The victorian Era (sana lumabas sa exam)
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
THE VICTORIAN ERA
What Era is when the aristocratic upper class began to lose its domination for both political and economic reasons. The class of agricultural workers decreased in size as work in mills, factories, and mines supplanted farm work.
Growing middle class
Who could afford such things now that they were inexpensively produced in quantity; the decorative and the ornamental became the dominant theme of all design.
Britain's Queen Victoria, battle of the styles
The Roots of Victorian Style The long reign of __________ ___________ _______ (1837-1901) overlapped the period of revivals and the________ _____ _____ _______and coincided with a major part of the Industrial Revolution and the Arts and Crafts or Aesthetic movement in England.
England , America , over-decorative, ornamentation
As a style, however, "Victorian" has come to mean an aspect of 19th c. design in ________and _______(and parallel developments in other European countries) that was characterized by the proliferation of various types of decorative, and even ____________, ____________.
lowest point of quality
Many 20th c. design historians and critics have dismissed Victorian design as representing the____ ____ __ ______, a riot of tasteless excess verging on absurdity.
functional and the practical , ornamentalism and sham
What mixtures is the characteristic of Victorian design that makes this period so complex, so contradictory, and so interesting.
Stirling Single
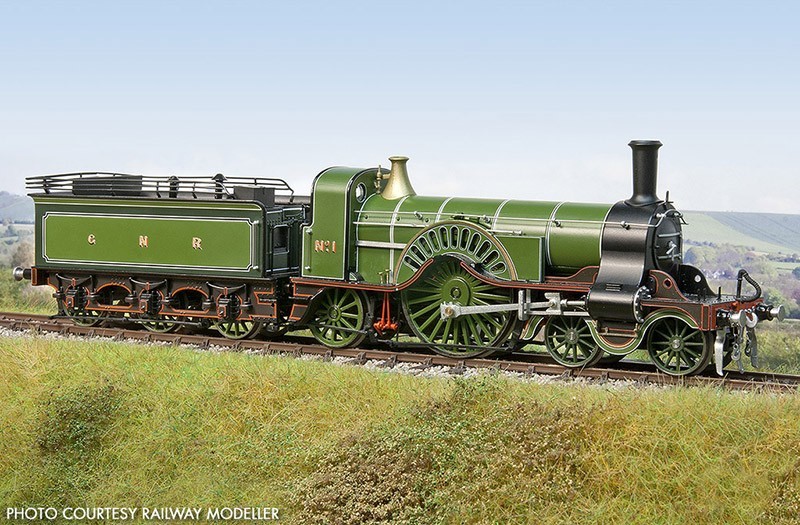

The Royal Saloon , Queen Victoria
What is the name of the Carriage and its rider
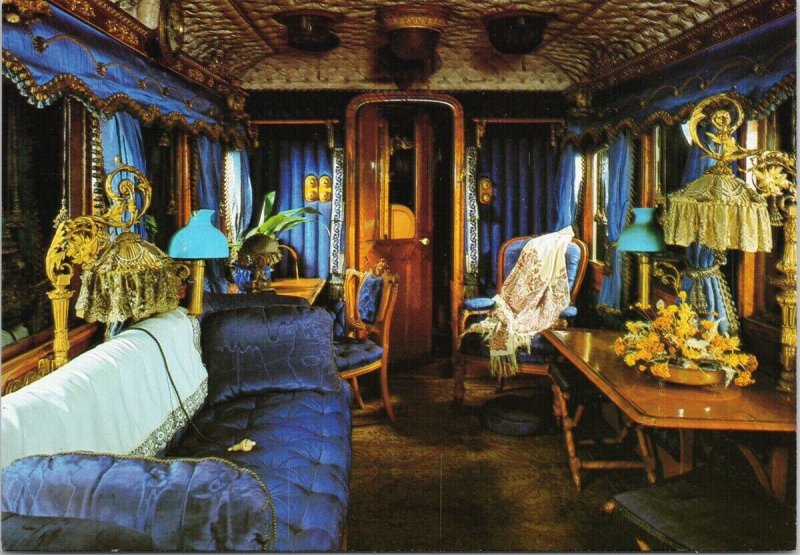

