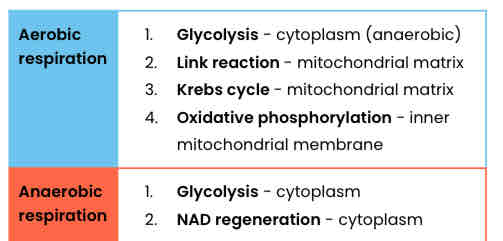
Topic 5 - Energy transfers in and between organisms
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
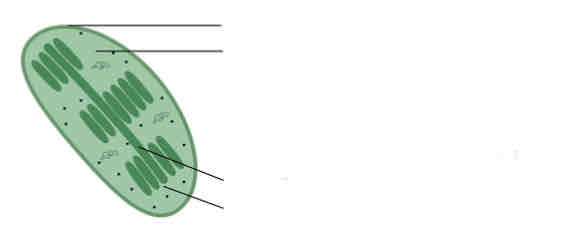
Label this diagram
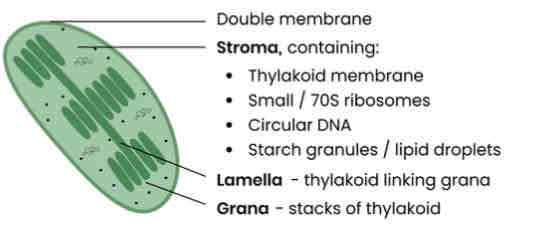
What are the stages of photosynthesis?
1. Light dependent reaction
○ Thylakoid membrane of chloroplast
2. Light independent reaction
○ Stroma of chloroplast
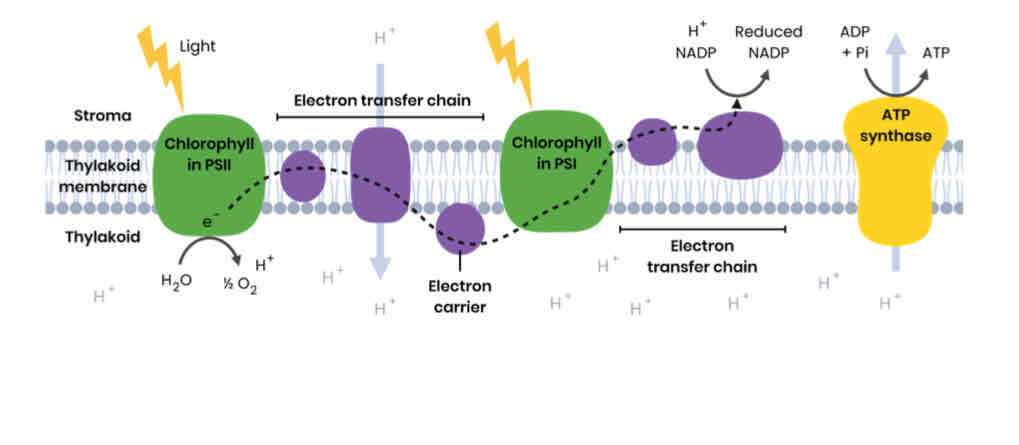
Describe photoionisation in the light-dependent reaction (LDR)
● Chlorophyll absorbs light energy which excites its electrons (higher energy level)
● So electrons are released from chlorophyll (chlorophyll becomes positively charged)
Describe what happens after photoionisation in the LDR
1. Electrons move along electron transfer chain (electron carriers), releasing energy
2. energy is used to pump protons from stroma into thylakoid
3. Protons move by facilitated diffusion down electrochemical gradient into stroma via ATP synthase
4. Energy used to join ADP and Pi to form ATP (photophosphorylation)
5. NADP accepts a proton and an electron to become reduced NADP
Describe photolysis of water in the LDR
● Water splits to produce protons, electrons and oxygen (H2O → 1⁄2 O2 + 2e- + 2H+) ○ Electrons replace those lost from chlorophyll
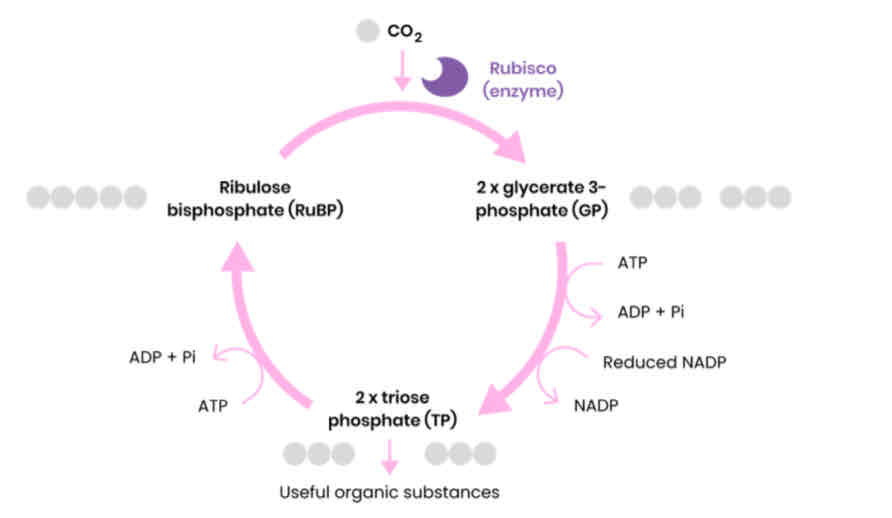
Describe and draw the light-independent reaction of photosynthesis (Calvin cycle)
1. CO2 reacts with ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP)
○ Catalysed by the enzyme rubisco
2. Forming 2 glycerate 3-phosphate (GP) molecules
3. GP reduced to triose phosphate (TP)
○ Using products from LDR - reduced NADP and energy from ATP
4. Some TP converted to useful organic substances (eg. glucose) = 1/6
5. Some TP used to regenerate RuBP in the Calvin cycle (using energy from ATP)
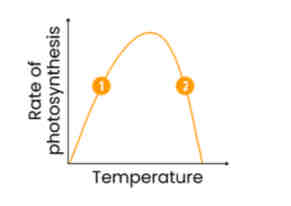
Describe and explain how temperature affects rate of photosynthesis
1. As temperature increases, rate increases
○ Enzymes eg. rubisco gain kinetic energy
○ So more enzyme-substrate (E-S) complexes form
