AP World History: Unit 5 A31-A42 Terminology
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Geocentric Theory
Falsely-held Medieval model where bodies orbit around earth
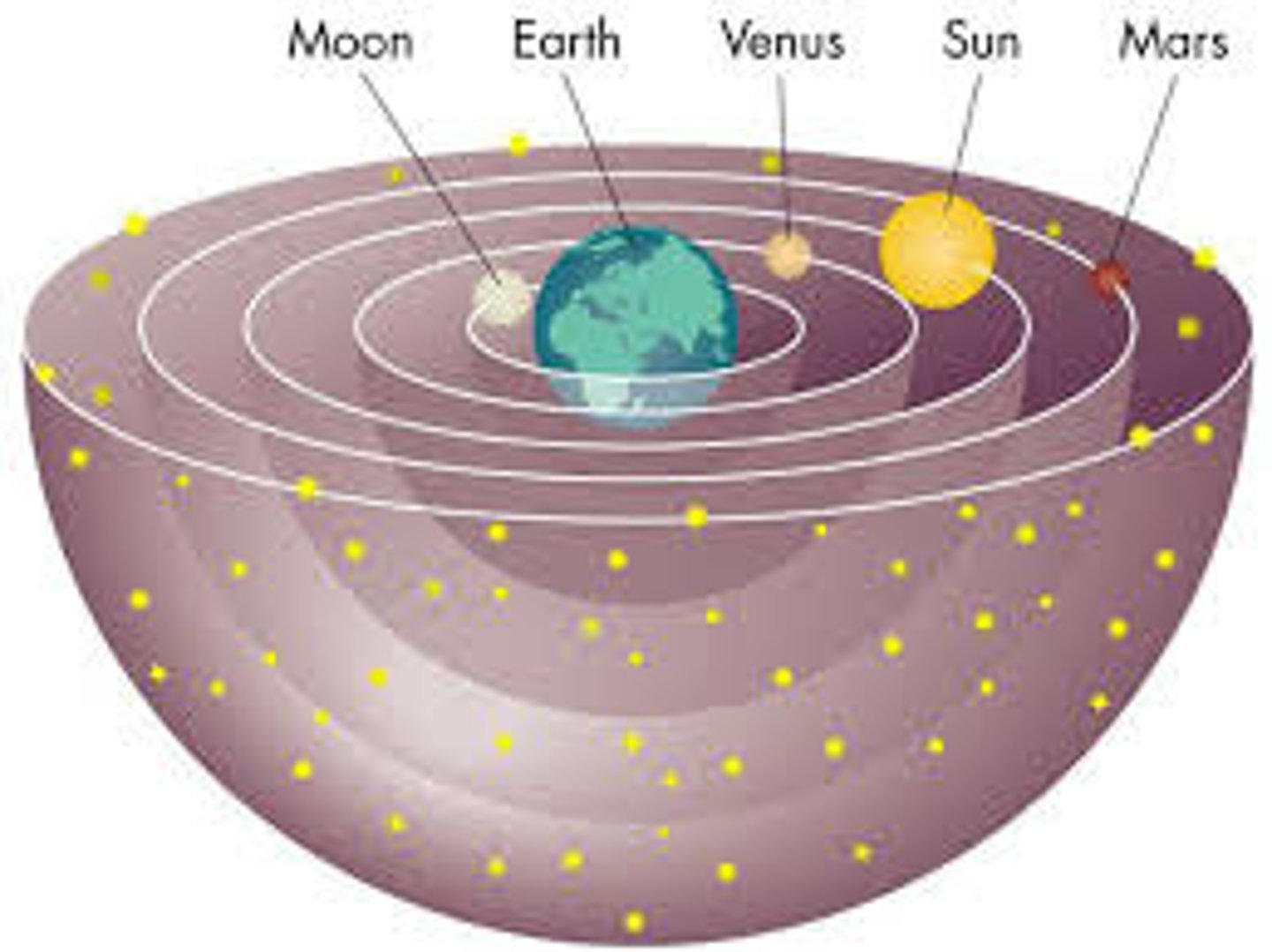
Heliocentric Theory
Astronomical model with earth and planets orbiting the sun; championed by Copernicus & Galileo
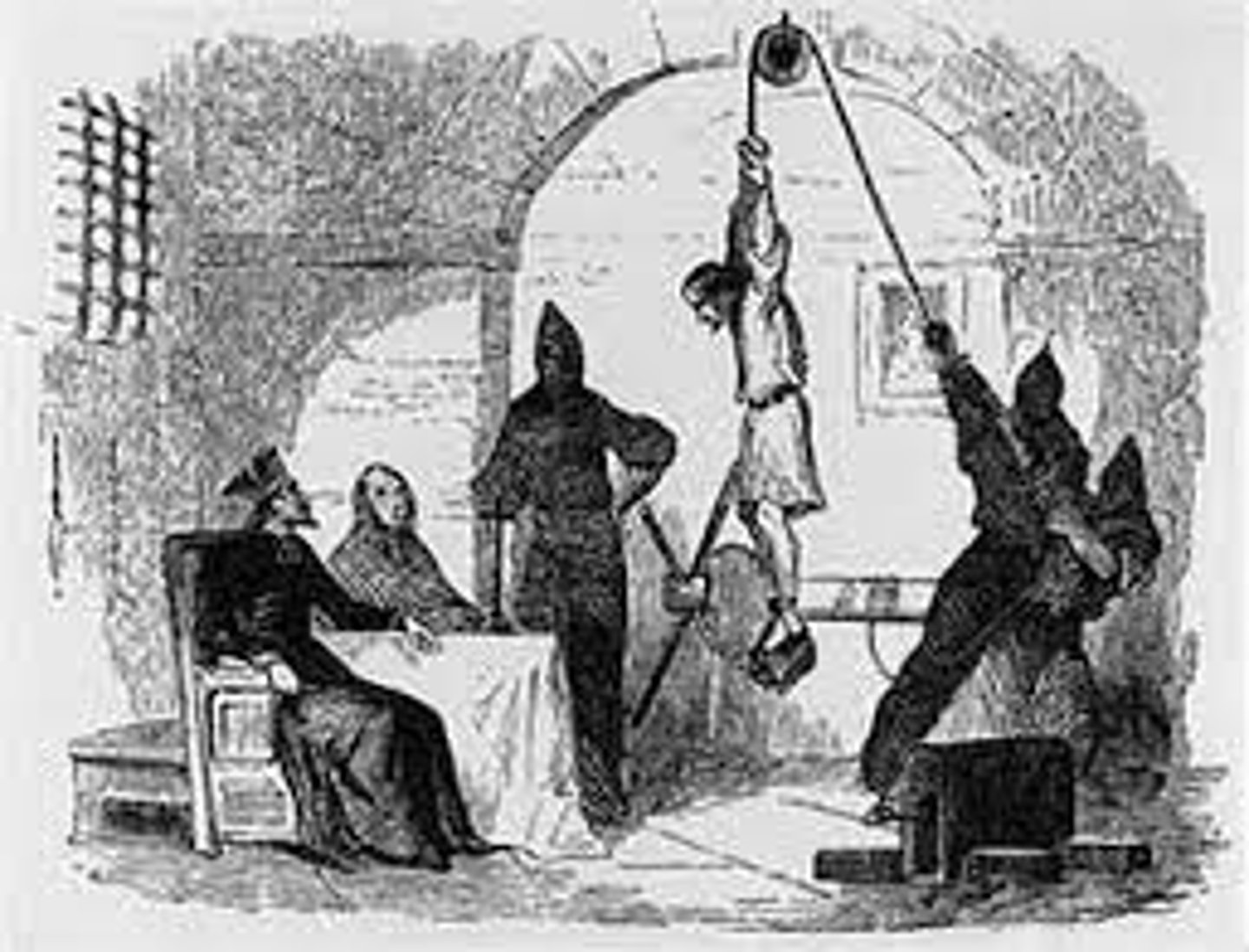
The Inquisition
Institution within the Catholic Church that arose following the Protestant Reformation using arrests, trials, penance, torture, and execution to combat heresy; active in Italy, Spain, Portugal, and the Iberian colonies in the Americas

Empiricism
Theory that knowledge can only be derived from evidence from sense experience; in other words, seeing is believing as opposed to taking something on faith or because someone else said it was true; outlook behind Scientific Method

Reason
Logic; central to Enlightenment thought; in opposition to faith

Natural Rights
Rights that are fundamental or inalienable; rights that all people are born with; only corrupt governments take them away; sometimes life, liberty, and property are enumerated natural rights

