Neurological Disorders
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Alzheimer's Disease, brain cancer, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's Disease, and myasthenia gravis, + different reasons why they may be difficult to treat.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Epilepsy
characterized by recurrent seizures due to abnormal brain activity.
= neurons malfunction, electrical signals firing uncontrollably
Symptoms:
Confusion
Aura (Deja vu, a sense of oncoming)
Strange Sensations/Emotions
Convulsions
Sudden Falls
Loss of consciousness
Staring
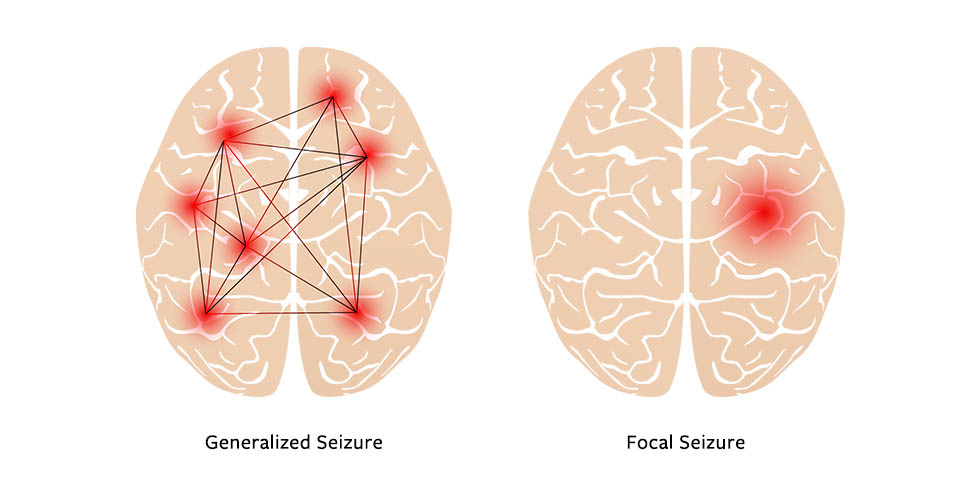
Focal vs. Generalized Seizure
when a seizure is in one area vs when a seizure spreads across the brain (the more the electrical discharges spread, more neurons malfunction, more intense the symptoms)
Mutation in ion channel —> enhanced excitability (more AP)
What causes epilepsy?
Epilepsy is difficult to treat because various underlying triggers —> hard to find the right treatment for each individual
ex.
genetic factors,
brain injuries,
infections,
certain medications
Why is epilepsy difficult to treat?
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
an auto-immune disorder
loss of myelin on usually myelinated axons
symptoms
changes to vision
muscle weakness, stiffness, and spasms
numbness/pain
loss of balance
difficulty with cognitive function
mood changes
Why is Multiple Sclerosis difficult to treat?
because each individual with MS experiences it differently, so there isn’t one treatment for everyone, because it would have different effects for each MS patient
also because the underlying cause is not really known, it has been controversial (genetics, environmental factors, etc. ??)
Alzheimer’s Disease
= a neurodegenerative disease
reduction of neurogenesis (growth of new neurons) in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus
reduction of ability to form new memories
Symptoms of Alzheimer’s
decline in
memory
reasoning
language
coordination
mood
behavior
Parkinson’s Disease
= loss of dopaminergic neurons (neurons that dispel dopamine as their neurotransmitter)
so less dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra (midbrain)
less dopamine supplied to striatum (subcortical structure)
leads to disrupted motor movement (motor cortex)
Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
Early Non-motor symptoms
loss of smell
drooling
constipation
sleep problems (ex. restless leg syndrome)
mask-like facial expressions
motor symptoms
slowed movements
tremors
rigid/stiffness
autonomic nervous system issues:
less blinking
trouble swallowing
unstable posture/uneven gait
Brain Cancer
= mass or abnormal/uncontrollable growth of cells in the brain or near it
Brain Cancer Symptoms
headaches
seizures
nausea/vomiting
confusion
blurred vision
sleep-wake disturbances
hearing loss
balance issues