Trace Evidence - Hair
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Hair is made of ___?
Keratin
What is the structure of hair?
Cuticle (outside)
Cortex (main)
Medulla (middle)
Properties of the Cuticle
Made of overlapping scales that form the protective layer of hair
Scales point towards the distal end of the hair
Has a high cystine concentration
Coronal Scale Pattern

Spinous Scale Pattern

Imbricate Scale Pattern
Pattern found in human hair.

Pigment is contained in the ___?
Cortex
Eumelanin
Brownish-black pigment
Pheomelanin
Reddish-yellow pigment
Properties of the Medulla
Located in the center of the hair, and runs down lengthwise
Made of air-filled vacuoles
NOT present in all hair
Can be classified as:
Fragmentary/trace
Discontinuous/broken
Continuous
Uniserial ladder structured medulla

Multi-serial ladder structured medulla

Cellular (vacuolated) structured medulla

Lattice structured medulla

What are the three phases of hair growth?
Anagen
Catagen
Telogen
Anagen Phase Characteristics
Active growth phase
Follicle extends to greatest depth
Roots will be soft and formless. May have tissue and pigment adhering to them
If a found hair root is in this phase, it is a good indication that the hair has been pulled out.
85% - 95% of human scalp hairs in this phase.
Lasts 2 - 6 years
Catagen Phase Characteristics
Hair will start to form a keratinized root bulb, with a bulbous appearance
Melanin production ceases
1% - 2% of hair in this phase
Lasts several weeks
Telogen Phase Characteristics
The resting phase of the hair
Root is enlarged and bulbous in humans
Hairs naturally shed in this phase (exogen)
10% - 15% of hairs in this phase
Period lasts a few months
How fast does hair grow?
On average of 1cm a month
Can you determine age of an individual based on microscopical examination of the hair?
Yes, to some extent.
0 - 3 years will have hair that increases in cross section size, slowing at age 3, but continuing into adolescence.
Ratio of medulla’s size to hair diameter (medullary index). Tends to increase in advancing age.
Pigment is produced in gray hair; T/F
False
Why must a known sample of hair be collected?
To perform microscopic hair comparison.
Known samples are typically pulled from the scalp and pubic regions
Collected by both combing and plucking
Important to collect 25 hairs from head/pubic region.
If from head: 5 from top, front, back, and both sides
Important to collect complete hairs (with roots!)
How many types of human hair are there?
Three
Lanugo Hair
Vellus Hair
Terminal Hair
Lanugo Hair Characteristics
Present before or shortly after birth. Fine, with no medulla (unmedullated) or pigment.
Vellus Hair Characteristics
Fine, no medulla (unmedullated), no pigment. Present on all skin surfaces, save for friction ridge skin.
Terminal Hair Characteristics
Primary terminal hairs include head, eyebrow, eyelash hairs.
Secondary terminal hairs include pubic, axilla, and beard hairs. Resulted from vellus hairs becoming terminal hairs.
How many types of animal hairs are there?
Three:
Guard hair (overhairs)
Fur hairs (underhairs)
Vibrissa (whiskers)
Guard Hairs (Overhairs)
Longer and stiffer than other hairs.
Have the morphological characteristics that allow them to be classified as that particular animal.
Fur Hairs (Underhairs)
Fine and undulating hairs which mostly lack morphological characteristics.
Vibrissa (whiskers)
Long, stiff hairs that are less likely to be encountered in forensic casework.
Is the cuticle colored?
Depends.
Unless the hair has been dyed, apart from the natural yellowish color of keratin, the cuticle will not be colored.
What are ovoid bodies?
Large agglomerations of pigments found in the cortex
Characteristics of the Medulla
Air Filled
Not present in all hairs
Appears black in transmitted light.
Appears white in reflected light.
No more than 1/3 of the hair diameter and are not structured. (amorphous)
Animal hairs show variation in diameter. What is the shield?
The thicker part of the hair.
Animal hairs show variation in diameter. What is the shaft?
The thinner part of the hair.
Banding
Abrupt pigment changes in animal hair.
Cortical Fusi
Small, elongated air spaces in the cortex.
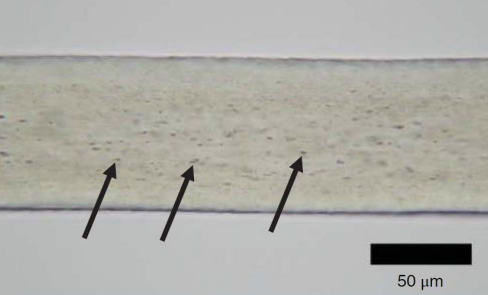
Animal Hair Medulla Characteristics
Wide/structured medullas
Have pigment in the medulla.
will be black in transmitted light
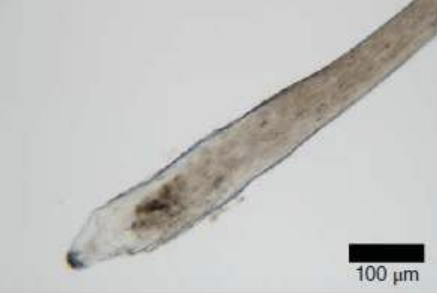
Anagen hair characteristics
Roots not fully keratinized
Pigmentation fully extends to roots
Exposure to air will cause roots to harden
Expect to see a follicular sheath
Indication that the hair was pulled
Root may also be sticky

Telogen hair characteristics
will be highly keratinized
Shaft proximal to root will lack pigment, but may have cortical fusi
Human hairs form into a club shaped root
Will lack a medulla

Catagen hair characteristics
root bulb will be forming and starting to keratinize
Some root sheath may be present
Postmortem changes to hair
Hairs may develop a band in the shaft proximal to an incompletely keratinized root of a hair that is still attached to a deceased individual.