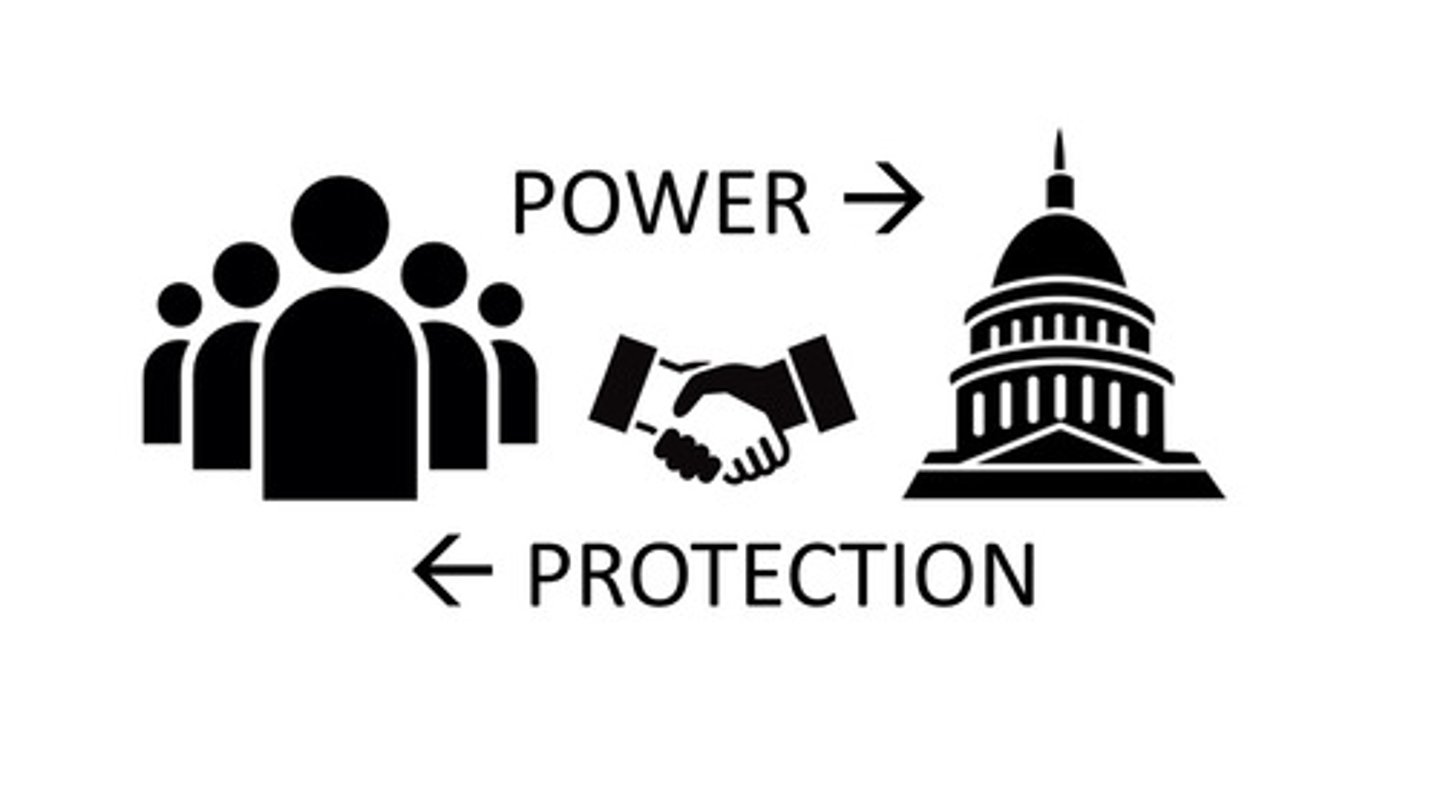
Social Contract
An implicit agreement among members of a society to give up unlimited freedoms in the name of the common good in exchange for state protection of most freedoms and rights; Rousseau championed this.
Salon
A gathering of thinkers and philosophers, typically in the home of a progressive, wealthy Parisian woman; showing some allowed participation of women in movement

Consent of the Governed
A government's legitimacy is only valid and lawful if the people being governed agree to its policies and legitimacy; i.e. government exists for the benefit of the people; this is in contrast to the Divine Right of Kings theory

Separate Branches of Government
When the executive, legislative, and judicial branches are separate rather than under the authority of a monarch or individual

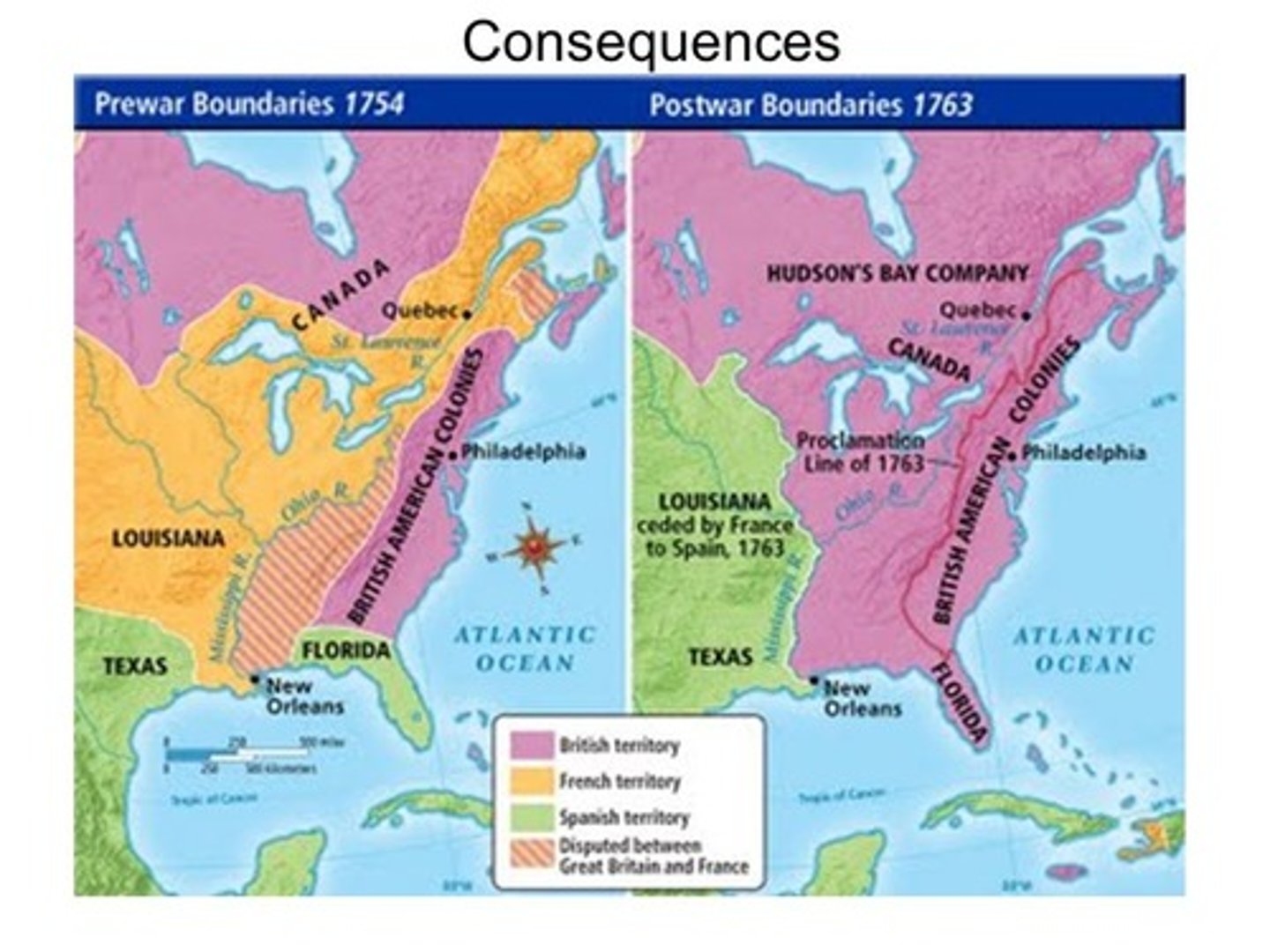
Seven Years' War
Global conflict between Great Britain and France fighting for overseas colonial holdings; France expelled from Canada and rest of North America; France expelled from India; Creates debt which causes Great Britain to tax American colonists (Stamp Act and Tea Act) leading to rebellion
Common Sense
A pamphlet written by Thomas Paine in 1775 advocating for American independence from Great Britain on grounds of liberty and consent of the governed; widely read in the 13 colonies

Stamp Act
A tax levied on printed materials in the American colonies by British Parliament; causes outrage among colonists who cry Taxation without Representation

Declaration of Independence
A formal declaration stating the rationale for the United States to declare its independence from Great Britain adopted on July 4, 1776. Language declares "all men are created equal" and insists on "consent of the governed"

Loyalists
Colonists in the Thirteen Colonies who remained loyal to the British Crown during the American Revolutionary War; typically more conservative, southern, and had trade ties to Great Britain; many fled to Canada

Suffrage
The right to vote; in context of newly independent United States, only wealthy white men with property enjoyed suffrage at first

Three-Fifths Compromise
An absurd arrangement in the House of Representatives in which black slaves in the American south are counted as 3/5 of a person to give southern states more political power even though blacks are treated like property and given no rights at all.
Bourgeoisie
Middle class; in context of French Revolution, they are NOT nobles so are represented by Third Estate; some may be rich