2. Above an optimum temperature, rate decreases
○ Enzymes denature as H bonds in tertiary structure break
○ So fewer enzyme-substrate (E-S) complexes form
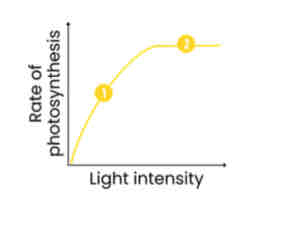
Describe and explain how light intensity affects rate of photosynthesis
1. As light intensity increases, rate increases
○ LDR increases (eg. more photoionisation of chlorophyll) so more ATP and reduced NADP produced
○ So LIR increases = more GP reduced to TP and more TP regenerates RuBP
2. Above a certain light intensity, rate stops increasing
○ Another factor is limiting eg. temperature / CO2 concentration
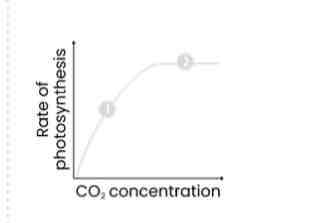
Describe and explain how CO2 concentration affects rate of photosynthesis
1. As CO2 concentration increases, rate increases
○ LIR increases
○ As more CO2 combines with RuBP to form GP
○ So more GP reduced to TP
○ So more TP converted to organic substances and more RuBP regenerated
2. Above a certain CO2 concentration, rate stops increasing
○ Another factor is limiting eg. temperature / light intensity
Explain the key consideration when evaluating data relating to agricultural practices used to overcome the effect of limiting factors
● Agricultural practice should increase rate of photosynthesis, leading to increased yield
○ As more glucose produced for faster respiration
○ So more ATP to release energy for growth eg. cell division, protein synthesis
● But profit from extra yield should be greater than costs (money & environmental costs)

Label this mitochondria
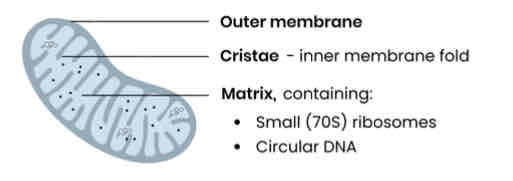
Why is respiration important?
● Respiration produces ATP (to release energy)
● For active transport, protein synthesis etc.
Two types of phosphorylation occur during respiration:
1. Substrate-level: glycolysis & Krebs cycle
A single reaction involving the direct transfer of a phosphate group from a donor molecule to ADP.
2. Oxidative: electron transport chain
A series of oxidation reactions that produce sufficient energy to form ATP from ADP and phosphate.
