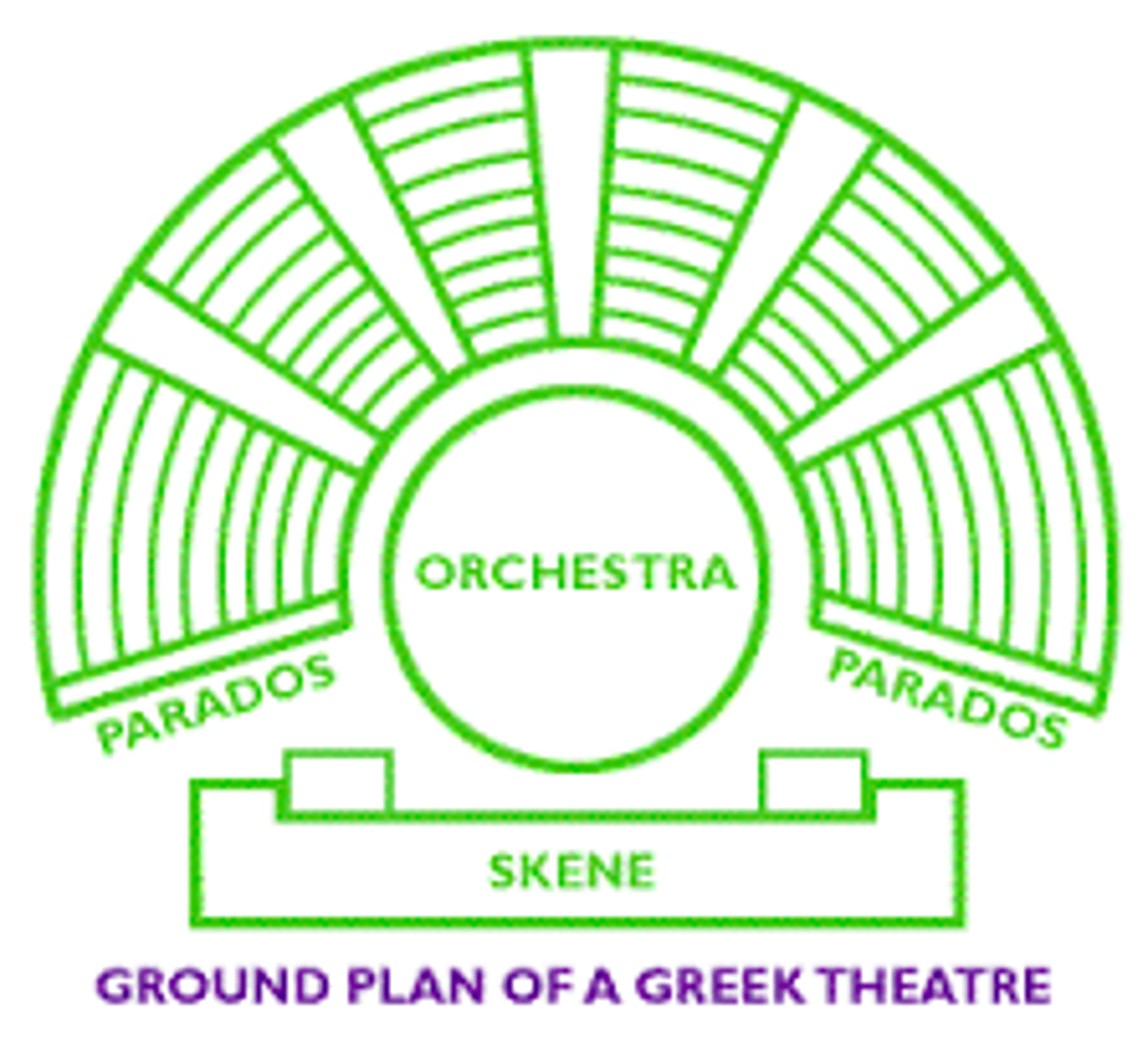
Orchestra
in an ancient greek or roman theater, the circular or semicircular space between the auditorium and the stage building
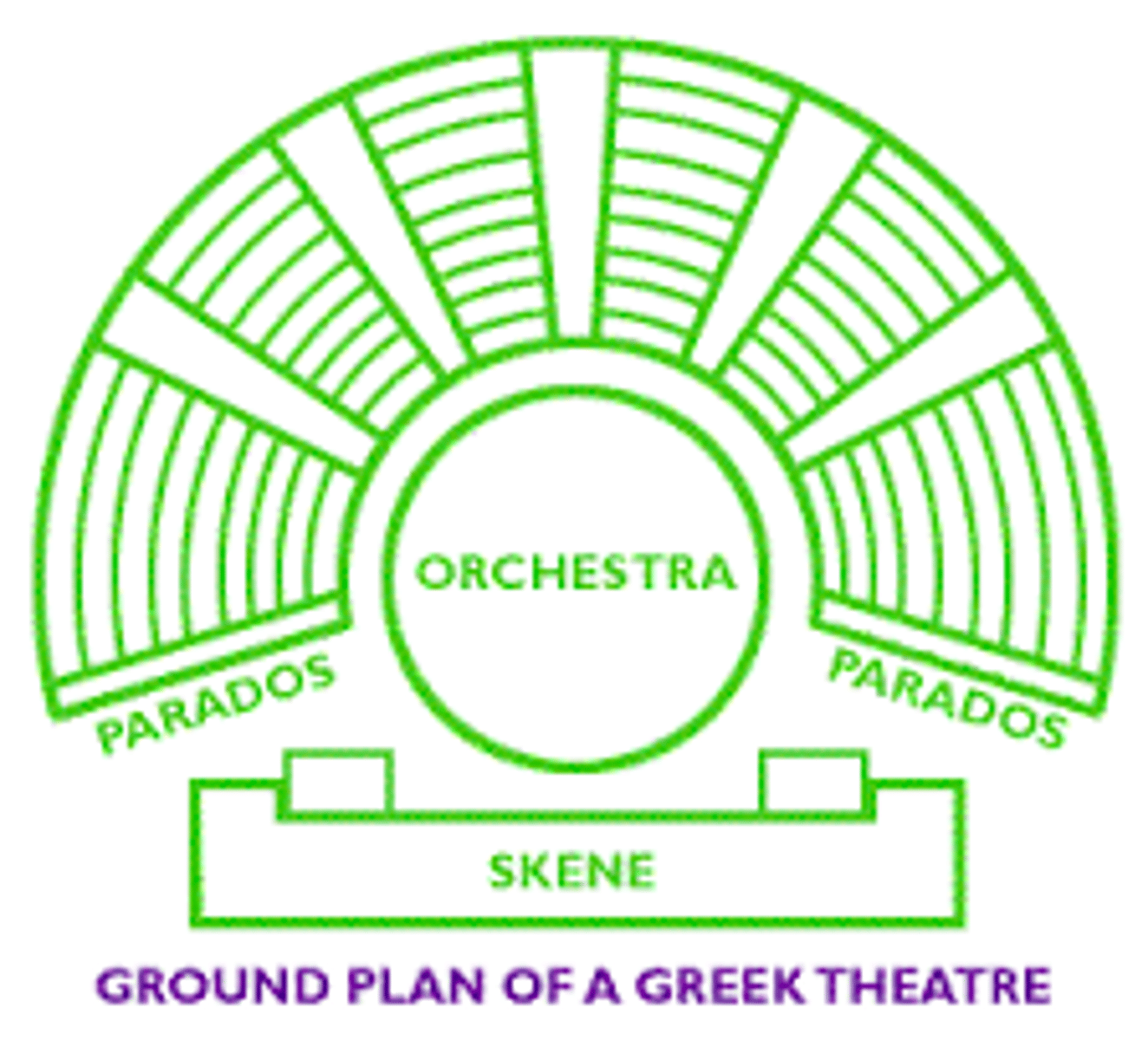
cavea
the tiered, semicircular seating area in an ancient Roman theater
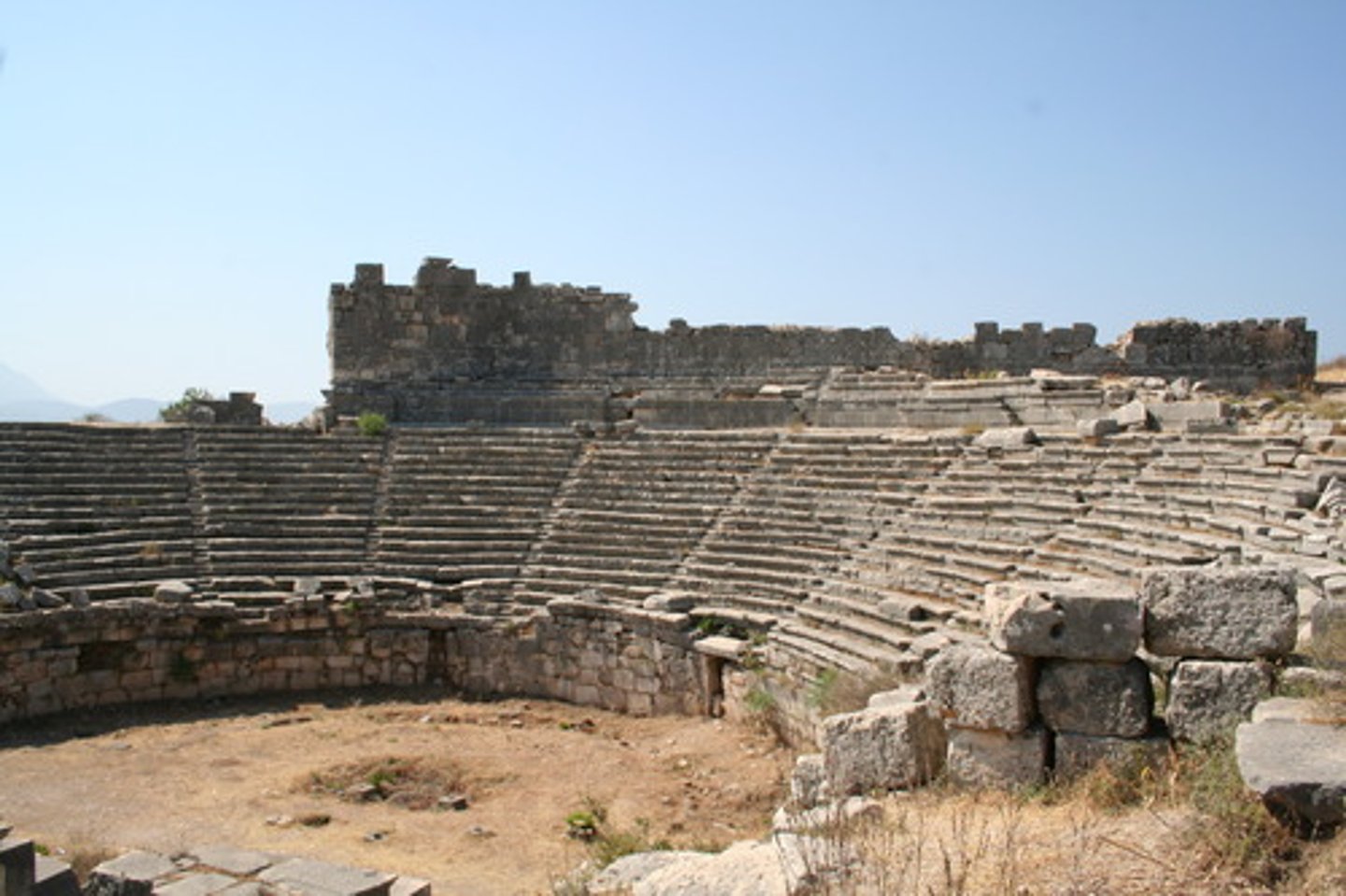

skene
building used as dressing room
agora
The open meeting space or marketplace in an ancient Greek city
Acropolis
the upper town or elevated stronghold of an ancient greek city, containing its chief temples