Despot
A ruler who has absolute power; suggests tyrannical rule
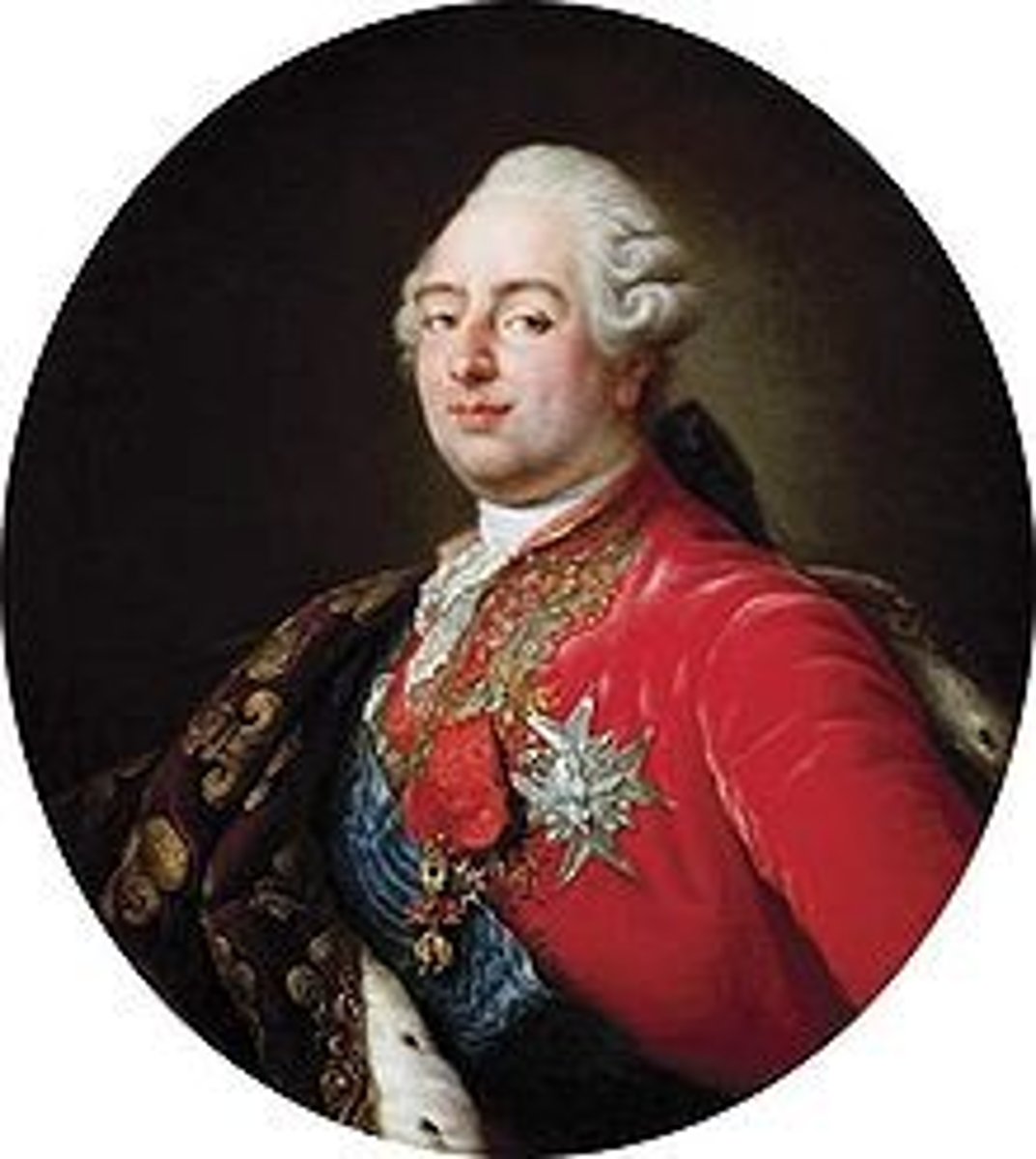

Tithe
Obligatory one-tenth tax owed to the Catholic Church before the revolution

Estates General
The French parliament until 1789 consisting of three estates - 1st, 2nd, and 3rd
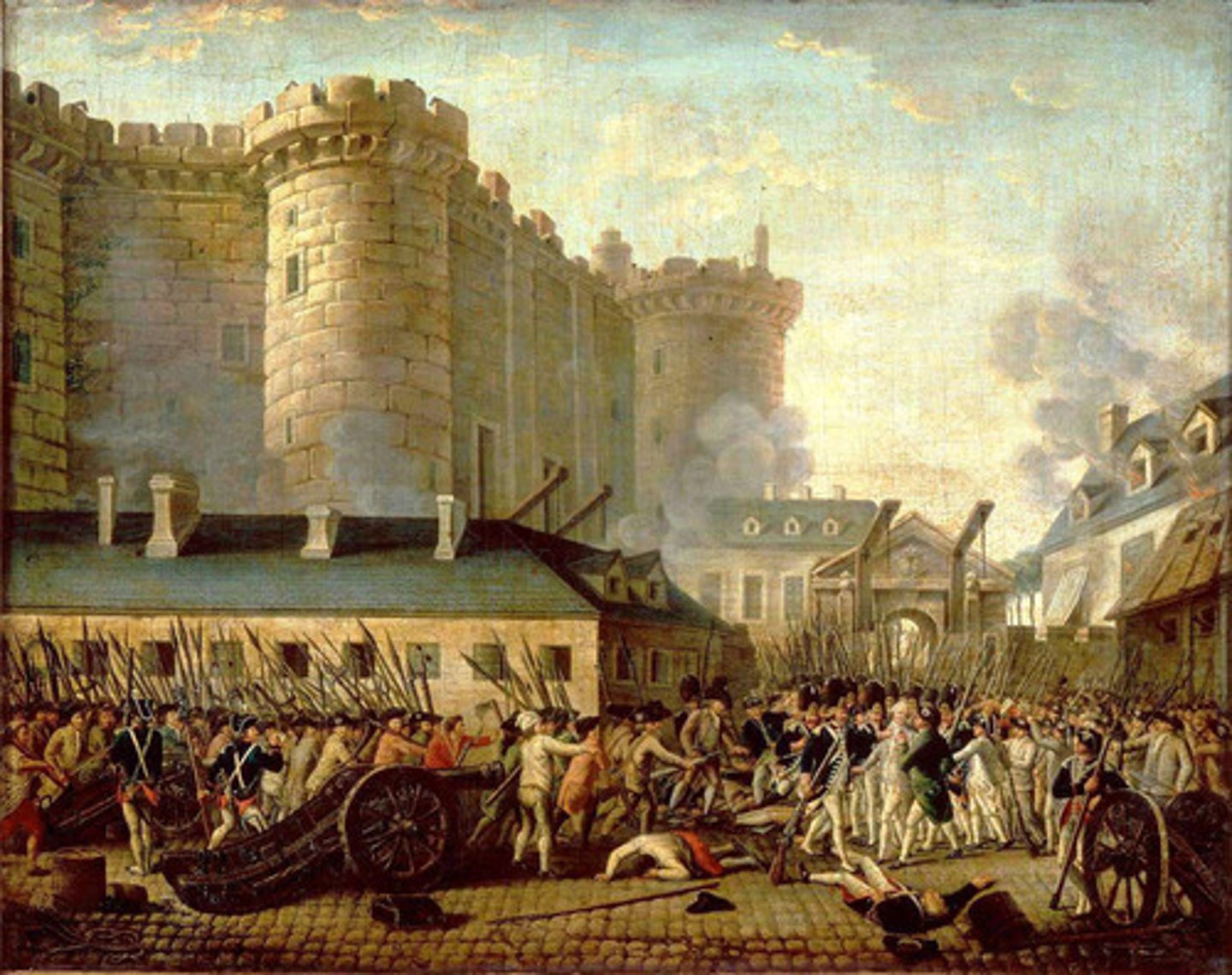
Bastille
A prison fortress in Paris used by kings to imprison political prisoners; stormed in 1789
Declaration of the Rights of Man
A civil rights document produced during revolution; considered very influential Enlightenment Document; describes "natural and inalienable rights" "men are born free" "equality before the law" "innocent until proven guilty"

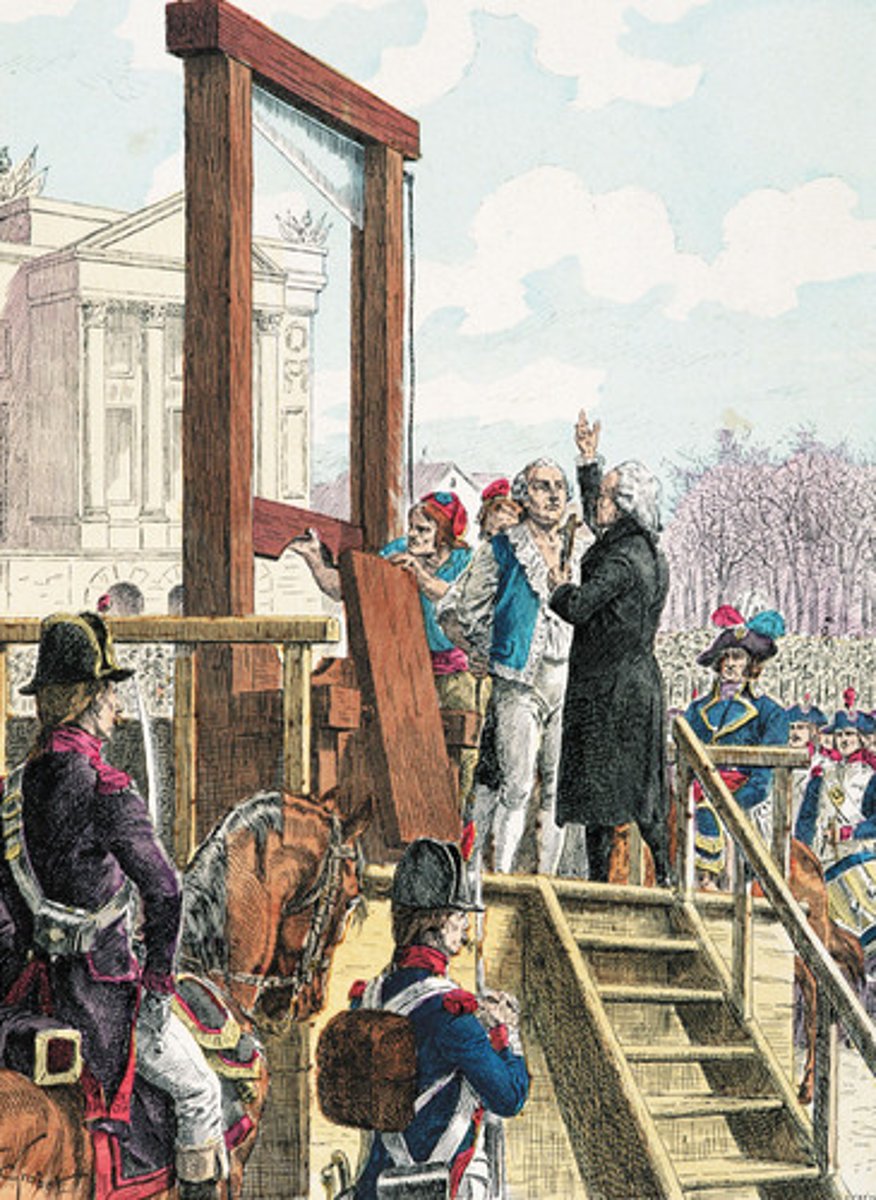
Guillotine
An apparatus designed to humanely decapitate a person

