DSA10 - Benign Leukocytes, Lymph Nodes Disorders and Review of the Spleen and Thymus
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
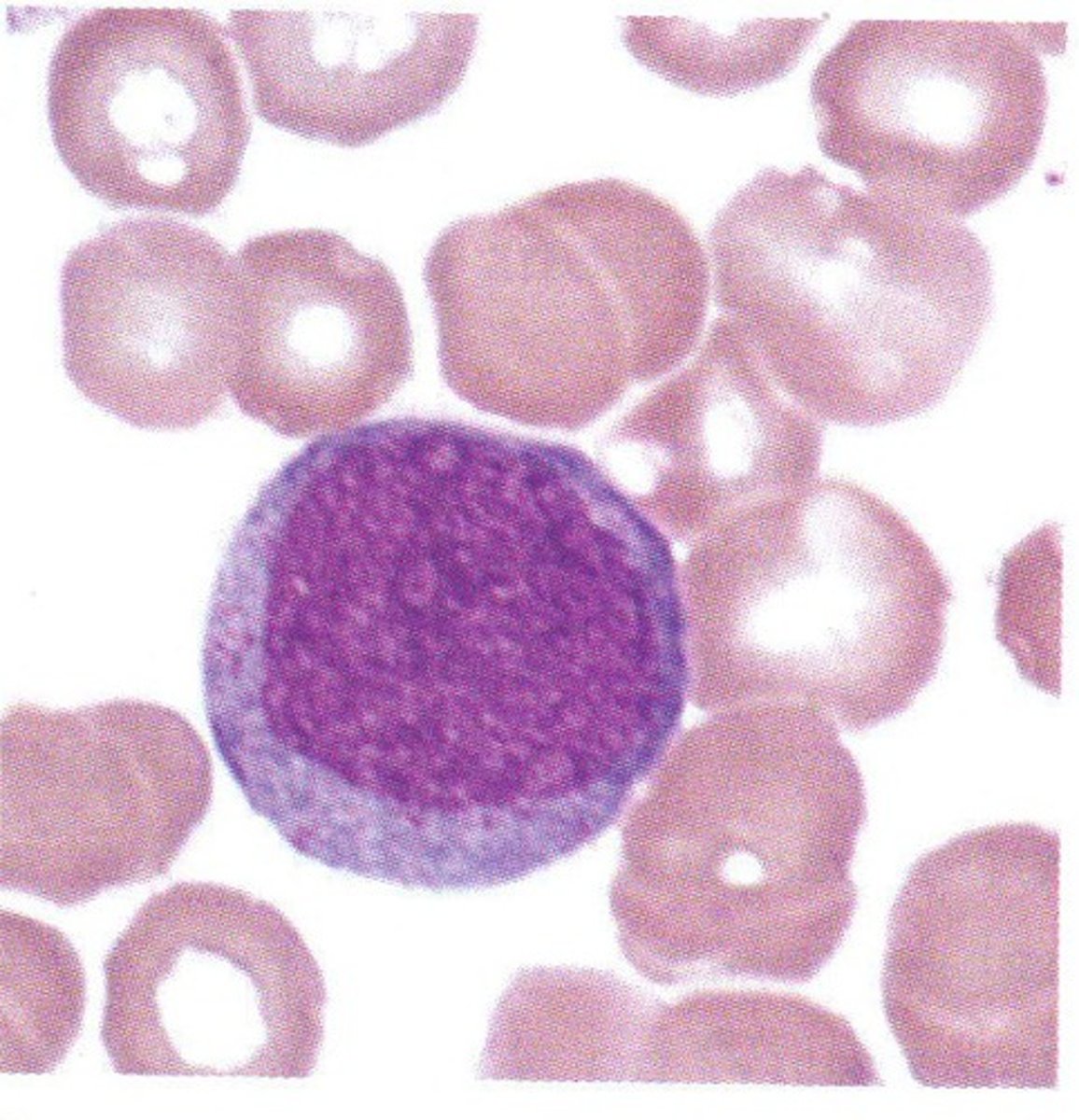
Myeloblast
Prominent Nucleoli (round to oval)
Diffuse immature chromatin (no clumping)
Define Stage of Granulopoiesis
True
T/F - Blasts should NOT be seen in peripheral blood
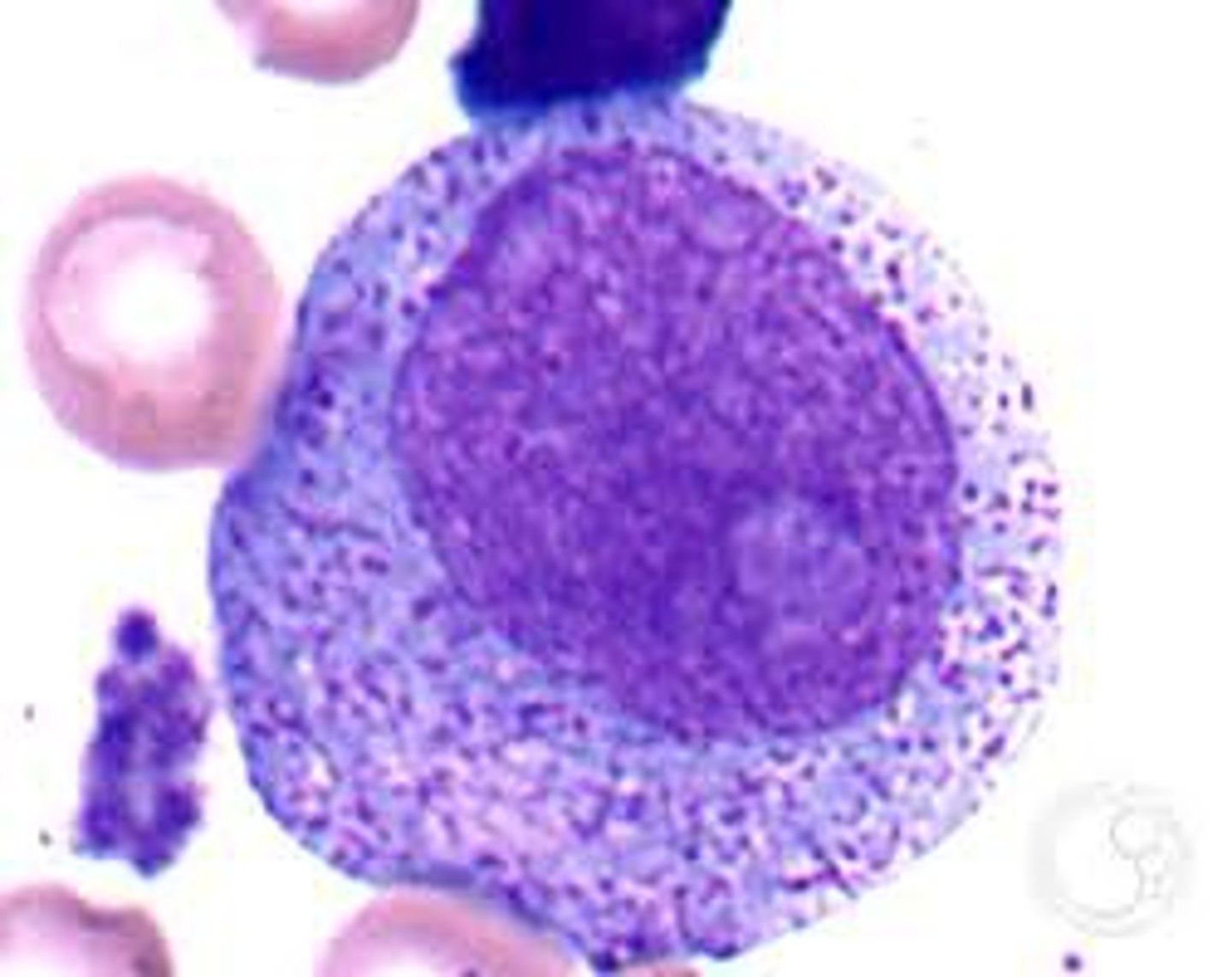
Promyelocyte
Round nucleus
Reddish-blue and fine to slightly condensed chromatin
Large cell
Primary (Azurophilic) granules appear
Define Stage of Granulopoiesis
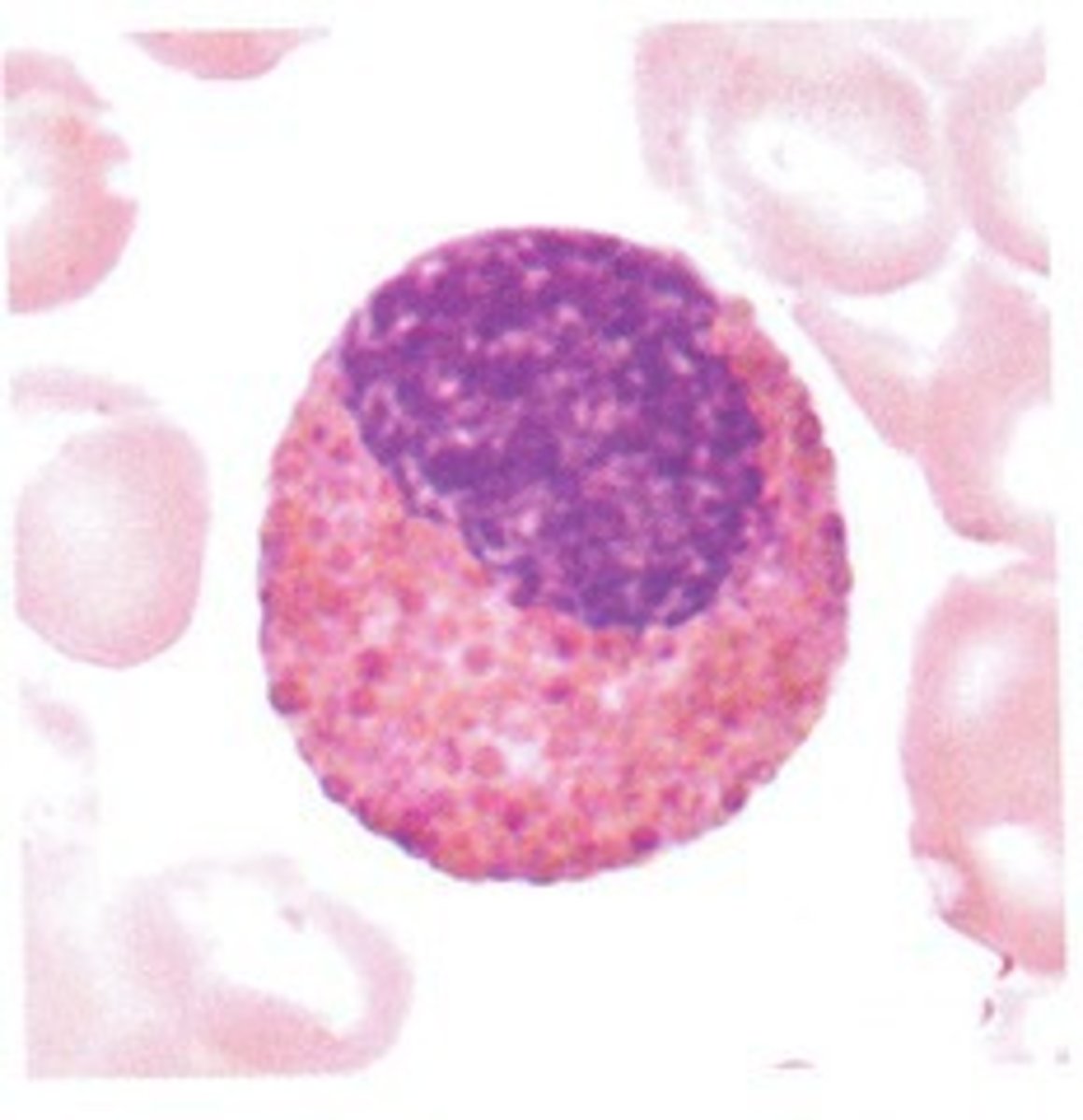
Myelocyte
Oval/Round nucleus
Reddish-blue and slightly granular chromatin
Secondary granules appear (with primary granules still there) = Eosinophilic, Neutrophilic & Basophilic granules
Moderate bluish pink cytoplasm
Define Stage of Granulopoiesis