Summarise the stages of aerobic & anaerobic respiration
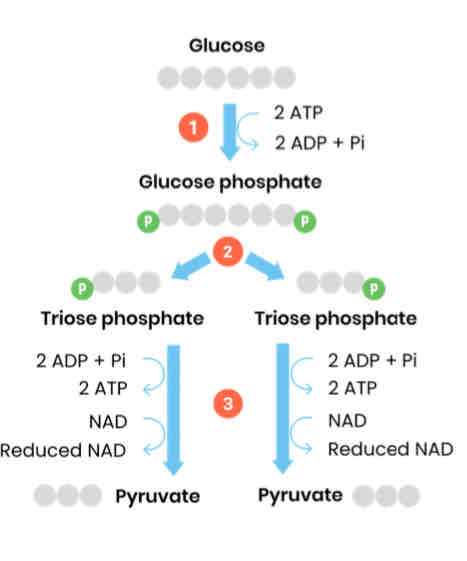
Describe and draw the process of glycolysis
1. Glucose phosphorylated to glucose phosphate
○ Using inorganic phosphates from 2 ATP
2. Hydrolysed to 2 x triose phosphate
3. Oxidised to 2 pyruvate
○ 2 NAD reduced
○ 4 ATP regenerated (net gain of 2)
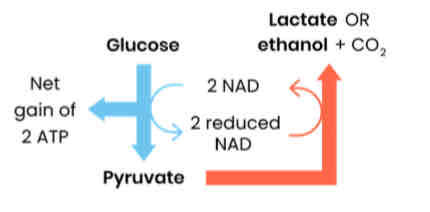
Explain and draw what happens after glycolysis if respiration is anaerobic
1. Pyruvate converted to lactate (animals & some bacteria) or ethanol (plants & yeast)
2. Oxidising reduced NAD → NAD regenerated
3. So glycolysis can continue (which needs NAD) allowing continued production of ATP
Suggest why anaerobic respiration produces less ATP per molecule of glucose than aerobic respiration
● Only glycolysis involved which produces little ATP (2 molecules)
● No oxidative phosphorylation which forms majority of ATP (around 34 molecules)
What happens after glycolysis if respiration is aerobic?
Pyruvate is actively transported into the mitochondrial matrix.
Describe the link reaction
1. Pyruvate oxidised (and decarboxylated) to acetate
○ CO2 produced
○ Reduced NAD produced (picks up H)
2. Acetate combines with coenzyme A, forming Acetyl Coenzyme A
Products per glucose molecule: 2 x Acetyl Coenzyme A, 2 X CO2 and 2 X reduced NAD
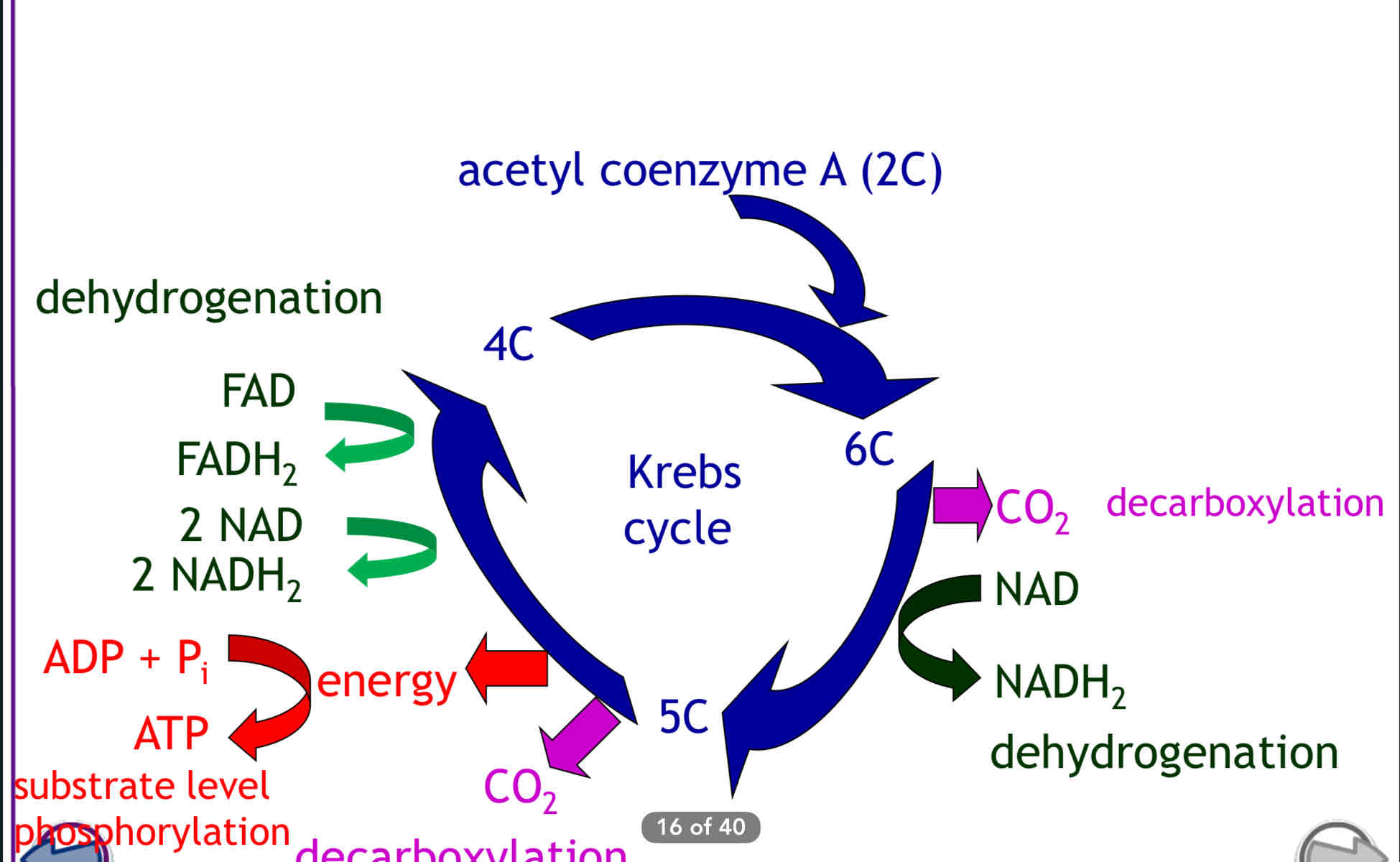
Describe and draw the Krebs cycle
1. Acetyl coenzyme A (2C) reacts with a 4C molecule
○ Releasing coenzyme A
○ Producing a 6C molecule that enters the Krebs cycle
2. In a series of oxidation-reduction reactions, the 4C molecule is regenerated and:
○ 2xCO2lost
