Molecular Geometry
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
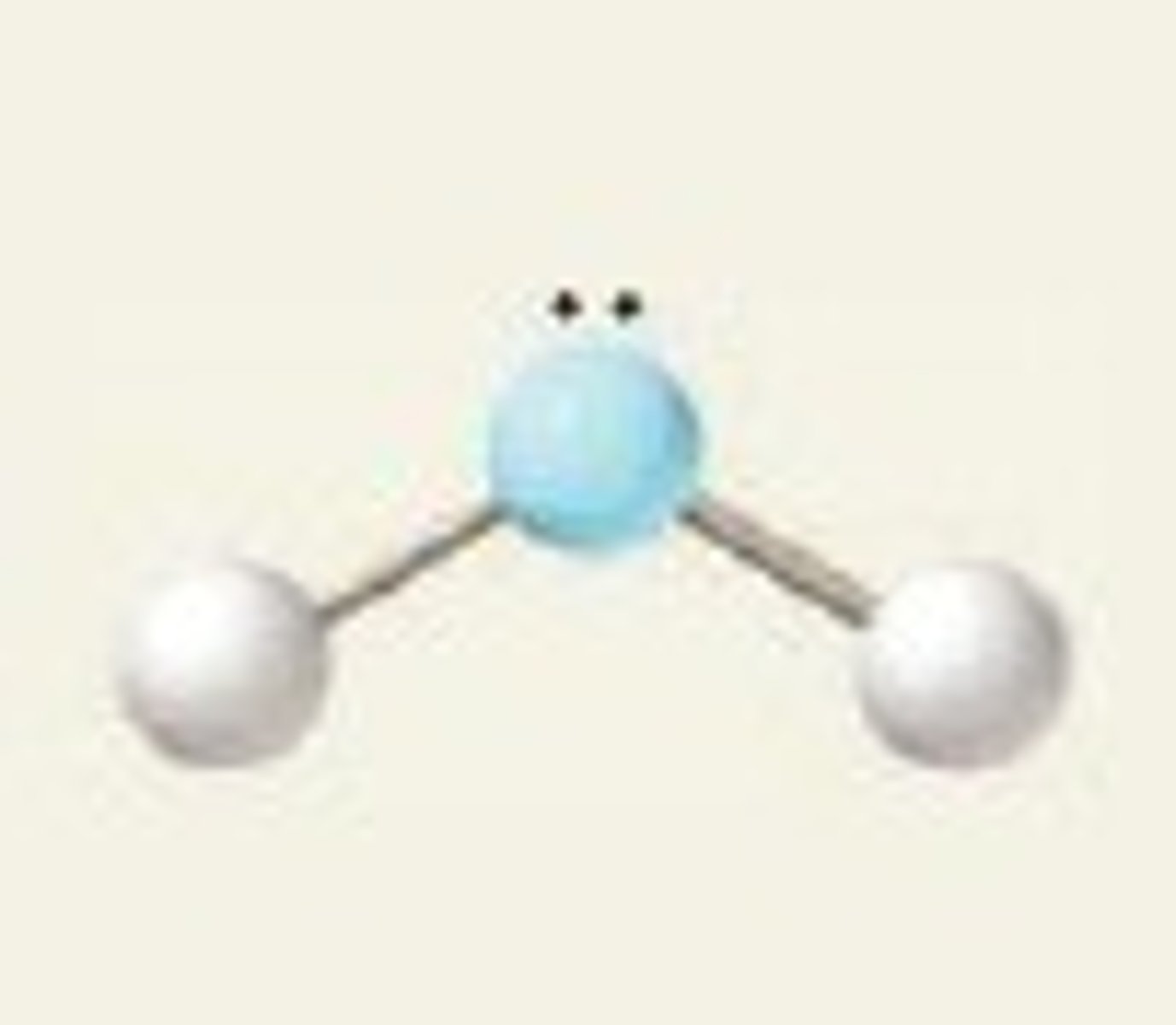
bent, 120
2 BP and 1 LP

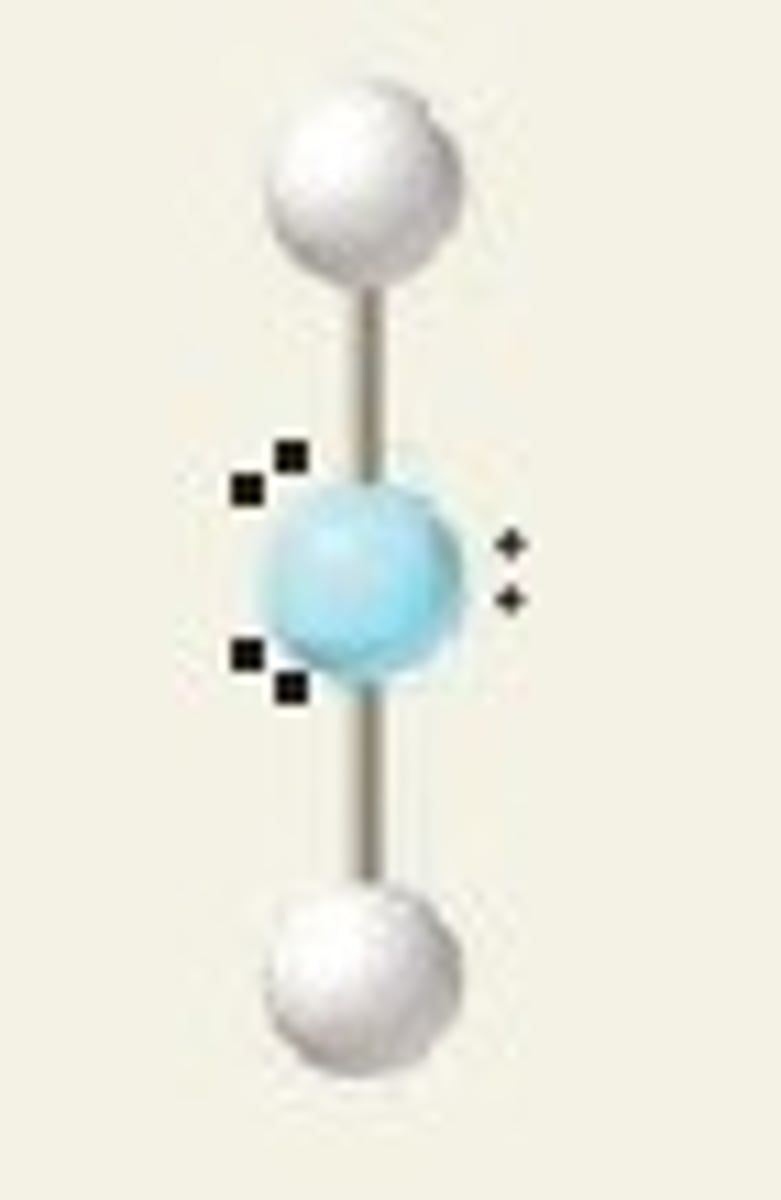
linear, 180
2 BP and 3 LP
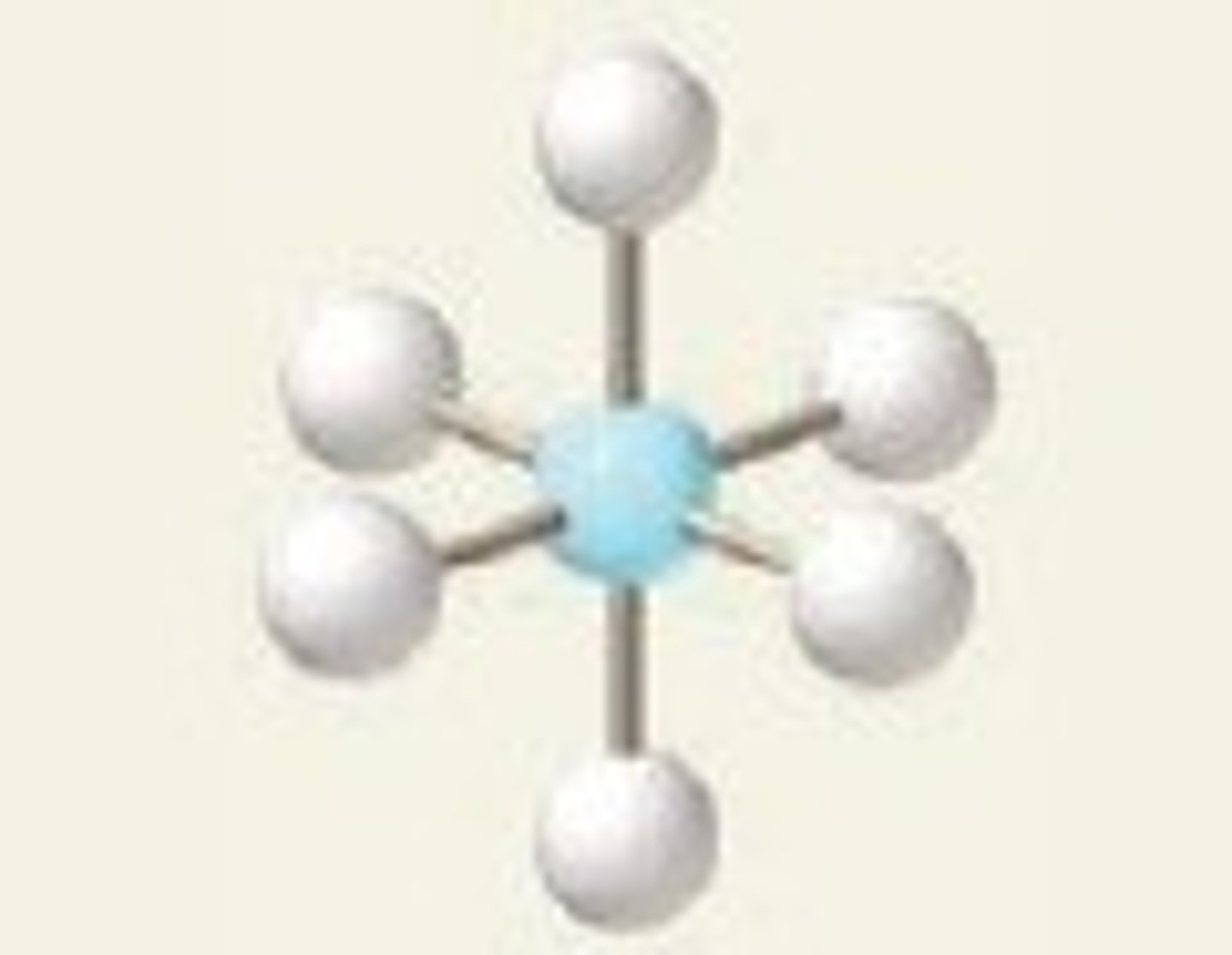
octahedral, 90
6 BP
