financial accounting
0.0(0)Studied by 13 people
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Last updated 11:08 AM on 11/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
1
New cards
cash flow from operating activities
- working capital = current asset - current liabilities
- indicator of company's ability to generate sustainable cash flows through operations and management of working capital
- focus on income statement and changes in current assets and liabilities from balance sheet
- indicator of company's ability to generate sustainable cash flows through operations and management of working capital
- focus on income statement and changes in current assets and liabilities from balance sheet
2
New cards
Cash inflows for operating activities
1. sale of goods or services
2. collection of interest and dividends
2. collection of interest and dividends
3
New cards
cash outflows for operating activities
1. purchase of inventory
2. payment for operating expenses
3. payment of interest
4. payment of income taxes
2. payment for operating expenses
3. payment of interest
4. payment of income taxes
4
New cards
cash flow from investing activities
focus on changes in PPE, long term investments and assets from balance sheet(depreciation, gains/losses on sale of PPE and other LT assets)
5
New cards
cash inflow for investing activities
1. sale of debt/equity investments
2. sale of PPE
3. Collection of loan/notes receivable
2. sale of PPE
3. Collection of loan/notes receivable
6
New cards
cash outflow for investing activities
1. purchase of PPE
2. purchase of debt or equity
3. loans to other corporations
2. purchase of debt or equity
3. loans to other corporations
7
New cards
cash flows from financing activities
focus on long-term debt and stockholder's equity from balance sheet
8
New cards
cash inflows for financing activities
1. issuance of bonds or notes payable
2. issuance of stock
3. reissuance of treasury stock
2. issuance of stock
3. reissuance of treasury stock
9
New cards
cash outflows for financing activities
1. repayment of bonds or notes payable
2. acquisition of treasury stock
3. payment of dividends
2. acquisition of treasury stock
3. payment of dividends
10
New cards
noncash activities
-significant investing and financing activities that do not affect cash
-reported after the cash flow statement or in a note to the financial statements
Examples
- purchase long term assets by issuing debt
-reported after the cash flow statement or in a note to the financial statements
Examples
- purchase long term assets by issuing debt

11
New cards
indirect method (operating activities)
1. begin with net income
2. list adjustments to net income to arrive at operating cash flows
2. list adjustments to net income to arrive at operating cash flows
12
New cards
direct method (operating activities)
adjust the items in the income statement to directly show the cash inflows and outflows from operations
13
New cards
operating activities (indirect method adjustments)
1. Non cash items (depreciation expense)
2. Non operating items (gains and losses on sale of assets)
3. changes in current assets and current liabilities (increase in account receivables is the amount of revenue reported in the income statement but not yet collected in cash)
2. Non operating items (gains and losses on sale of assets)
3. changes in current assets and current liabilities (increase in account receivables is the amount of revenue reported in the income statement but not yet collected in cash)
14
New cards
indirect method (adjustment for non-cash activities included in net income)
+ amortization expense
+depreciation expense
+depreciation expense
15
New cards
indirect method (adjustment for non-operating activities included in net income)
+ loss on sale of assets
- gain on sale of assets
- gain on sale of assets
16
New cards
indirect method (adjustment for non cash part of operating activities included in net income)
- increase in a current asset