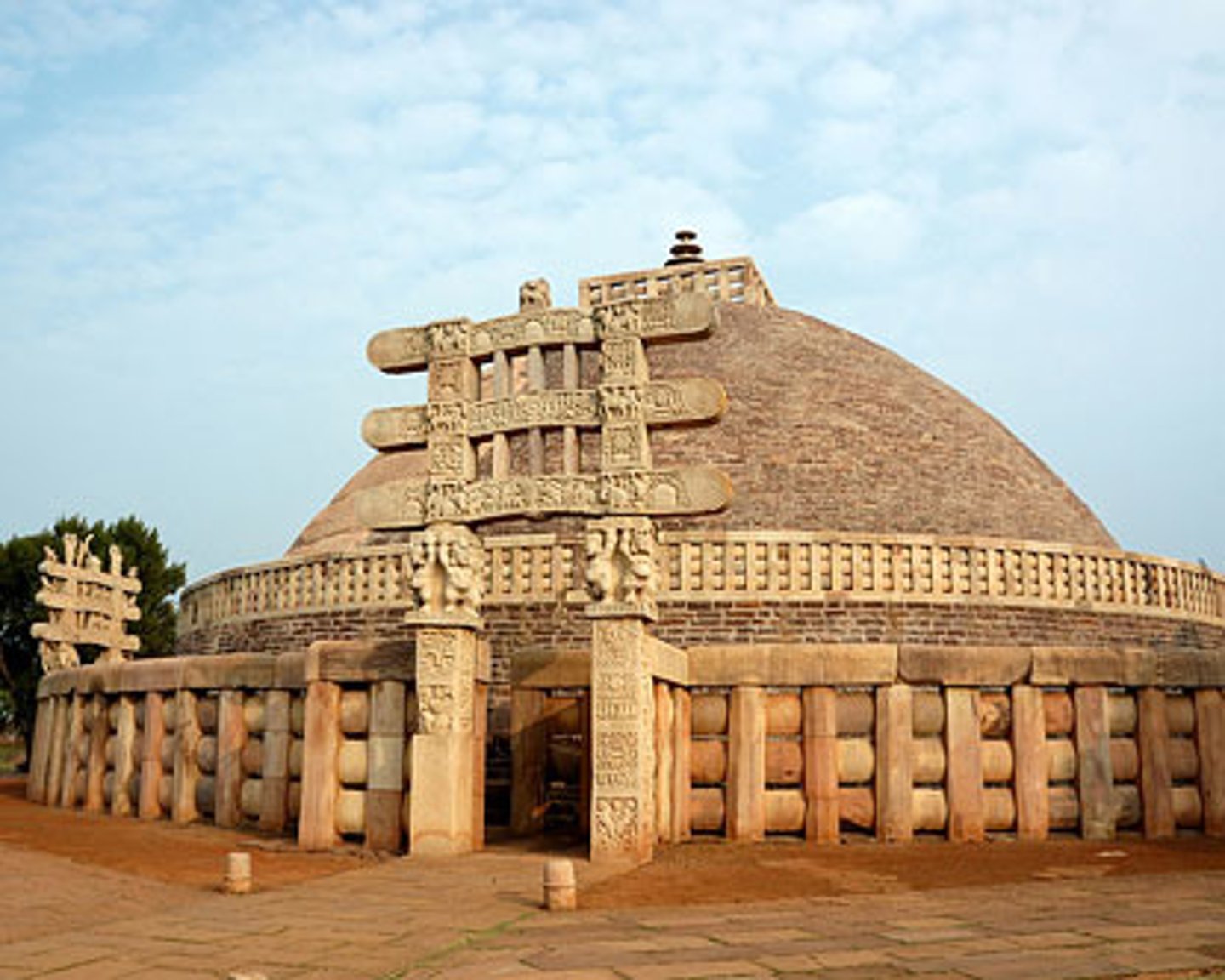
mauryan
(321-185 BCE) This was the first centralized empire of India whose founder was Chandra gupta Maurya.
ashoka
265-238 BCE. Leader of the Mauryan dynasty of India who conquered most of India but eventually gave up violence and converted to Buddhism. built stupas/stambhas to spread dharma. chandra gupta's grandson
buddhist
one who follows the teachings of Buddha
dharma
a code of nonviolence that promoted the tolerance of all religions and opinions, obedience and respect for elders and priests, generosity to others, and fair treatment of slaves
stupa
A Buddhist memorial mound that enshrines relics or marks a sacred site

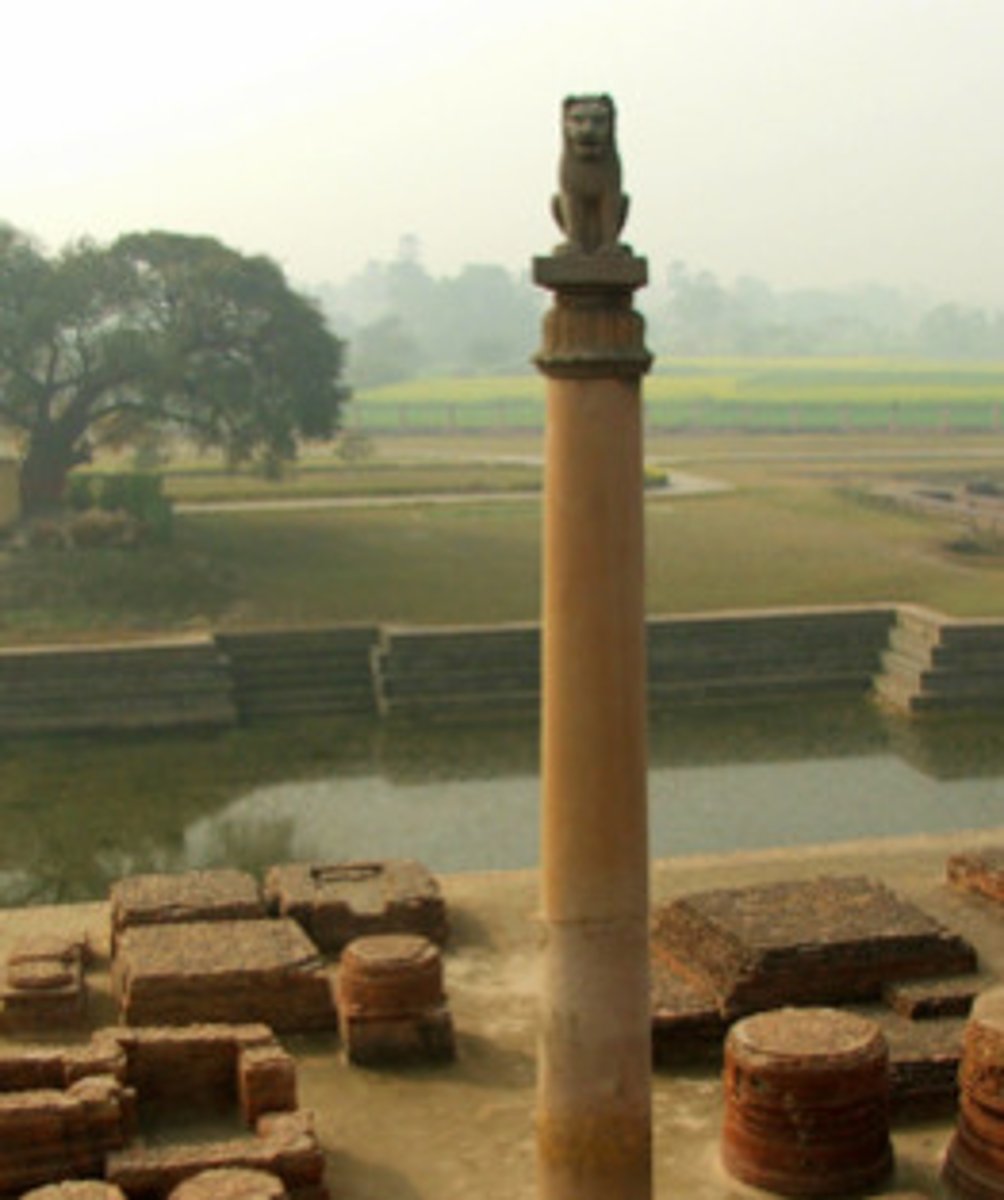
Ashoka Pillar
The pillars of Ashoka are a series of columns dispersed throughout the Indian subcontinent, erected or at least inscribed with edicts by the Mauryan king Ashoka during his reign in the 3rd century BC.