○ Coenzymes NAD & FAD reduced
○ Substrate level phosphorylation
(direct transfer of Pi from intermediate compound to ADP) → ATP produced
Products per glucose molecule: 6 x reduced NAD, 2 x reduced FAD, 2 x ATP and 4 x CO2
Describe the process of oxidative phosphorylation
1. Reduced NAD/FAD oxidised to release H atoms → split into protons (H+) and electrons (e-)
2. Electrons transferred down electron transfer chain (chain of carriers at decreasing energy levels)
○ By redox reactions
3. Energy released by electrons used in the production of ATP from ADP + Pi (chemiosmotic theory):
○ Energy used by electron carriers to actively pump protons from matrix → intermembrane space
○ Protons diffuse into matrix down an electrochemical gradient, via ATP synthase (embedded)
○ Releasing energy to synthesise ATP from ADP + Pi
4. In matrix at end of ETC, oxygen is final electron acceptor (electrons can’t pass along otherwise)
○ So protons, electrons and oxygen combine to form water
Give examples of other respiratory substrates
Breakdown products of lipids and amino acids, which enter the Krebs cycle. For example:
● Fatty acids from hydrolysis of lipids → converted to Acetyl Coenzyme A
● Amino acids from hydrolysis of proteins → converted to intermediates in Krebs cycle
The formula for working out a respiratory quotient is:
Respiratory Quotient (RQ) = volume of CO2 produced/ volume of O2 used
R.Q. values of different respiratory substrates:
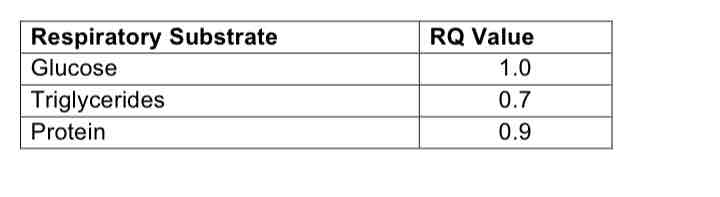
An RQ value of greater than 1 indicates an
organism is short of oxygen and having to respire anaerobically as well as aerobically.