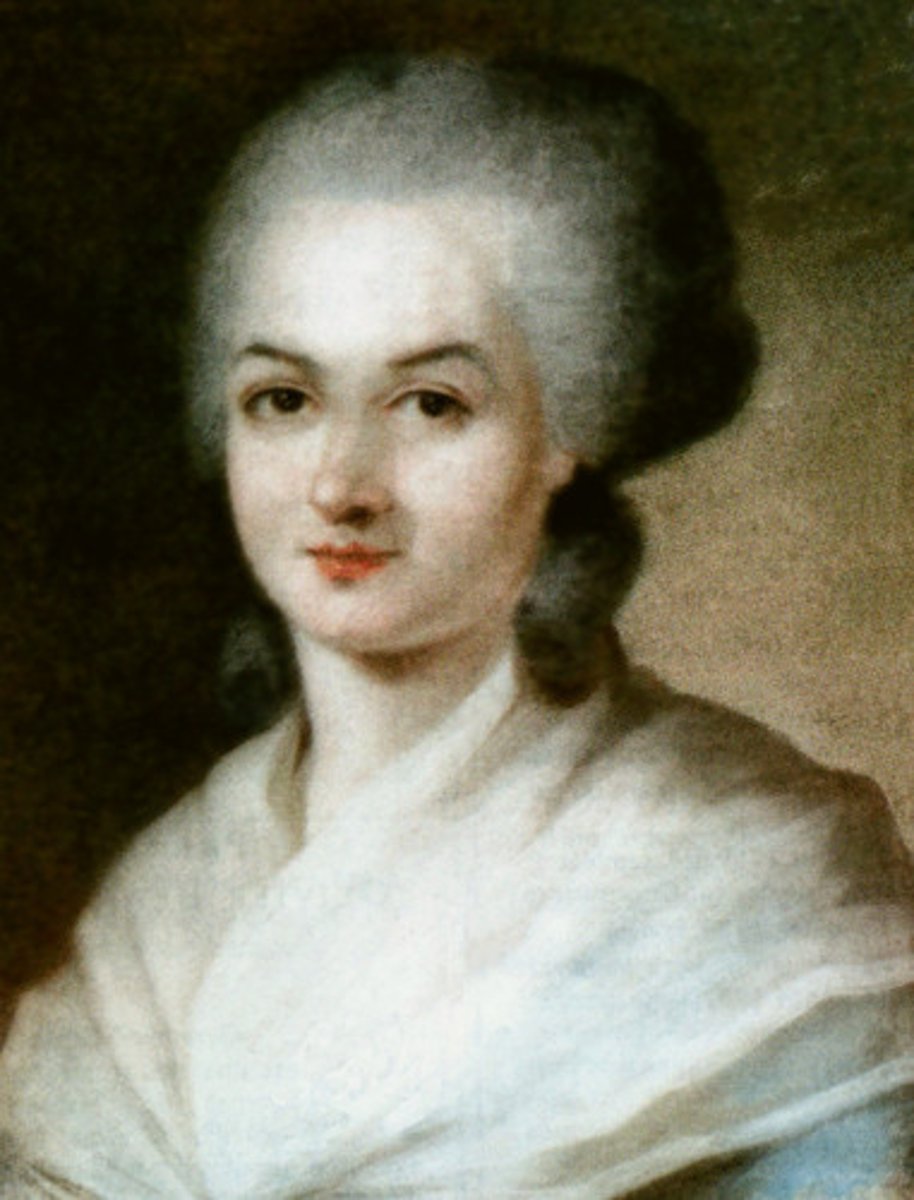
Olympe de Gouges
French Enlightenment playwright and activist who supported abolition of slavery and women's rights; wrote Declaration of the Rights of Woman as counter to Declaration of the Rights of Man; was executed by guillotine when she criticized Robespierre

Maximilien Robespierre
A radical leader of the Revolution who engineered the Reign of Terror

Reign of Terror
A period of arrests, executions, and imprisonment led by radical Jacobins; shows excessive violent stage of the Revolution

Coup D'état
An overthrow of the government using force; Napoleon takes power this way; shortened to coup

Toussaint L'Ouverture
Former slave in Haiti who was freed and became the leader of the Haitian slave rebellion and independence movement; captured by French forces and died in French prison

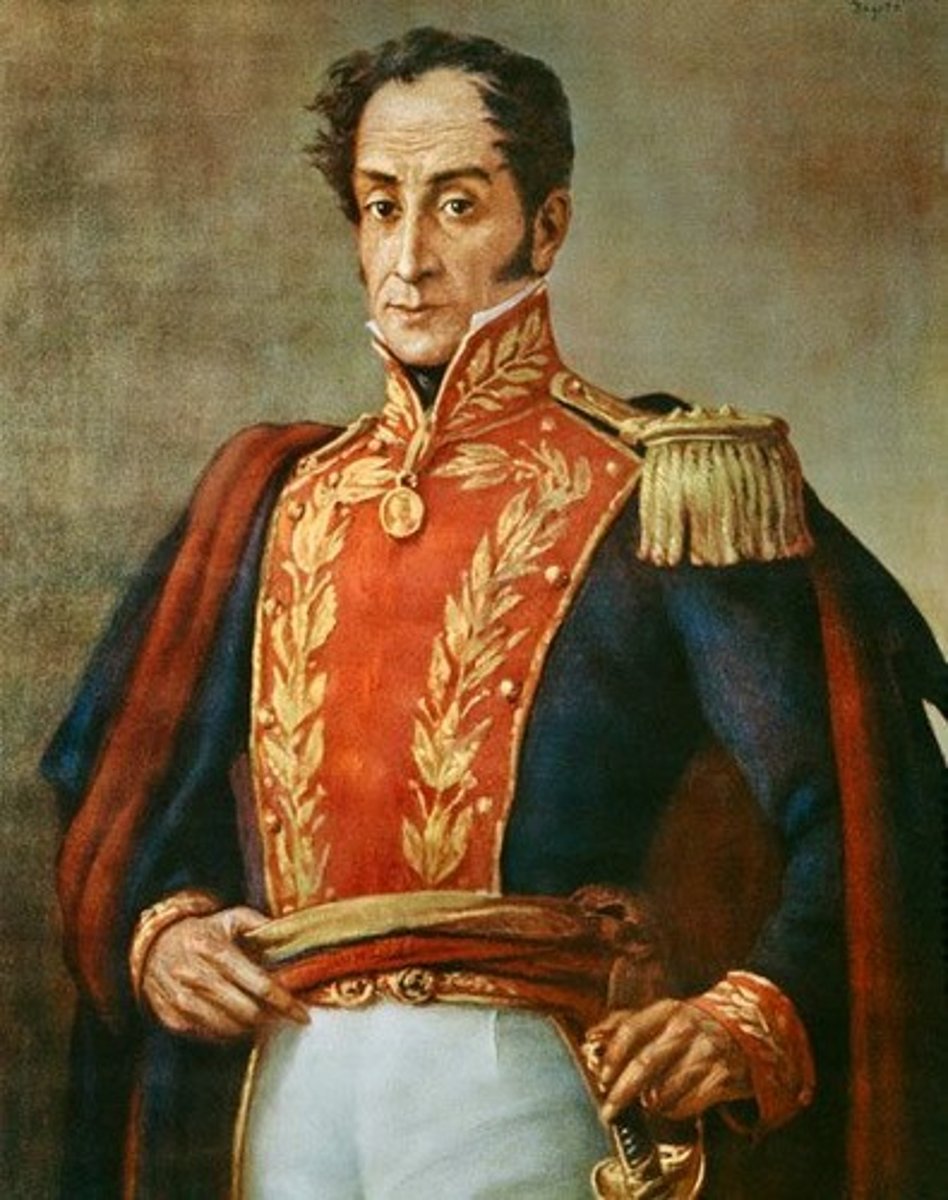
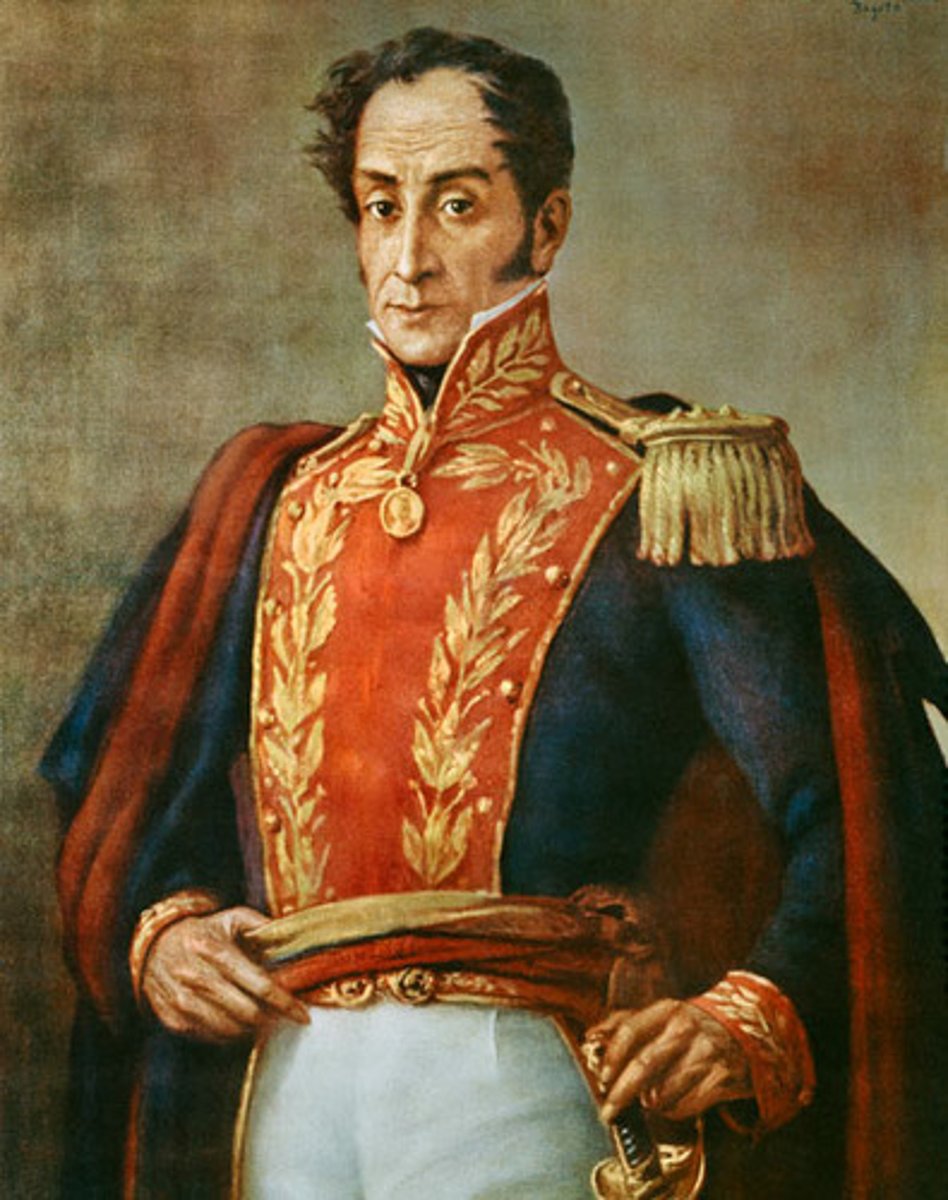
Simon Bolivar
Wealthy creole from Venezuela who successfully led the independence armies of all the northern South American colonies against Spain; considered the Liberator of America (South America)

