BIOL 3000 Regulation of Gene Expression
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Gene expression determines what
A cell’s function
Prokaryotic organisms
Single cell organisms that lack a defined nucleus
Has free floating DNA in the cell
Transcription, translation, and protein formation occur almost simultaneously
What is the primary method of controlling gene expression in prokaryotes?
Transcription
Eukaryotic organisms layers of regulation
Chromatin
Transcription
RNA processing
Translation
Post-translation
Chromatin remodeling
Has two major protein classes that regulate:
ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes
Histone modifying complexes
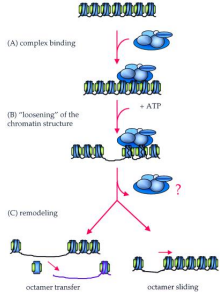
ATP-Dependent chromatin remodeling complexes
Protein complexes that regulate expression by moving, ejecting, or restructuring nucleosomes
Uses energy from ATP to loosen everything
Once protein complex binds to DNA around the nucleosome, chromatin structure is loosened allowing movement of the histone core octamer
Histone/DNA modifying complexes
Protein complexes that enzymatically modify N-terminal histone tails. (Include: methylation, phosphorylation, and acetylation)
Trans-activating factors
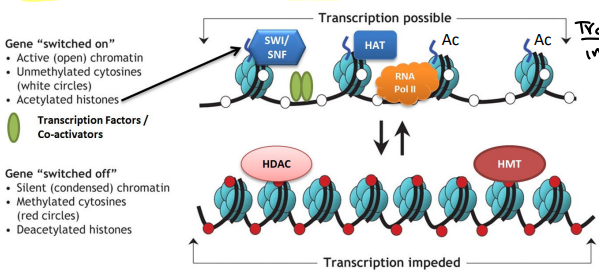
Histone acetylation
Allows expression
Histone de-acetylation
Silences the gene
DNA methylation
Silences the gene
DNA de-methylation
Allows the expression of the gene
Added to the promotor region
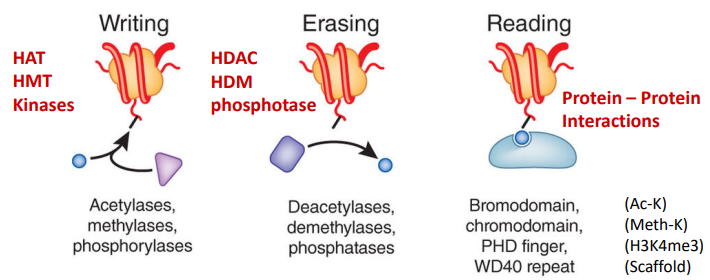
Histone Code Hypothesis
The hypothesis that transcription of DNA is regulated in part by specific chemical modifications to histone proteins
Modifications to the histone proteins themselves recruit other proteins to the modified histone
The recruited proteins act to alter chromatin structure or affect transcription
Transcriptional regulation
The signaling control of gene expression, “on/off”
Several things must happen for a gene to be expressed:
Some kind of initiating signal
Signaling Pathway Cascade
Activation of a Transcription Factor
Recruits other member of the Transcription Complex
Transcriptional Complex recruits RNA Polymerase II
Transcription is initiated at the Promoter Site
Modulating Gene Activity
Any step along the path can be changed to stop the transcription factors.
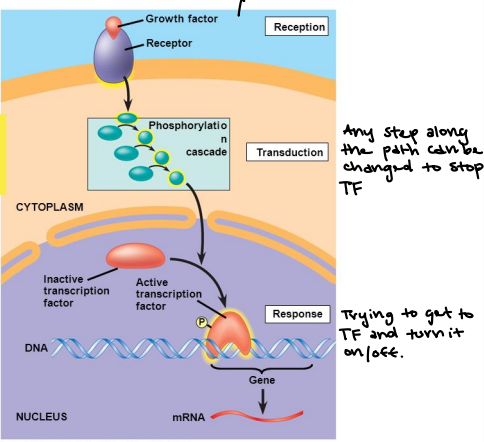
When is the best way to stop gene expression?
As early as possible because cells do not like using energy
Hormone
A molecule that is produced in one cellular location but whose effects are seen in another.
They require the target cell to have receptors specific for that hormone.
Ex: glucocorticoid, testosterone, estrogen
If there is no receptor then there is no?
Response
Estrogen
Controls the expression of many different kinds of proteins
Ex: cell cycle proteins, heat shock proteins
Transcription factors
Controls the rate of gene transcription either by helping or hindering RNA polymerase binding to the DNA. They can cause or block protein production.
They interact with other proteins to build a transcription complex that may increase transcription as much as 100-fold.
Contains DNA binding domains in their tertiary structure that attach to specific DNA sequences
A single gene may have multiple what and why?