axis mundi
a monumental building marking the center of the world for Neolithic cultures
gupta
320-550 CE The decentralized empire that emerged after the Mauryan Empire, and whose founder is Chandra Gupta.
hindu
A religion and philosophy developed in ancient India, characterized by a belief in reincarnation and a supreme being who takes many forms
Roman Empire
753 BCE - 476 CE Conquered entire Mediterranean coast and most of Europe. Ruled by an emperor. Eventually oversaw the rise and spread of Christianity.
barrel vault
a long, rounded vault
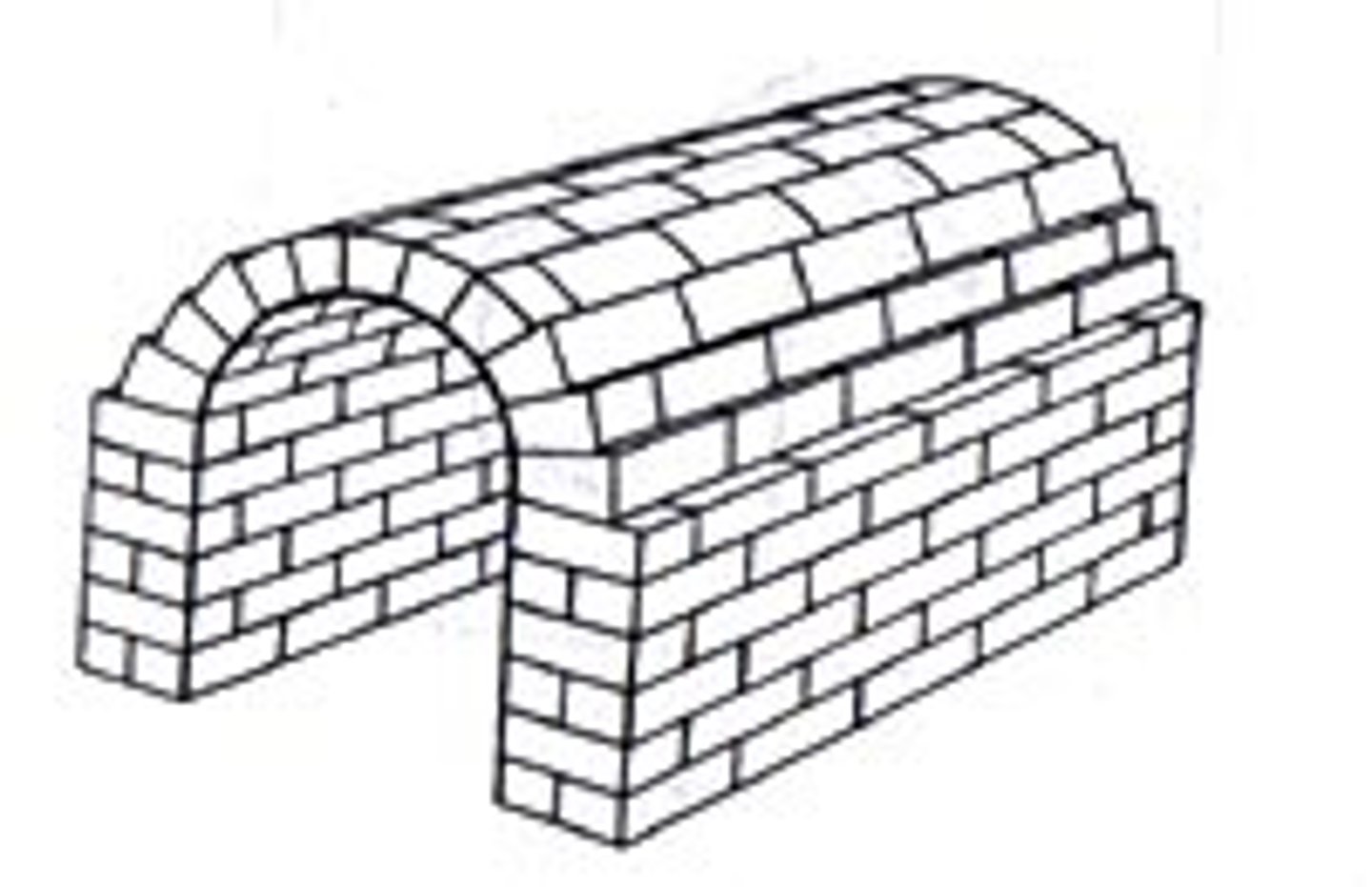
groin vault
the cross-vault spanning a bay of a Gothic structure
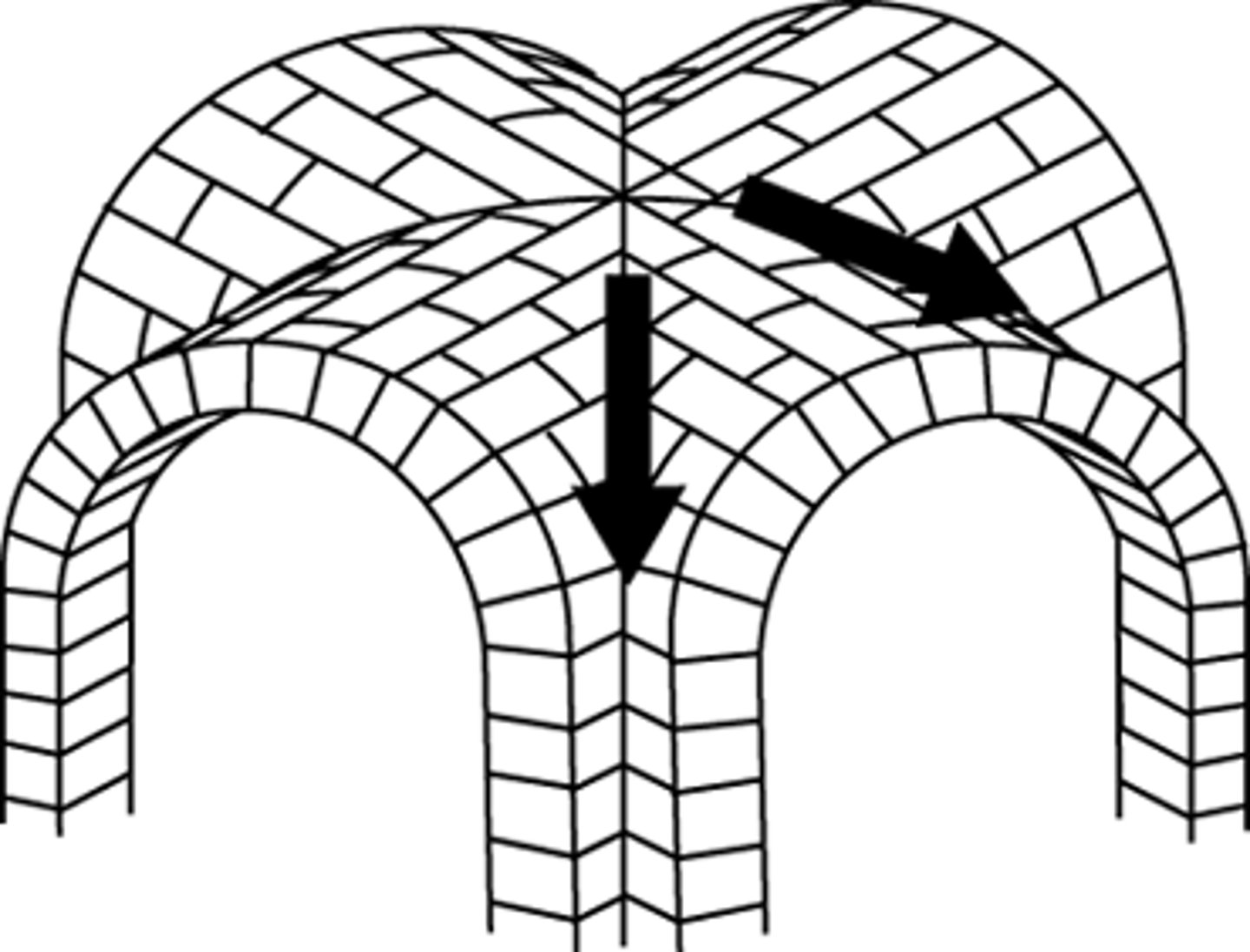
concrete
artificial stone made of a mixture of cement, water, gravel, and sand
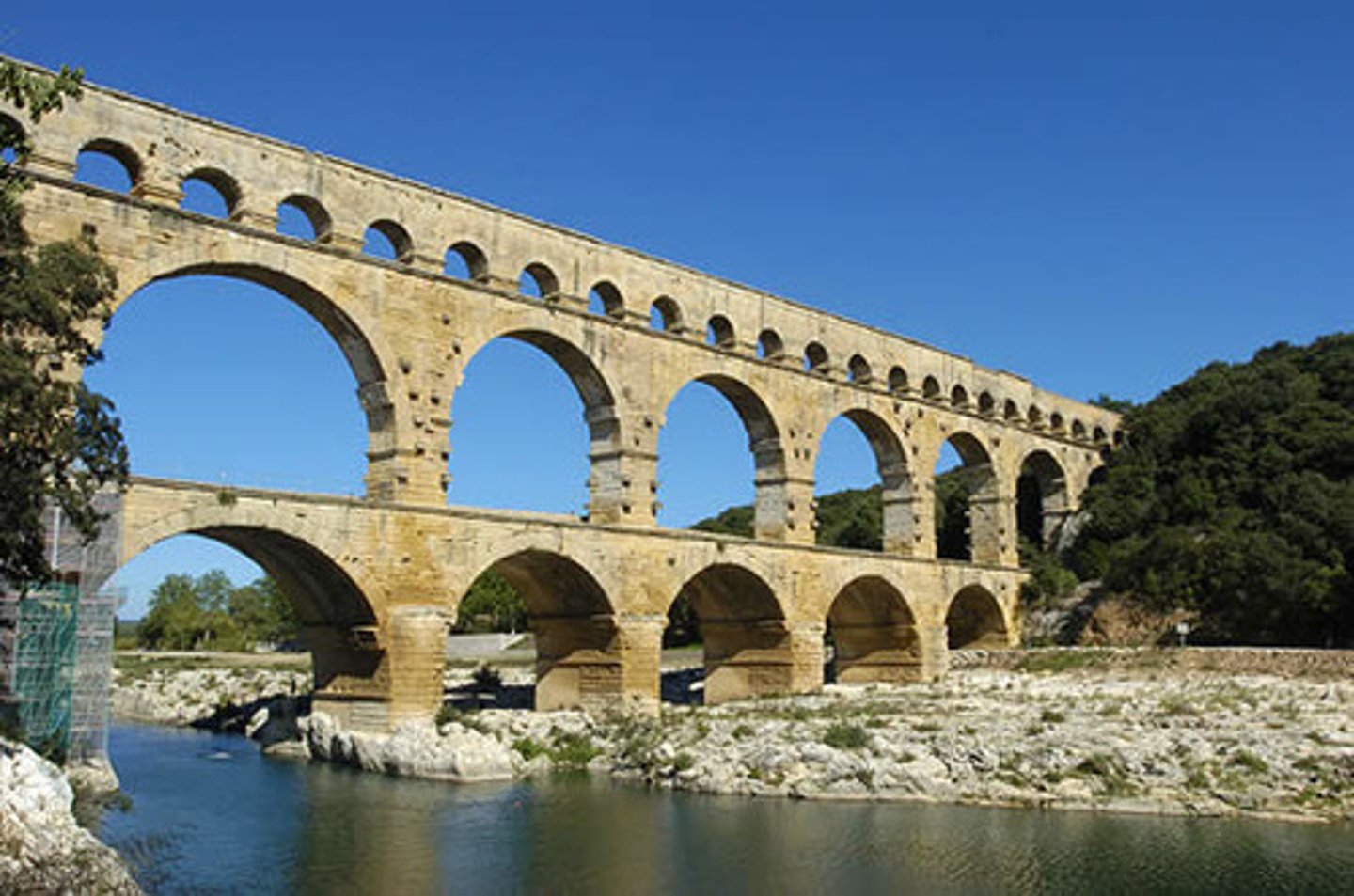
Aqueduct
an artificial channel for water, sometimes underground but often elevated on arches

Basilica
an ancient Roman meeting hall, oblong in plan, with a high central space lit by clerestory windows
the form of an early christian church, oblong, with high, clerestoried nave ending in an apse, flanked by two lower aisles and covered with timber oof