florid decoration, functional tradition
Victorian design split into two worlds:
florid decoration
Dominating the formal and "respectable" worlds of home life, religion, and government
functional tradition
developed in industry, transport, and in the growing fields of science and technology.
Great Exhibition , Crystal Palace
A striking demonstration of this seemingly inconsistent development can be studied in the documentation of the _______ _______of 1851 at the ________ ________.
Power looms
easily produced elaborately ornamented textiles and carpets
Cast iron
ideal material for making ornamental carving and repeating an elaborate design through molds that resulted in cheap, easy, and cost-effective products. In fact, ornamentation could conceal minor defects in castings that would be objectionable in plain surfaces.
made easy and its cheap , generated wealth
The reasons behind this typically Victorian frenzy of decorative excess seem to be based in the congruence of two related developments:
eclectic
meaning borrowing from many sources, is descriptive, but that term has become so attached to a more formal practice of the 20th century that its use for Victorian examples creates confusion.
Gothic Revival, Richard Norman Shaw , Queen Anne Revival
Britain Styles/Inspirations during the Victoria Era
Gothic Revival , newly wealthy [nouveau riche]
The ______ _______ lasted until well into the 1880s as one of a number of stylistic directions that competed for the patronage of ______ ______ ________ _________merchants, manufacturers, bankers, and other "self- made" men, who were all anxious to have great houses comparable to those of the titled aristocracy.
Tudor, Elizabethan, Jacobean, Carolean
The great houses of ____, ________, _______, and _______times were at hand as models, and castles could sometimes be bought in ruined states, so that real antiquity could combine with sham extensions.
Queen Anne Revival
Introduced in the 1860s, to revive a past style or to create a new historical style like the Greek or Gothic Revivals.
home, tradition, middle-class comfort
Queen Anne architecture is an attempt to create an image of ____, ________, and _______ ________. The style appeals to Americans also, who translate it into wood instead of the brick of England.
English vernacular, Elizabethan, Tudor, and Japanese , 17th, 18th
Although its name suggests the early 18th c. period of Queen Anne, the eclectic style combines characteristics from _________ _______, __________, _____, and ____________architecture as well as that of the ____and early ____centuries.
Richard Norman Shaw
_______ ________ ________ produced a large body of work quintessentially English Victorian in character.
Queen Anne
His early work belongs to the Gothic Revival, but by about 1870, he developed a more creative and individualistic style which came to be called_____ _____. This design has little to do with the Queen Anne style of the early eighteenth century.
Red brick, white-painted wood trim
______ _____ and _________ _____ _____ are the primary materials
Gothic Revivalism
There is a hint of ______ _____ along with some reference to Dutch Renaissance work, but Shaw's work is unique and original.
asymmetrical, nooks, bays,
Interiors in his houses, rich in decorative detail, are full of __________ spaces with_____, ______, and other irregularities that favor comfort and charm.
framed pictures ornamental objects
Shaw's clients, and Shaw himself in his own house, filled Queen Anne interiors with _______ _______, ________ _______, and the ornate furniture that was was so beloved of Victorians.
framed pictures, ornamental objects, ornate furniture
Shaw's clients, and Shaw himself in his own house, filled Queen Anne interiors with ________ ______, _________ ______, and the ______ _______ that was so beloved of Victorians.
Richard Norman Shaw, Swan House
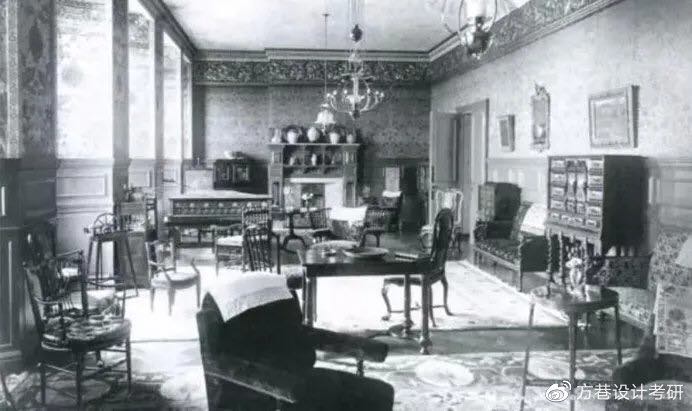

