CHEM 2B Ch9
1/29
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
q > 0
system absorbs heat
When energy is added to the system as heat, the effect is to increase the internal energy of the system (ΔE > 0), and q must be a positive number.
q < 0
system evolves heat
When the system loses energy as heat to the surroundings, the effect is to decrease its internal energy (ΔE < 0), and q must be a negative number
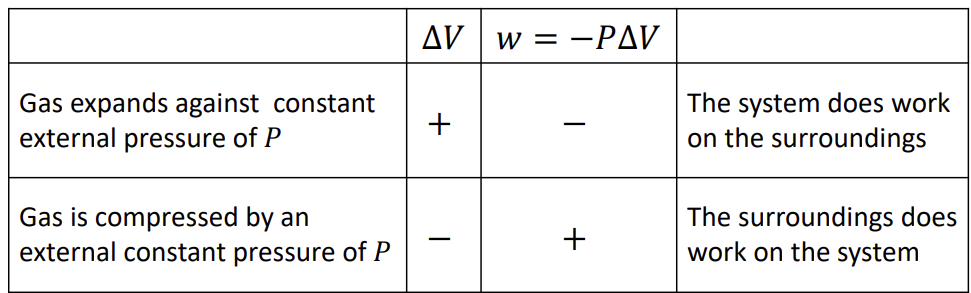
w > 0
surroundings does work on system
When the surroundings does work on the system, the effect is to increase the internal energy of the system, and w must be a positive number
w < 0
system does work on surroundings
When the system does work on the surroundings, the effect is to decrease its internal energy and w must be a negative number
(U)
Internal Energy
(U) = Thermal energy + Chemical Energy
Thermal Energy
~Kinetic energy
Chemical Energy
~Potential Energy
q
heat, internal energy transferred between system and surroundings
J
SI Unit for heat, 1 cal = 4.184 J
qsys
heat of the system, positive when it gains heat, negative when it loses heat
qsurr
heat of the surroundings, positive when it gains heat, negative when it loses heat
Relationship between qsys and qsurr
qsys+qsurr = 0
qsys = -qsurr
C
heat capacity
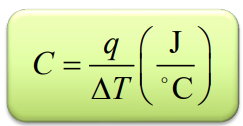
Csp and C(molar) in relation to q
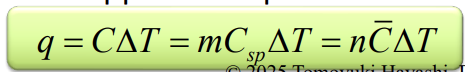
Bond breaking
Chemical energy absorbed, heat
Bond forming
Chemical energy released, heat released
Exothermic
releases heat, -H, qrxn = negative
Endothermic
absorbs heat, +H, qrxn = positive
Bomb Cal equations
qrxn = -qcal
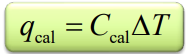
Pressure-volume work
wsys = (-F)(h)
= -(F/A)(hA)
only works if P is constant
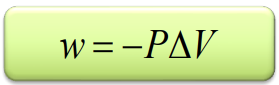
Sign convention of work
Intensive state function
Does not depend on the quantity of the substance
Ex) pressure, temp
Extensive state function
Depends on the quantity of the substance
Ex) volume, U
Path dependent function
functions that depend on how the system changes from the initial state to the final state
Ex) Heat, work
Law of thermodynamics in relation to U
If we know q and w we can get deltaU
The energy of a isolated system is constant
q=0 w=0 → dealtaU=0
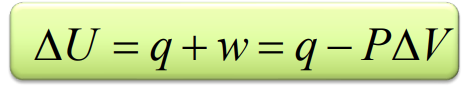
Enthalpy
H = U +PV
at constant P, the change in enthalpy is the heat gained or lost
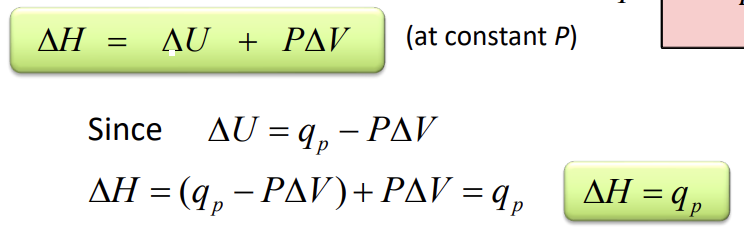
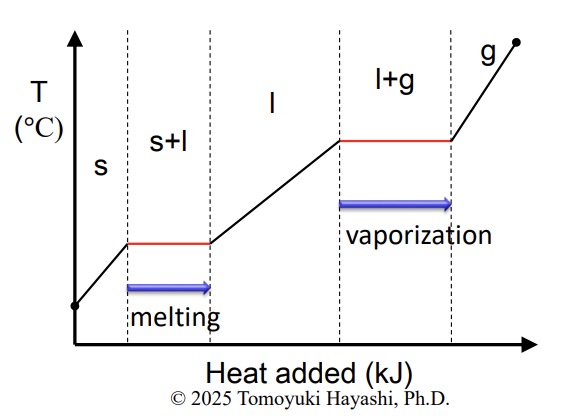
Enthalpy of fusion
The enthalpy change of 1 mol of a substance during fusion
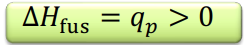
Enthalpy of vaporization
enthalpy of change of 1 mol of a substance during the vaporization
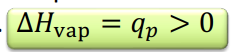
Fusion
melting
Heating curve