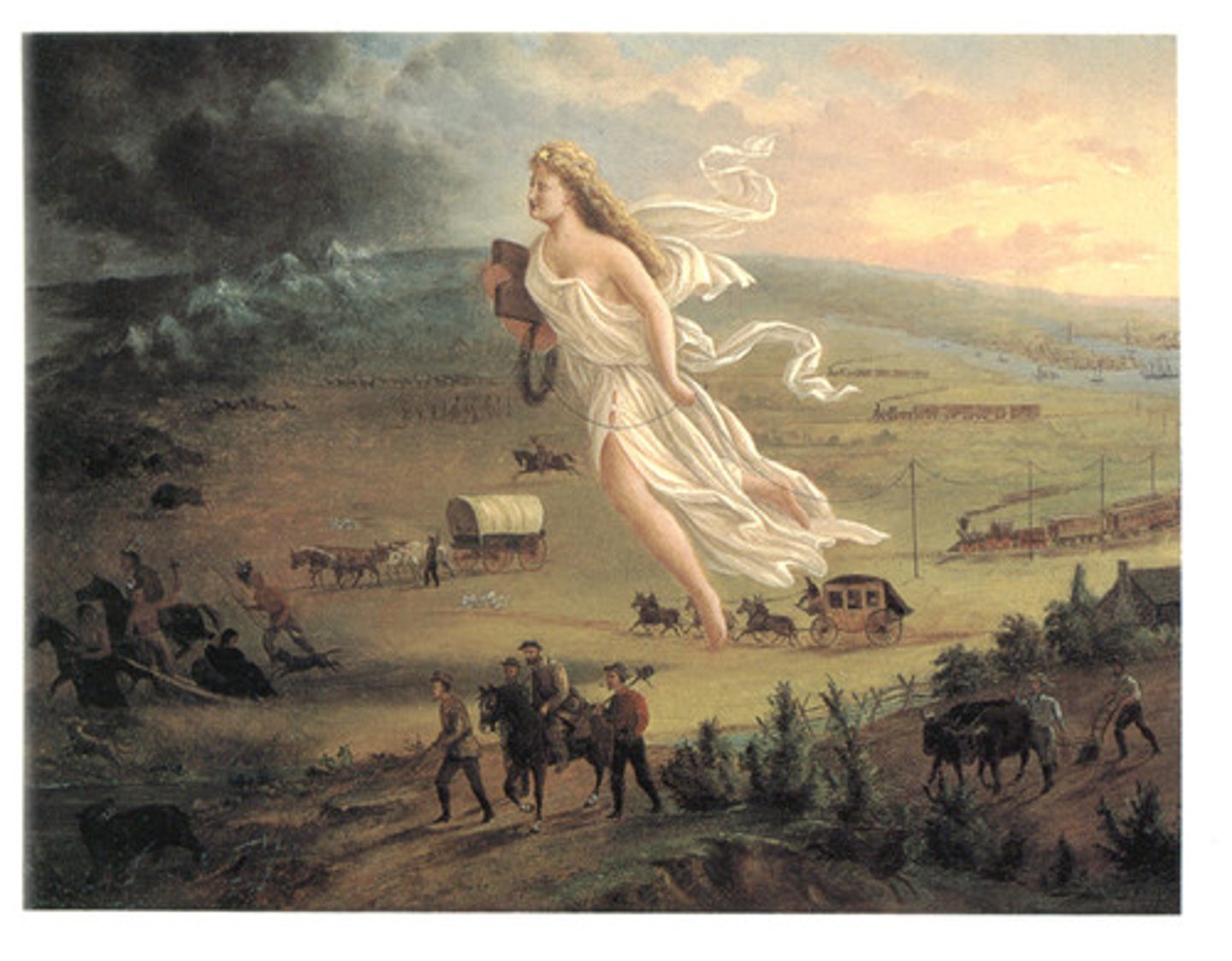
Manifest Destiny
A cultural belief in the 19th-century United States that the United States was destined to expand westward across North America to the Pacific; justification for Mexican-American War, Homestead Act, and war against Native Americans

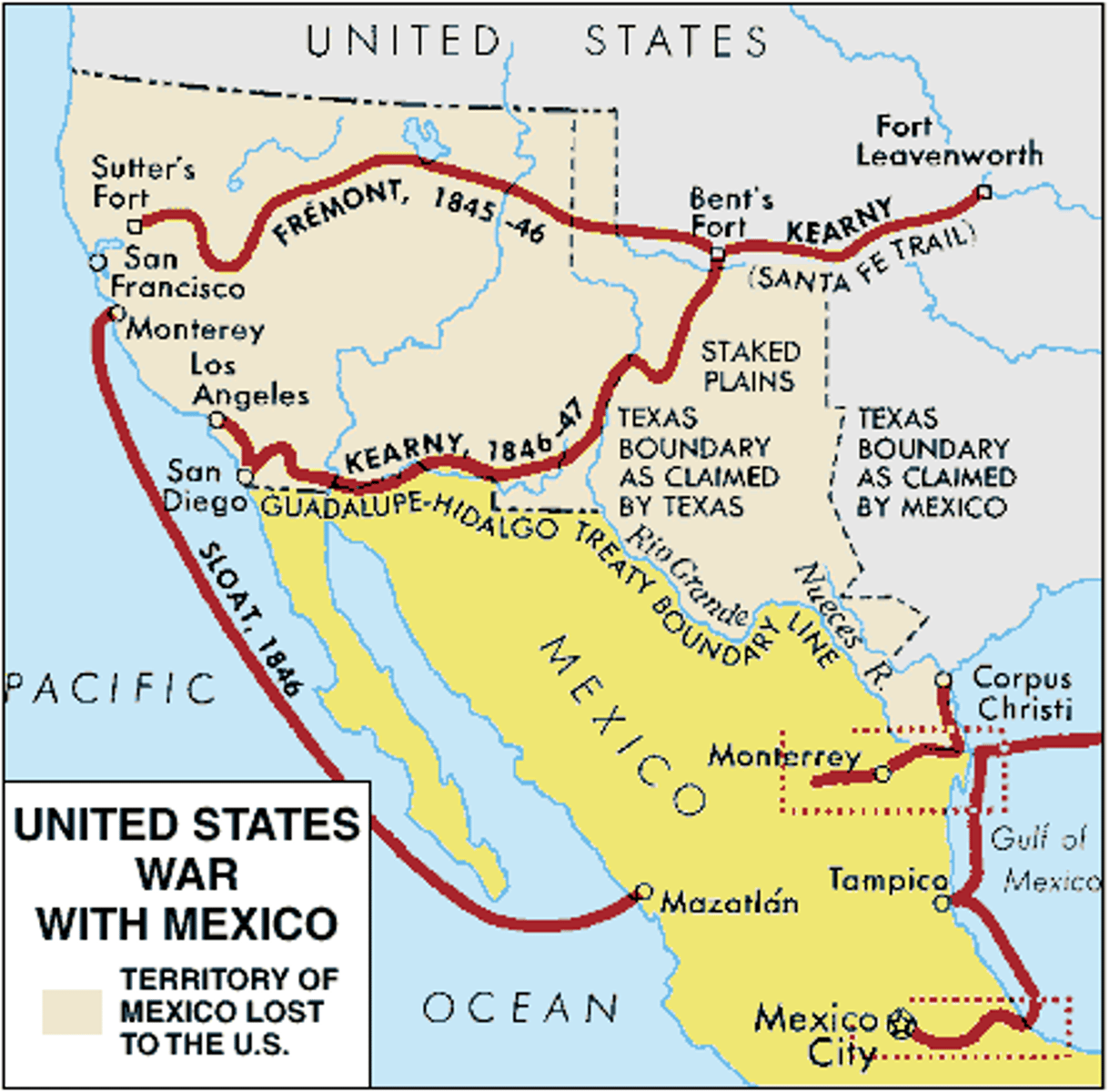
Mexican-American War
War begun by United States resulting in seizure of California, Nevada, Arizona, New Mexico, Utah, and Colorado from Mexico; 1846-1848
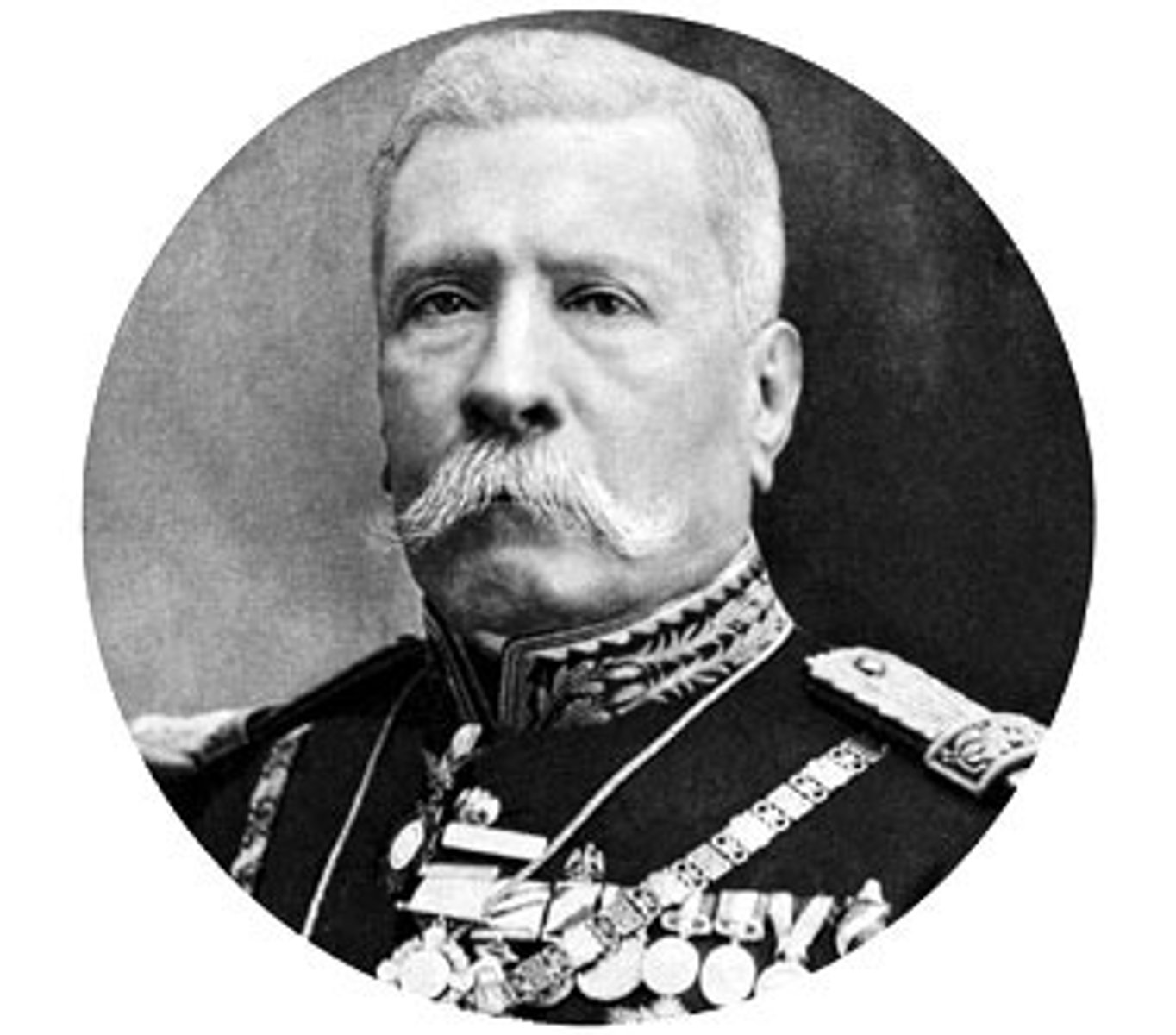
Porfirio Diaz
Period of rule in Mexico by Porfirio Diaz from 1876-1911 characterized by foreign investment in resource extraction and modernization projects, exploitation of poor, undemocratic rule; will be toppled in Mexican Revolution