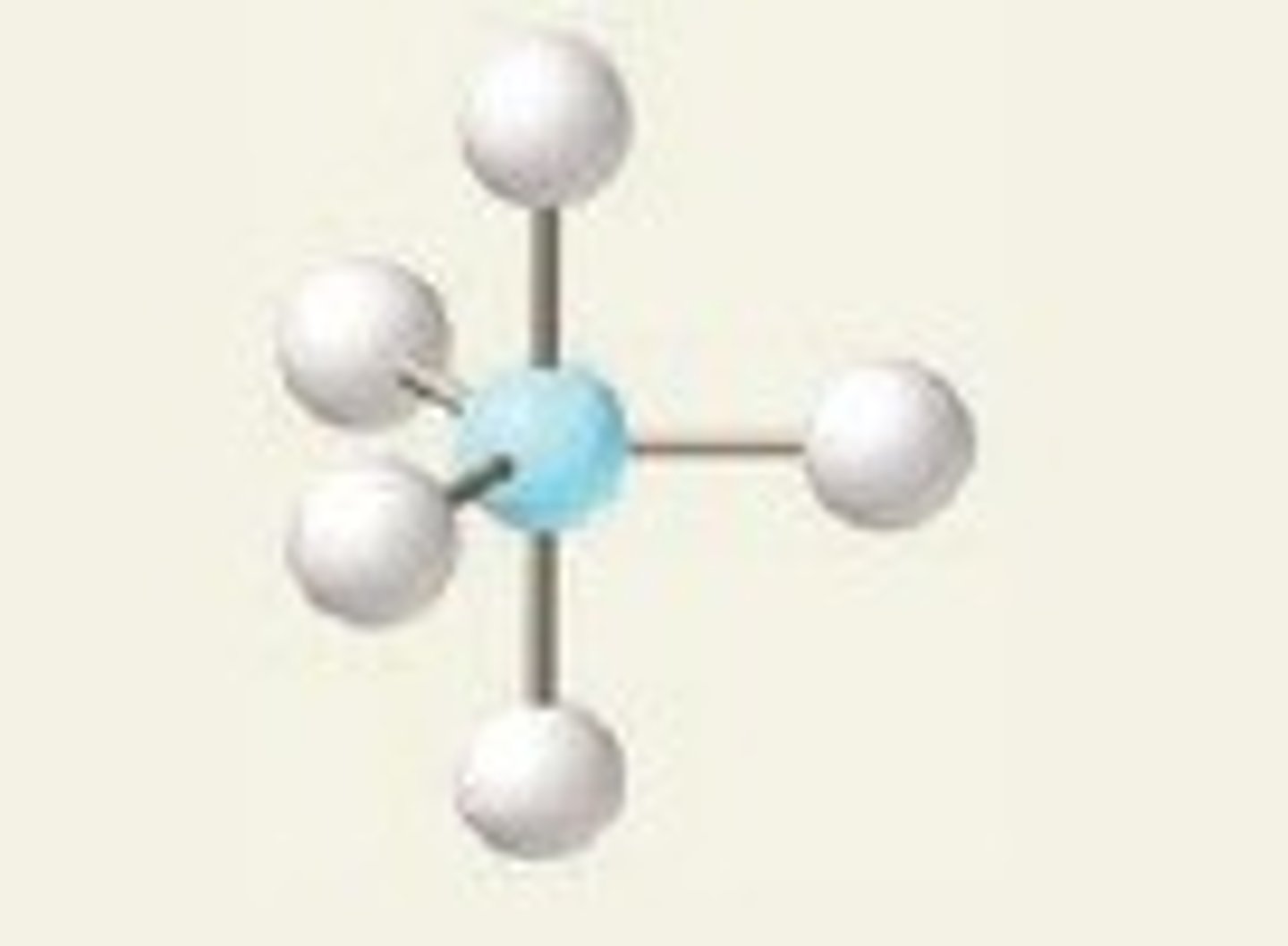
see-saw, 90 and 120
4 BP and 1 LP
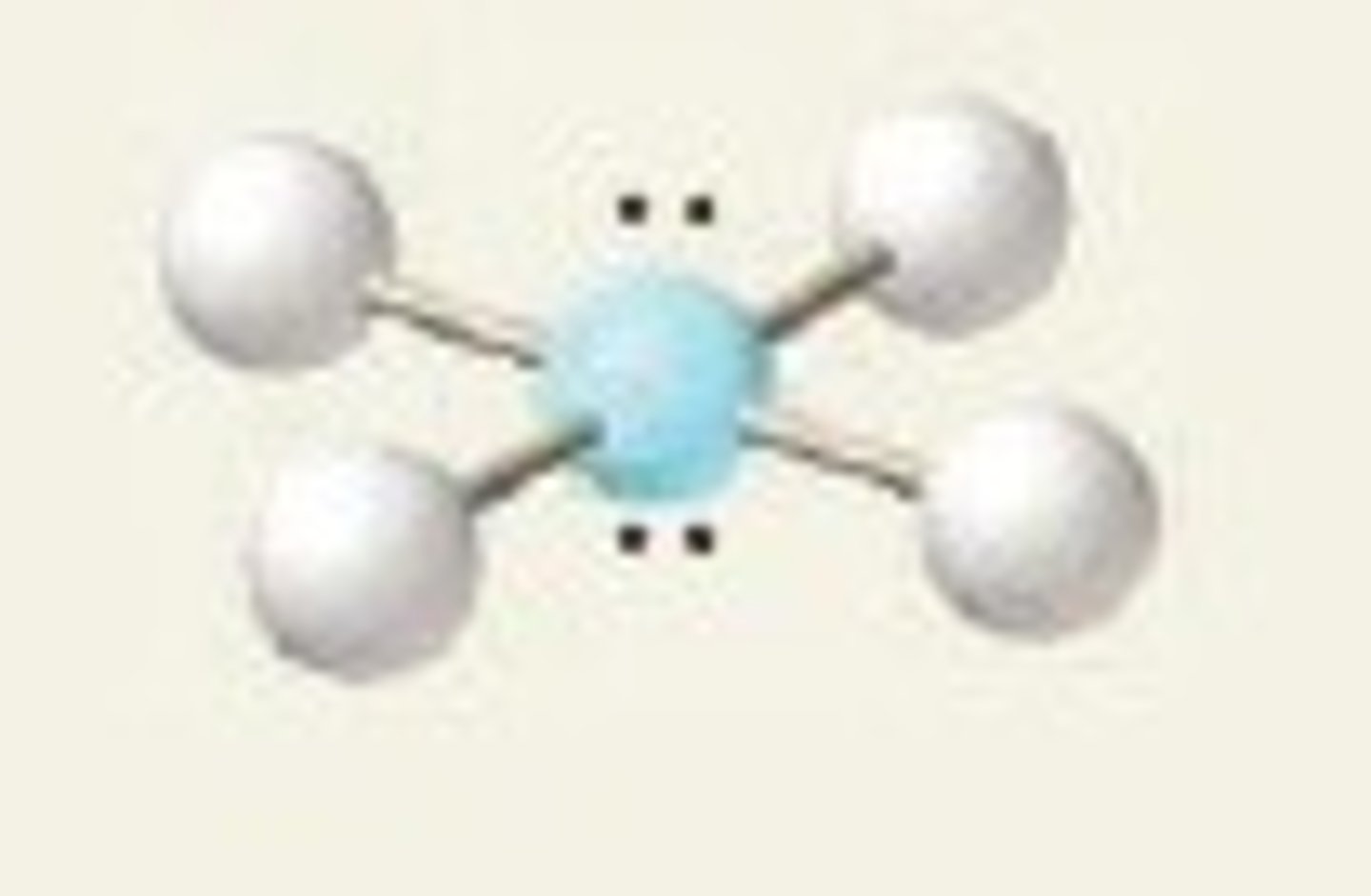
square planar, 90 and 180
4 BP and 2 LP
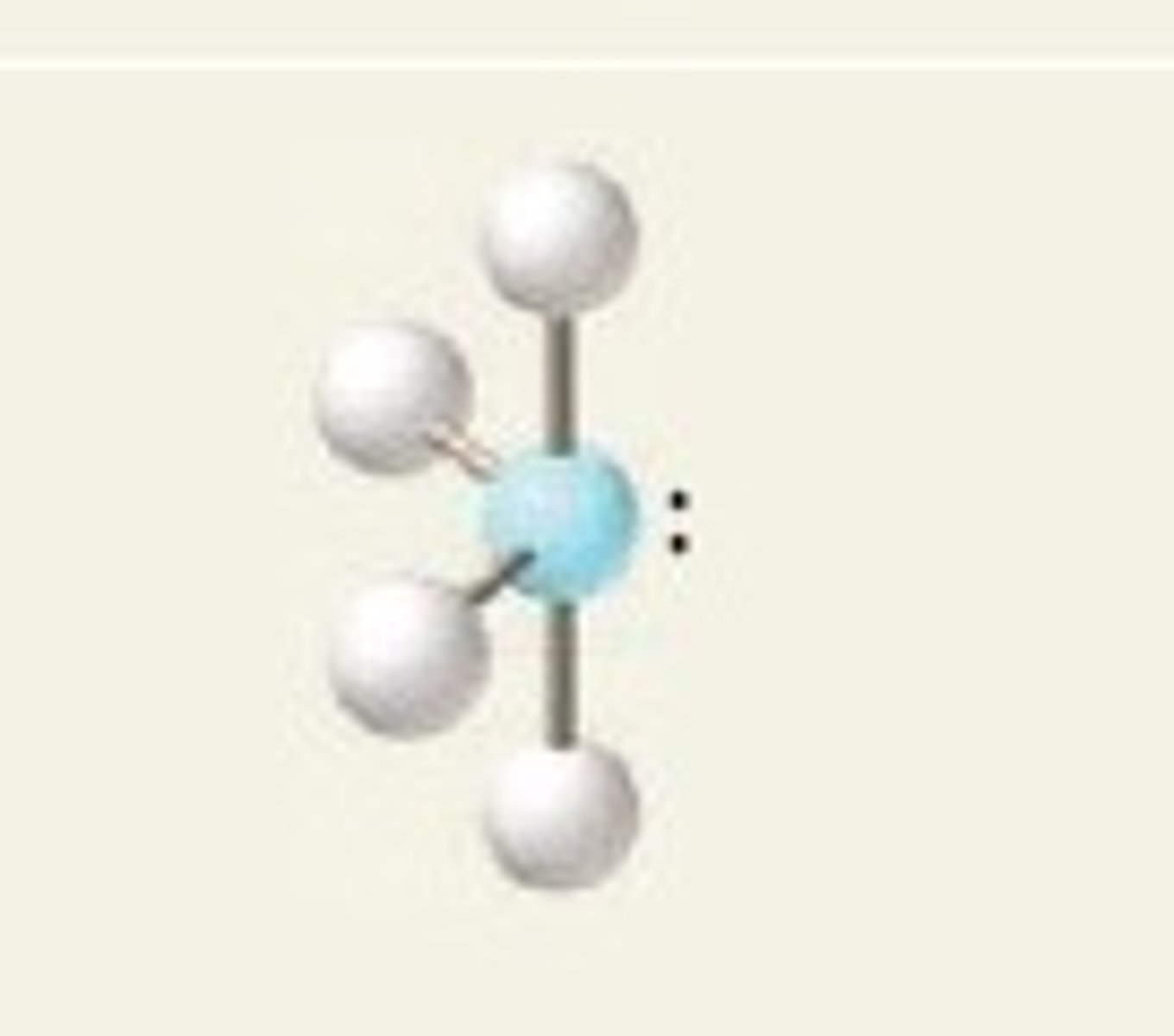
square pyramidal, 90 and 180
5 BP and 1 LP
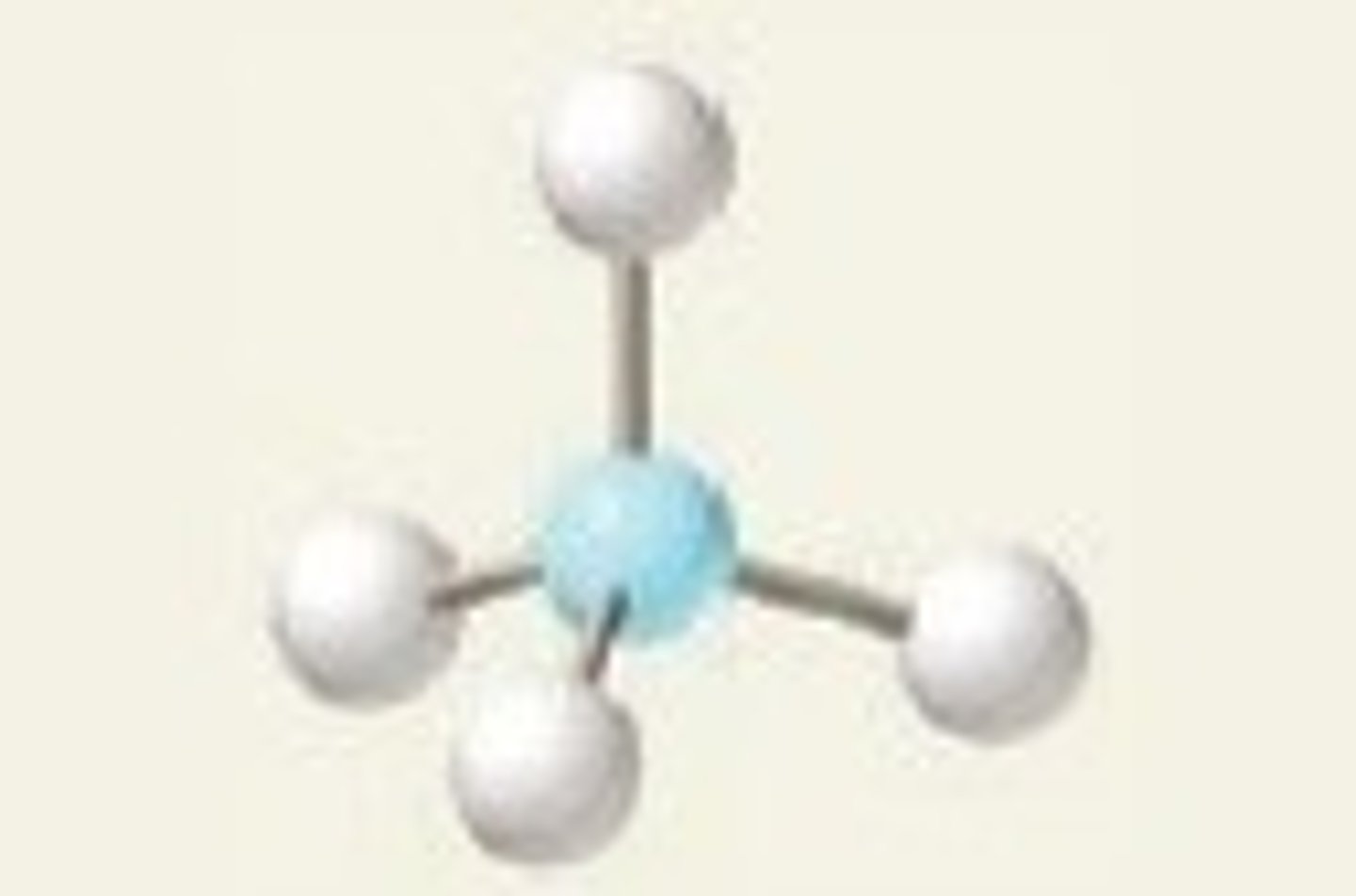