mansion, middle-class houses, public buildings
3 Types of Building in Britain
Half-timbered, keeps, clock towers
Britain mansions exterior features. ________ gabled blocks, ______with battlemented defenses, and ________ ______ visible for miles around were favorite external features.
Timber construction
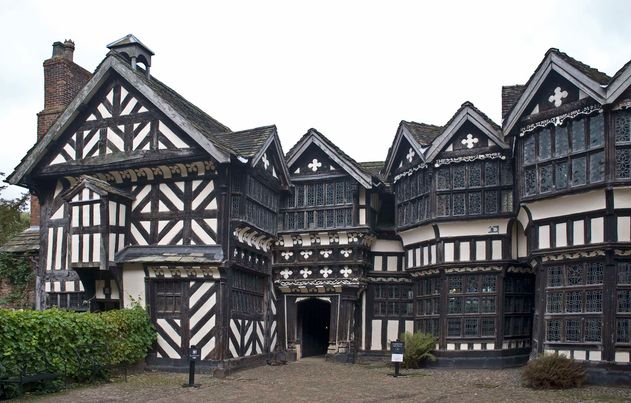

Anthony Salvin, Peckforton Castle
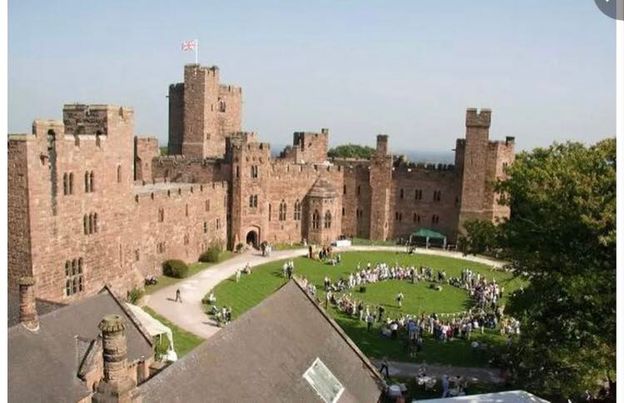

Elveden in Suffolk, John Norton

Town houses
Parts of rows, or even whole neighborhoods, that adhered to restrained design based on Georgian traditions of classicism. The interiors often exhibited acquisition and display in ornamental chaos. It is hard to imagine how the occupants managed to walk about or sit down.
Robert Taft, A Chelsea Interior, Carlyle's House, London, 1857

Suburban neighborhoods
__________________ ______________ developed around British cities during the Victorian era.
Row houses, villas
______ _______ were built for those of modest means, and "_______" in pairs or free-standing for those who could afford more.
Regency , Gothic Revival
The exterior is usually some version of __________ or ________ _________, sometimes with touches of Victorian decorative detail. Inside, the occupants arranged whatever level of Victorian detail that appealed to them.
gas light
Most public spaces were carpeted, padded, and stuffed in order to achieve a special comfort typical of the "_____ _____" era that provided the settings in which Arthur Conan Doyle's famous fictional detective, Sherlock Holmes, conducted his practice.
American Victorian
what design was characterized by free improvisation compared to its English counterpart? which was somewhat more ordered and disciplined, more "professional" and therefore perhaps less creative.
Ornamentalism
what was supported by an increasing flow of imports from Europe. In architecture and interior design, preference for the more pretentious and ostentatious aspect of Victorian taste developed.
Books and magazines
What offered "ideal" plans and design incorporating ornamental details that could be factory made, bought from a lumber yard, and added to a basic house
The Centennial Exhibition
in Philadelphia in 1876, was a showcase for Victorian design in America, much as the Great Exhibition had been in England.
Department stores
cities offered a wide choice of goods of every sort, so that the Victorian shopper could compare, select, and order delivery of everything needed for household decoration at one stop.
Carpenter Gothic, Italiante, Mansardic, Queen Anne
United States Styles during this period
Carpenter Gothic
The term applied to the vernacular adaptation of the Gothic Revival style in America.
Richard Upjohn

