Genomics test 4
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What is Serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE)
Converting the mRNA into cDNA and sequencing all the clones is laborious and time-consuming.
SAGE yields short sequences (as short as 12 bp) each representing mRNA from the transcriptome, and therefore allowing for the identification of genes coding for all the mRNA that are present.

how do you generate 12 bp tags using SAGE method?
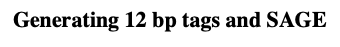
1.mRNA is immobilized in a chromatography column by annealing the poly(A) tails to oligo (dT) strands that has been attached to cellulose bead
2.The mRNA is converted into double stranded cDNA and then cut with an RE (AluI) that recognizes a 4bp target site and cut frequently in each cDNA.
3.The terminal restriction fragment remains attached to the beads, and all other fragments are eluted.
4.An oligo with a BsmFI recognition sequence is attached to the free end of each cDNA
5.BsmFI cuts 10-14bp downstream of its recognition sequence, generating fragments averaging 12bp from the end of each cDNA
6.These fragments are collected, ligated, sequenced and the tagged sequences are compared with the sequences of the genes in the genome.
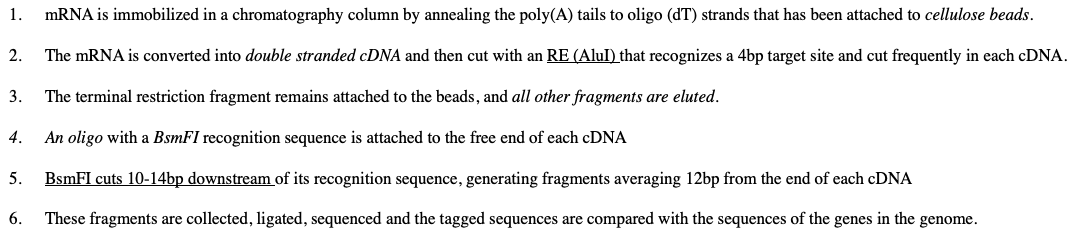
What is The difference between microarray and DNA chip analysis

a chip carries an array of immobilized oligos synthesized in situ on the surface of a wafer or silicon while microarrays is made up of DNA molecules (PCR products or cDNA) that have been spotted onto the surface of a glass slide or nylon membrane.
What is the comparison of SAGE and microarray and chip analysis?
this approach provides a rapid evaluation of the differences between two or more transcriptomes by hybridizing different cDNA preparations to identical arrays and comparing the hybridization patterns.
Microarray analysis
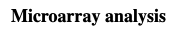
cDNA preparation is labeled with a fluorescent marker and hybridized to the microarray. The label is detected with confucal laser scanning and the signal intensity converted into a pseudocolor spectrum

what are the key objectives of studying a transcriptome
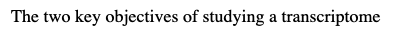
-to identify the genes whose mRNA are present and the relative amounts of the various mRNA
-all the relevant genes must be represented
-The need to determine the relative amounts of mRNA

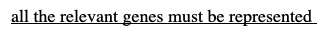
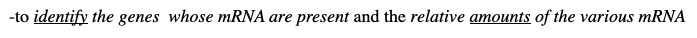
what does each position in the microarray contain?
Each position in the microaray contains a cDNA or PCR product from a gene of interest, whereas each position in a DNA chip contains a mixture of oligos that match different segments of the relevant gene
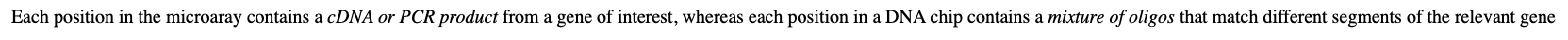
what are some limitations of chip analysis and microarrays
1.There may be insufficient specificity to distinguish between every mRNA that is present because two different RNAs might have similar sequence leading to cross-hybridization.
- This may happen when two or more paralogous genes are present in the samples
2. Two or more mRNA derived from the same gene (as a result of alternate splicing)
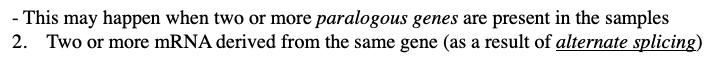
when comparing two or more transcriptomes, differences in hybridization intensities must reflect genuine differences in mRNA levels and not what?
(a) the amount of target DNA
(b) the efficiency with which the probe has been labeled
(c) effectiveness of hybridization
how do we minimize these limitations when comparing two or more transcriptome in the experiment?
(a)including adequate controls; For eukaryotes, actin genes are often used as positive controls
(b)Scanning arrays at the same wavelengths.
(c) Data normalization: allows for results from different experiments to be accurately compared by removing any background signal.