tetrahedral, 109.5
4 BP
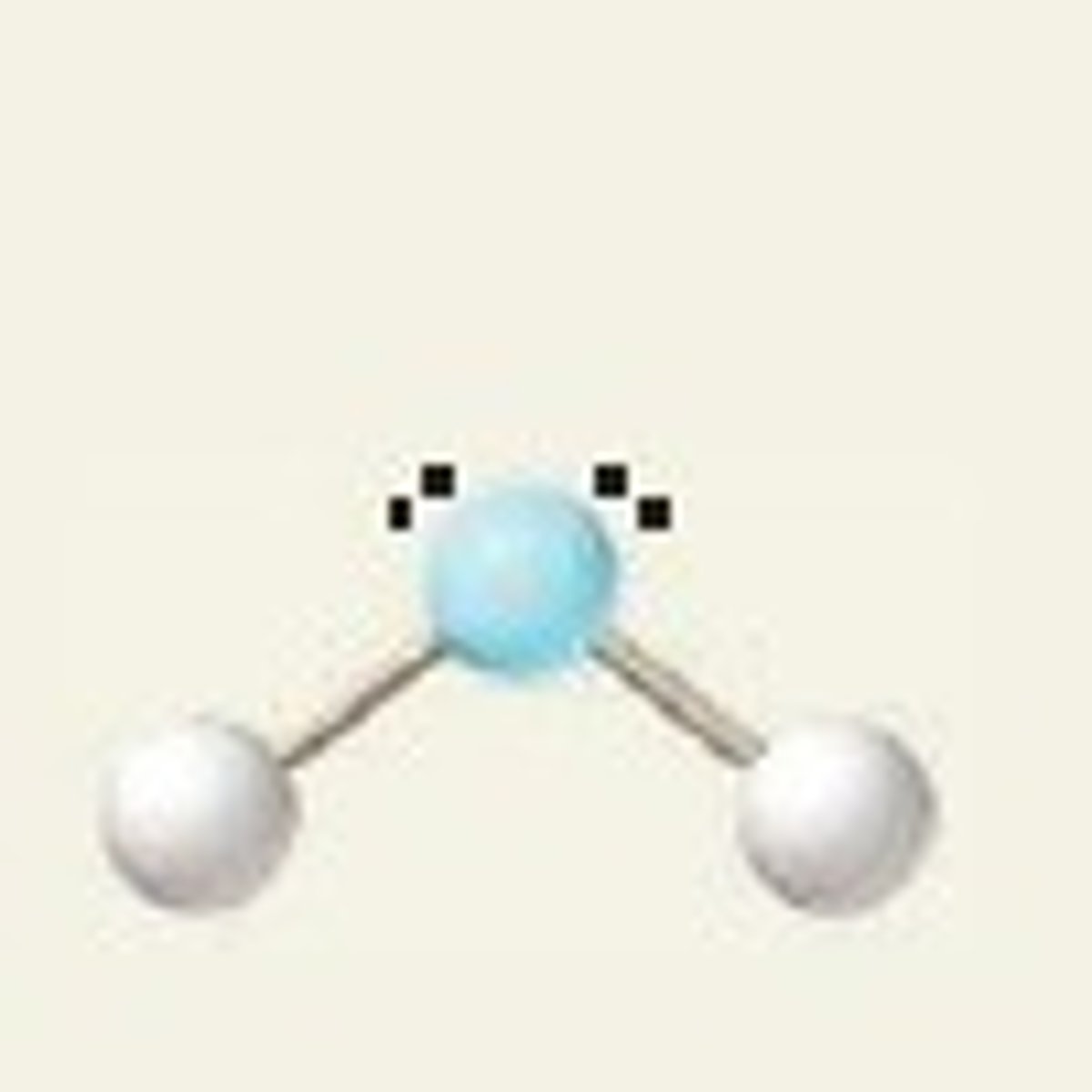
Bent, 109.5
2 BP and 2 LP
trigonal bipyramidal, 90 and 120
5 BP
trigonal planar, 120
3 BP
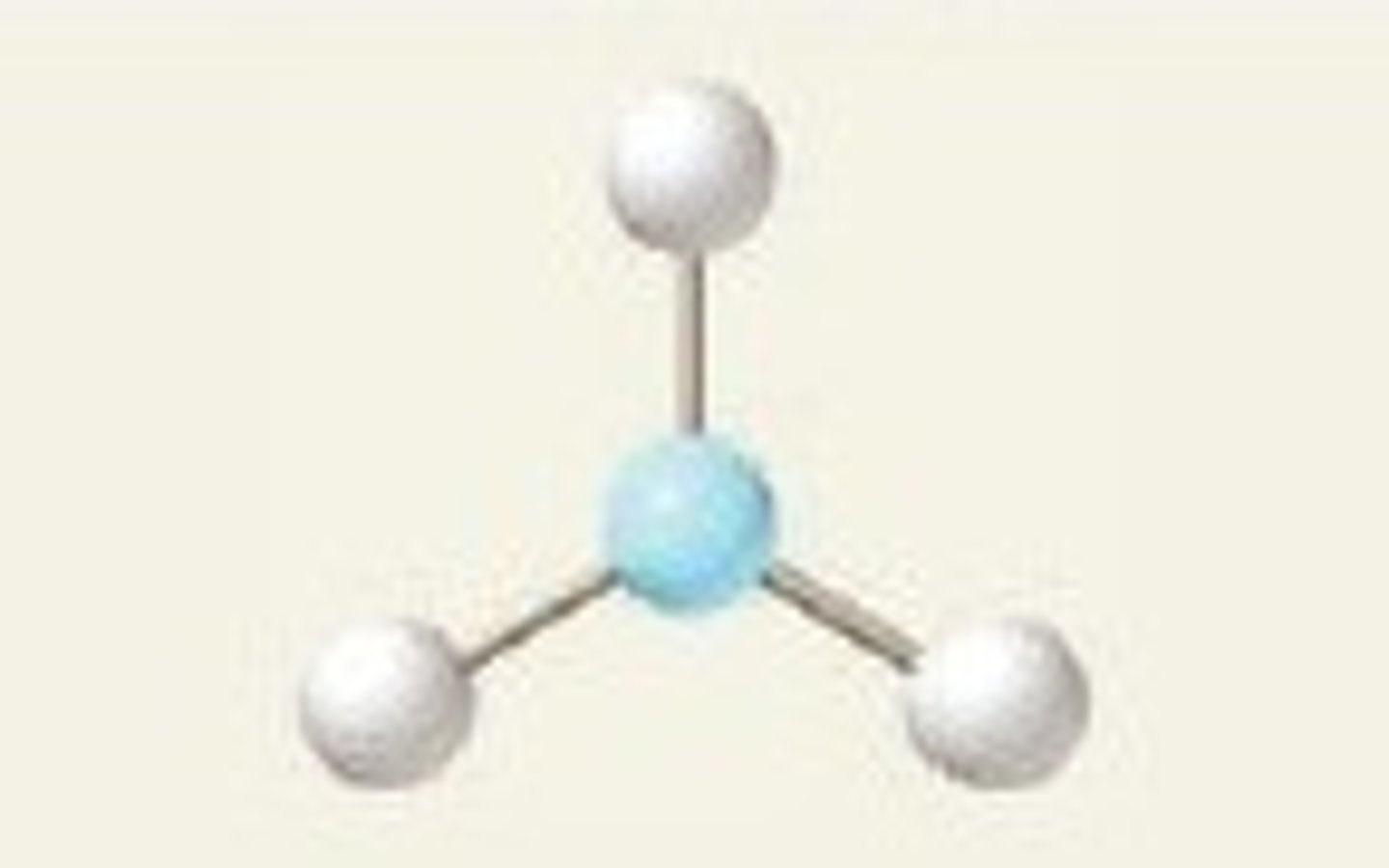
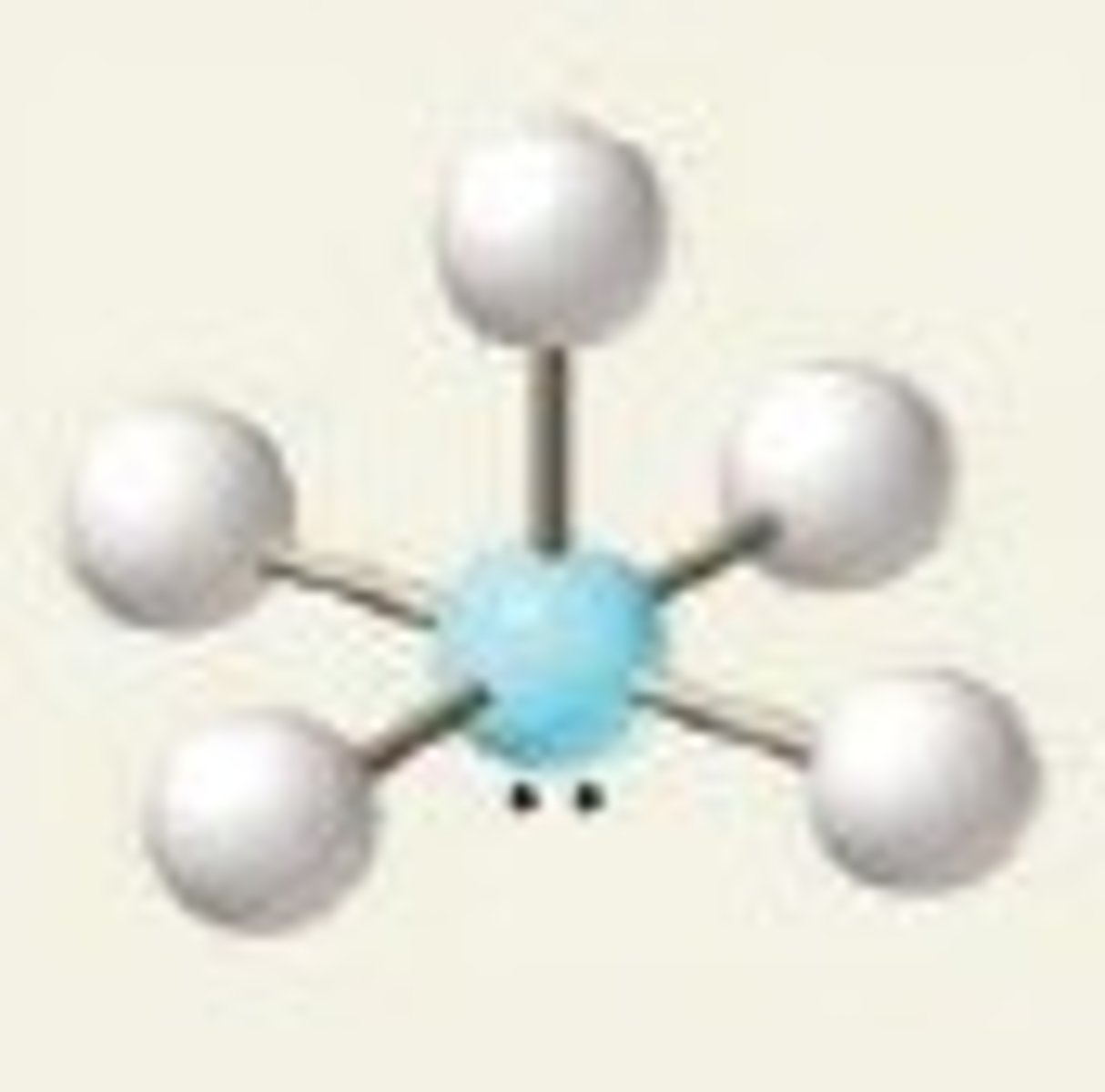
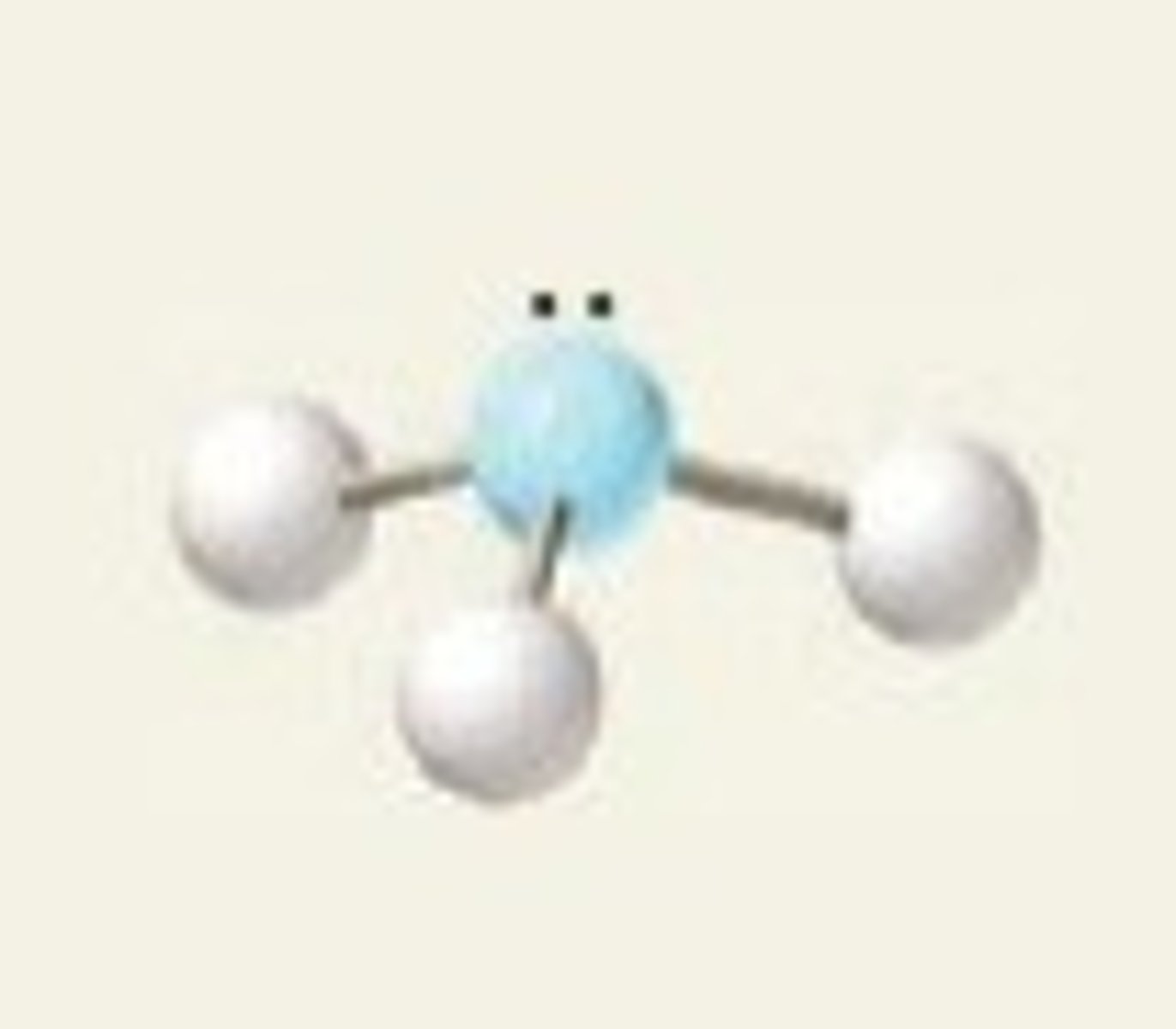