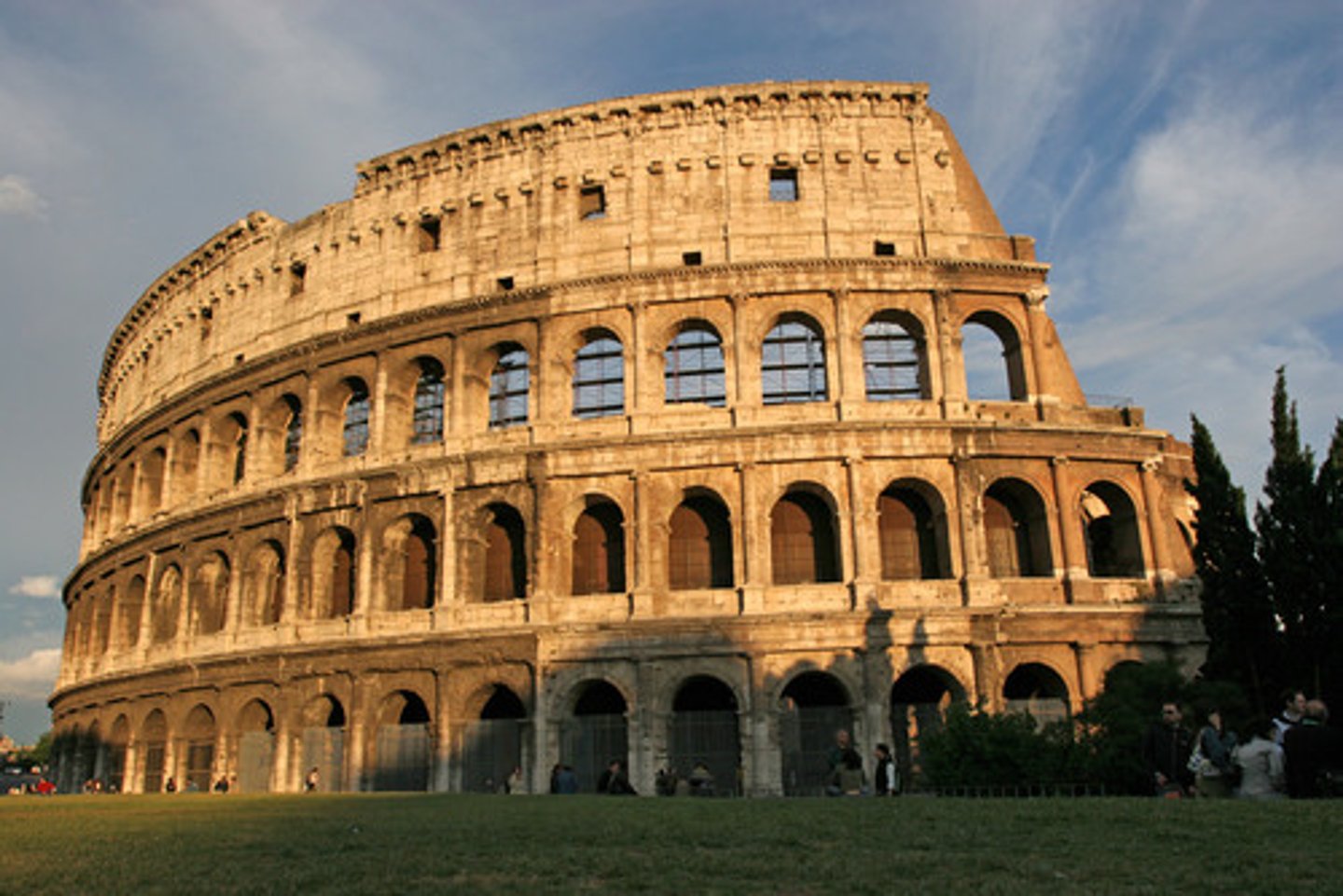
amphitheater
a round, semicircular, or oval outdoor arena surrounded by rising tiers of seats

annular barrel vault
Vault designed in the shape of a ring.

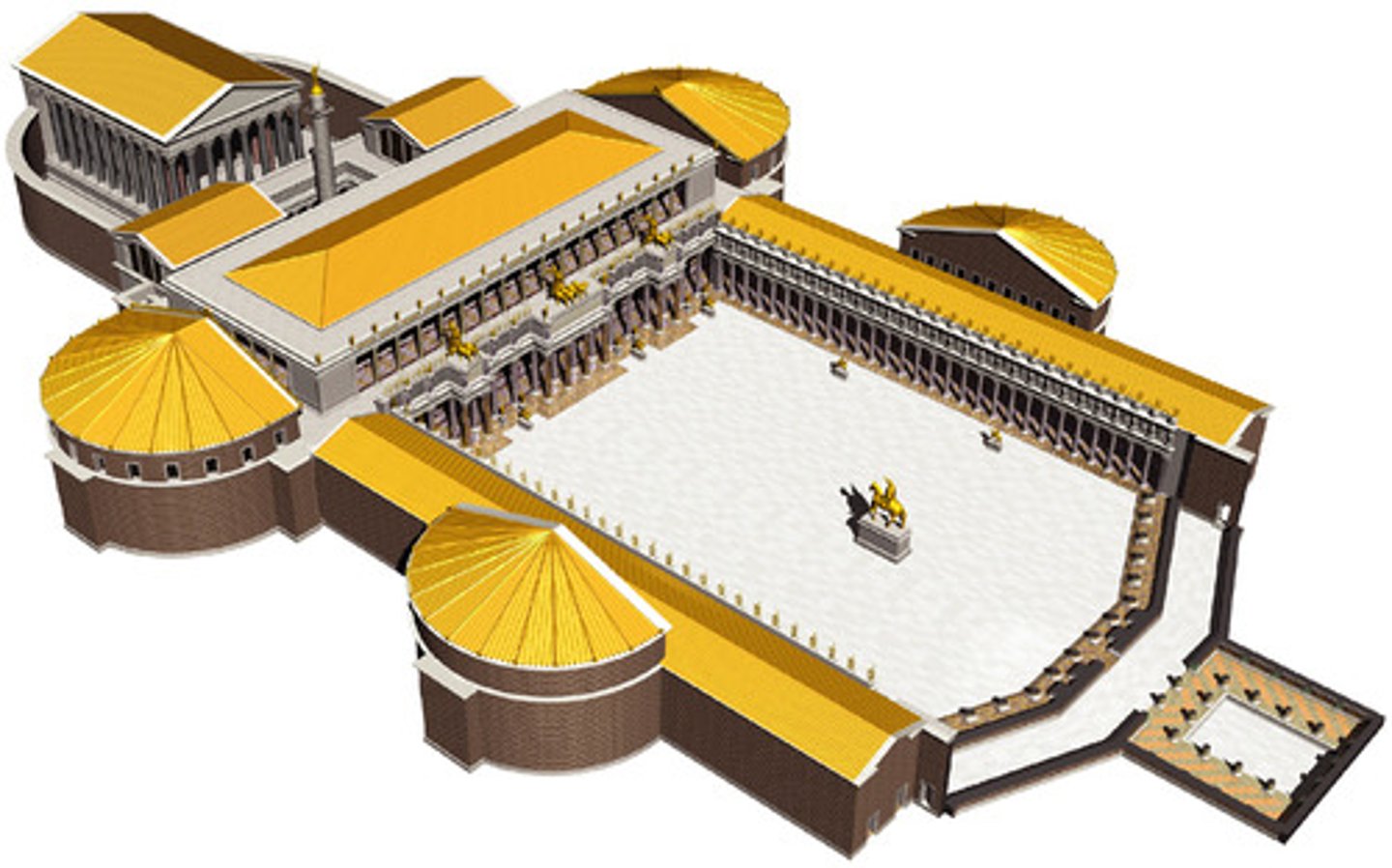
Roman Forum
An area for people to gather to hear speeches, shop, worship at temples, and socialize
heart of public life
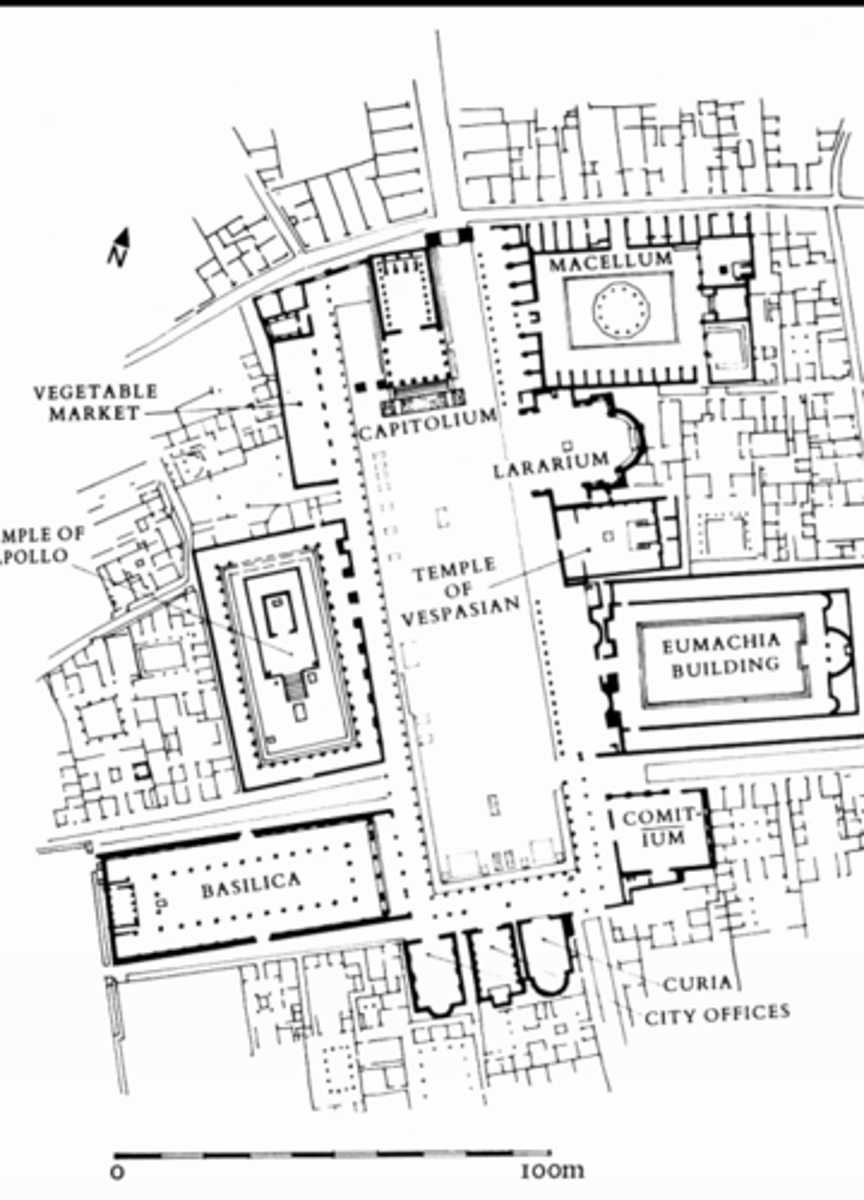
Imperial Fora
built by various emperors for various purposes , monumental public spaces, sometimes commemorated military victories, members of the new dynasty
-not a part of the Roman Forum
-Julius Caesar initiated the building