Metamyelocyte
Kidney-bean shaped nucleus
Define Stage of Granulopoiesis
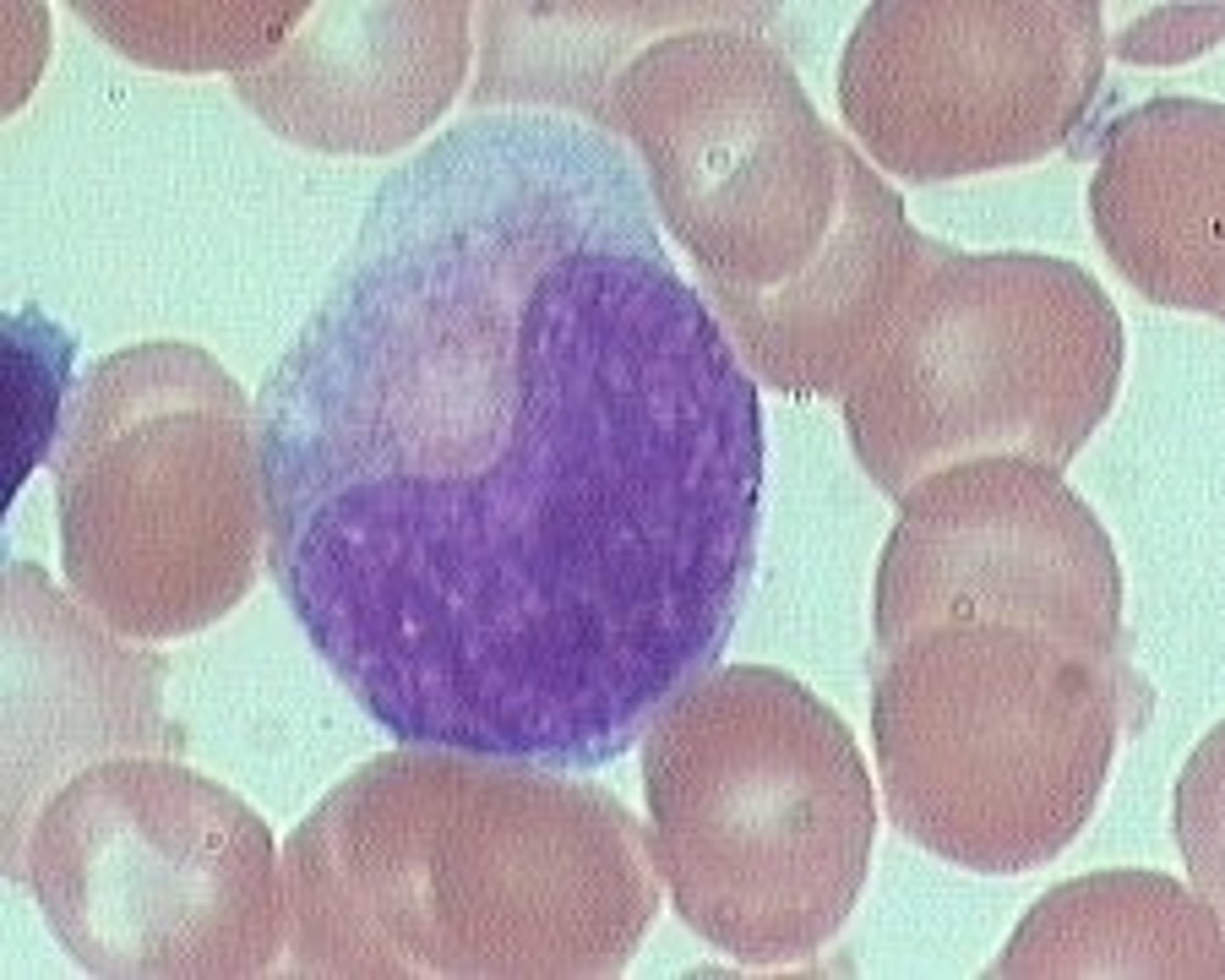
Band-Form Neutrophil
Condensed band-shaped nucleus
Define Stage of Granulopoiesis
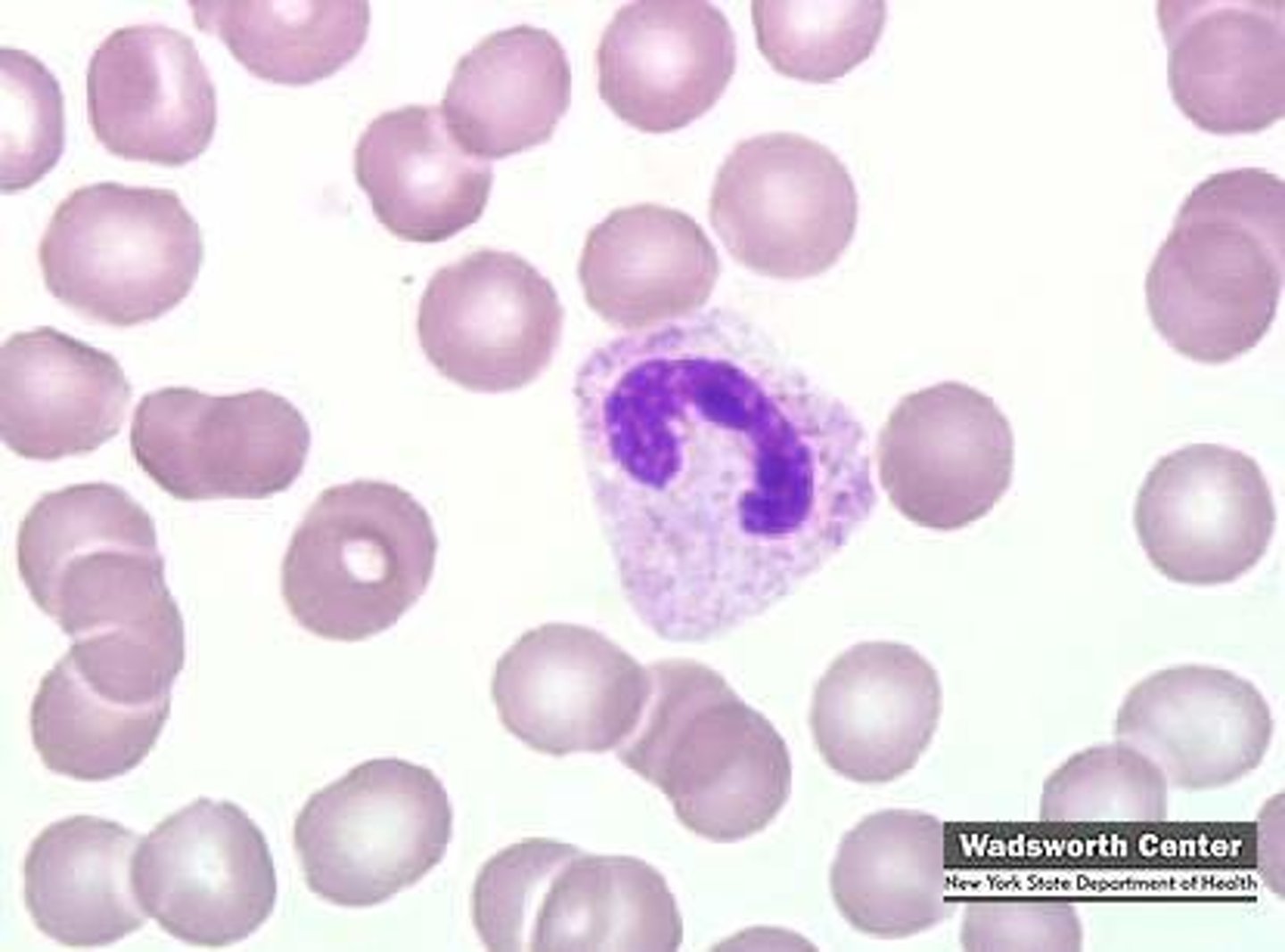
Neutrophil
Condensed, multilobed nucleus
Define Stage of Granulopoiesis
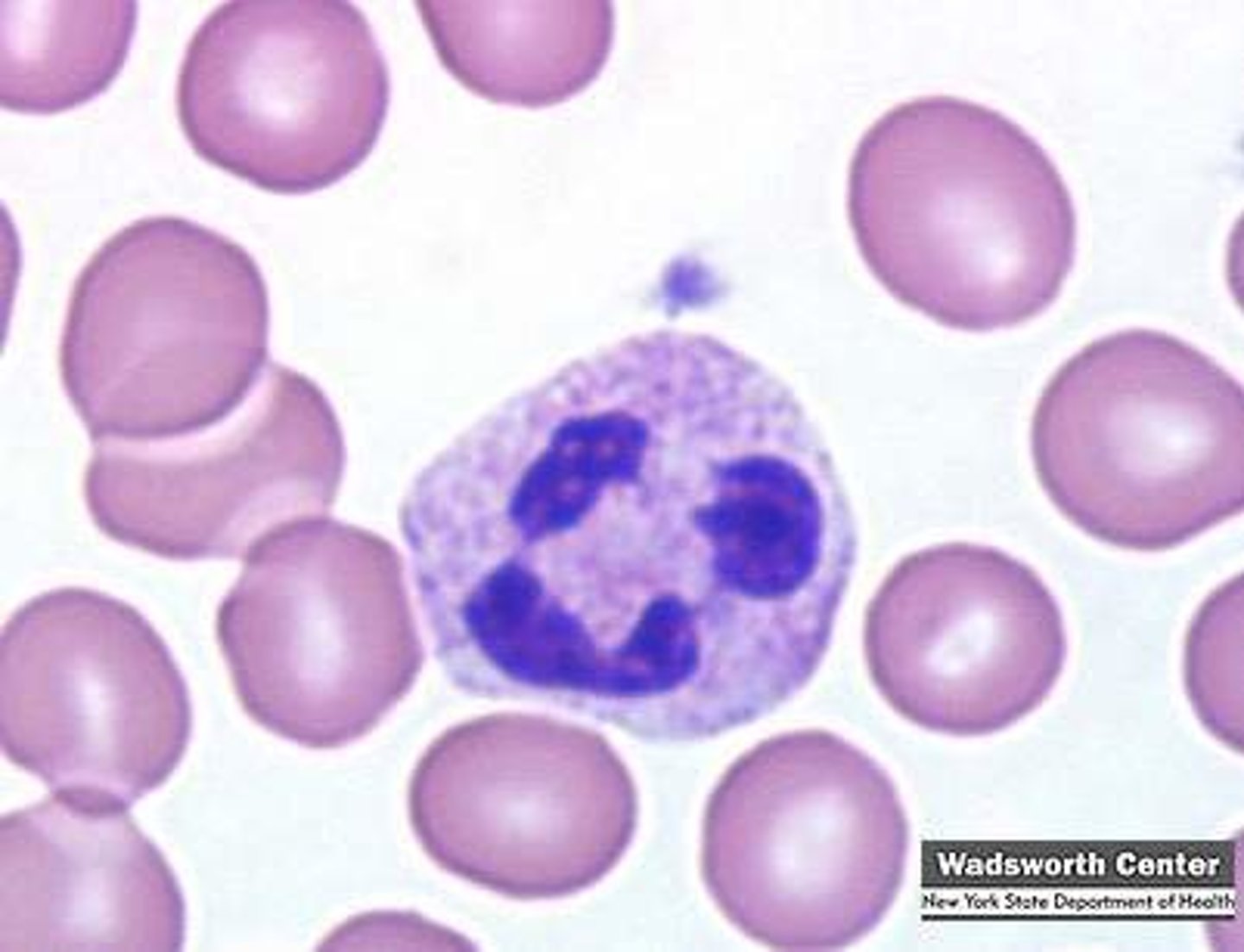
Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC)
What is more important for WBC count - Differential Count or Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC)?
Neutrophilia
Define this WBC Abnormality:
Increase in Neutrophils in peripheral blood
-Hx:
> Infex
> Cancer
> Meds
> Metabolic Disorders
> Myeloid Neoplasms
> Constitutional (rare)
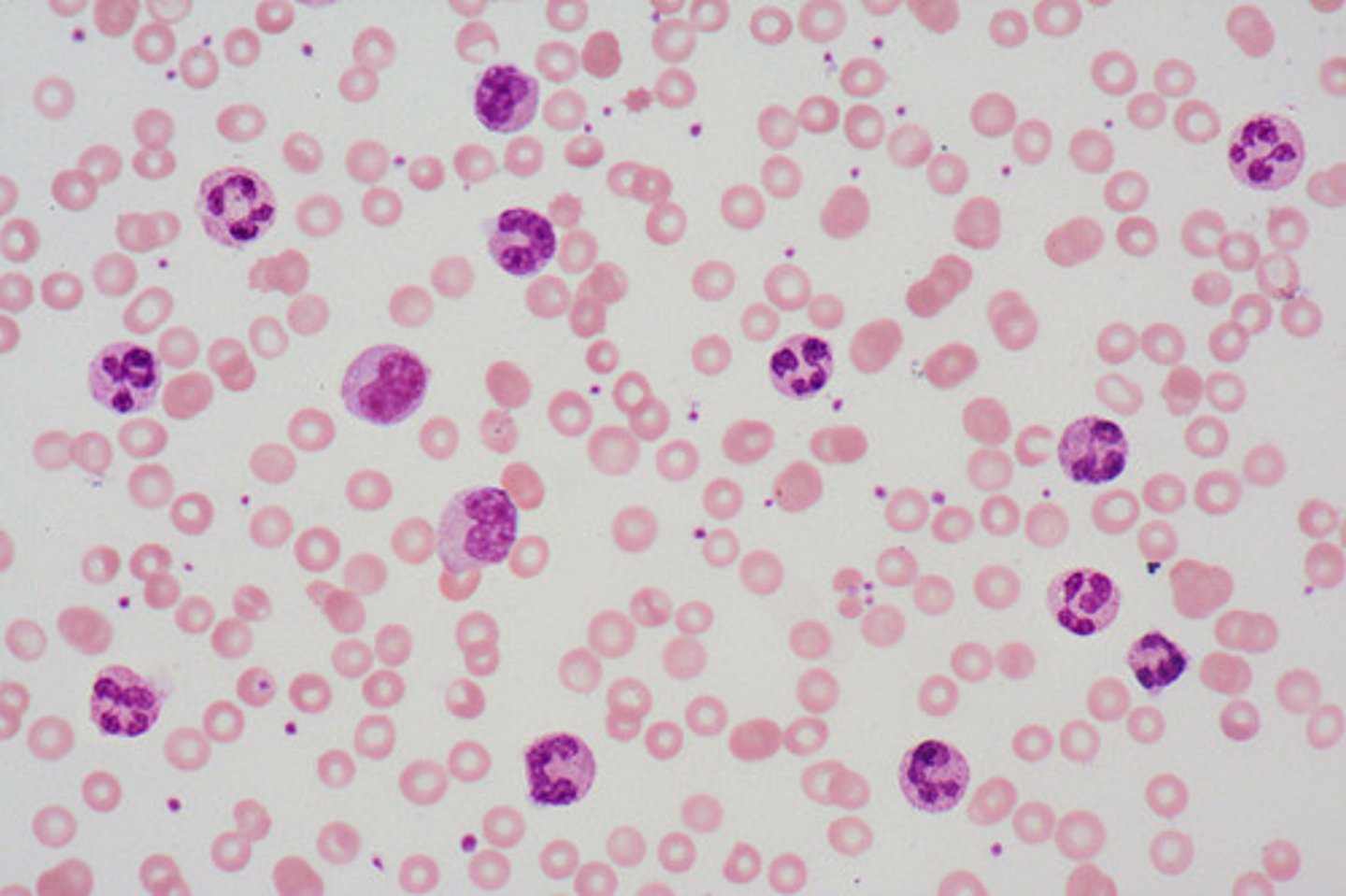
More immature leukocytes (signals infection)
What is the significant of a "left shift" in Differential WBC Count?
