MAME Ch. 1 - 3
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These are the questions asked during discussions and quizzes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
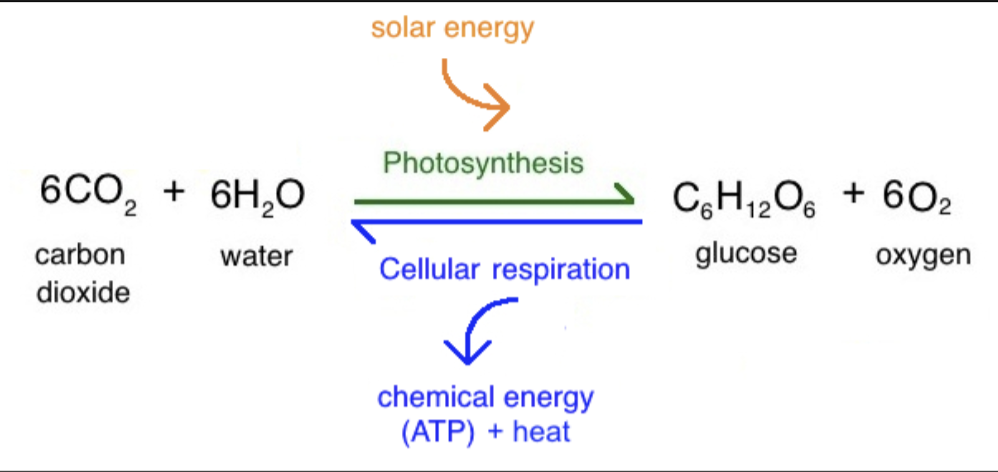
Knowing the difference between primary production (commonly called photosynthesis) and decomposition (also known as “respiration”) is easiest if you can recognize which types of compounds (organic or inorganic) are on which side of the equation. The forward and reverse reactions for respiration and photosynthesis are shown in the above image from Khan Academy College Biology. There is a Carbon-containing molecule on each side of the equation. On which side of the equation is the Carbon molecule an ORGANIC molecule?
Right
Although the individual steps in performing cellular respiration and photosynthesis are different, there is something common for both of these cellular processes. This thing in common is used for the same purpose: acquiring and storing energy. What is it?
Redox reactions (reactions involving electron transfers)
What are the three Domains encompassing all life on earth?
Bacteria, Archaea, & Eukarya
What is the structural difference between gram negative and gram positive bacteria?
Thickness of the peptidoglycan layer
Features shared by prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Genetic materials, ribosomes, cell membranes, and cytoplasm
Features unique to prokaryotic cells
Smaller, no organelles, cell wall, no nucleus, binary fission, and circular chromosome
Features unique to eukaryotic cells
May or may not have a cell wall, membrane-bound organelles, linear
chromosomes, and the nucleus
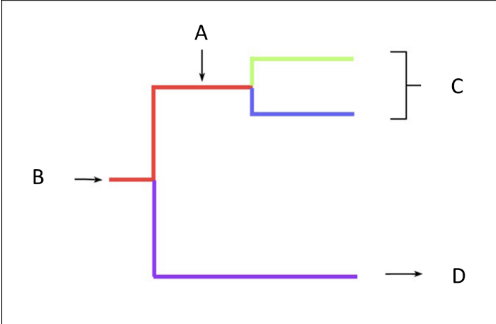
There are four features (labeled A, B, C, and D) on the cladogram shown below. Name and briefly describe each of the four features in the space below. What feature is C?
Root – last common ancestor of all organisms in a cladogram
Node – last common ancestor of organisms on this branch/part of tree
Leaf/Tip/Organism – individual species/organism
Time/distance scale – the measurement of divergence in either sequence differences or time
Clade – group of related organisms
Clade
Which type of organisms have linear chromosomes?
Eukaryotes
Unit of organization in eukaryotic DNA; humans have 23 pairs ______.
chromosome
Alternate forms of a gene
Allele
A segment of DNA that codes for the production of a particular protein
Gene
Write the name of the biological molecules next to their appropriate monomers.
Nucleic acids
Nucleotides
Write the name of the biological molecules next to their appropriate monomers.
Proteins
Amino acids
Write the name of the biological molecules next to their appropriate monomers.
Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides
Write the name of the biological molecules next to their appropriate monomers.
Lipids
Fatty acids
Cell wall composition can help us tell different groups of organisms apart. Which group of organisms listed below has chitin as a unique cell wall component?