what is a dendrogram used for?
constructed showing the degree of the relationship between the expression profiles of the genes

What is the proteome?
The proteome plays a central role as the link between the genome and biochemical pathways of the cell. Characterization of the proteome is key to understanding how the genome operates and how dysfunctional genome activity may lead to diseases.
Some proteins undergo physical and/or chemical modifications before becoming functional.
proteomics
The methodology used to study the proteome
what is Protein Profiling

methodology for identifying the proteins in a proteome
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
is the standard method for separating the proteins in a mixture
what can be used for the basis of separation?
Different chemical and physical properties
what does Sodium dodecyl sulfate
do?
denatures proteins and confers a negative charge just about equivalent to the length of the unfolded polypeptide, so that proteins separate according to their molecular masses
what does Isoelectric focusing allow for?
for protein separation in a gel containing chemicals which establish a pH when the electrical charge is applied
•Takes advantage of the fact that overall charge on the molecule of interest is a function of the pH of its surroundings
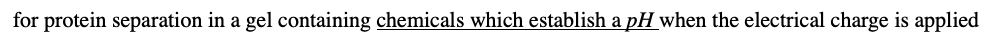
what is the significance of the isolelectric point?
it is where the protein migrates to, and the position in the gradient where its net charge is zero.
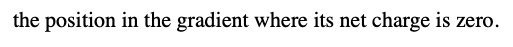
two-dimensional gel electrophoresis describe this method
-In the first dimension, the gel is separated by isoelectric focusing
-Following soaking in Na dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and rotated 90 degrees, the proteins are then separated based on size (molecular mass) in the second dimension.
-visualize this with silver solution
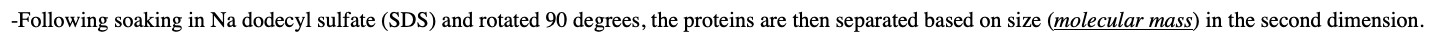
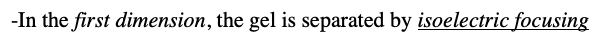
how do you identify proteins in the proteome?
-Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF)
Describe MALDI-TOF
-interest is purified and digested with a sequence-specific protease, such as trypsin which cuts following arginine or lysine residues to produce peptides of 5-75 amino acids in length.
-Following ionization, the mass-to-charge ratio of a peptide from its time-of-flight within the mass spectrometer as it passes the ionization source to the detector.
-The mass-to-charge ratio enables the molecular mass to be worked out, which in turn allows for the amino acid composition of the peptide to be deduced.
-When a number of peptides from a single protein spot are analyzed, the resulting compositional sequence are related to the genome sequence in order to identify the gene that specifies that protein.
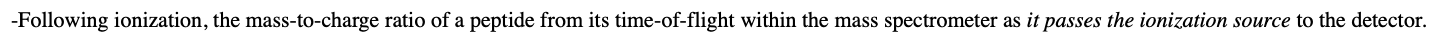
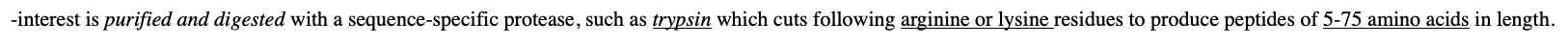
how do you use MALDI-TOF in protein identification

In the mass spectrometer, the peptides are ionized by a pulse of energy from a laser and then accelerated down the column to the reflector and onto a detector.
The time-of-flight of each peptide depends on its mass-to-charge ratio
The data is then visualized as a spectrum.
The computer contains a data-base of the predicted molecular masses of every trypsin fragment of every protein encoded by the genome of the organism under study.
Computer compares mass of detected peptide with the database and identify the most likely source protein.

what is ICAT

(isotope coded affinity tag)
what is ICAT used for
analyzing two proteomes
How do you analyze two proteomes by ICAT (isotope coded affinity tag)

If the difference between two proteins are relatively large, then the difference will be apparent by stained gels.
ICAT provides for detecting small-scale changes
-The constituent of two proteomes are labeled with different fluorescent markers (isotope coded affinity tag) – normal H atom and deuterium.
- This would allow two proteomes that are mixed together to be identified during the MALDI-TOF stage of the profiling.