trigonal pyramidal, 109.5
3 BP and 1 LP

t-shaped, 90 and 180
3 BP and 2 LP
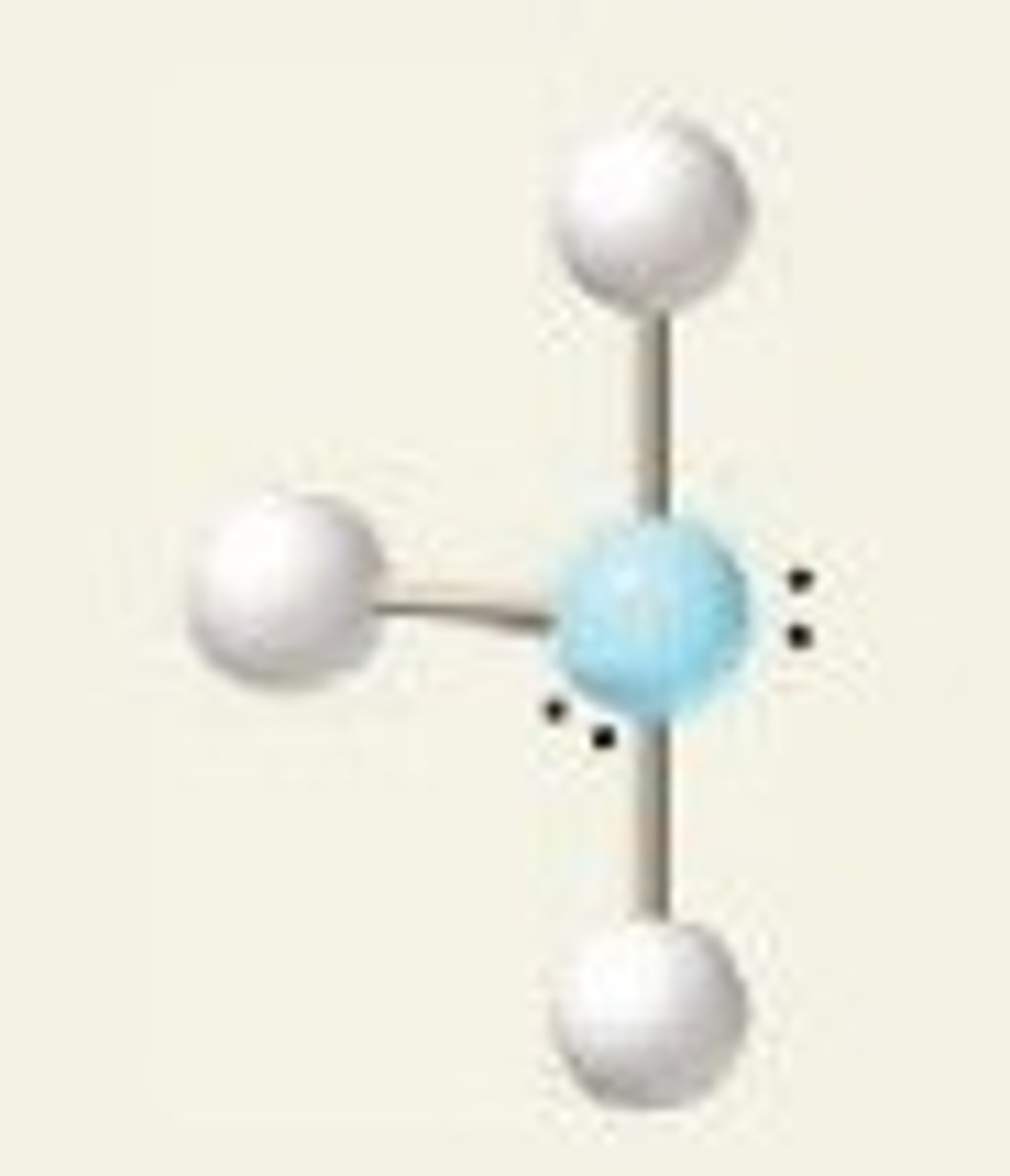
109.5
Tetrahedral Angle
120
Angle between bonds in trigonal planar geometry
90
Angle between bonds in Octahedral Geometry
Pairs of electrons arrange themselves so as to have the maximum distance between them and their neighbors. Model for predicting geometry.
VSEPR
Bonded Pair
2 electrons shared by two atoms
Lone Pair
2 electrons on an atom that are not involved in a bond; takes up more space than a bonded pair
Single Bond
2 shared electrons; bond order of 1
Double Bond
4 shared electrons; bond order of 2
Triple Bond
6 shared electrons; bond order of 3
Octet Rule
Atoms will share electrons so that they have 8 electrons in their outer shell (to achieve noble gas configuration)
Resonance
When a molecule can have two or more equivalent structures, usually with different arrangement of double bonds
electron deficient
atoms that can have less than an octet; B and Be
expanded octet
atoms that can have more than an octet; must be in 3rd period and below on periodic table
formal charge (on an atom)
# valence electrons from P.T. - # electrons assigned to the atom in the Lewis structure; lower formal charges usually indicate "better" lewis structures
anion
negative ion; has additional electrons
cation
positive ion; has fewer electrons