+decrease in a current asset
-increase in a current liability
+decrease in a current liability
+decrease in a current asset
-increase in a current liability
+decrease in a current liability
17
New cards
direct method (cash received from customers)
net sales-increase in accounts receivable=cash received from customers
18
New cards
direct method (cash paid to suppliers)
cost of goods sold - decrease in inventory = purchases
purchases + decrease in accounts payable = cash paid to suppliers
purchases + decrease in accounts payable = cash paid to suppliers
19
New cards
direct method (cash paid for operating expenses)
operating expenses + increase in prepaid rent = cash paid for operating expenses
20
New cards
direct method (cash paid for interest expense)
interest expense - increase in interest payable = cash paid for interest
21
New cards
direct method (cash paid for income taxes)
income tax expense + decrease in income tax payable = cash paid for income taxes
22
New cards
cash flow from operating activities
+sale of long-term assets
-purchases of long term assets
+collections of notes receivables
-loans to others
-purchases of long term assets
+collections of notes receivables
-loans to others
23
New cards
cash flows from financing activities
+ issuance of shares
- purchases of treasury shares
+ sale of treasury stock
+issuance of notes and bonds payable (face value)
-payment of notes and bonds payable
-payment of dividens
- purchases of treasury shares
+ sale of treasury stock
+issuance of notes and bonds payable (face value)
-payment of notes and bonds payable
-payment of dividens
24
New cards
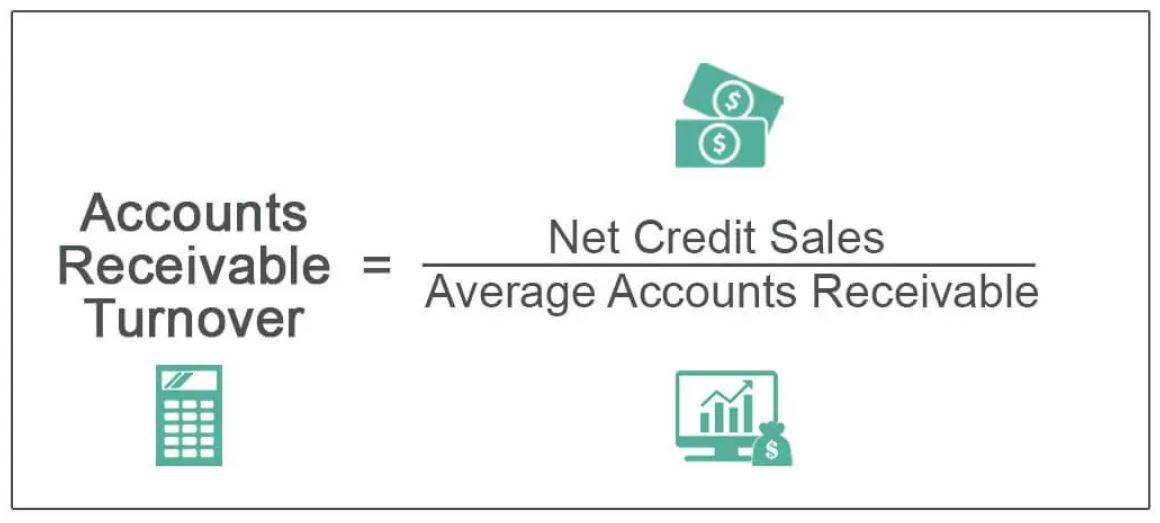
receivables turnover ratio (risk ratio)
measures how many times receivables are collected during year
higher ratio indicates ability to quickly turn receivables into cash
low ratio indicates trouble collecting receivables
higher ratio indicates ability to quickly turn receivables into cash
low ratio indicates trouble collecting receivables
25
New cards
average collection period(risk ratio)
measures the days it takes to convert receivables into cash
shorter period maximize the speed of cash inflow
AVP= 365/receivables turnover ratio
shorter period maximize the speed of cash inflow
AVP= 365/receivables turnover ratio
26
New cards
inventory turnover ratio(risk ratio)
measures how many times average inventory is sold during the year
ITR= cost of goods sold/average inventory
ITR= cost of goods sold/average inventory
27
New cards
Average days in inventory(risk ratio)
measures the average number of days it takes to sell its entire inventory during the year
ADI=365/inventory turnover ratio
ADI=365/inventory turnover ratio
28
New cards
current ratio(risk ratio)
compares current asset to current liabilities
A high current ratio indicates sufficient assets to cover its current obligations
CA= current assets/current liabilities
A high current ratio indicates sufficient assets to cover its current obligations
CA= current assets/current liabilities
29
New cards
Acid-test ratio(risk ratio)
more conservative measure of a company's ability to pay current liabilities
ATR= (cash+current investments+A/R)/current liabilities
ATR= (cash+current investments+A/R)/current liabilities
30
New cards
Debt to Equity Ratio(risk ratio)
indicates the risk of bankruptcy
DtoER=Total liabilities/stockholder's equity
DtoER=Total liabilities/stockholder's equity
31
New cards
times interest earned ratio(risk ratio)
compares interest payments with income available to pay them
measure of solvency
TIER=(net income + interest expense +tax expense)/interest expense
measure of solvency
TIER=(net income + interest expense +tax expense)/interest expense
32
New cards
gross profit ratio (profit ratio)
indicates the portion of each dollar of sales above its cost of goods sold
GPR=gross profit/net sales
gross profit = net sales - cost of goods sold
GPR=gross profit/net sales
gross profit = net sales - cost of goods sold
33