Exaggerated leukocytosis usually > 50 x 10⁹/L; Usually includes marked neutrophilia with left shift
Define Leukemoid Reaction
Leukoerythroblastic Reaction
Define WBC Abnormality:
BM microenvironment disrupted by metastatic tumor and/or fibrosis
-Hx: Myelophthisis (BM Disruption)
-Dx:
> Left shift w/ circulating immature granulocytic immune cells
> nRBCs
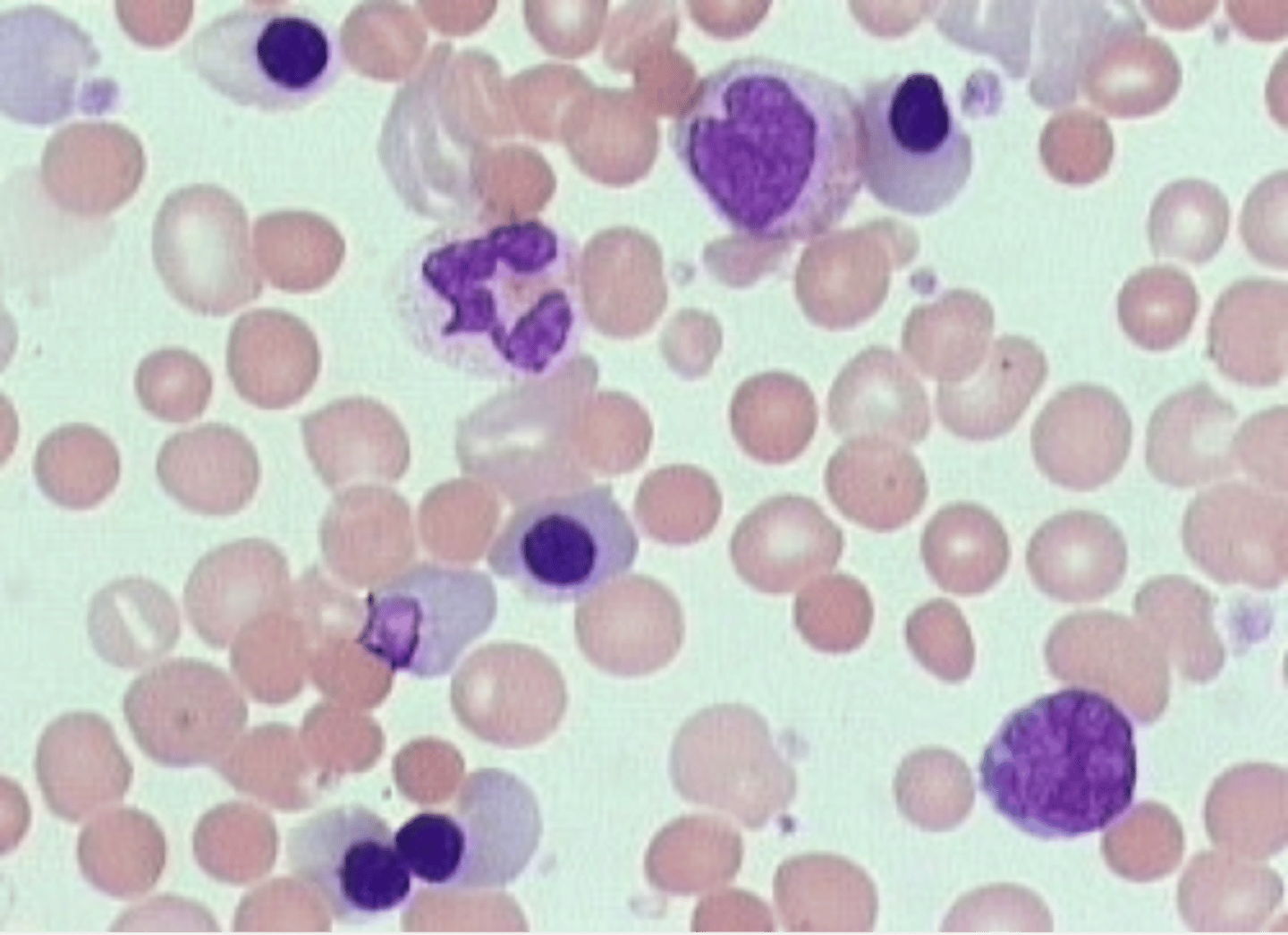
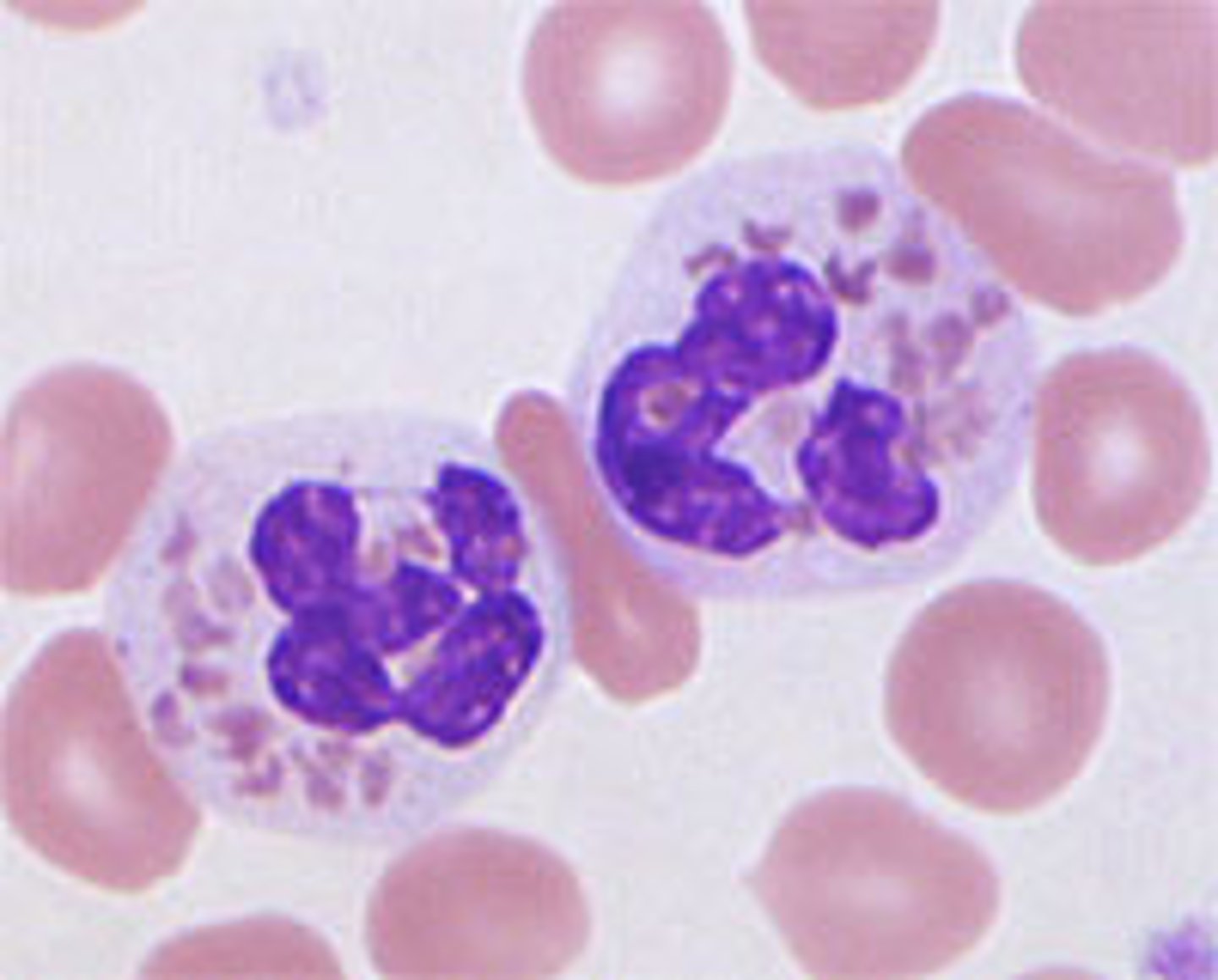
Toxic Granulation (mostly SECONDARY granules)
What is this reactive change in neutrophils?
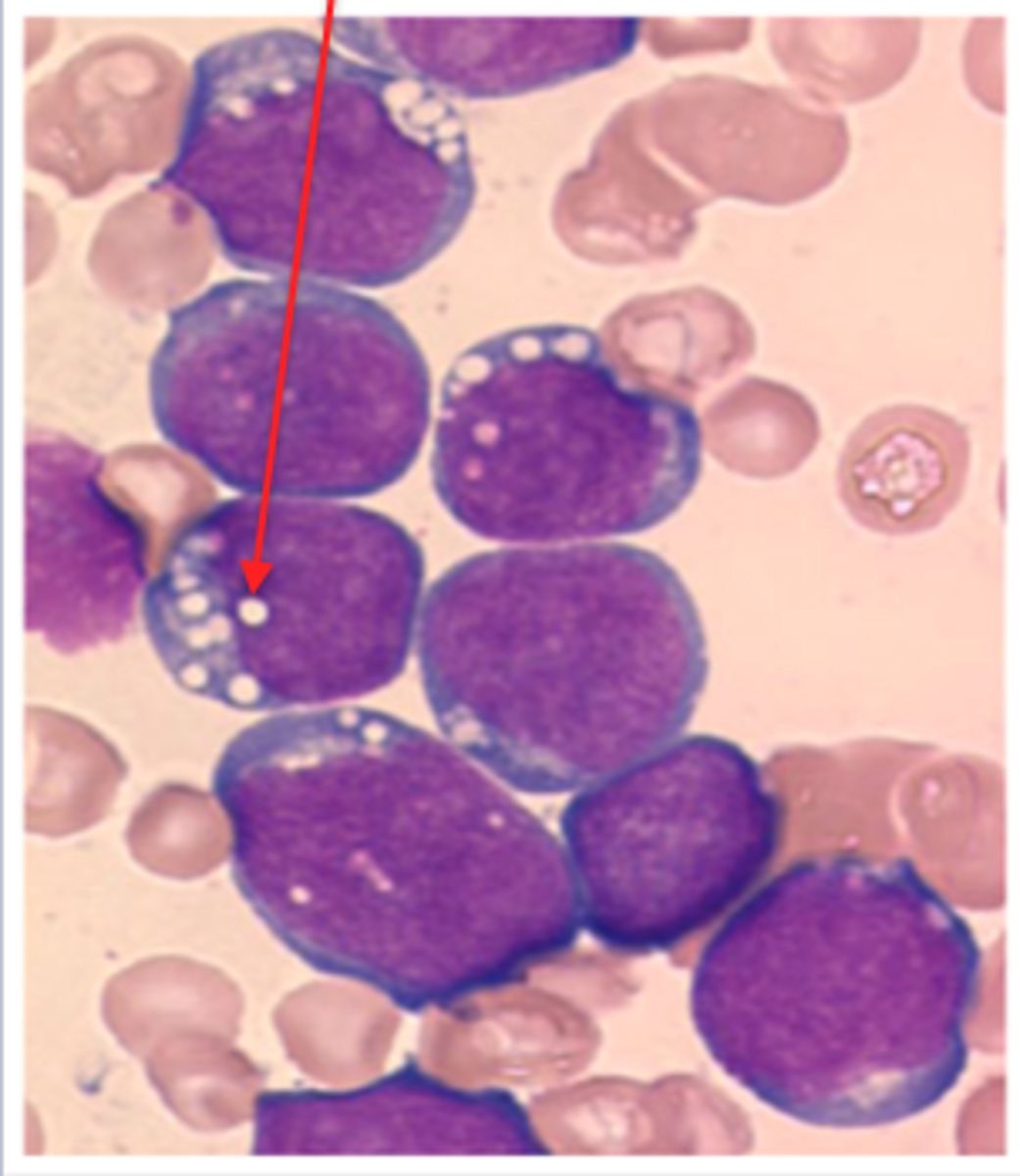
Cytoplasmic Vacuoles
What is this reactive change in neutrophils?
Dohle Bodies (small, pale blue-gray structures that are found in the cytoplasm of neutrophils, made up of ribosomes and endoplasmic reticulum)
What is this reactive change in neutrophils?
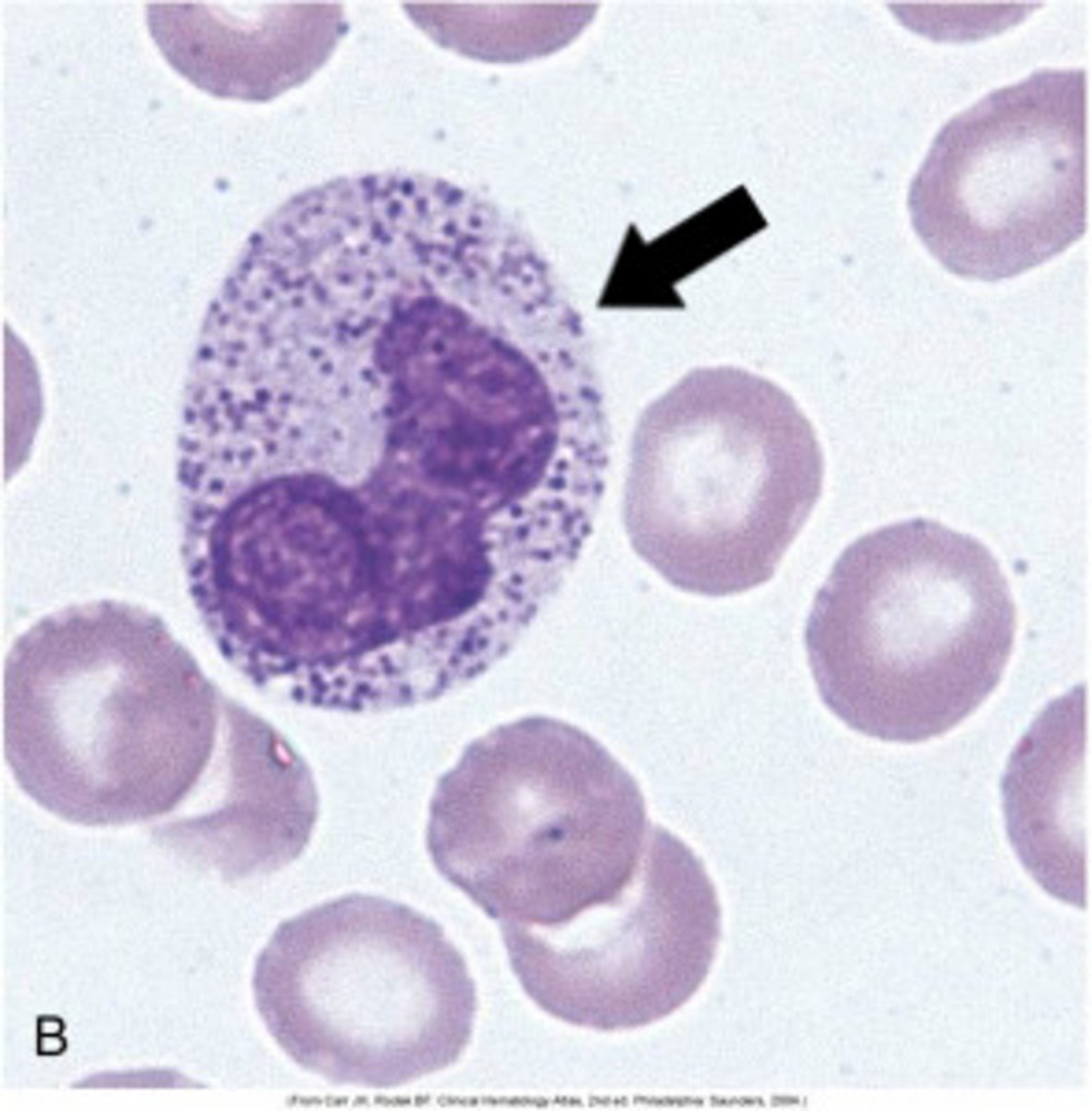
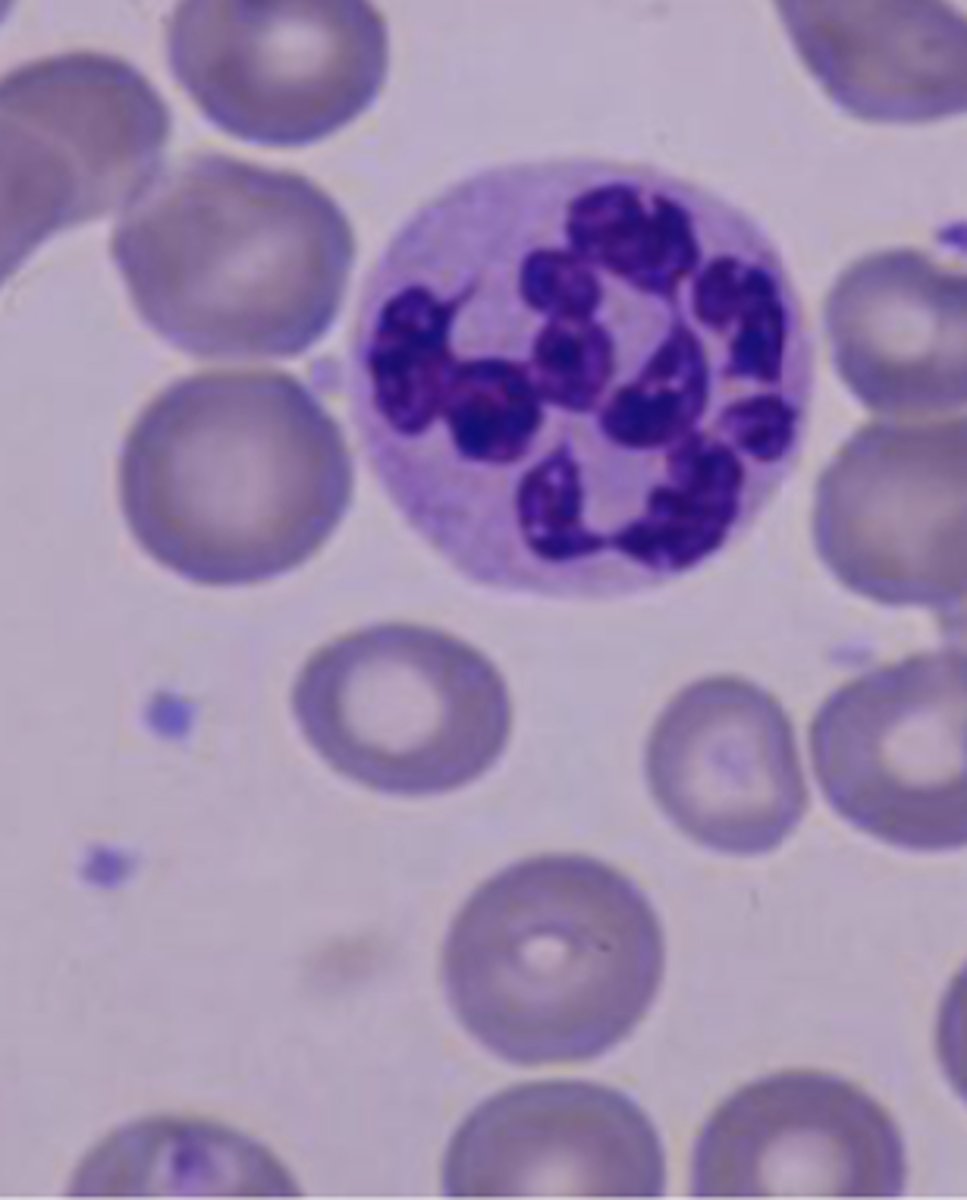
Hypersegmented Neutrophils; Vitamin B12/Folate Deficiency OR Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS)/Iron Deficiency/Certain Meds
What is this Neutrophil Abnormality? What might this be a sign of?
