Experiment 4: Properties of Carbohydrates
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Carbohydrates
Originates from the fact that many, but not all members of this class have the general molecular formula Cn(H2O)n and thus were considered hydrates of carbon
Monosaccharides
Simplest carbohydrates which can either be polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones
Polyhydroxy aldehydes
Have the general structure A and are referred to as aldoses
Polyhydroxy ketones
Have the general structure B and referred to as ketoses
3-6 carbons
How many carbons does monosaccharide have?
3C
Trioses
4C
Tetroses
5C
Pentoses
6C
Hexoses
Ribose, Glucose, and Fructose
Examples of monosaccharides
Ribose
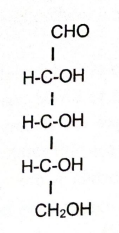
Glucose
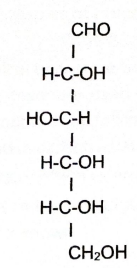
Fructose
Cyclic hemiacetal
Most monosaccharides exist in a cyclic form the aldehydes or ketone group reacts with one of the -OH groups on the other end of the same molecule to form a _______
a-D-glucose and B-D-glucose
Different anomers of glucose
Inter-converted
The rings are constantly opening and closing again. In this way the a and B forms can be?
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharides may be combined with the loss of one molecule of water
Glycosidic bond
The bond that connects 2 monosaccharide units in a disaccharide
Sucrose and Lactose
Examples of disaccharides
Table Sugar
Other term for sucrose
Milk Sugar
Other term for Lactose
Polysaccharide
Consists of many monosaccharides linked together
Starch, Pectin, Glycogen, and Cellulose
Examples of polysaccharides
Hans Molisch
Discovered the Molisch’s Test
Molisch’s Test
Involves the addition of Molisch’s reagent to the analyte and the subsequent of a few drops of concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
Purple or purplish-red ring
Confirms the presence of carbohydrates in the analyte
Tetroses and trioses
Exceptions for positive reaction for Molisch’s test given by almost all carbohydrates
Reducing Sugar
Carbohydrate that is oxidized by a weak oxidizing agent in basic aqueous solutions
Non-reducing Sugar
Not-oxidized
Aldoses
True reducing sugar because they contain the aldehyde functional group
Ketoses
Do not contain aldehyde (they contain ketone)
They also show reducing properties
Keto-enol tautomerization
Ketoses in basic aqueous solutions undergo ______ converting them to mixture of aldoses.
Free anomeric carbon
The only disaccharides that are reducing sugars are those that contain_______
It has the capacity to open and expose the aldehyde group
Monosaccharides
All _____ are reducing
Polysaccharides
All_____ are non-reducing
Benedicts test
Based of the fact that Cupric Ion (Cu2+) will oxidize aliphatic aldehydes including a-hydroxyaldehydes such as aldoses
Can also be used to quantitatively estimate the amount of sugar in a solution
This is also used to detect glucose in the urine
Brick red precipitate / vary from red to orange to green
Positive test for Benedicts Test
Green Color
Combination of blue solution and some are orange precipitate from Benedict’s test
Blue Solution
Negative Test for Benedict’s Test
Green/Yellow ppt
Traces of reducing sugar in Benedict’s Test
Orange red ppt
Moderate traces of reducing sugar in Benedict’s Test
Picric Acid Test
Saturated picric acid solution is used in oxidizing agent
Yellow
Color of picric acid solution
10% Na2CO3
The environment is made alkaline by _______
Mahogany red colored solution
Positive test for Picric Acid Test
Picric acid to Picramic Acid
The mahogany red colored solution is due to what kind of reduction?
Moore’s Test
At basic environment, this carbonyl groups can undergo aldol condensation
caramel with a brown color and characteristic odor
Positive result for Reducing Sugar (Moore’s Test)
Barfoed’s Test
Like Benedict’s test, it depends on the reducing properties of sugars. However, because of the specific conditions employed for the test, it is possible to distinguish between monosaccharides and disaccharides
Test for Monosaccharides
Cupric Ion (Cu2+)
Oxidizing agent used in Barfoed’s test just like Benedict’s test
Brick red precipitate of Cu2O within 2-3 minutes
Positive test for Barfoed’s test in Monosaccharides
Disaccharides in Barfoed’s Test
Require a longer time, providing the precipitate only after about 10 minutes in Barfoed’s test
Seliwanoff’s Test
Used to distinguish aldoses from ketoses
Test for Ketoses
Seliwanoff’s Reagent
Dehydrates ketoses more rapidly to give furfural derivatives
Furfural Derivatives
Undergo condensation reaction with resorcinol
Cherry red complex solution (2 minutes)
Positive test for Seliwanoff’s test for ketoses
Bial’s Test
Used to distinguish pentoses from hexoses
Test for pentoses
This distinction is based on the color that develops in the presence of the reagent
Bluish green solution
Positive reaction of pentose for Bial’s test which reacts with orcinol and ferric ion
Muddy-brown, yellow or gray solution
Positive reaction of hexoses for Bial’s test which are dehydrated and reacts with orcinol and ferric ion
Polysaccharides
Have highly coiled structures, such as starch
Iodine test
A very specific test for polysaccharides
Iodine
Forms a coordinate complex between the helically coiled polysaccharide chain and iodine centrally located within the helix due to the adsorption
Brown
Original color of iodine
Different colors
What colors do polysaccharides produce?
Ribose
5 carbon ring glucose
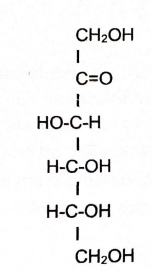
Fructose
Contains ketone
Benedict’s Reagent
Fehling’s Reagent
Tollen’s Reagent
Nylander’s Reagent
Picric Acid with Sodium Carbonate
Weak oxidizing Agent
Darkish Violet
Starch
Darkish orange/Brown
Glycogen
Light Yellow
Inulin
Cloudy Yellow
Cellulose