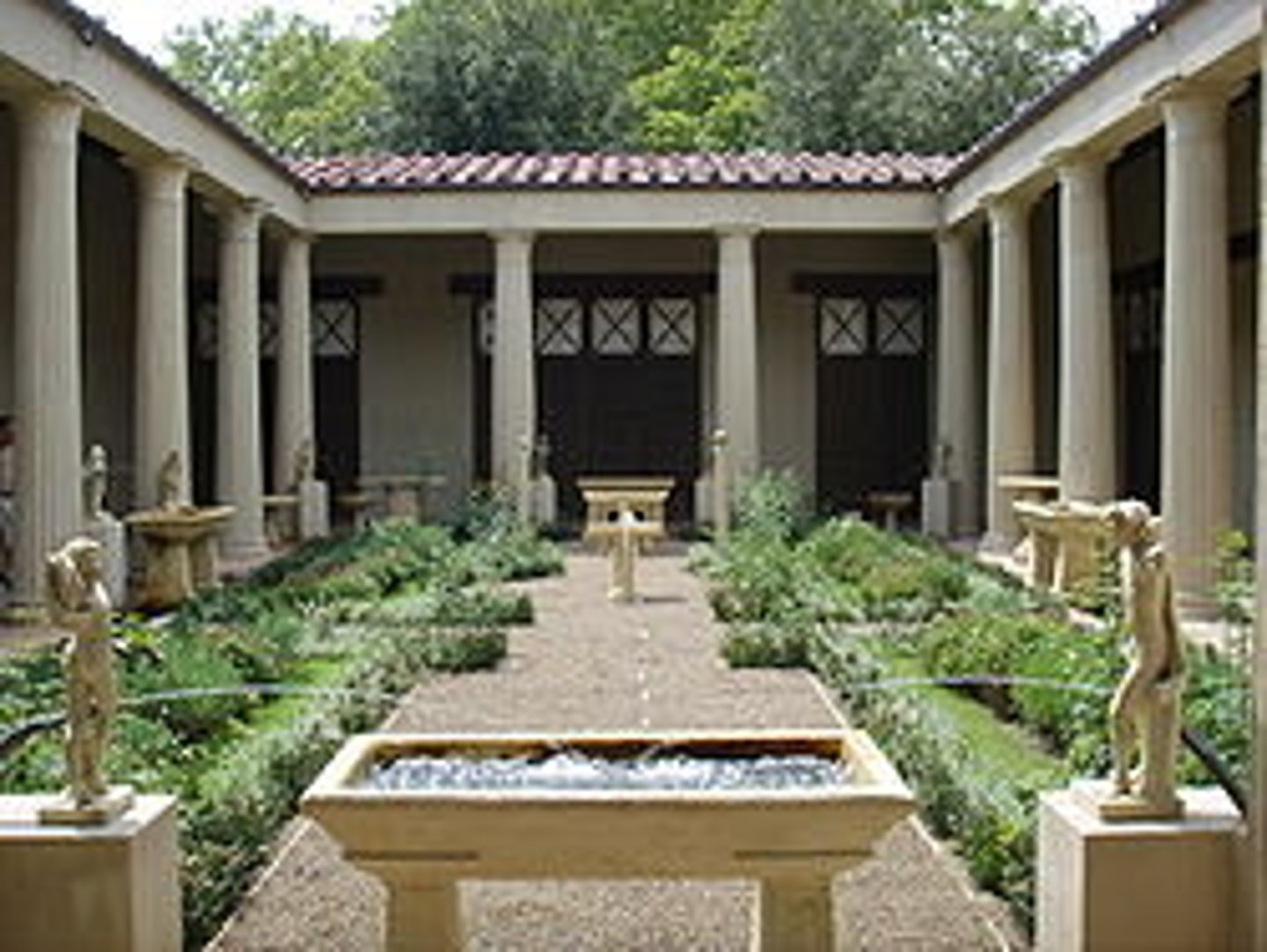
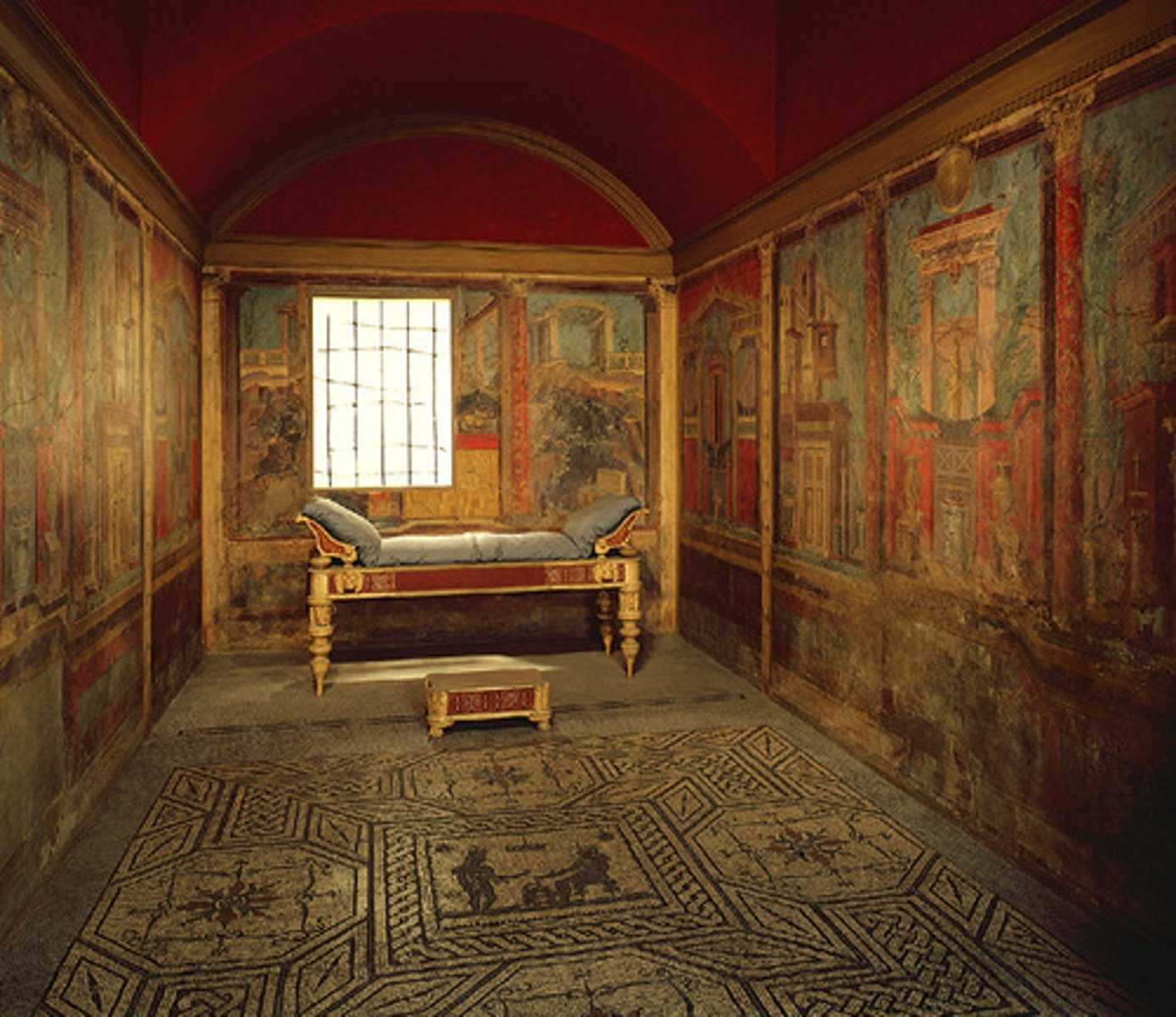
domus
an ancient roman house for wealthy citizens, usually served by an atrium
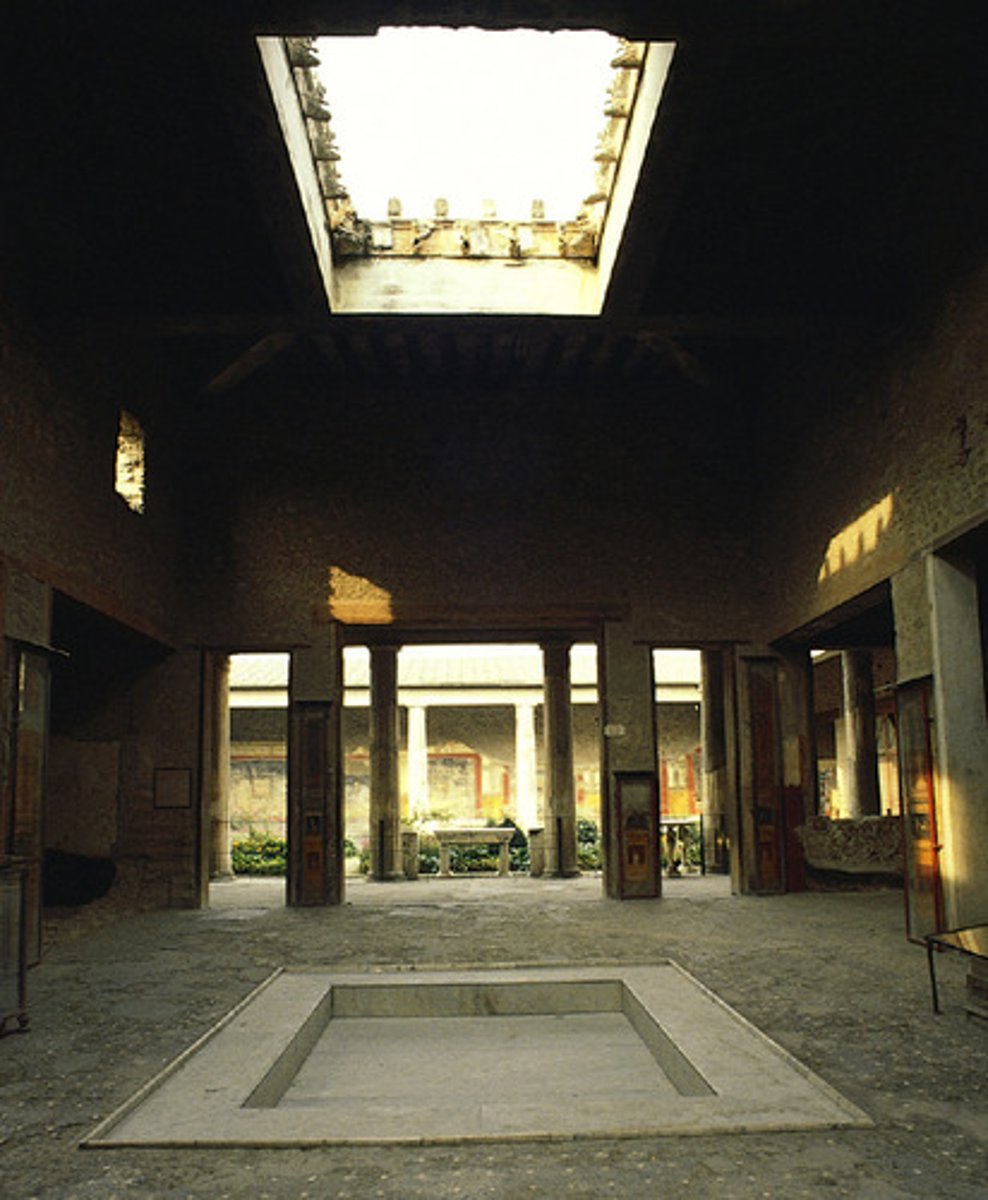