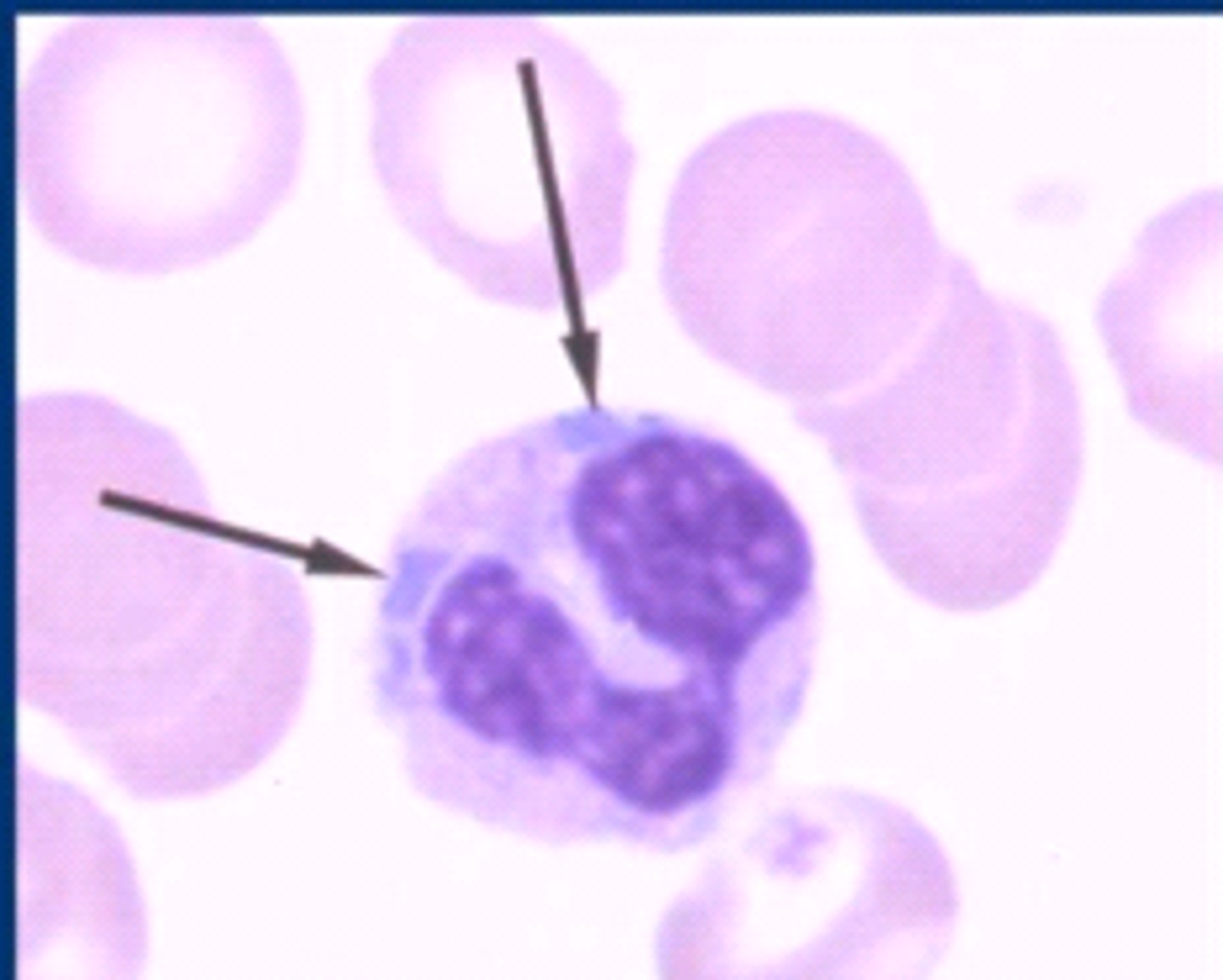
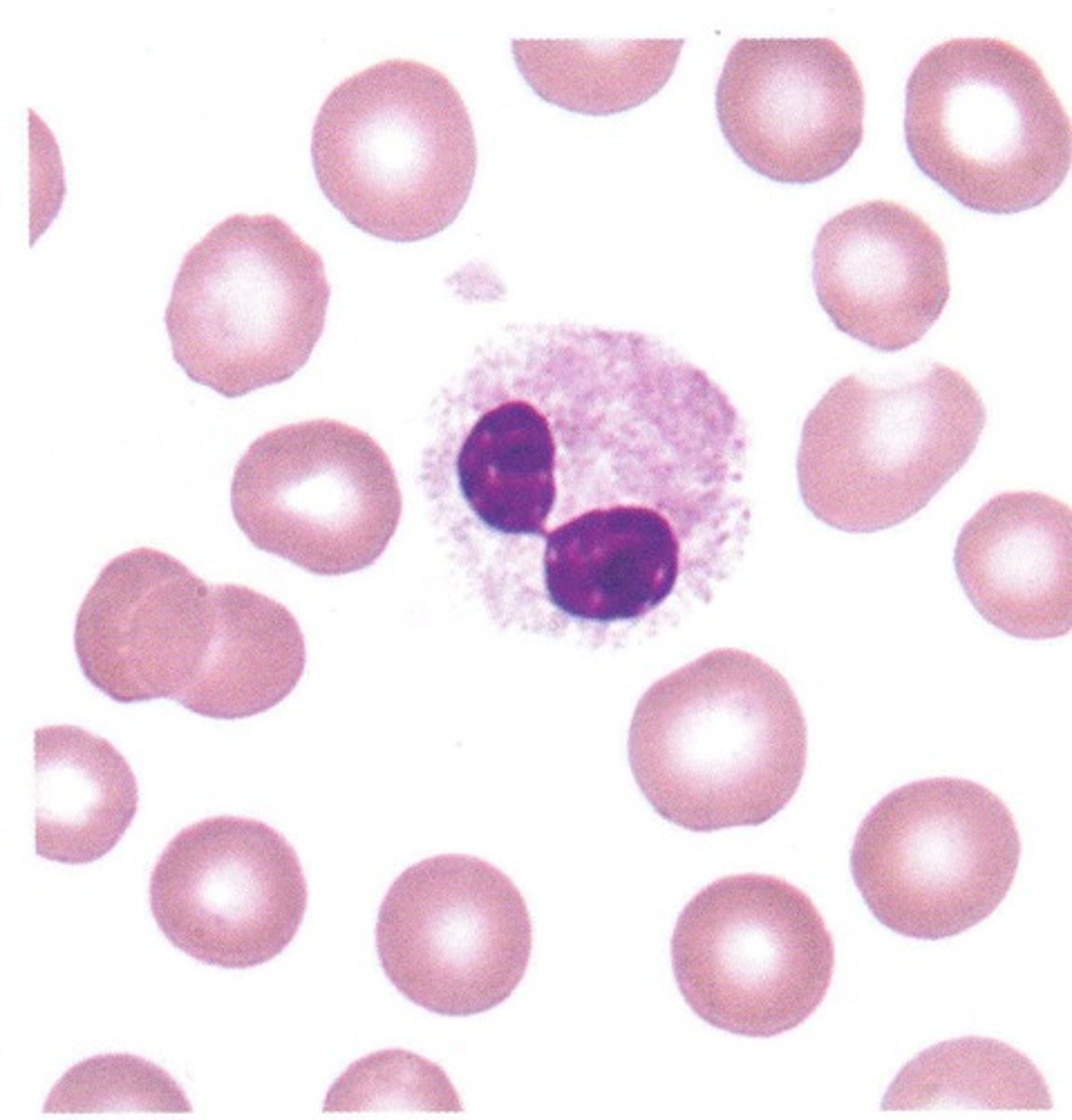
Pelger Huet Anomaly (PHA)
ID this Abnormality:
Nuclear Hypersegmentation of Neutrophils - bilobed or mononuclear
-Hx:
> Familial
>> AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT
>> Defect in scaffolding proteins that control shape of nuclear membrane
>> ALL granulocytic lineage affected
>> Neutrophil function normal
> Acquired
>> Meds = sulfa drugs, mycophenolate, ganciclovir, ibuprofen, valproic acid
>> Infex = HIV, influenza, malaria, TB, COVID-19
>> Myelodysplasia
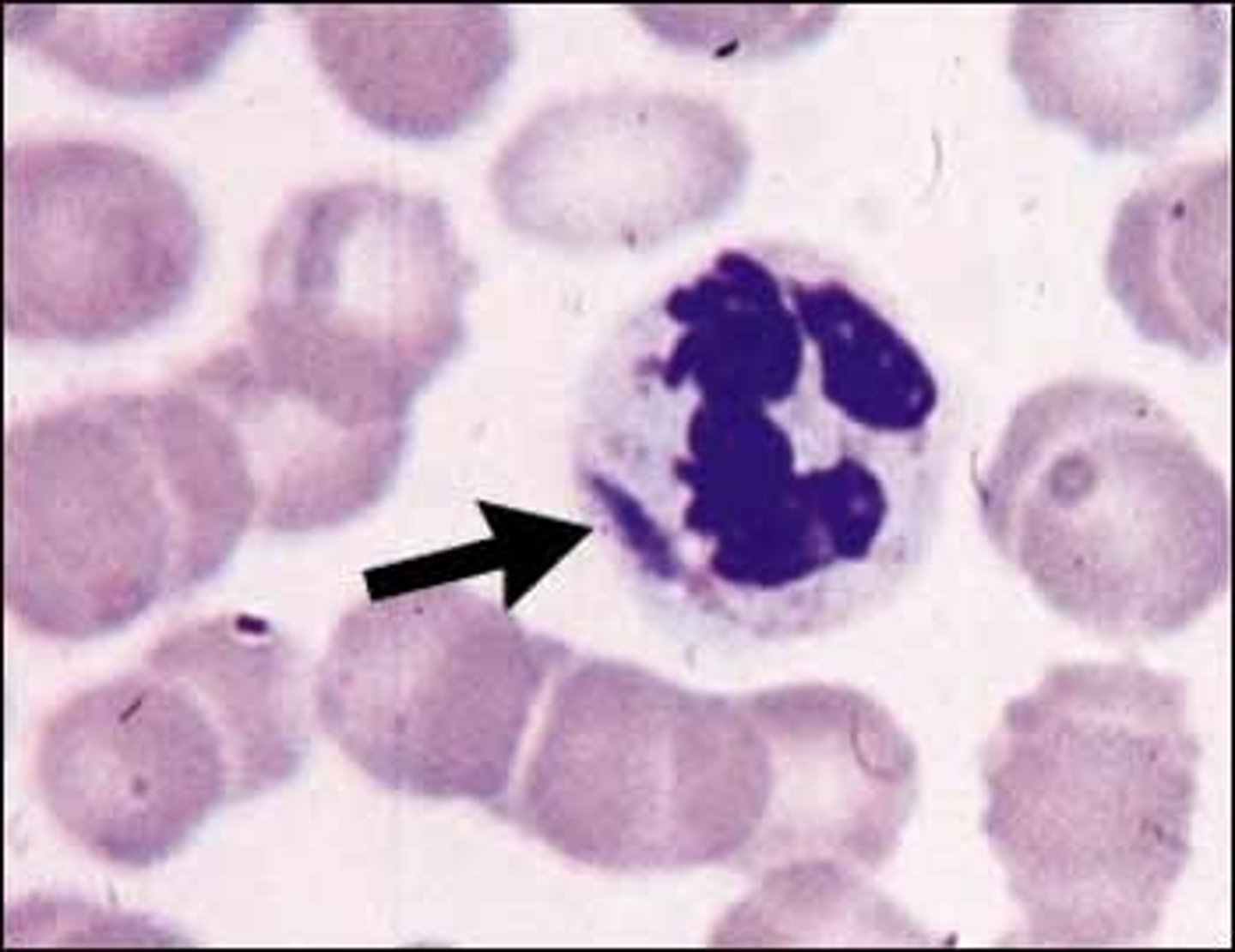
May-Hegglin Anomaly (MHA)
ID this Abnormality:
AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT disorder d/y MYH9 mutation
-Sx:
> Sensorineural hearing loss
> Presenile cataracts
> Glomerular nephropathy
-Dx:
> Dohle like Bodies = Abnormal aggregates of MHY9 protein in neutrophil cytoplasm
> Thrombocytopenia (bleeding tendency)
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome
ID this Abnormality:
Rare AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE condition --> a/w abnormally large leukocyte granules from fusion of lysozymes
-Sx:
> Partial Oculocutaneous ALBINISM (Giant melanosomes in ocular and skin tissues result in hypopigmentation)
-Dx:
> Platelets LACK dense granules
> Platelet function abnormal
> Deficiency of Serotonin & ADP-containing granules ==> Impaired Platelet aggregation
Alder Reilly Anomaly (ARA)
ID this Abnormality:
Lysosomal stoarge disease from deficiencies of lysosomal enzymes & other essential proteins
-Dx:
> WBCs = Increased Granulations & Inclusions
> Neutrophils = Extreme Toxic Granulation
> Accumulation of undigested substrates (mucopolysaccharides, glycosphingolipids, glycoproteins) d/t enzyme deficiencies
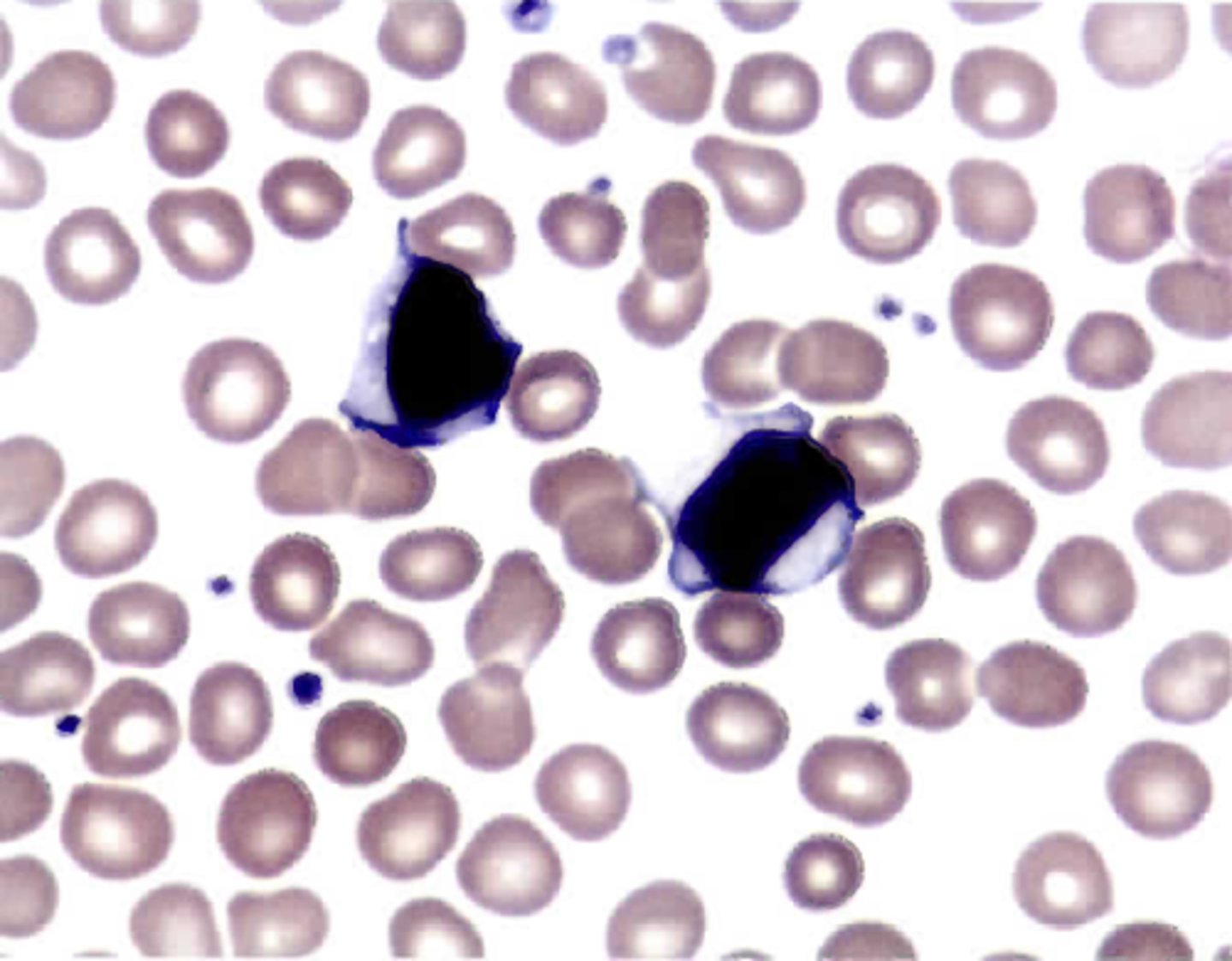
Neutropenia
ID WBC Abnormality:
-Hx:
> Birth/Infancy (Infex, Maternal factors = Autoimmune or Alloantibody, Constitutional)
> Childhood (Infex - usually TRANSIENT Viral Infex)
> Adults
>> Meds/Toxins/Homeopathic Remedies
>> Immune disorder/Chronic Infex
>> Neoplasms
-Prog: Increased Risk of Bacterial Infex
-Tx: Abx Tx & Prophylactic Vaccination
> Bone Marrow (B-cells and other blood cells)
> Thymus (T-cells)
What are the central/generative lymphoid organs?
> Lymph Nodes
> Spleen
> Mucosal & Cutaneous Lymphoid Tissues
What are the peripheral lymphoid organs?
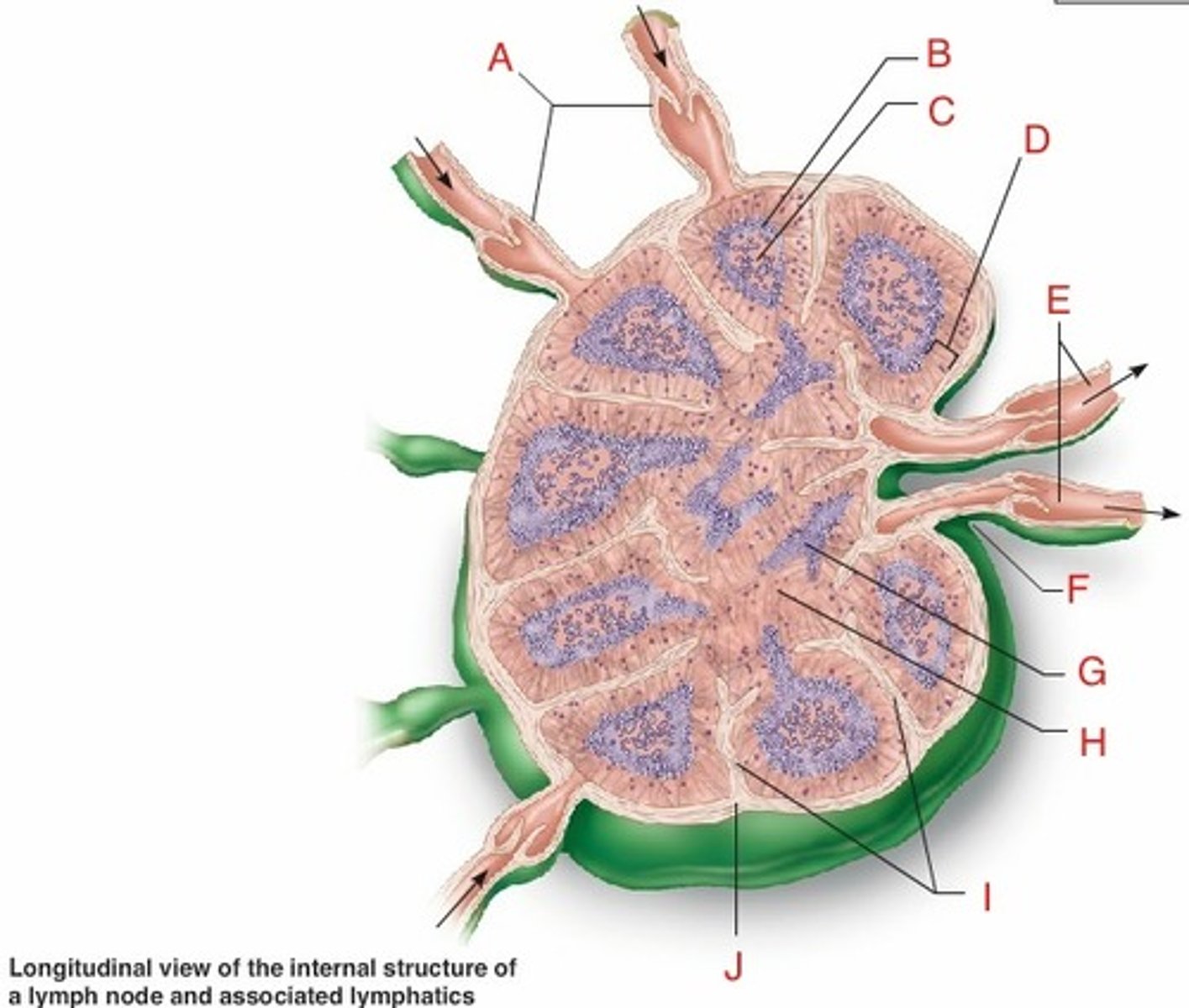
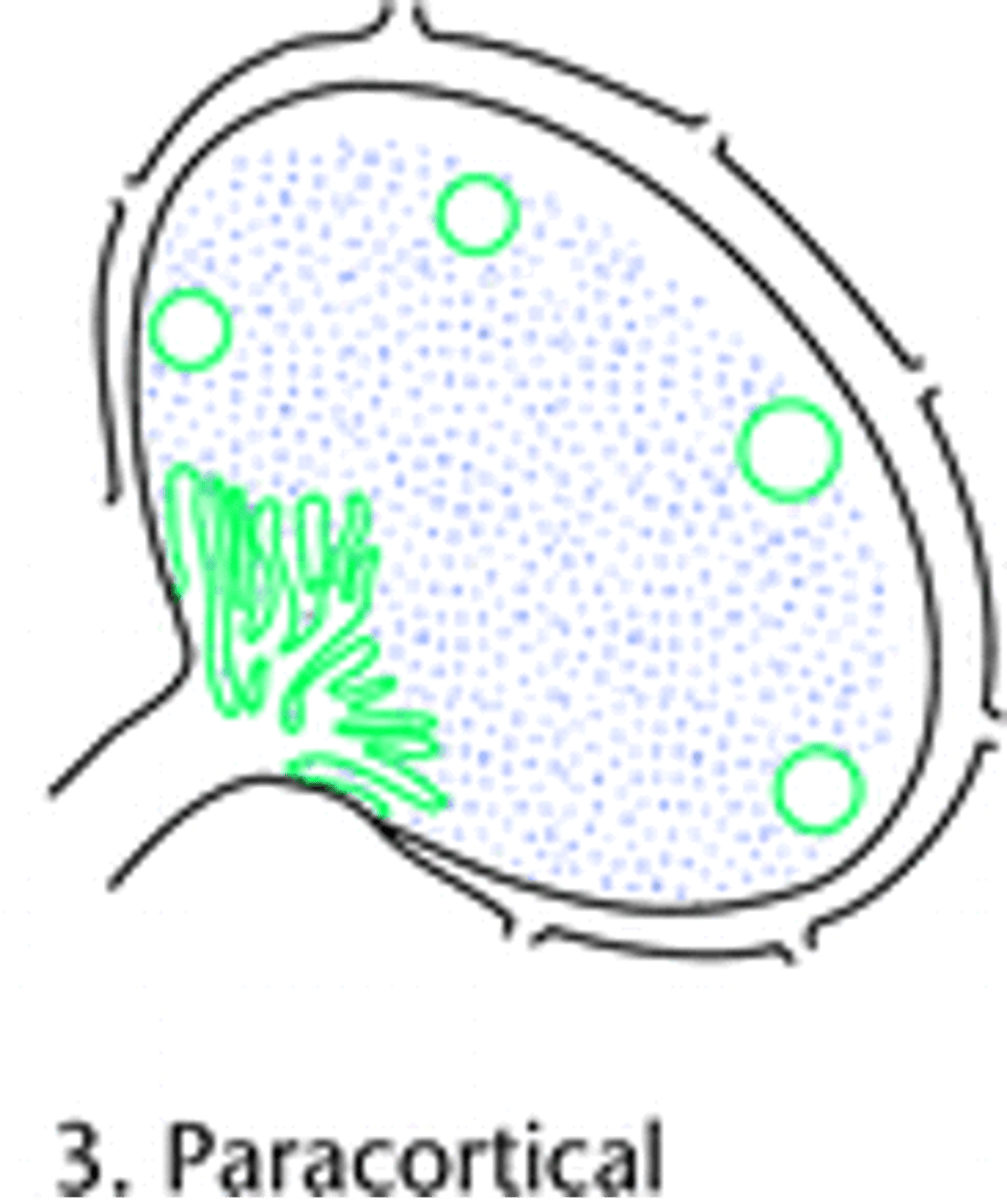
Lymph Node (Cortex = B cells, Paracortex = T cells)
What is this Peripheral Lymphoid Organ?