Neocolonialism
When a former colony continues to be locked in unequal relationships with more powerful countries as it continues to export cash crops and raw materials while not developing its own manufacturing sector

Economic Imperialism
The dominance of weaker countries by more powerful countries often through the corporate ownership of the weaker countries' raw materials and cash crop production; An example is US and Great Britain in Latin America

Guano
The excrement of seabirds and bats used as fertilizer in farming; a natural resource in South America

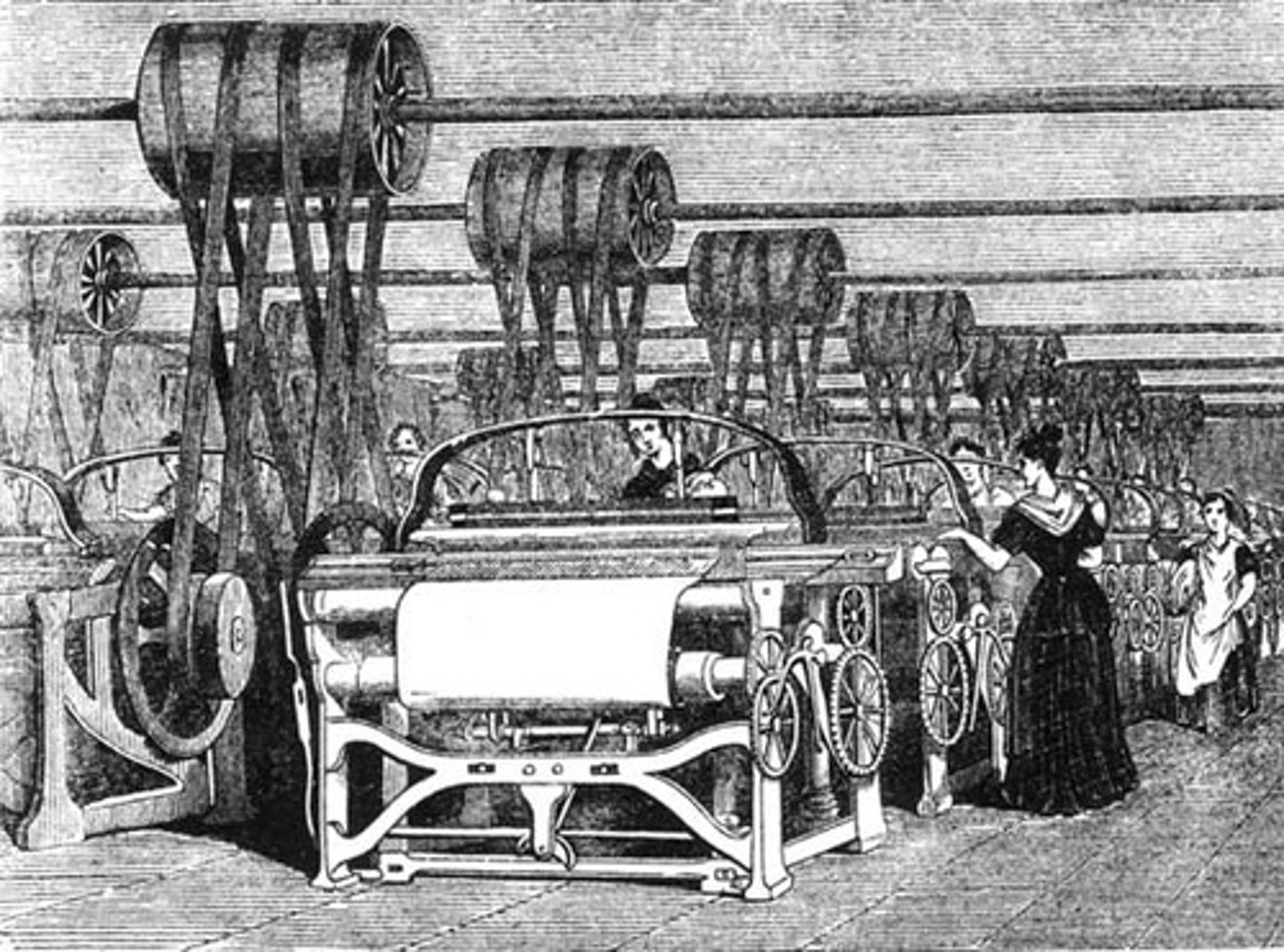
Industrial Revolution
The transition from manufacturing by hand to manufacturing using machines in a factory setting begun in Great Britain; also, advancements in transportation, communication, and power technology
Agricultural Revolution
A dramatic increase in agricultural productivity on Great Britain's farms from crop rotation, a transition to larger farms, livestock breeding, and farming machinery; crop increase will help feed a country with a shift from farmers to factory workers
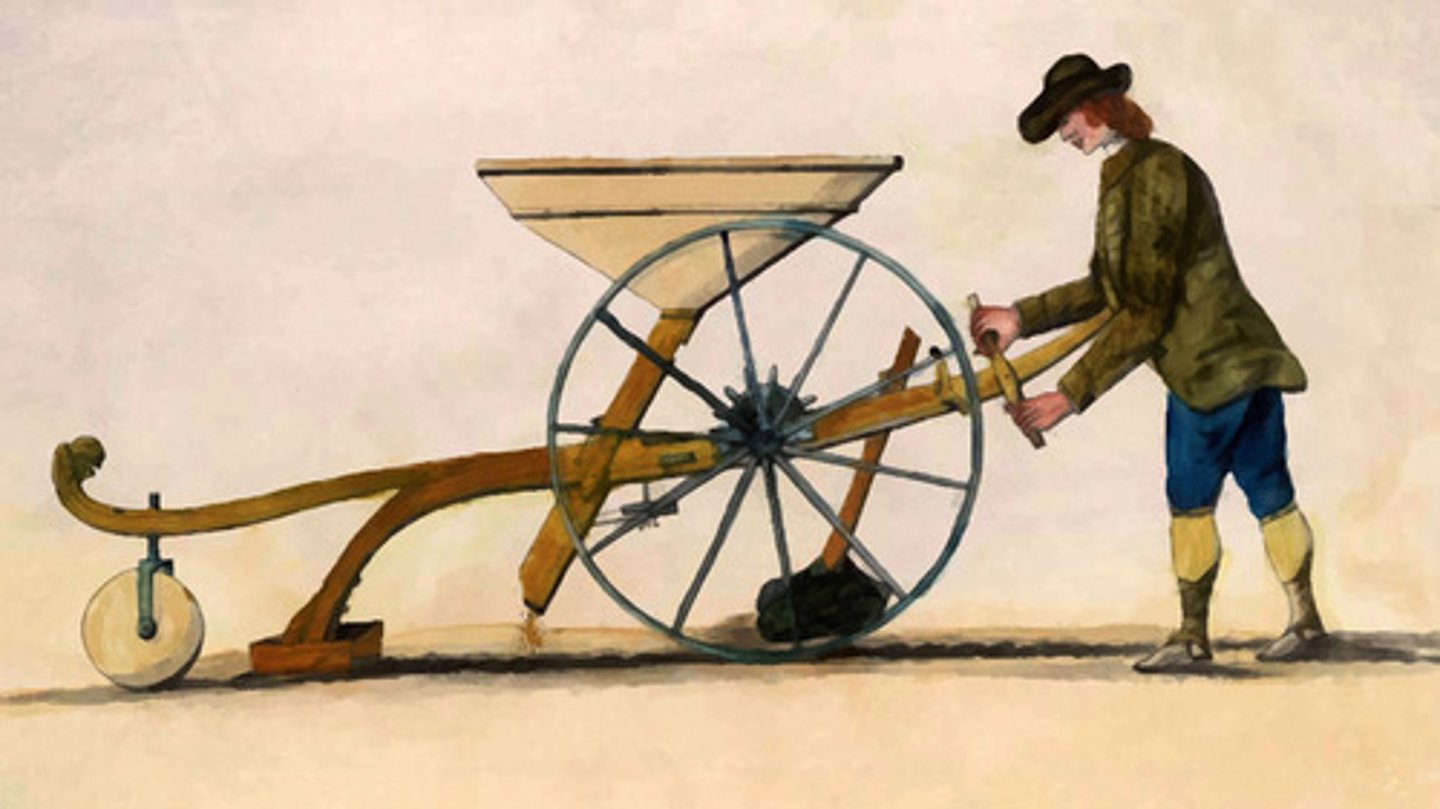
Crop Rotation
The practice of switching from one crop to another in the same field over a series of harvest seasons in order to avoid nutrient depletion in the soil; turnips and clover introduced; replaces practice of leaving fields fallow; leads to greater crop gains; provides food for livestock