Fungi
Top-down Control
Pressures that are applied by a higher trophic level to control the population dynamics of the ecosystem
Bottom-up Control
Pressures that are applied to lower trophic levels (e.g. producers) – such as the limited availability of resources
All types of marine bacteria grow at the same rate.
False
“Who” among the wide variety of marine microbes are at the base of the food web in ocean surface waters, and briefly, how/why?
Phytoplankton. Phytoplankton use pigments like Chlorophyll a to capture energy from light, converting light energy into chemical energy
How do different types of marine microbes, like phytoplankton that make their own food and bacteria that break down organic material, affect whether the ocean is producing more oxygen than it uses, or using more than it produces?
Phytoplankton create oxygen through photosynthesis, while bacteria consume oxygen through respiration.
For most types of bacteria, we know the nature of the genome is _______.
Haploid, circular chromosome
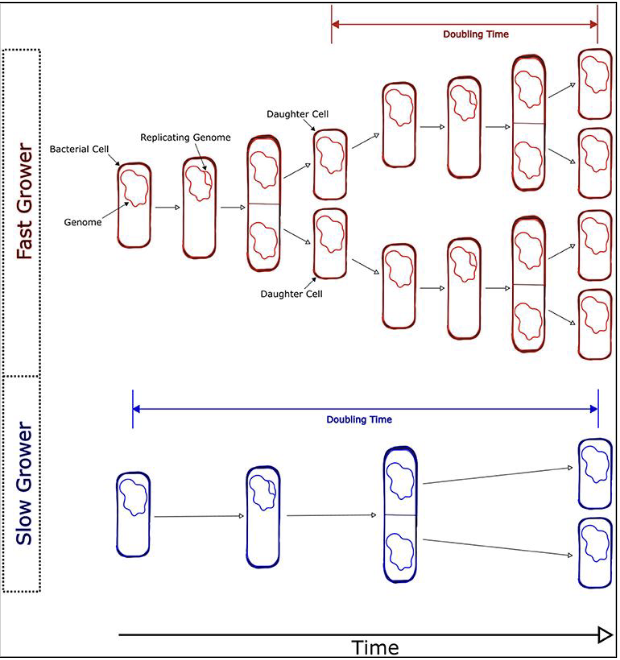
For a bacterium in the open ocean with a doubling time (generation time) of 2 days.
Consider the population of this species: In one mL, the population is 1,000 cells.
After 6 days (3 generations), what will be the abundance of that species’ cells in that 1 mL of seawater?
Assumptions:
No predation
No viral infection/lysis
Enough organic material for the growth of this species at this growth rate
8,000 cells/mL
The average large zooplankton cell is approximately ____ than the average marine virus.
10,000 times larger
What type of plankton net can be used to catch marine bacteria for getting their DNA?
None; collect water with a Niskin bottle, then bring on board and filter with 0.2 μm filter, then extract DNA from the filter.
I understand that eDNA can reveal information about bacterial genes, but how do scientists distinguish whether a detected gene is actively being expressed in the environment instead of DNA merely present in dormant cells?
We extract RNA from the filtered seawater and determine if the gene of interest is in the mRNA.
Consider these two different strains of bacteria:
Strain A has high codon redundancy for an important protein involved in cellular growth.
Strain B has low codon redundancy for the amino acids in the sequence of the protein mentioned above.
Which of the following is the most likely outcome for the growth rate of Strain A compared to Strain B, and why?
Strain A will have a faster growth rate because the high codon redundancy allows for more efficient protein synthesis and quicker cellular response.
Let’s compare two extreme “types” of bacteria:
The types of bacteria that live in humans (e.g. E. coli, a strain within the gut bacteria)
* E. coli genome is ~4,6000,000 bp long
Those that live as free-floating bacterioplankton way out in the open ocean
* A very famous one (SAR11), genome is ~1,3000,000 bp long
Which one has a doubling time of 20 minutes and which one has a doubling time of 2 days?
SAR11 is 2 days, and E. coli is 20 minutes
For a particular marine macro-organism, what percent of the bacteria associated with their external microbiomes and/or in their gut microbiomes originated from seawater bacterioplankton?
What percent of their microbiomes’ microbes are descendants of bacterioplankton that were originally floating in the surrounding seawater bacterioplankton community?
Which question would you ask FIRST to then start to answer the questions on the left?
How old is the macro-organism?