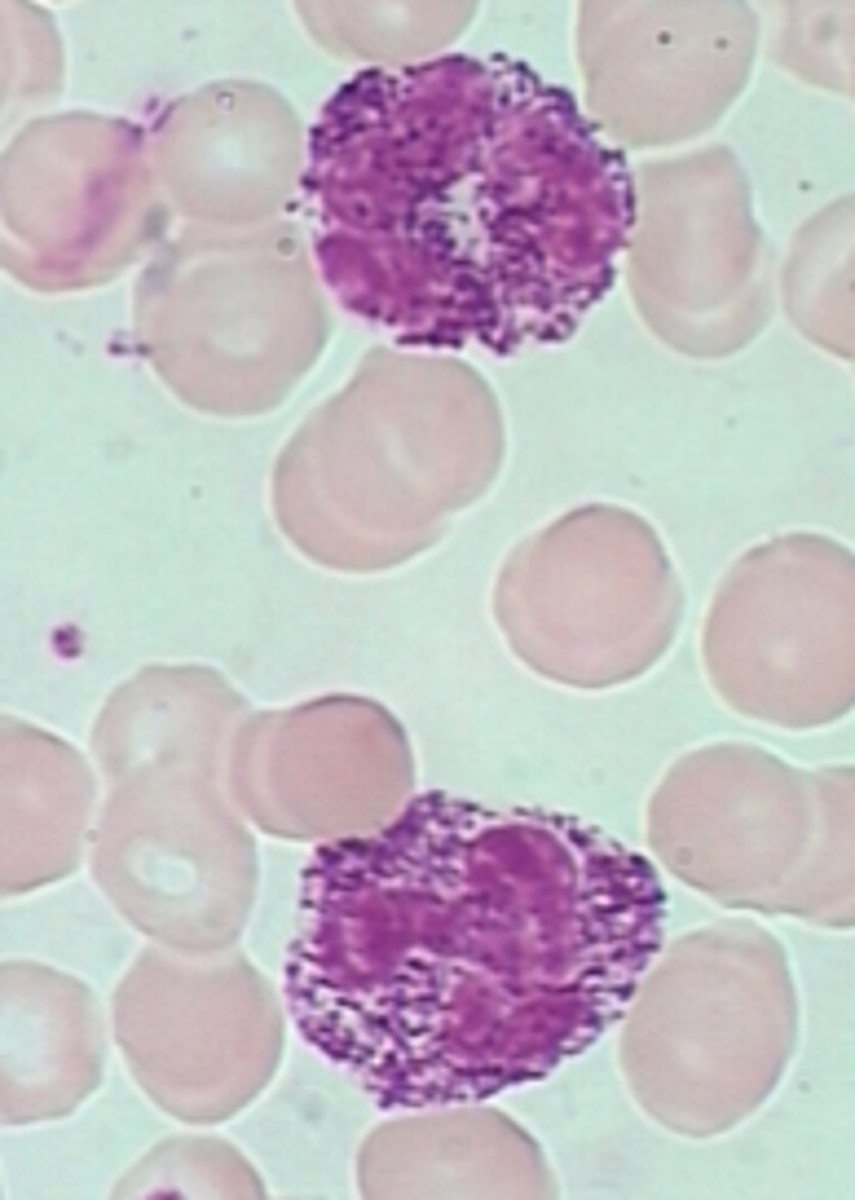
Lymphocytosis with Reactive Morphology
ID WBC Abnormality Type:
-Hx:
> Viral Infex (EBV/CMV)
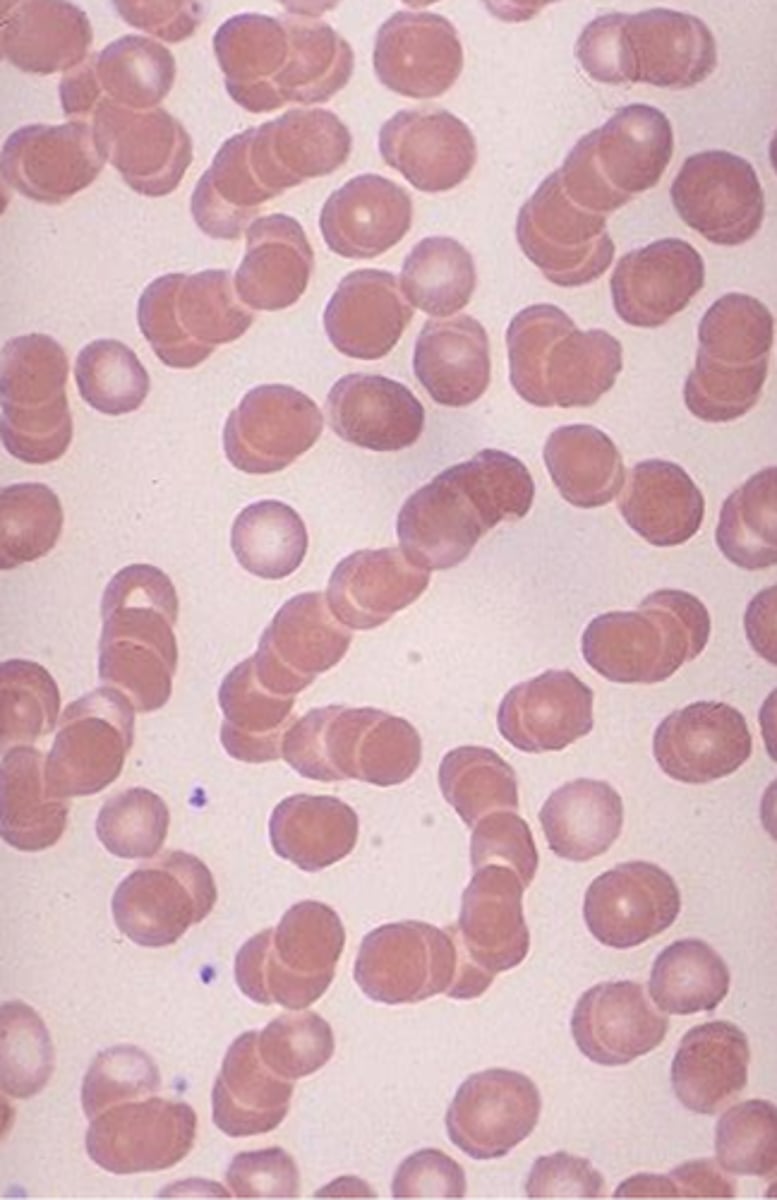
Bone Marrow Plasmacytosis
ID Condition:
Increase in polyclonal (polytypic) plasma cells above normal range in bone marrow often accompanied by increased polyclonal serum immunoglobulin levels
-Hx:
> Infex (HIV, Hep C, EBV)
> Autoimmune Disorders
> Marrow Malignancies
-Dx:
> Peripheral = Rouleaux formation
Lymphocytosis w/ Nonreactive Morphology
ID WBC Abnormality Type:
-Hx:
> Pertussis (Whooping Cough)
> Transient Stress
> Persistent Polyclonal B-cell
Bordetella Pertussis (Whooping Cough)
ID Condition:
D/t infection-related toxin blocking migration of lymphocytes form blood to lymphoid organs
-Dx:
> STRIKING Lymphocytosis (up to 10 x 10⁹/L with nonreactive morphology)
-Tx: Abx
Infectious Mononucleosis
ID Condition:
-Hx:
> Epstein Barr Virus (EBV) - type of Herpesvirus
-Path:
> Seronegative “kissing disease” usually involves direct oral contact
> Infects B-cells (becomes activated and proliferate d/t several viral proteins --> produce IgM Abs against capsid proteins)
-Sx/PE:
> Fever
> Sore Throat
> Generalized Lymphadenitis/Lymphadenopathy (in posterior cervical, axillary, groin regions)
> Enlarged Spleen
-Dx:
> Lymphocytosis of activated, CD8+ T Cells
> Marked paracortical expansion and focal areas of necrosis
>> Paracortical (interfollicular) infiltrate was polymorphous and included small lymphocytes
>> Plasmacytoid lymphocytes
>> Plasma cells
>> Occasional medium-sized cells consistent with immunoblasts
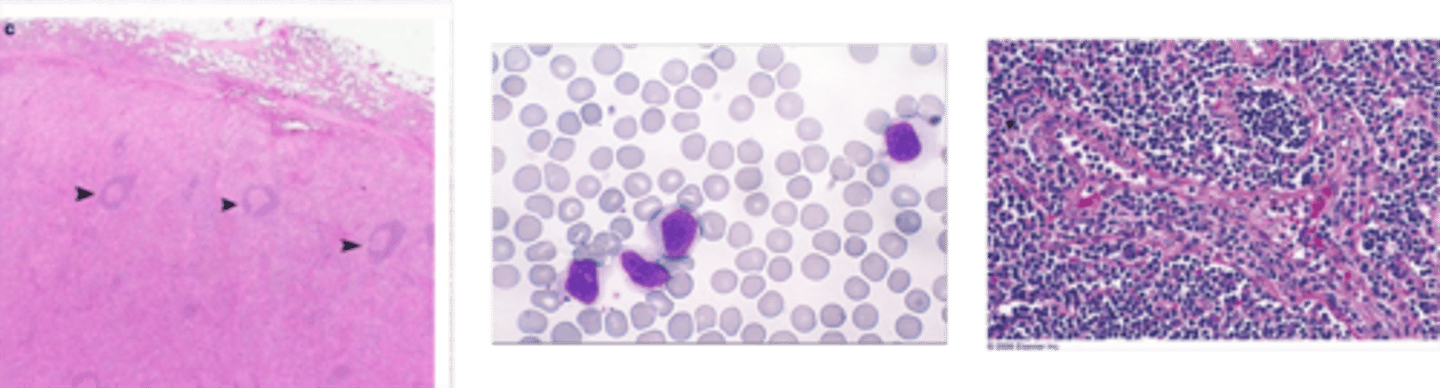
Sinus Histiocytosis
ID Condition:
Distention and Prominence of Lymphatic Sinusoids (d/t marked hypertrophy of lining endothelial cells & macrophage infiltrate)
-Hx:
> LNs draining cancers
> Immune Response to Tumor or Tumor Products
> Response to TATTOO PIGMENTS
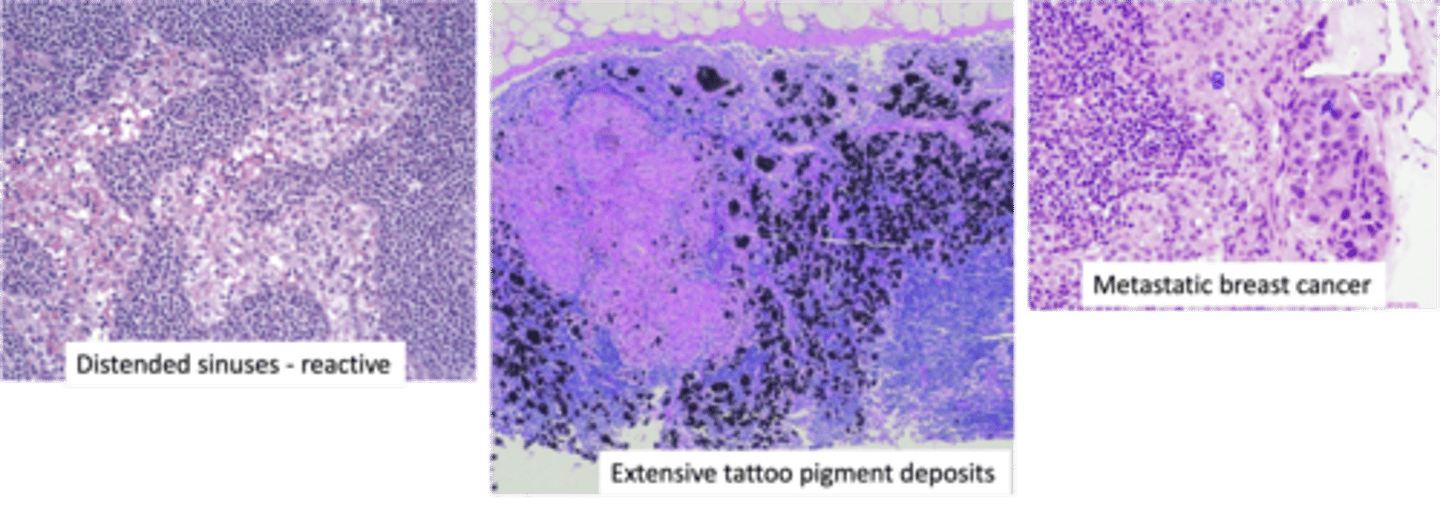
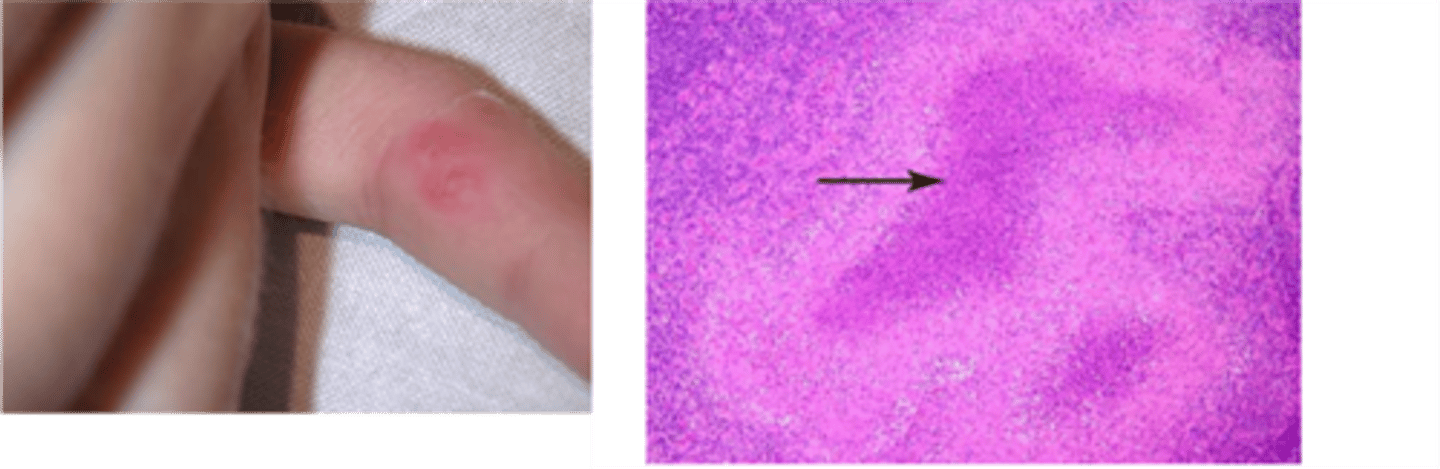
Cat Scratch Disease (CSD)
ID Condition:
Self-limited lymphadenitis d/t Bartonella henslae (bacteria)
-Hx:
> CHILDHOOD
-Sx/PE:
> Regional LAD (axilla & neck) - 2 wks post inoculation, lasts 2-4 mo
-Dx:
> Histo = Foci of "stellate-microabscesses" (foci of necrosis bounded by palisaded histiocytes)
Large Granular Lymphocytosis
ID WBC Abnormality Type:
-Hx:
> T-cell large granular
> Chronic NK-cell
> Neoplasia
> Postsplenectomy
> Hypersensitive Reactions
> Medication Reaction
What are other causes of Lymphocytosis?