atrium
the main inner court of a roman house, with an open roof and a central basin to catch rainwater
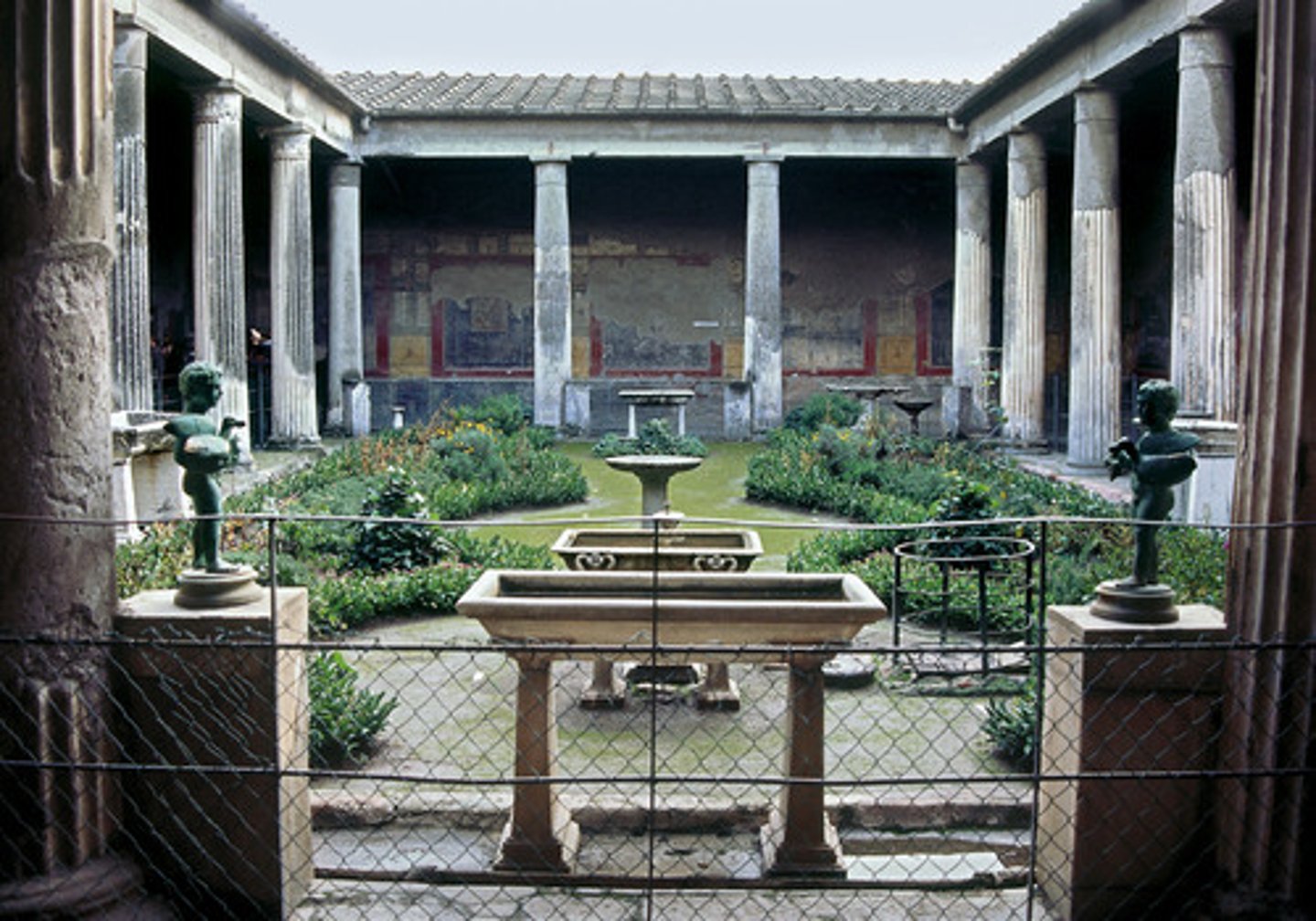

cubiculum
private room in a domus

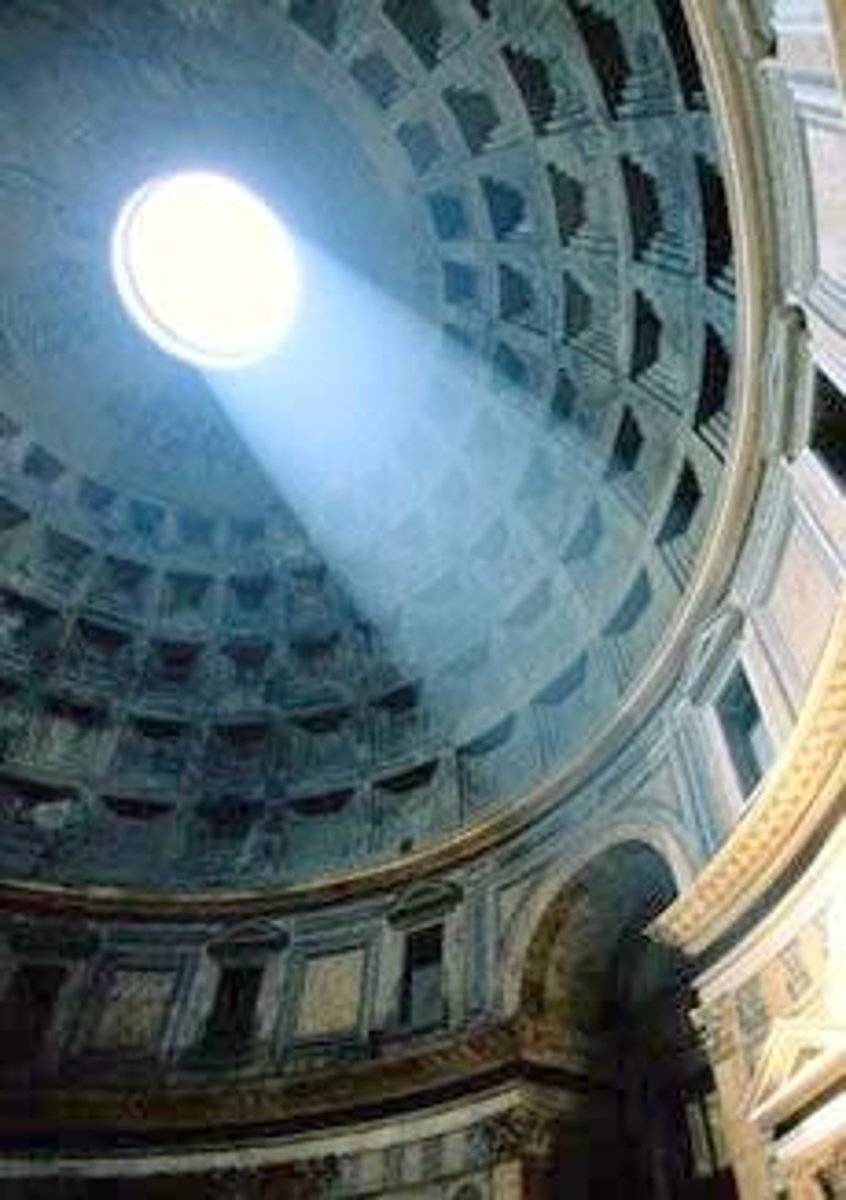
oculus
a round window, usually at the apex of a dome