Binding sites for distinct transcription factors
Ex: multiple transcription factors can affect the expression of a single gene
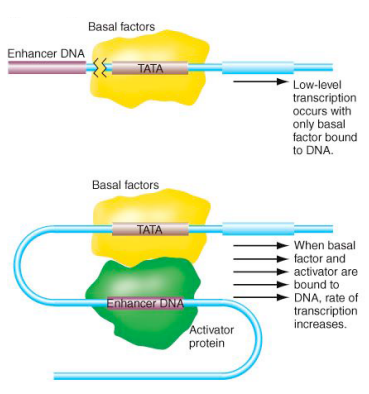
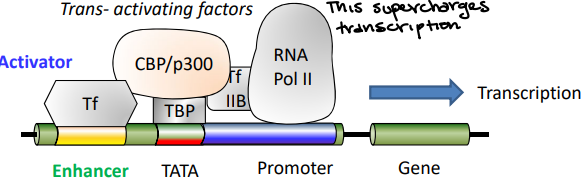
Activator proteins
Can supercharge the basal factors at the TATA box. They do not need to be directly at the basal factor, just around it.
TATA Box
DNA sequence found in the promoter region where Transcription Factor Complex proteins bind, specifically TATA Binding Protein
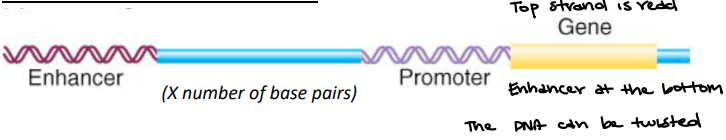
Promoter
The region of DNA located upstream but near the transcription start site of a particular gene that initiates transcription
The site of the TATA-binding protein and basal factor binding; responsible for basal level of expression. Binding to general transcription factors.
Cis-acting DNA elements
Enhancer
The region of DNA that binds to Activator Proteins to activate the transcription process.
Looping of DNA brings transcription factors and trans-activating factors together. It leads to higher efficiency transcription of gene of interest.
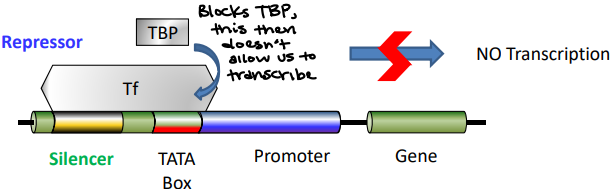
Silencer
The region of DNA that binds to the Repressor Proteins to prevent binding of RNA Pol II to the promoter. It turns off the expression of protein product
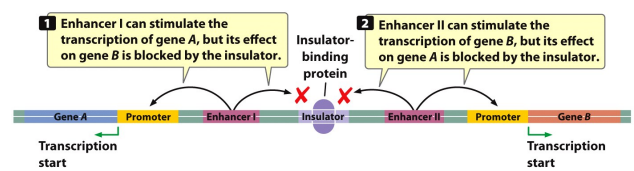
Insulator
The region of DNA that blocks that interaction of enhancers with promoters.
It prevents transcription of Non-Target Genes. It only turns on one gene.
Promoter-proximal elements
The site of additional activator protein binding; responsible for induced/repressed level of expression. Binding by tissue specific transcription factors. It is somewhere close to the promoter.
It can lie “far away” from the gene of interest. It retains its function even when the element is reversed (5’-3’ or 3’-5’)
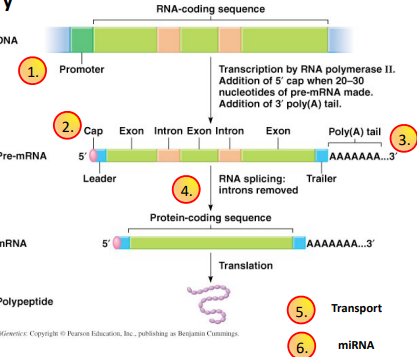
RNA Processing (Post-Transcriptional Regulation, Pre-mRNA Regulation)
The process where primary transcript RNA (nascent hnRNA) is converted to mature messenger RNA (mRNA)
5’ Capping
When a growing RNA chain is ~30 nucleotides long, a guanine group is added to the 5’ end by capping enzymes. The cap protects the growing RNA chain from degradation by nucleases. The entire process occurs co-transcriptionally, or before transcription is finished.
3’ Polyadenylation
Nascent RNA is cleaved by Ribonuclease downstream of the conserved AAUAAA site. Poly(A) Polymerase adds adenine ribonucleotides to the 3’ end of the RNA molecule. Happens post-transcriptionally
Enhances the stability of the RNA molecule and regulates transport to the cytoplasm
Splicing
The mechanism by which introns are removed
Introns
Intervening sequences of RNA not expressed in proteins
Exons
Retained in mature mRNA and are expressing sequences
Spliceosome
Protein/RNA complex that directs and insures proper RNA splicing. It is responsible for both cleavage of the intron from the RNA and ligation of the remaining exons
RNA Transport
Export of mature mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm is controlled by a large number of Messenger Ribonucleoproteins (mRNPS). mRNA export is through large multi-protein pore complexes. Kind of like a pickleball.