what methods do you use to identify proteins that interact with one another

(1) Phage display
(2) Yeast-two hybrid studies
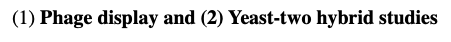
phage display
uses a special type of cloning vector such as bacteriophage λ or M13
-The bacteriophage genome has a
unique restriction enzyme site located
within a gene for a coat protein
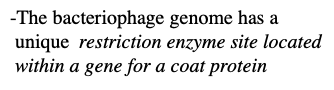
Disadvantage of phage display?
-Time-consuming.
-Requires some prior information on
possible interactions

what is a more powerful approach than phage display?
phage display library

what is phage display library?

a collection of clones displaying a range of proteins, and identifying which member of the library interact with the test protein
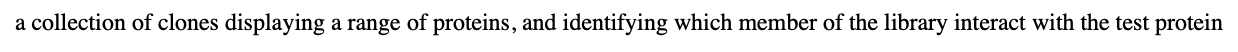
what are the steps to use a phage display library?
-The test protein is immobilized within a well of a microtiter plate and the phage display library is added.
-After washing, the phages that are retained are those displaying a protein that interacts with the test protein.

Two-hybrid system (yeast two-hybrid screening or Y2H)?
ia technique used to discover protein-protein interactions and protein-DNA interactions by testing for physical interactions (such as binding) between two proteins or a single protein and a DNA molecule.
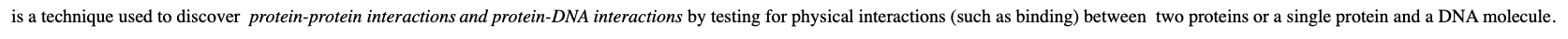
what happens in the two hybrid system?
a gene of a human protein has been ligated to the gene for the DNA-binding domain of a yeast activator.
Following transformation, the construct
specifies a fusion protein, part human
protein and part yeast activator.

What happens In screening?
for protein interactions, the two sets of constructs are mixed and transformed into yeast.
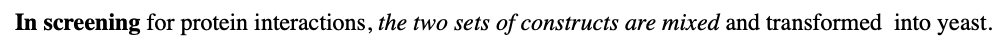
What happens when the reporter gene is expressed?
it contains fusion proteins whose human segments interacted, thereby bringing the DNA binding and activation domains into proximity and stimulating the RNA polymerase.
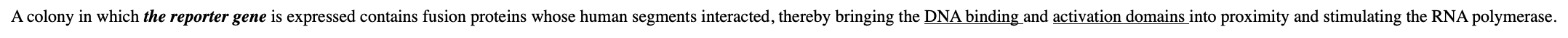
Methods for Identifying the components of a multiprotein complex?
1..Affinity chromatography
2.TAP (Tandem-affinity Purification)

what is Affinity chromatography

the test protein is attached to the chromatography resin and placed in a column.
-The cell extract is placed in a low-salt buffer, which allows for the formation of the hydrogen bonds that hold proteins together in a complex.
-The proteins that interact with the bound test protein are retained in the column, while the other proteins are washed away.
-Interacting proteins are eluted with a high-salt buffer.
-Major disadvantage is the need to purify the test protein which is time-consuming and difficult to use in large screening programs

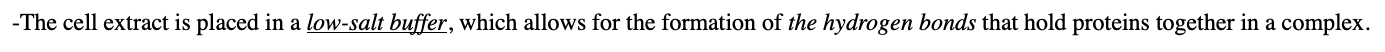
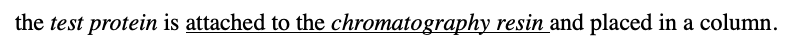
what is TAP (Tandem-affinity Purification)
the gene for the test protein is
modified so that the C-terminal extension
binds to a second protein calmodulin.
-The resin in the column contains the modified calmodulin molecules which is able to trap the protein complex when the cell extract is passed through the column.
-In both methods, affinity chromatography and TAP, the protein identities are identified through mass spectrometry.

what is a major disadvantage of affinity chromatography methods
that a single member of the protein complex is used as a “bait”, so that a member of the complex may not be isolated if it does not interact with the bait.
what is Metabolome?
this is the complete collection of metabolites present in a cell or tissue under a particular set of conditions.
what does Metabolomics or biochemical profiling
do?
gives a precise description of the biochemistry underlying different physiological states e.g. disease state
Molecular phylogenetics?

focuses on comparing genomes

How do genomes evolve?
gradual accumulation of mutations
what is a phylogeny
a classification scheme indicating the similarities among species and their evolutionary relationships.
who came up with phylogeny?
Carl Linnaeus
phylogenetic tree (or
dendrogram).
the evolutionary
relationships among a group of organisms
what is a phylogenic tree made of?
nodes and branches