Enclosures Movement
The practice of the confiscation of commons lands by wealthy landowners and the forced fencing of lands meant to deprive small landowners of their land; poor farmers were displaced and went to live in cities and became the factory workers of the Industrial Revolution

Urbanization
A population shift from rural areas to urban ones leading to the rise in the sizes of towns and cities; seen as both a cause of and a product of industrialization
Canal
An artificial waterway; used for the transport of raw materials and manufactured products during the Industrial Revolution
Markets
In economic terms, these are locations comprised of consumers who purchase goods

Demand
In economic terms, this is consumer interest in buying a product

Patent
A type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time; this will help provide incentives for inventors

Capital
Money that is available for borrowing in order to finance a project, like the building of a factory

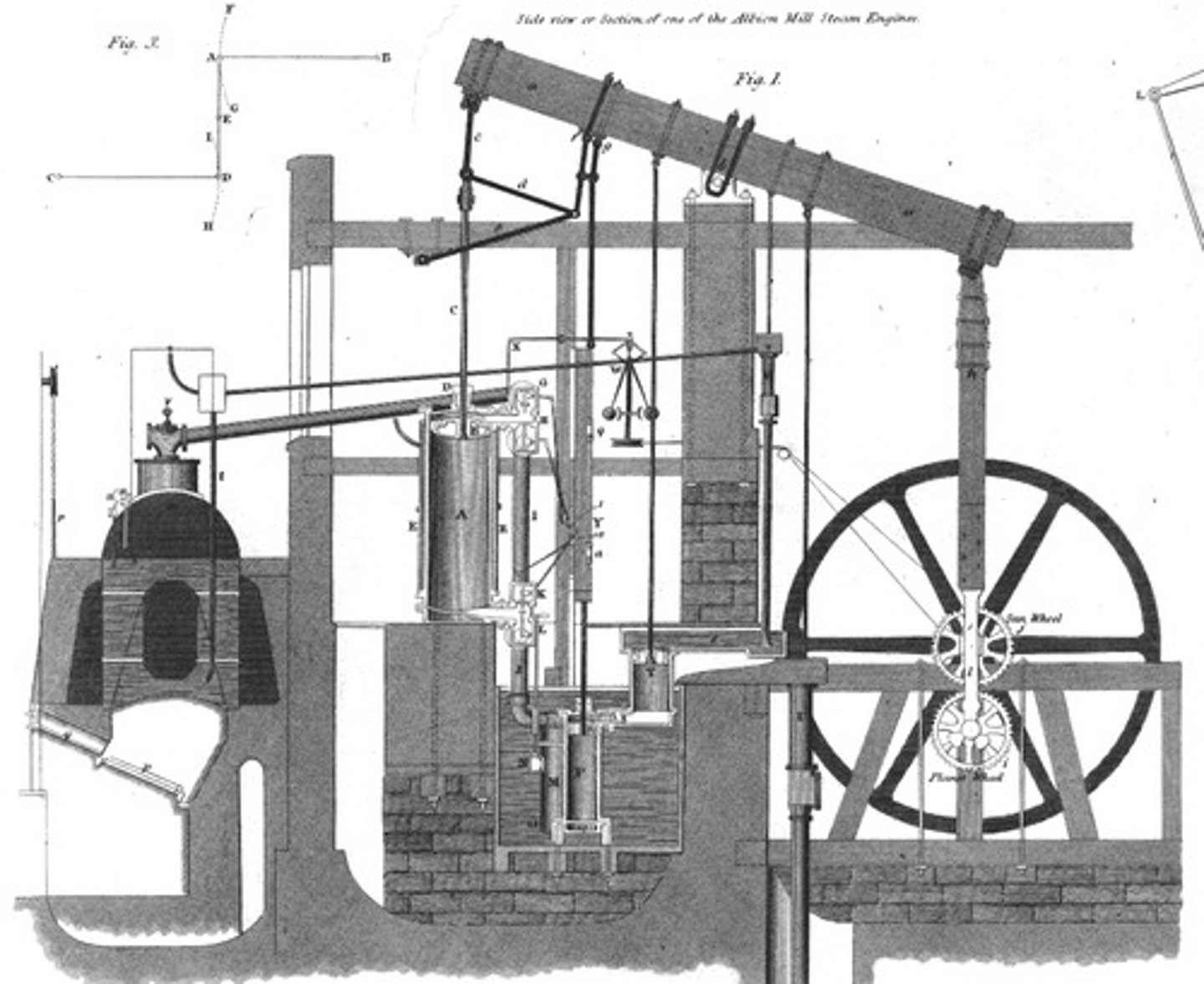
Steam Engine
An engine that performs mechanical work using steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder; requires a fuel (charcoal or coal) to boil the water to produce the steam; used in factories to power machinery and on locomotives and steamships
Internal Combustion Engine
An engine in which the combustion of a fuel (like gasoline) occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber; the explosion of the fuel forces a piston back and forth inside a cylinder; used in cars

Specialization of Labor
The separation of the tasks in the manufacturing process so that workers may specialize in a stage of production and complete that stage with speed; helps lower costs, increase profits, and contribute to a lower cost of the final product