Italianate
This term describes designs using low-sloping hipped roofs, porches, and loggias with columns, bracketed roofs, and cornices, and often a tower. Windows and doors are often topped with semicircular arches.
Lewis house in Upstate New York
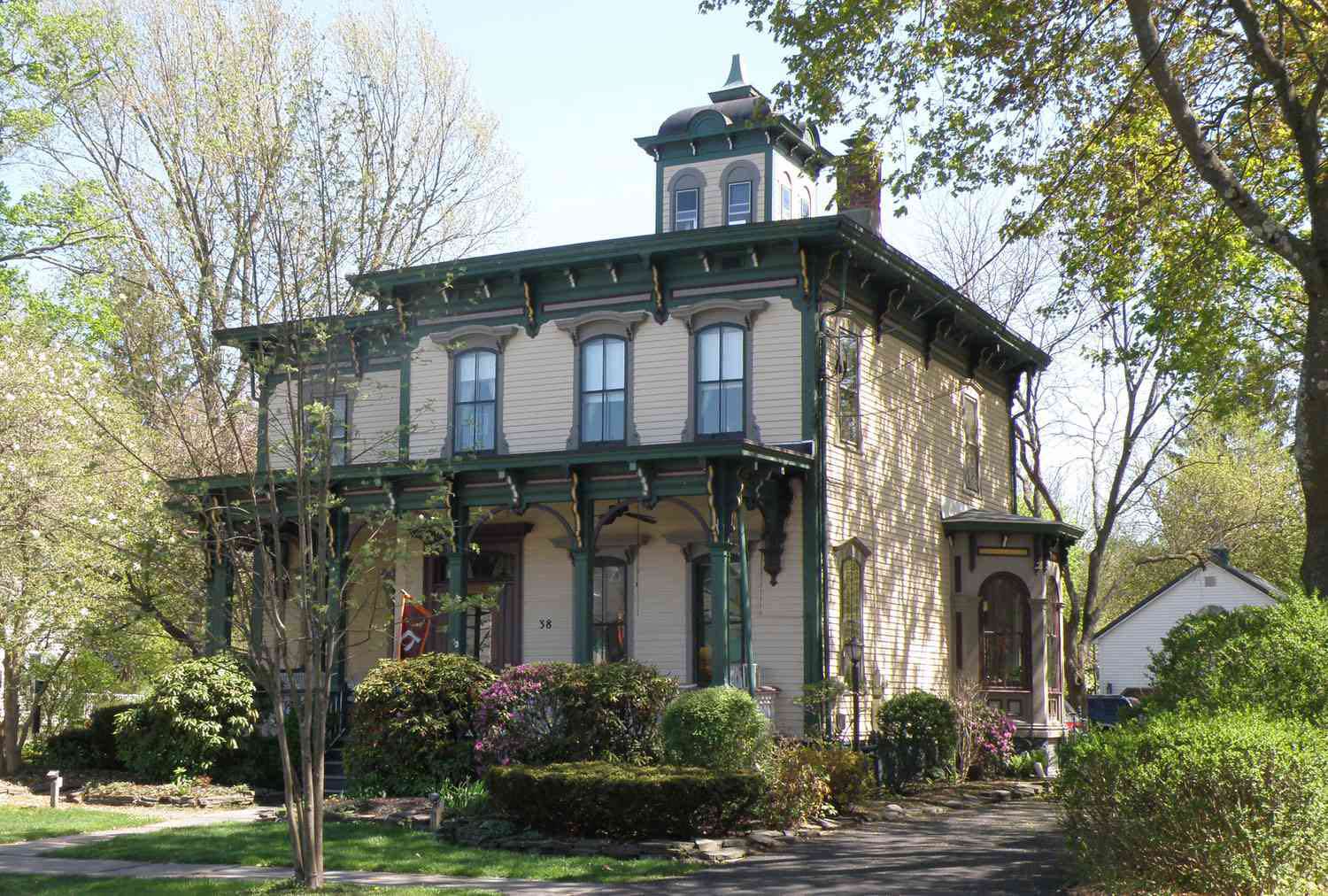