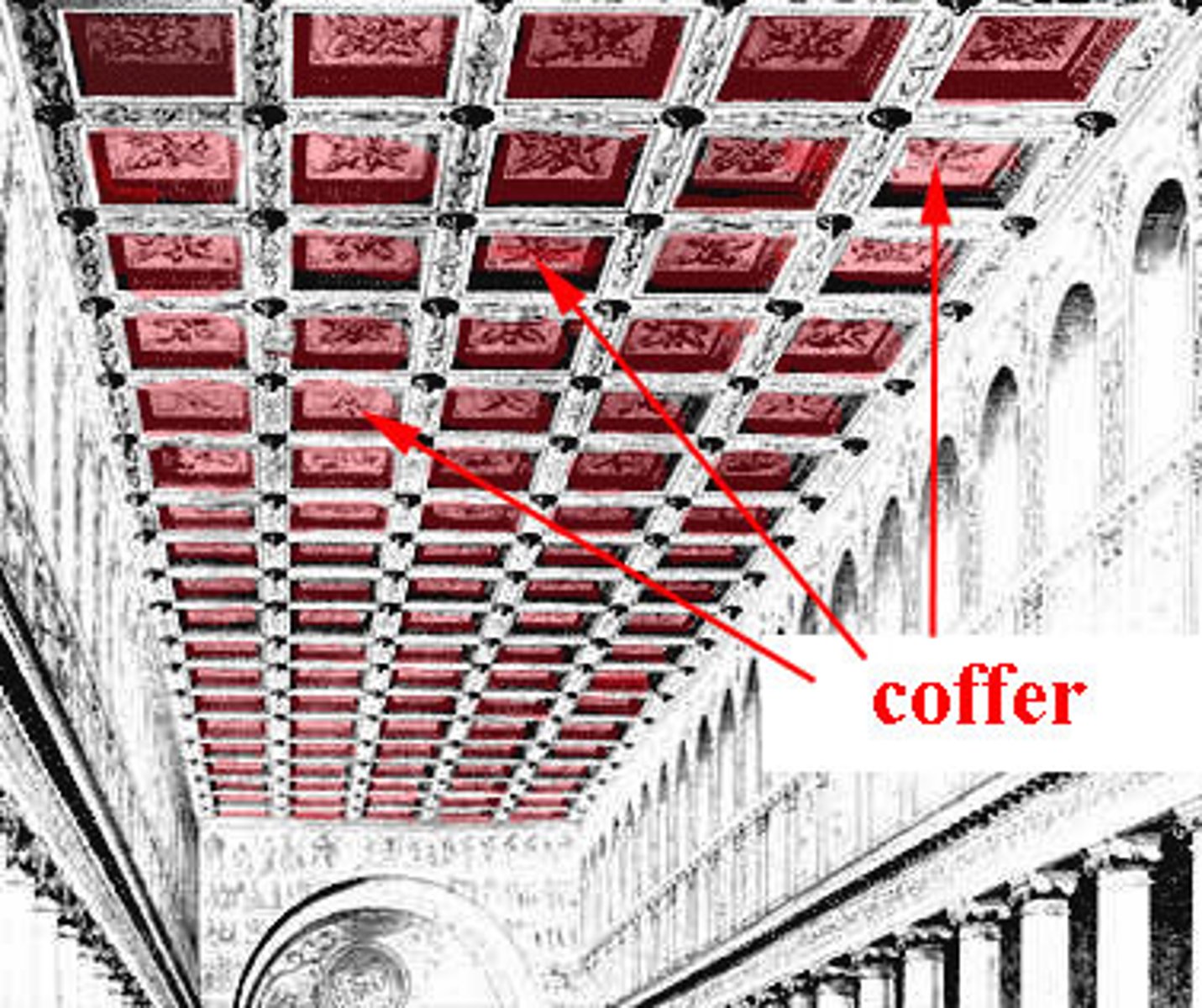
coffer
a square or polygonal decorative panel embossed into a ceiling or an arch
trajan
98-117 CE Leader of the Roman Empire who disguised it as a republic, and under who the Roman Empire came to be at its greatest extent.
nero
54-68 CE. First Roman emperor to persecute Christians
Flavian Dynasty
69-96 CE
- Vespasian, Titus, Domitian
Helps rebuild Rome after the Civil War, including a Temple to Peace and the Colosseum
hadrian
"Romanized"and organized the empire- built bridges, roads, and aqueducts, ruled during the height of the Pax Romana, Built Hadrians Wall across Britain, strengthened borders
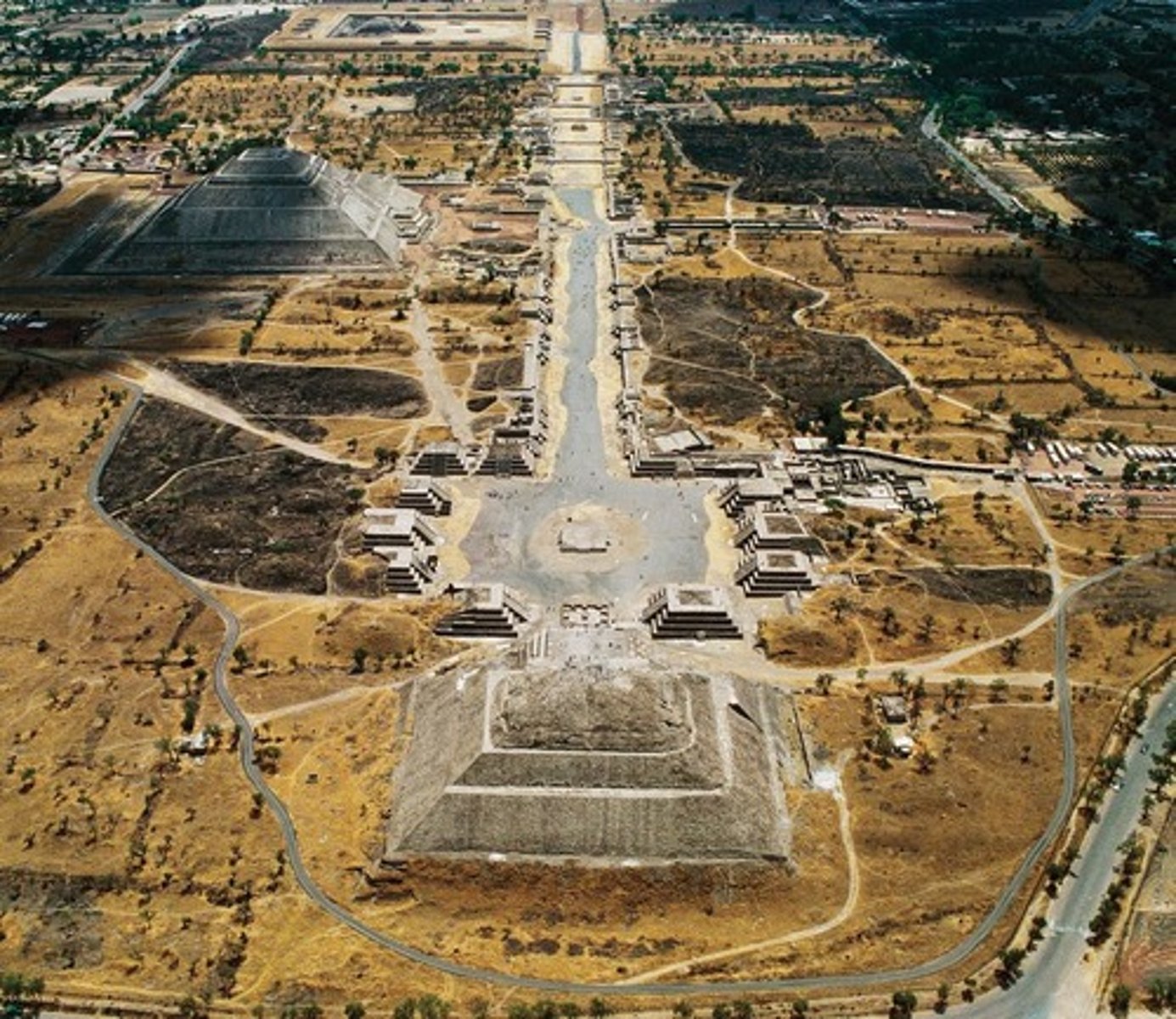
Teotihuacán
Translates to mean "the home of the gods." The first major city in Mesoamerica. Falls in 800 AD.
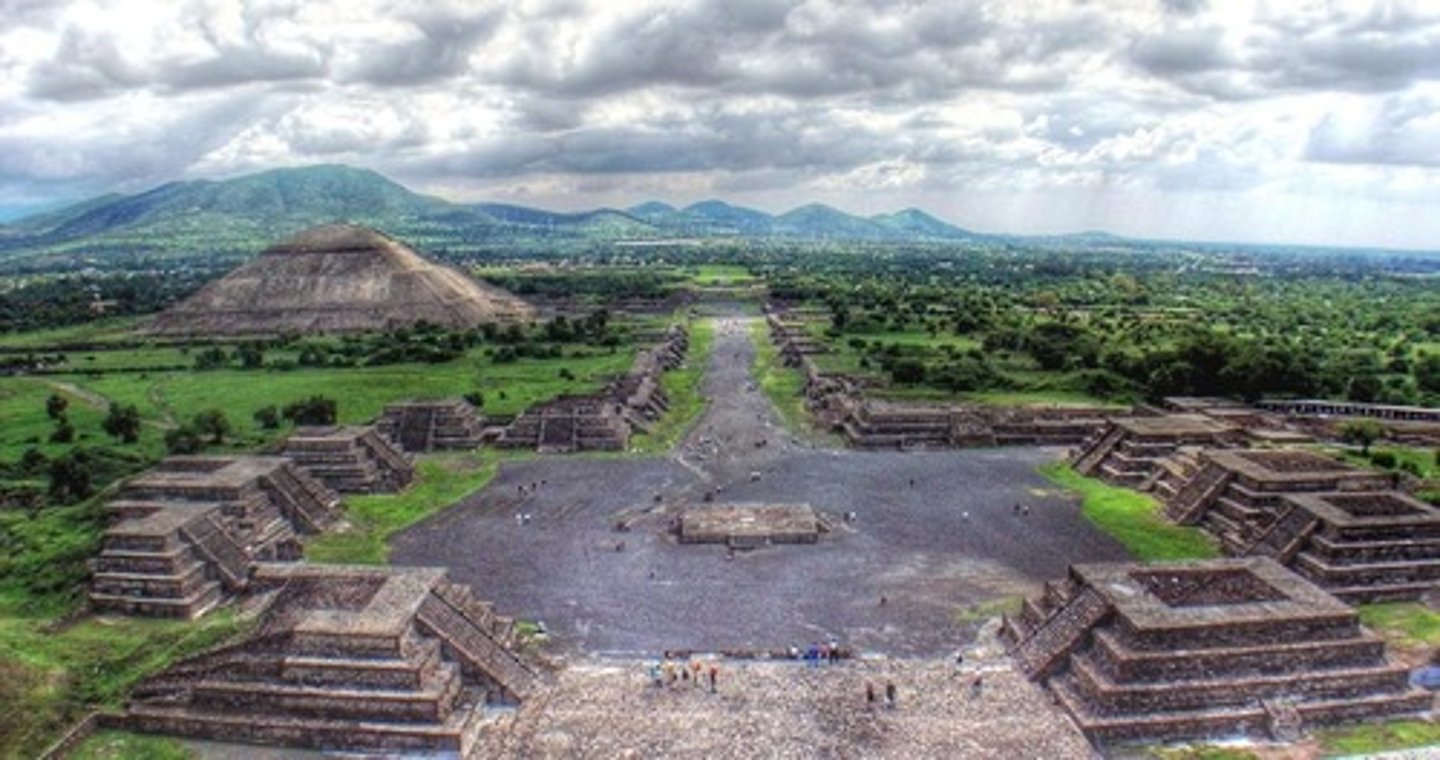

Axis mundi
a monumental building marking the center of the world and believed to connect the heavens and the earth