Presentation w/ enlarged lymph nodes
Define Lymphadenopathy
Acute Lymphadenitis
ID Condition:
Acute inflammation of Lymph Node(s)
-Hx:
> Bacterial Infex
-Sx:
> Rubor
> Calor (heat)
> Tumor
> Pain
-Dx:
> Peripheral
>> Few lymphoid cells in necrotic background
>> Follicular hyperplasia
>> Infiltration of PMN Cells
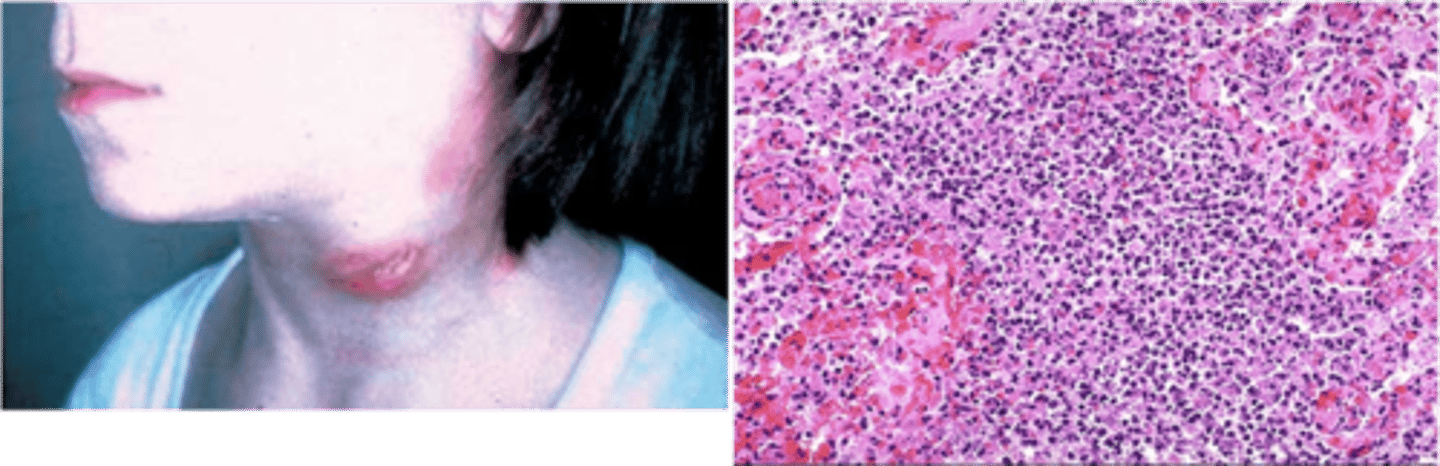
Reactive Follicular Hyperplasia
ID Abnormality:
-Hx:
> RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
-Dx:
> Histo = Follicular Hyperplasia + Polyclonal Plasma Cell Infiltration in interfollicular area
> BCL2 Negative (negative since normal germinal center B cells undergo apoptosis w/o appropriate antigen)
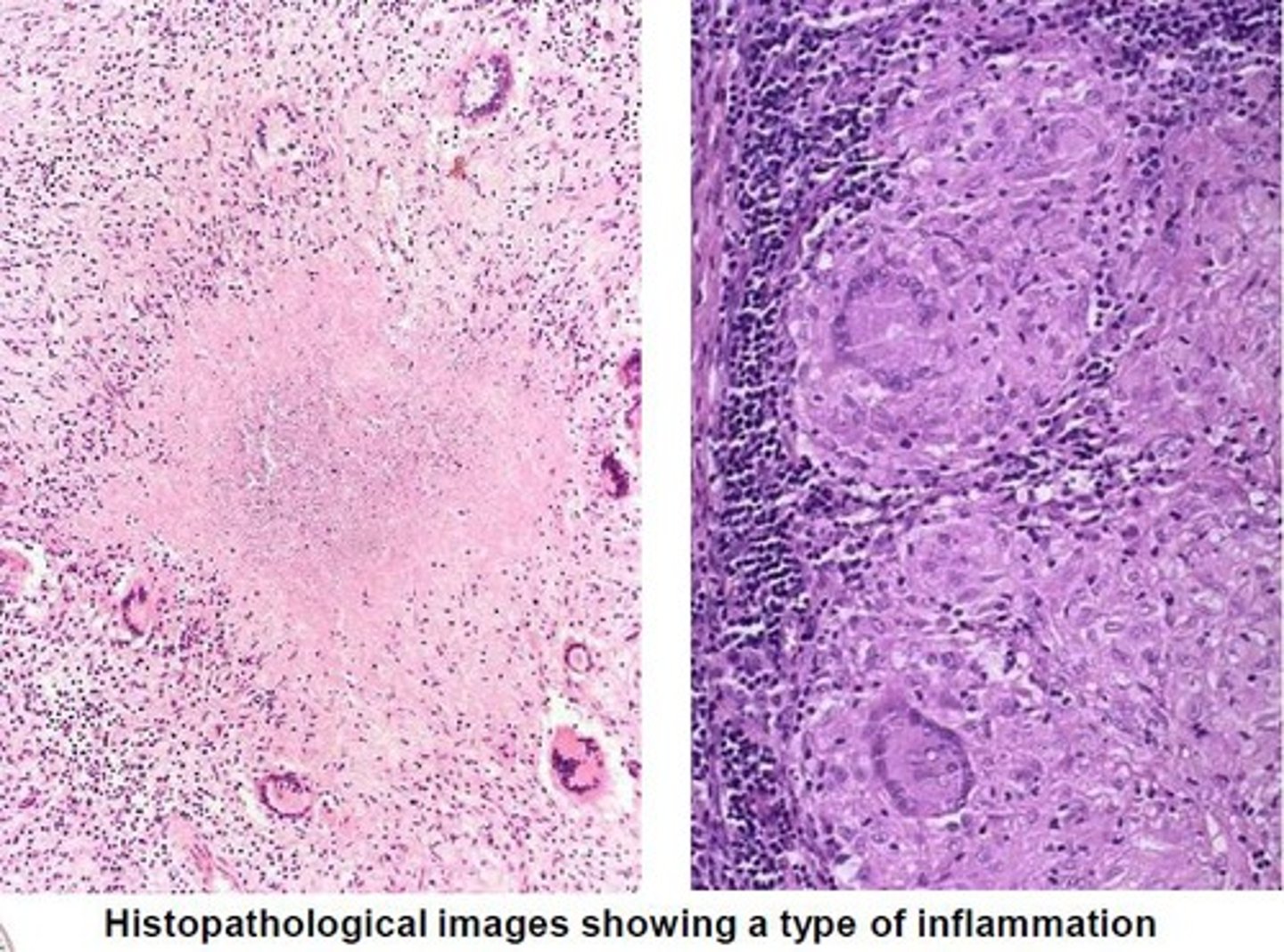
> TB
> Histoplasmosis
> Sarcoidosis
What are often causes of Granulomatous Inflammation?
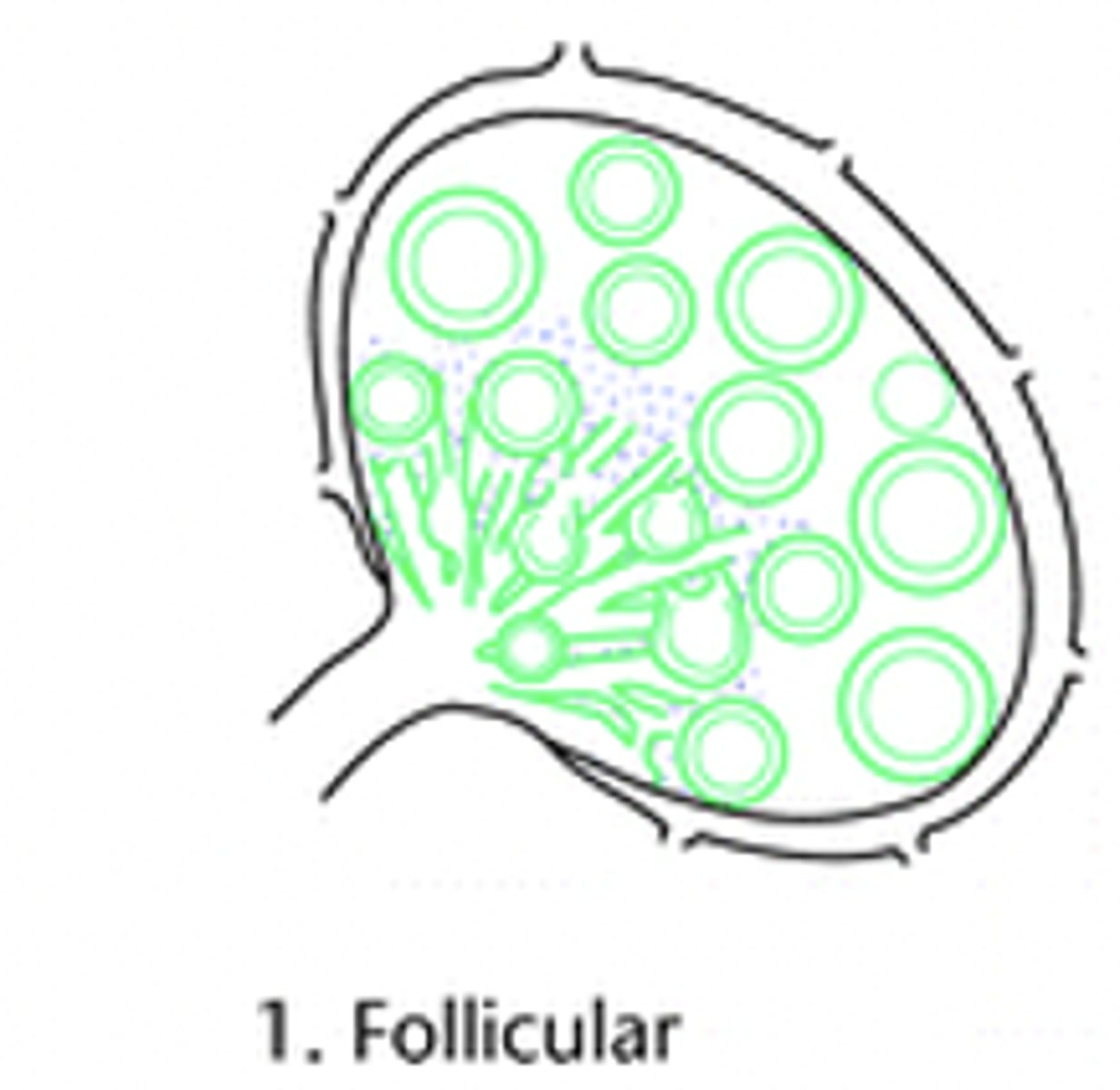
> Typical B cell Rxn
> Rheumatoid Arthritis
> Toxoplasmosis
> Early HIV Infex
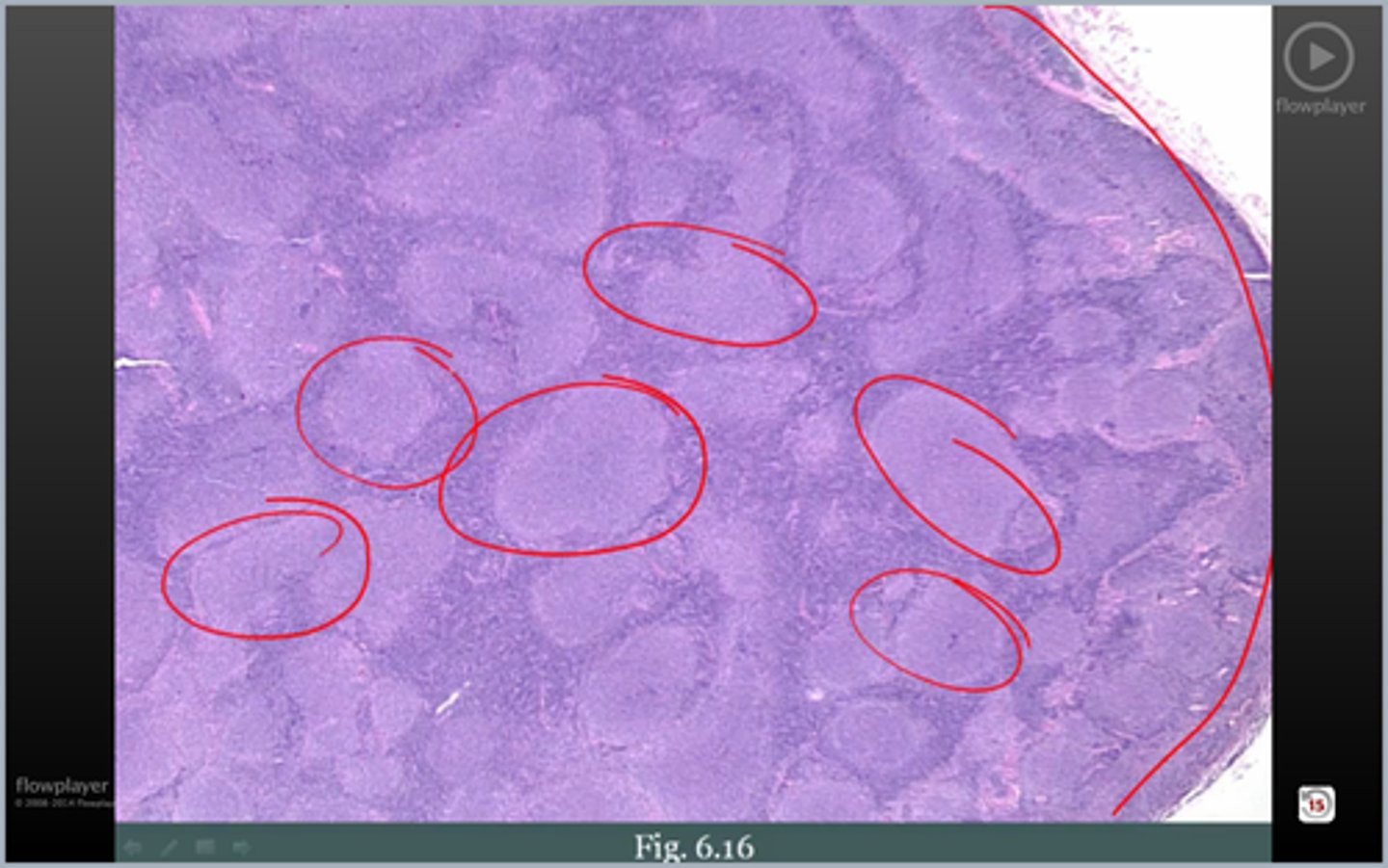
What are the causes of Follicular Chronic Lymphadentis?
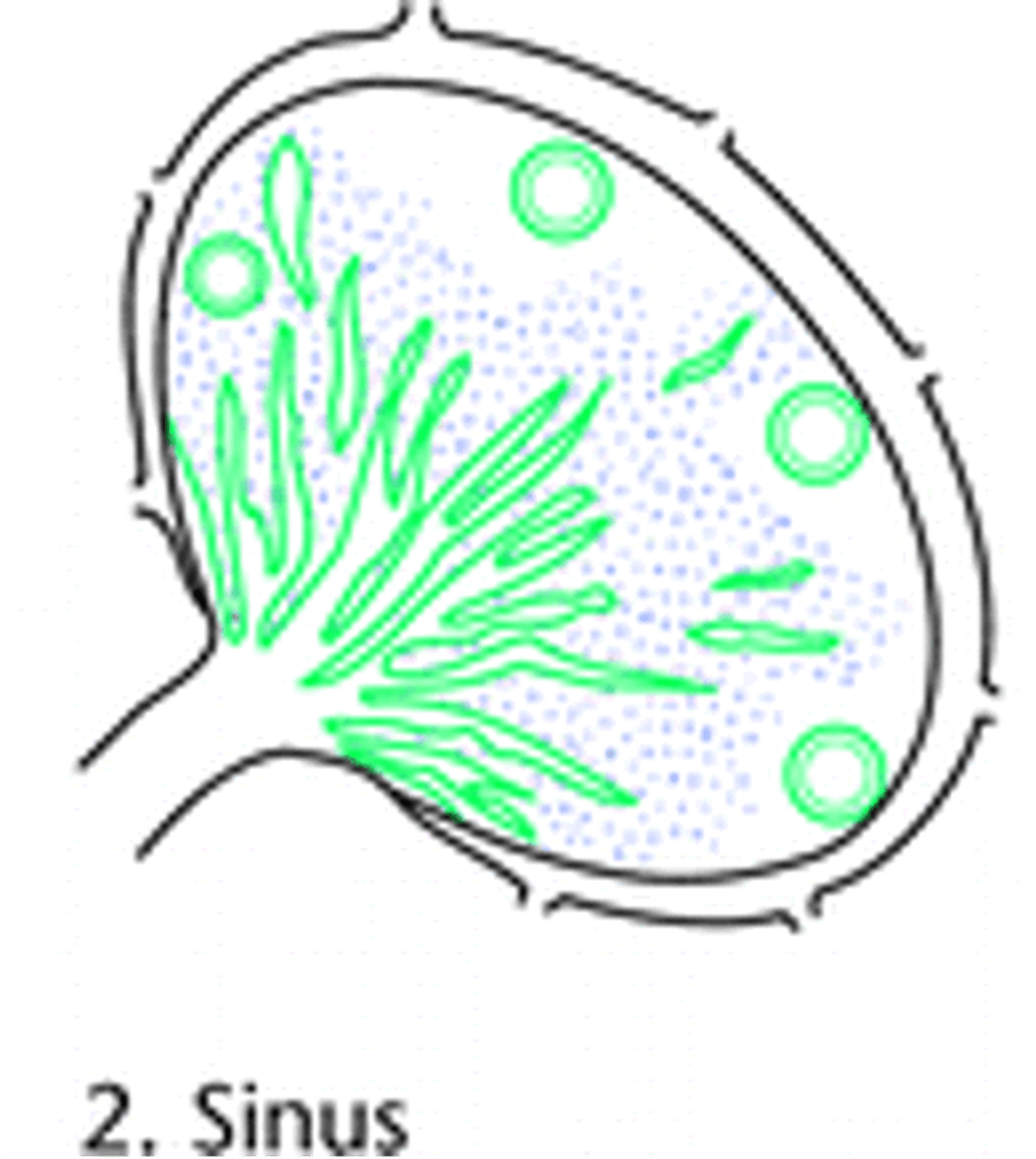
> Stimulation of Macrophages
> Lymph Nodes draining cancers (Breast Carcinoma)
What are the causes of Sinus Chronic Lymphadentis?
