natural killer cells
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
hunters for intracellular virus infections in the early phase, immunity
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What do NK cells respond to?
viruses infecting cells
what do NK cells make when activated?
cytokines to promote viral resistance and to prime the adaptive immune response
what is an NK cell?
a unique lymphocyte that protects against viruses
When a cell becomes infected with a virus, what does it do to call for help?
secretion of interferons
When these interferons are secreted from an infected cell, what happens?
induced resistance to viral replication in cells
increased MHC class I expression
presentation of antigens to lymphocytes
activation of NK cells to kill infected cells
Can macrophages activate NK cells? How?
yes, through the production of cytokine IL-12
What is a type 1 interferon?
a type 1 interferon is a cytokine that alerts cells that there are infected cells, they call out for activation of NK cells and start an adaptive immune response
How does an NK cell kill an infected cell?
It must be cell to cell contact
use perforin and granzyme B to lyse the target cell or trigger apoptosis
When an NK cell attacks a target, how does it protect itself from the enzymes it secretes?
Contains a protease called Cathepsin B
How are NK cells inhibited from killing cells at random?
normal cells have a self-MHC class I molecule bound to stop activation
there are inhibitory receptors on an NK cell that interact with the self MHCI
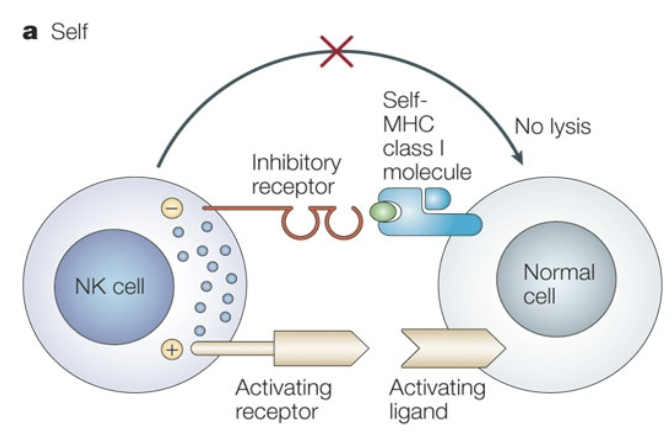
When an NK cell approaches a cell with lowered MHCI expression, what does it do?
attack the cell
What kinds of molecules can also be detected by an NK cell?
stress molecules and infection molecules
some times they can sense cancer and attack tumors
How does the cell account for surveillance in the cytosol?
cytosolic pattern recognition receptors
If there is pathogenic DNA in an endosome, how does the endosome respond?
there is a cytosolic receptor called TLR9 that drives the production of type 1 interferons to let cells know that this cell is infected
If there is pathogenic DNA in the cytosol, how does the cell respond?
There is a cytosolic receptor called cGAS-STING that signals to make type 1 interferons and cytokines to let cells know that cell is infected
Is DNA in the cytosol normal?
NAURRRR
If there is double stranded RNA in the cytosol, how does the cell respond?
the RIG-1 sensor binds to a structure called MAVS on the mitochondria and activates cytokines and type 1 interferons
When type 1 interferons like IF-alpha and IF-beta are released, what responses do they cause?
IFIT genes induce proteins to inhibit viral RNA translation
IFITM genes inhibit viral fusion at the cell membrane
MxA proteins cluster around viral proteins to inhibit replication
ISG-15 binds to viral proteins to inhibit functioning