Mansardic
These designs take their name from the mansard roof. A mansard roof has a steep, visible front surface, usually of slate, visible from the street.
public buildings
Mansardic design was often used for _____ _________, courthouses, and railroad stations as well as for houses.
General Grant style
The style was first seen in America in the 1850s and flourished after the Civil War. It was so commonly employed in that era that it was sometimes referred to as the "_______ _______ ______."
mansard roof
__________ _______, a staple of French architecture, came to prominence during the Baroque period. These roofs have two vertical slopes on each side of the building. The upper slope looks flat, and together they give the appearance of a lowered roof height
Farmhouses
The American ____ of the Victorian era moved away from its colorful and Gregorian predecessors to give up symmetry and classical detail in favor of “picturesque” irregular plans and more vertical proportions.
Gingerbread
Detail varied from the severe plainness of the houses of the settlers of the mid-west to the ornate _____ favored by more affluent families in the east and south.
houses, workers, mid-level managers
Around the factories of mill towns, districts of small ____ were built to accommodate _____ and ______ somewhat in the manner of modern suburbia.
Stick Style
The simplified version of the Shingle style is what Scully calls the ____ ____ which is a reference to board and batten exterios, which featured external frame members.
medieval half-timbered, wooden planks
Unique to the United States, the Stick Style in architecture combines the character of _____ ________ buildings with the new balloon framing construction method in its use of _____ _____ or sticks that form decorative surface patterns on exteriors.
Adirondack, New York
A minor sub-style of Victorian design has recently been given the name ______ in recognition of its development in that mountainous region of ____ ____
Pine Knot, Camp Cedars
Camps with quaint names such as ____ ____ and ____ ____ were made up of cottages and lodges filled with rustic furniture, rugs and cloth
Adirondack
_____ furniture is often made up of tree branches cleverly assembled to make benches, tables, and chairs, with smaller twigs used for ornamental detail.
19th century American Adirondack rocking twig chair

Early version of an original New York Westport Adirondack Chair

Shakers
The first ____ came to America from England in 1774, seeking freedom from religious persecution. ____ communities were villages built at the center of agricultural lands where members shared property and work in simple form of communism. By 1800 a number of these villages had been established.
Shakers
The typical bedroom of an elder of eldress in the ____ communal residence hall contains a simple rope bed and wooden washstand. The wood-burning stove in the foreground incorporates a ____ invention, the upper smoke box, which extracts extra heat from chimney grass. The wooden trim is painted in a tone the ____ called “Heavenly blue.”
Hancock Shaker Village, Hancock, New York c. 1820.