> T-cell Reaction (Acute Viral Infex = Mono)
> Vaccinations (Smallpox)
> Drug Immune Rxns (Phenytoin)
What are the causes of Paracortical Chronic Lymphadentis?
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH)
Define Condition:
-Path: Excessive release of IF-gamma from CD8+ T-cells –-> macrophage activation --> release of toxic levels of additional proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF and IL-6 --> phagocytosis of blood cells and their precursors
-Hx:
> Inherited = D/t defects in genes (ex: PRF1 encoding perforin) that regulates immune cell function
> Acquired = Infex, Malignancy (peripheral T cell lymphoma)
-Sx/PE:
> Fever
> Splenomegaly
-Dx:
> PANCYTOPENIA
> Peripheral = RBCs, Platelets or WBCs WITHIN CYTOPLASM OF MACROPHAGES
> BM = Phagocytic Histiocytes w/ ingested platelets and red cell precursos
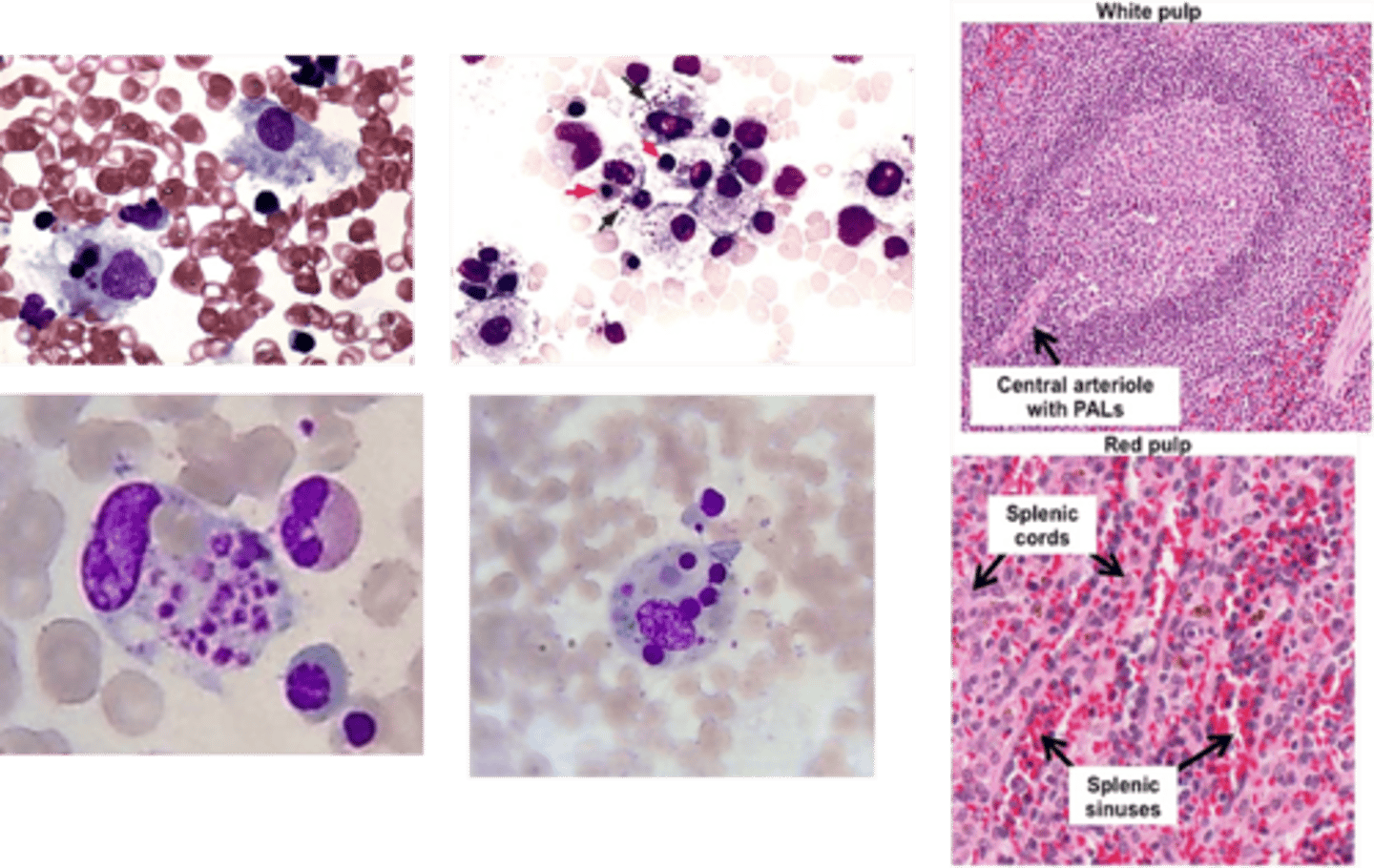
Hypersplenism
Define Condition:
Enlarged spleen leading to removal of cellular blood components
-Hx:
> LIVER CIRRHOSIS
> Infex
>> Brucellosis
>> CMV
>> Echinococcus
>> Histoplasmosis
>> Infex Mono
>> Leishmaniasis
>> Schistosomiasis
>> Syphillis
>> Toxoplasmosis
>> TB
>> Typhoid
> Congestive Splenomegaly
> Gaucher Disease
> Hemangioma
> Leukemia/Lymphoma
> Issues of Red Pulp
-Dx
> Widening of splenic cords (Inc macrophages or connective tissue --> premature destruction of normal blood components)
> Reactive Follicular Hyperplasia of White Pulp (if a/w cytopenias)
> Birth = 10-35 gm
> Until Puberty = 20-50 gm
> Progressive Involution = 5-15 gm (elderly)
How does the Thymus change over time?
1. T-cells start in BM as T-cell precursors
2. T-cell precursors leave BM then enter Thymus to undergo maturation
3. Immature Double Negative --> T cells enter thymus at capsule then to cortex for Double Positive --> Further maturation in medullary portion of Thymus for Single Positive T cells
4. Upon maturation, T cells leave thymus & enter circulation & other tissues
What are the stages of T-cell maturation?
DiGeorge Syndrome
Define Condition:
22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome
-Path: Born w/o thymus --> Deficient in T cells (susceptible to infex)
-Hx: INFANTS
-Sx/PE:
> Congenital Heart Defects
> Hypoparathyroidisms
Thymic Follicular Hyperplasia
Define Condition:
Hyperplastic Reactive Lymphoid Follicles w/n Thymus
-Hx:
> Myasthenia Gravis
> Graves Disease
-Dx: MG
> Thymic abnormalities lead to a breakdown in tolerance that causes an autoimmune-mediated attack on acetylcholine receptor (AChR) in myasthenia gravis + More severe EMG Abns
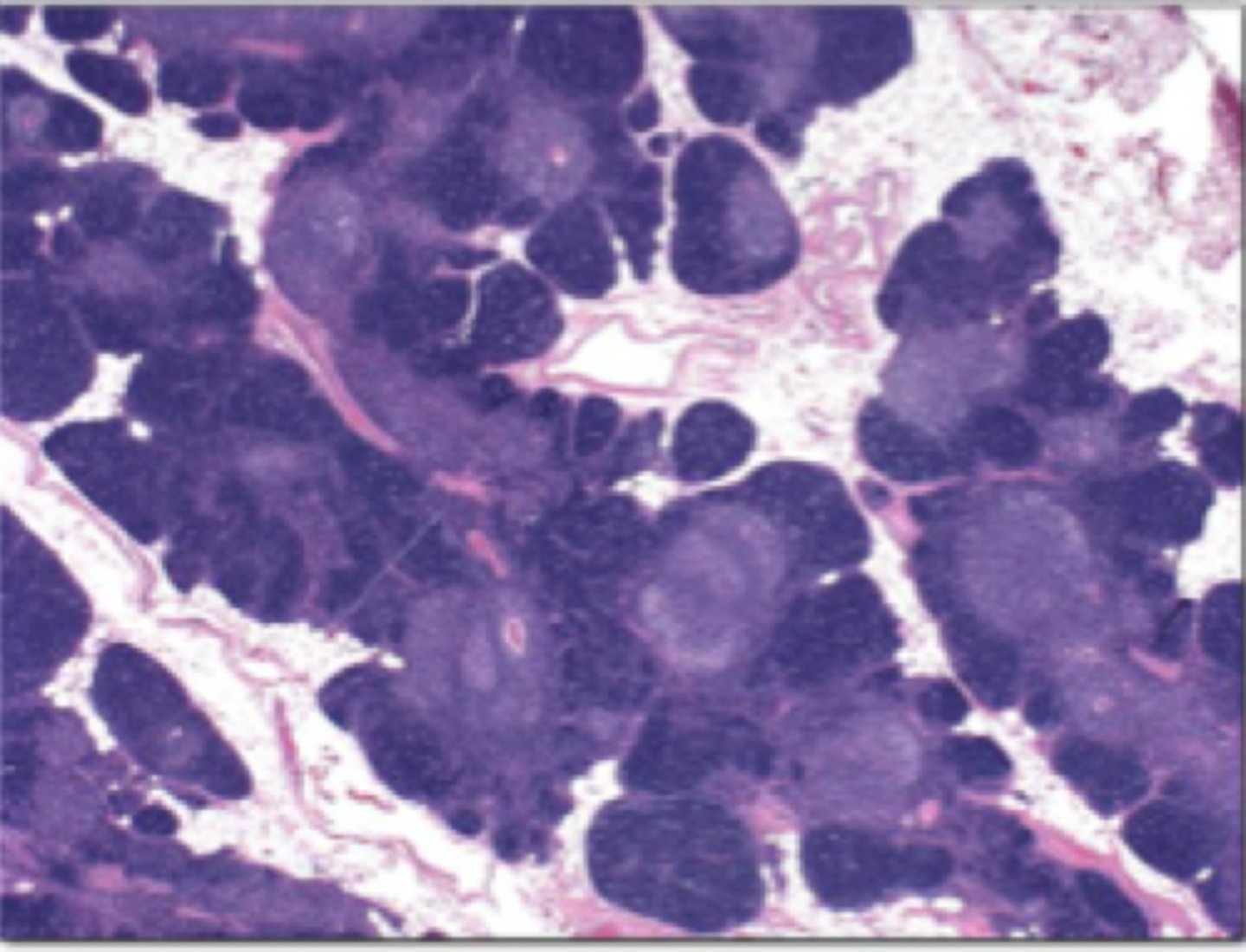
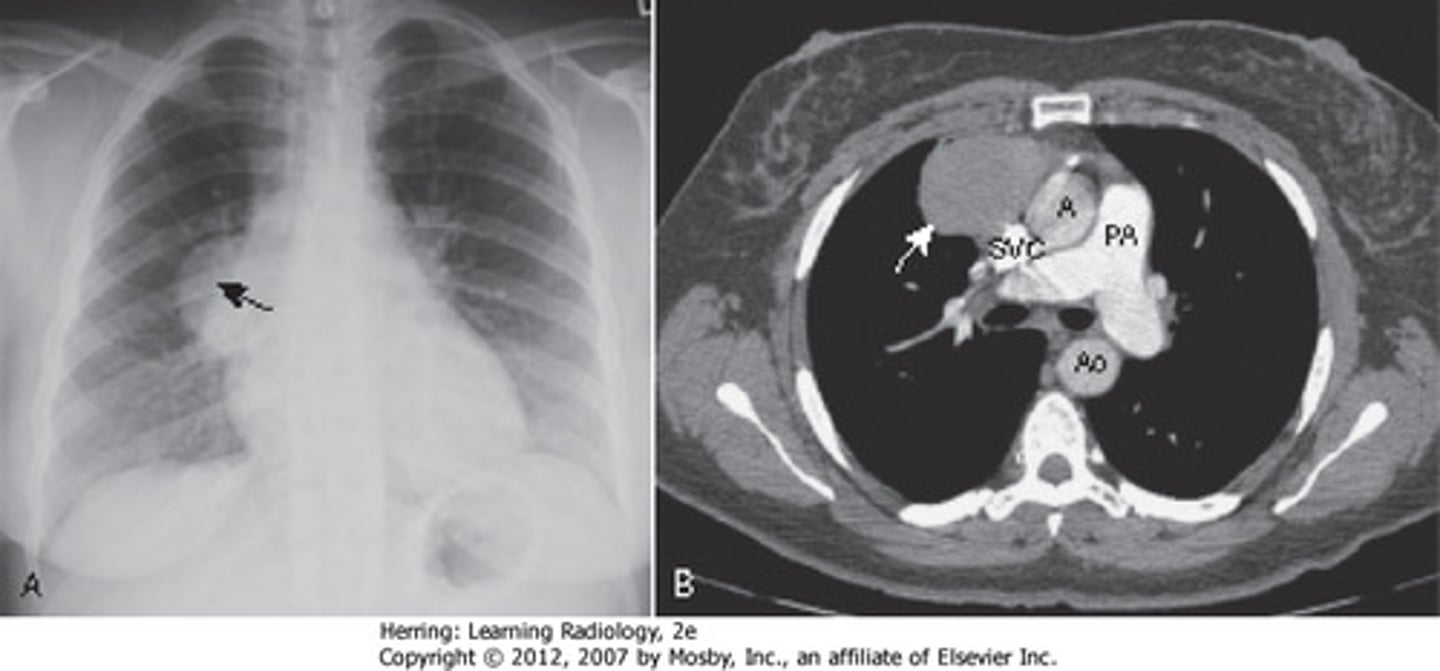
Thymoma
Define Condition:
Tumor originating from epithelial cells of thymus that may be benign OR malignant (carcinoma)
-Hx:
> Associated Autoimmune Disorder (MG, Pure Red Cell Aplasia)
-Sx/PE: D/t Compression of organs
> SVC Syndrome
> Dysphagia
> Cough
> Chest Pain
-Dx: MG
> Benign, Well-Differentiated & Encapsulated (can be REMOVED)