New cards
return on assets (profit ratio)
measures the income the company earns on each dollar invested in assets
ROA=net income/average total assets
net income/average total assets=(net income/net sales)*(net sales/average total assets)
ROA=net income/average total assets
net income/average total assets=(net income/net sales)*(net sales/average total assets)
34
New cards
profit margin (profit ratio)
measures the income earned on each dollar of sales
PM=net income/net sales
PM=net income/net sales
35
New cards
asset turnover (profit ratio)
measures sales volume in relation to the investment in assets
AT = net sales / average total assets
AT = net sales / average total assets
36
New cards
return on equity (profit ratio)
measures the income earned for each dollar in stockholders' equity
ROE= net income/average stockholders' equity
ROE= net income/average stockholders' equity
37
New cards
earnings per share (profit ratio)
EPS= (net income - dividends on preferred stock)/(average shares of common stock outstanding)
38
New cards
price-earnings ratio (profit ratio)
compares a company's share price with its earnings per share
PER= stock price/earnings per share
PER= stock price/earnings per share
39
New cards
balance sheet
Asset= liabilities + equity
assets = liabilities + (stockholder's equity + (revenue-expenses)-dividends)
net assets = assets - liabilities
assets = liabilities + (stockholder's equity + (revenue-expenses)-dividends)
net assets = assets - liabilities
40
New cards
income statement
Net income = revenues - expenses

41
New cards
statement of stockholder's equity
ending retained earnings = beginning retained earnings + net income - dividends
stockholder's equity = common stock/ share capital + retained earnings
stockholder's equity = common stock/ share capital + retained earnings
42
New cards
matching principle
Revenue of the period is matched with expenses required to create those revenues
43
New cards
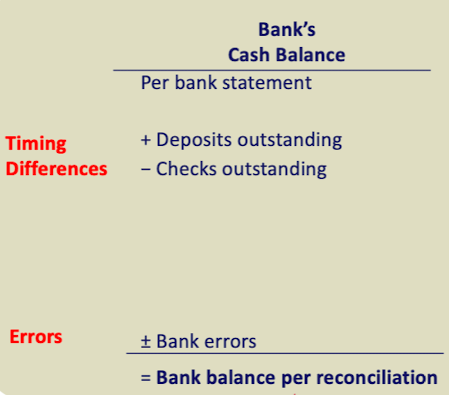
Bank's cash balance (bank reconciliation)
per bank balance
+deposit outstanding
-checks outstanding
+/- banks errors
+deposit outstanding
-checks outstanding
+/- banks errors
44
New cards
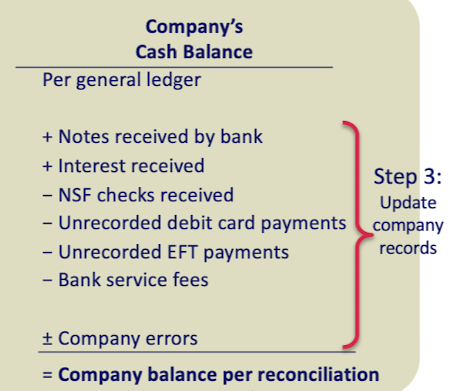
company's cash balance (bank reconciliation)
per general ledger
+notes received by bank
+interest received
-NSF checks received
-unrecorded debit card payments
-unrecorded EFT payments
-bank service fees
+/- company errors
+notes received by bank
+interest received
-NSF checks received
-unrecorded debit card payments
-unrecorded EFT payments
-bank service fees
+/- company errors
45
New cards
net sales
sales revenue (including trade discounts)-sales returns and allowances - sales discounts = net sales
46
New cards
FOB shipping point
-buyer pays for the freight charge
-freight is part of inventory cost
-buyer records it when the goods leave the supplier
-seller records it when the goods leave the seller
-freight is part of inventory cost
-buyer records it when the goods leave the supplier
-seller records it when the goods leave the seller
47
New cards
FOB shipping destination
- freight charge is paid by the seller
- freight charges become part of cost of goods sold
-buyer records it when they receive the goods
-seller records it when the buyer receive the goods
- freight charges become part of cost of goods sold
-buyer records it when they receive the goods
-seller records it when the buyer receive the goods
48
New cards
inventory purchases
purchase price + freight in - purchase returns - purchase allowances - purchase discounts = net purchases
49
New cards
freight in
transportation cost paid by the buyer under FOB shipping point
50
New cards
Inventory sales
sales revenue - sales returns and allowances - sales discounts = net sales
51
New cards
weighted average cost
average cost per unit = cost of goods available/number of units available
goods available = beginning inventory + purchases
goods available = beginning inventory + purchases