central business district
As cities grew larger, central districts developed that were devoted to business activities. Before telephone communication was available, proximity was an important consideration in making business communication fast and easy. The resulting need for offices crowded into a _____ _____ ______ led to high rents and high land values
passenger elevators
Real estate owners realized that their earnings were limited by the quantity of rental space that could be squeezed onto a lot of given area. Taller buildings became profitable with the development of ____ _____, but the height of buildings was still limited as long as masonry walls and columns were the main structural elements
Cast iron
_____ ____ - an extraordinarily useful and versatile material, enabled buildings to go higher, because its high-strength characteristics made it possible to reduce size of support columns within buildings.
Masonry
_____ remained the preferred material for outer walls because it offered a degree of fire safety by enclosing each building in a non-flammable barrier.
Fire safety
_____ _____ within a building was improved when wooden floors were replaced with systems using arches of brick or terracotta tile supported on iron beams and columns wrapped with tile heat insulation.
Fireproof structural framing
______ ______ ______ and elevators together made it possible to build to heights of eight, ten, or twelve stories.
Bessemer process
Still higher “skyscrapers” finally became possible at the very end of the nineteenth century when the _____ _____ made steel available for columns and beams.
New Materials
____ ____ and techniques were developed that made whole new categories of object possible.
Plywood
What was developed in continental Europe which became an alternative to solid wood, less costly and less subject to warping and splitting.
Plywood
____ panels, chair seats, and curved parts that could form seats and backs for benches and church pews were used in combination with solid wood components to form new furniture types.
Industrial materials
First made as plumbing pipes; ____ ____ were turned to use to make bed frames, creating the popular iron and brass head and foot boards.
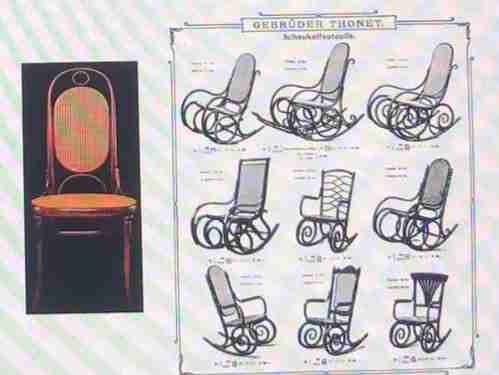
bentwood
Thonet chairs and other furniture types made up of a number of pieces of ____ were strong, light, and inexpensive, and so came into wide use as seating in cafés and restaurants and in informal residential inferiors.
Thonet chairs
What-not

What-not
Any otherwise unused spaces could be filled with such newly developed furniture types as the _____, a shelf unit intended to hold a display of generally useless ornamental objects.
mirrored hat-racks
Huge _____ ______ were favorite elements for halls and vestibules
Pianos
____, many made in rectangular “square” form, as well as in the familiar grand and upright parrerns, were important items for status-oriented display, and were designed with particularly rich, complex, and generally heavy ornamentation.
John Henry Butler
Most Victorian designs were ornate. This kind of design was seen in the products of the New York shops of _____ _____ _____
idk ano lagay…

exotic themes
As Victorian fashion sought out ____ ____, furniture makers responded with designs intended to relate to one or another popular style.
Upholstery Materials
____ is a dominant element in Victorian seating furniture. It was desired for comfort and for the appearance of opulence.
Cushions
What is usually attached to wooden frames, tend to be thick and bulging, with quilting and tufting to emphasize their forms.
Metal Springs
What is hidden under cushions were widely used to create soft and bouncy surfaces.
Cover materials, woven horsehair, leather
_____ _____ with elaborate and colorful woven patterns were the norm, with ____ _____ and _____ as alternatives.
textile design
Victorian ____ _____, separated from the process of hand weaving by the use of powered looms set up in large and efficient mills, emphasized heavy, elaborate, and colorful pattern, both woven and printed.
Trimming materials
____ _____ such as braiding, fringe, and tassels were added to make drapery rich and complex.
Carpets
____, now generally made on power looms, were designed with themes sinilar to those used for textiles.
Linoleum
____, a newly invented floorcovering material, was similarly produced in floral patterns and in designs imitating woven rugs.
Wooden floors, parquet
_____ _____ or floors of hardwood in ____ patterns, and floors of colored tile in varied patterns were also common.
Lace curtains
What were a popular, more modest window treatment.