talud-tablero style/construction
The alternation of sloping (talud) and vertical (tablero) rubble layers, characteristic of Teotihuacan architecture in Mesoamerica.
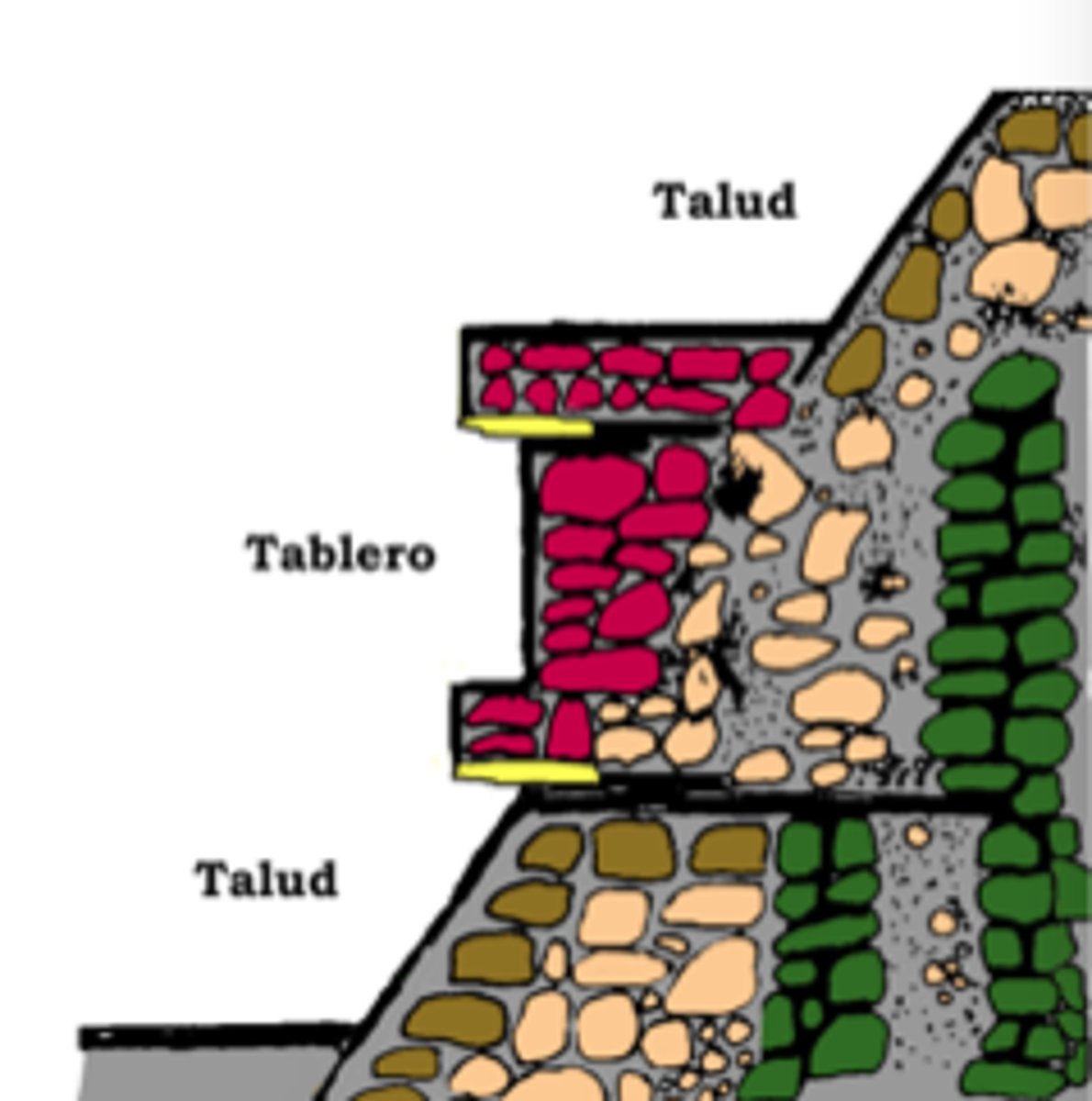
Axial alignment
arrangement of structural features along an axis (straight line that indicates the center of symmetry)
Orthogonal planning
type of city plan in which streets run at right angles to each other, forming a grid.

mayan
1500 BCE-300 CE
A Mesoamerican civilization of Central America and southern Mexico. Achievements include mathematics, architecture, and a 365 day a year calendar.
toltec
a member of an American Indian people that flourished in Mexico before the Aztecs.
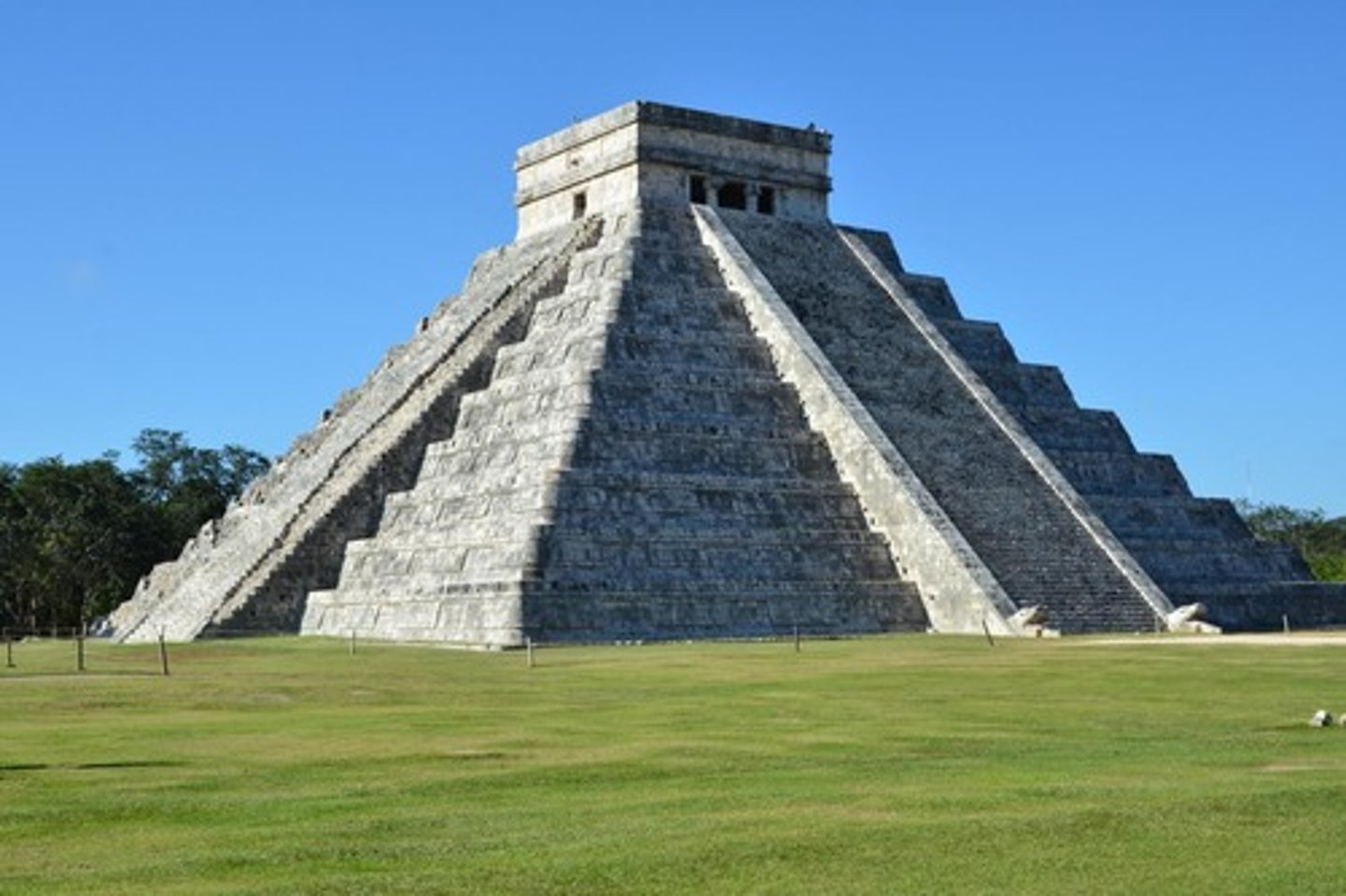
Chichén-Itzá
ca 890
very wealthy, controlled trade of obsidean and salt, attracted migrants from cities including Teotihuacán

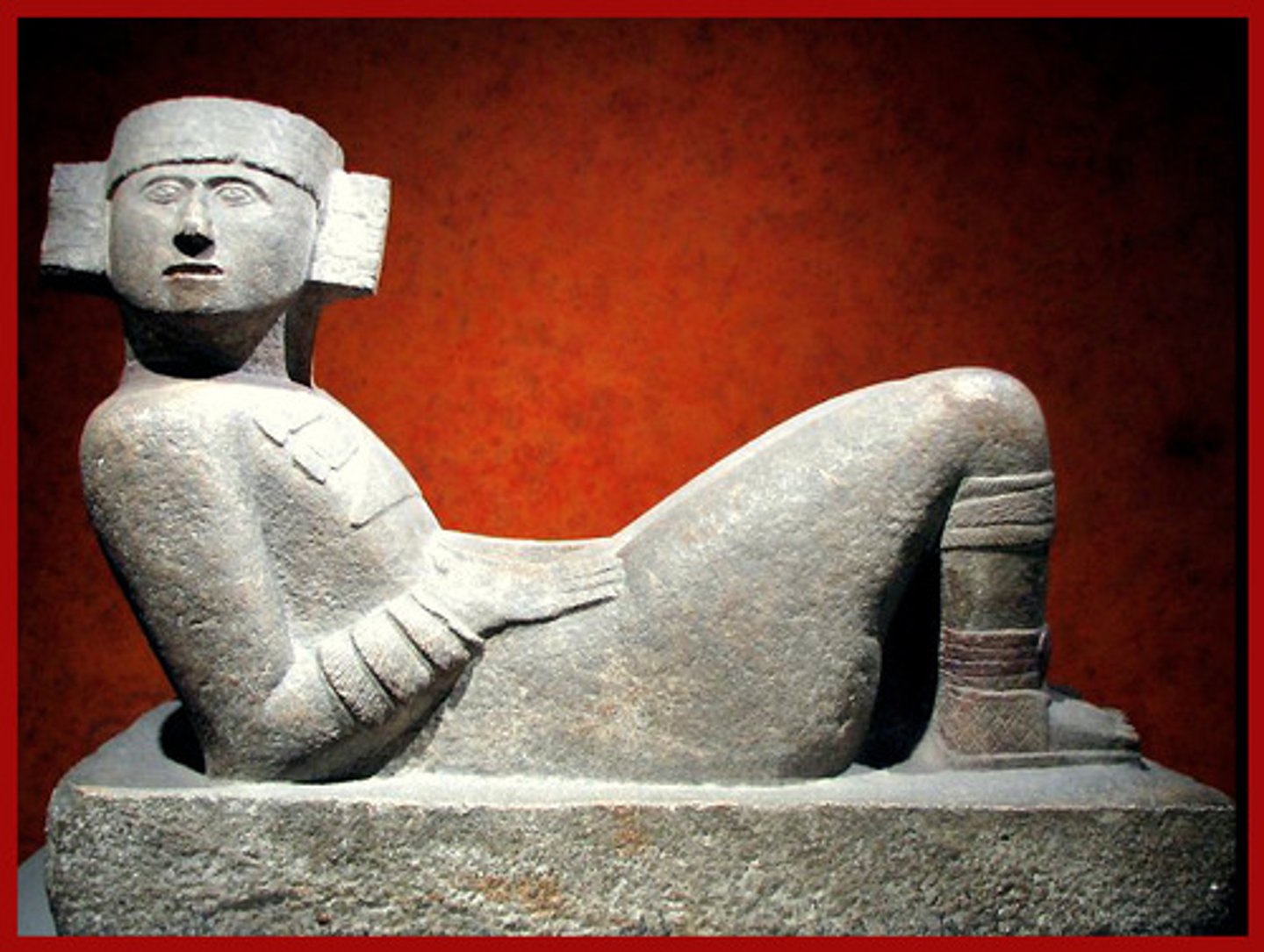
Chacmool
a Mayan figure that is half-sitting and half-lying on his back
human shaped altar where sacrifices took place

Zhou Dynasty
1100-256 BCE
the longest lasting Chinese dynasty, during which the use of iron was introduced.