Happens post-transcriptionally
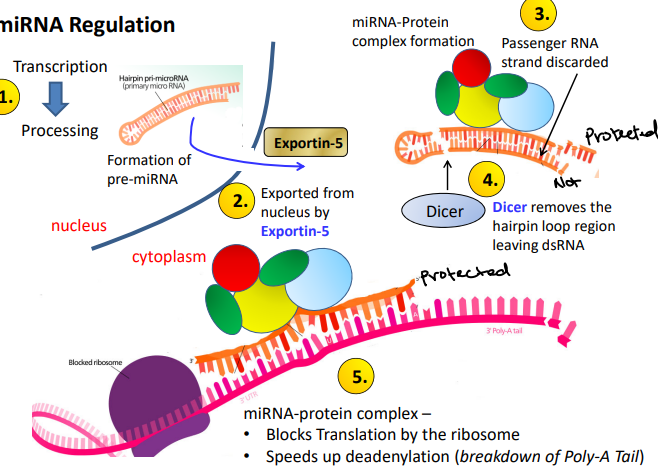
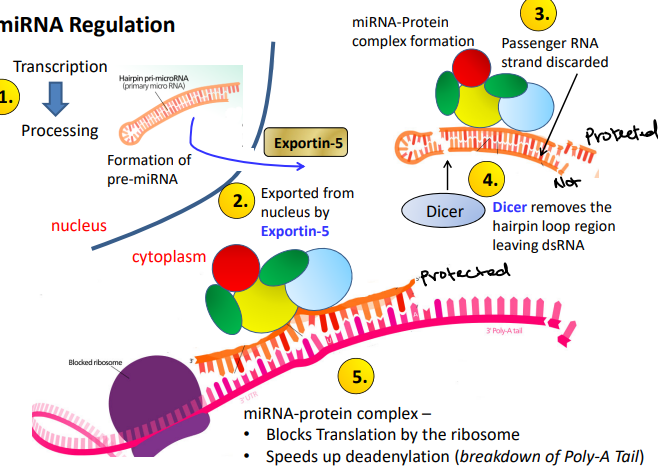
miRNA Regulation
Forms ‘hairpin’ loops made in the nucleus and transported out in the cytoplasm. Perturbed expression in tumors compared to healthy cells. It deregulates in different types of cancers, making them highly useful as biomarkers in future diagnostics as well as attractive drug intervention targets
Mature microRNA (miRNA)
A class of naturally occurring, small non-coding RNA molecules whose main functions is to down regulate gene expression. Approximately 20-25 nucleotides in length
Process of miRNA regulation
Transcription → Processing
Exported from nucleus by Exportin-5
Passenger RNA strand discarded
Dicer removes the hairpin loop region leaving dsRNA. Cuts the hairpin loop.
miRNA-protein complex: blocks translation by the ribosome, speeds up de-adenylation (breakdown of Poly-A tail)
RNA processing summary
Translational Regulation: Initiation
Ribosomal subunit proteins and initiation factors form a complex that recognizes the 5’-Cap of mRNA.
Once bound, the complex scans down the mRNA until the initiation codon (AUG) is located.
The initiation complex lines up the codon with the P site of the 60S ribosomal subunit and translation begins.
Translational regulation: Elongation
Dependent on ribosomal elongation factors
80S Ribosome reads down the mRNA strand resulting in synthesis of a polypeptide chain.
Ribosomal pausing
Stacking of ribosomes on an mRNA molecule caused by changes in cellular environment. Can result in release of the ribosome and premature degradation of the incomplete polypeptide
Translational regulation: Termination
Ribosome reaches a STOP codon and Release Factor binds to the ribosome.
Polypeptide chain is hydrolyzed from the ribosome and the protein is released from the ribosome
Post-translational Regulation
Modification of amino acids in a protein resulting in structural changes or attachment of other biochemical functional groups
Disulfide bonds
Between cysteine residues in close proximity as a result of a proteins tertiary structure
Proteolytic cleavage
Cleavage of a pre-protein resulting in a mature, functional protein
Ex: insulin
Myristoylation
Attachment of lipid chains resulting in membrane localization of a protein
Phosphorylation
Attachment of phosphate groups to specific amino acids resulting in regulation of enzymatic activity
Regulation of gene expression
Includes a wide range of mechanisms used by the cell to increase or decrease the production of specific genes
Up-regulation
The process which results in increased expression of one or more genes. Increasing functionality
Down-regulation
The process which results in decreased gene and corresponding protein expression