Loom
A device used to weave cloth; Industrial Revolution will see transition from hand looms to power looms
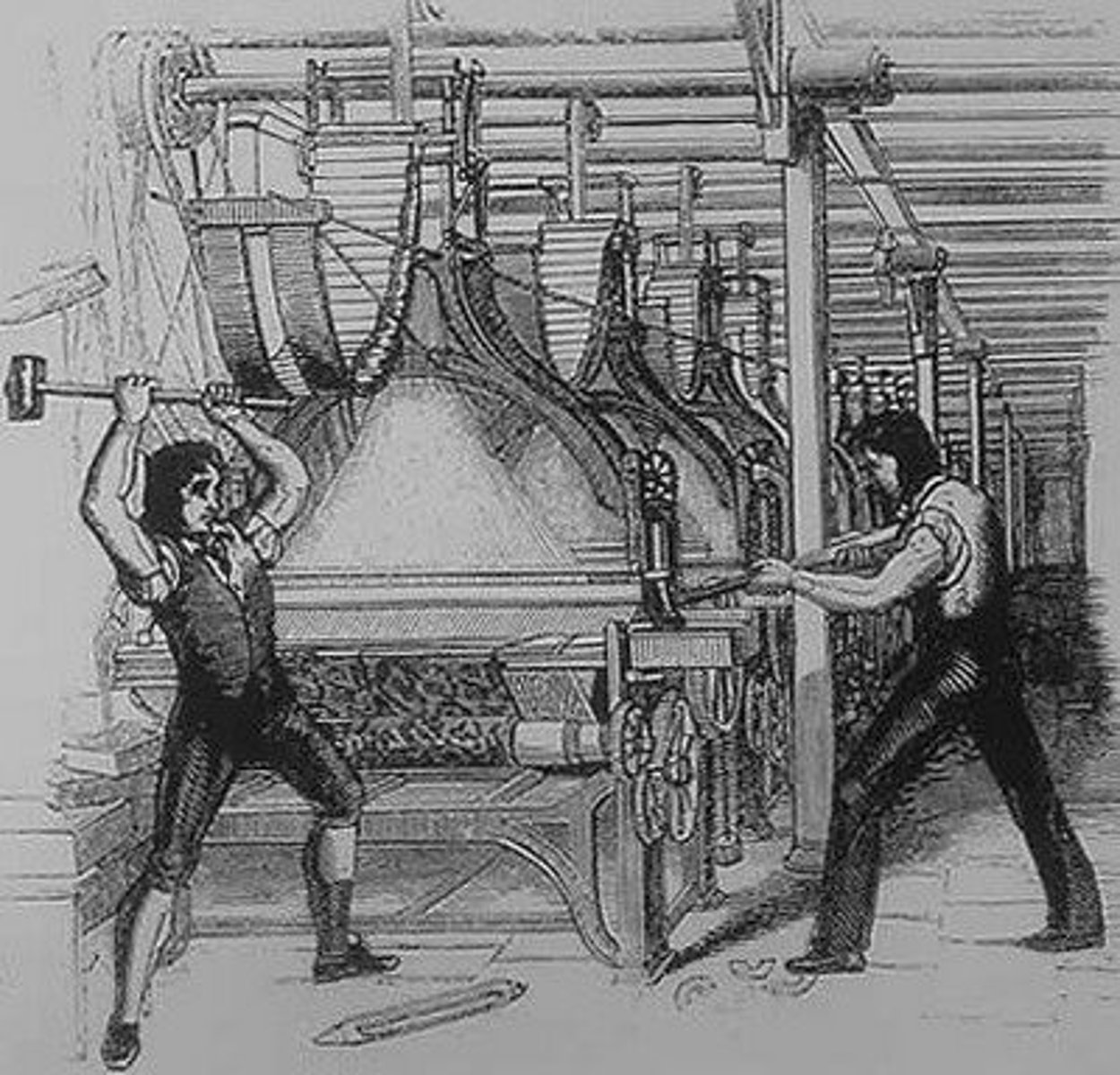
Luddites
An organization of English textile workers in the 19th century who formed a radical faction which destroyed textile machinery in factories to protest being put out of work by the factories which could sell products for less money
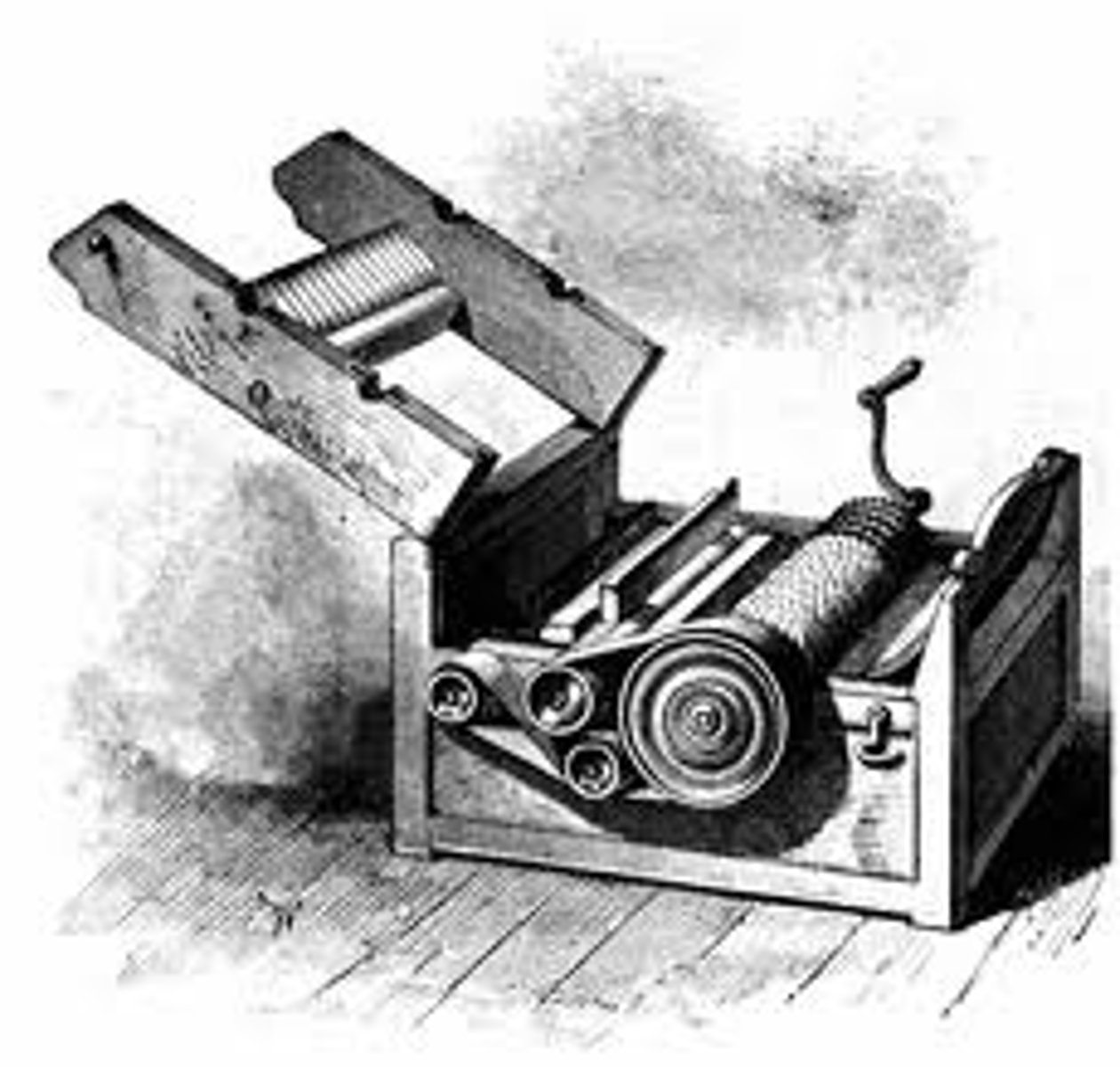
Cotton Gin
A machine that separates cotton fibers from their seeds, enabling much greater productivity than manual cotton separation; encouraged expansion of cotton farming in U.S. south and the expansion of the use of slave labor
Telegraph
A communication technology that emerged in the 1840s utilizing wires strung from utility poles which transmitted electrical currents to send a coded message using Morse Code
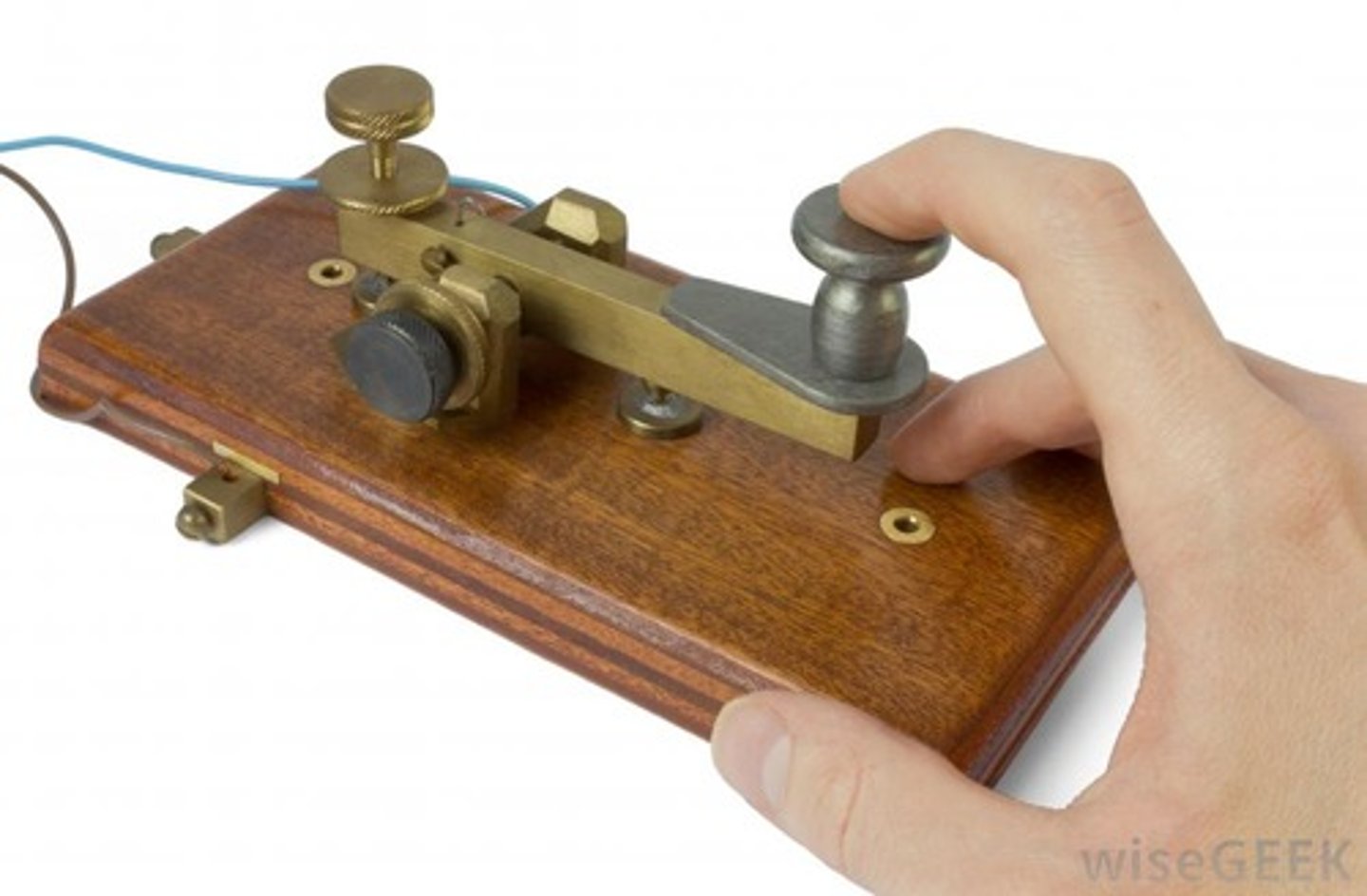

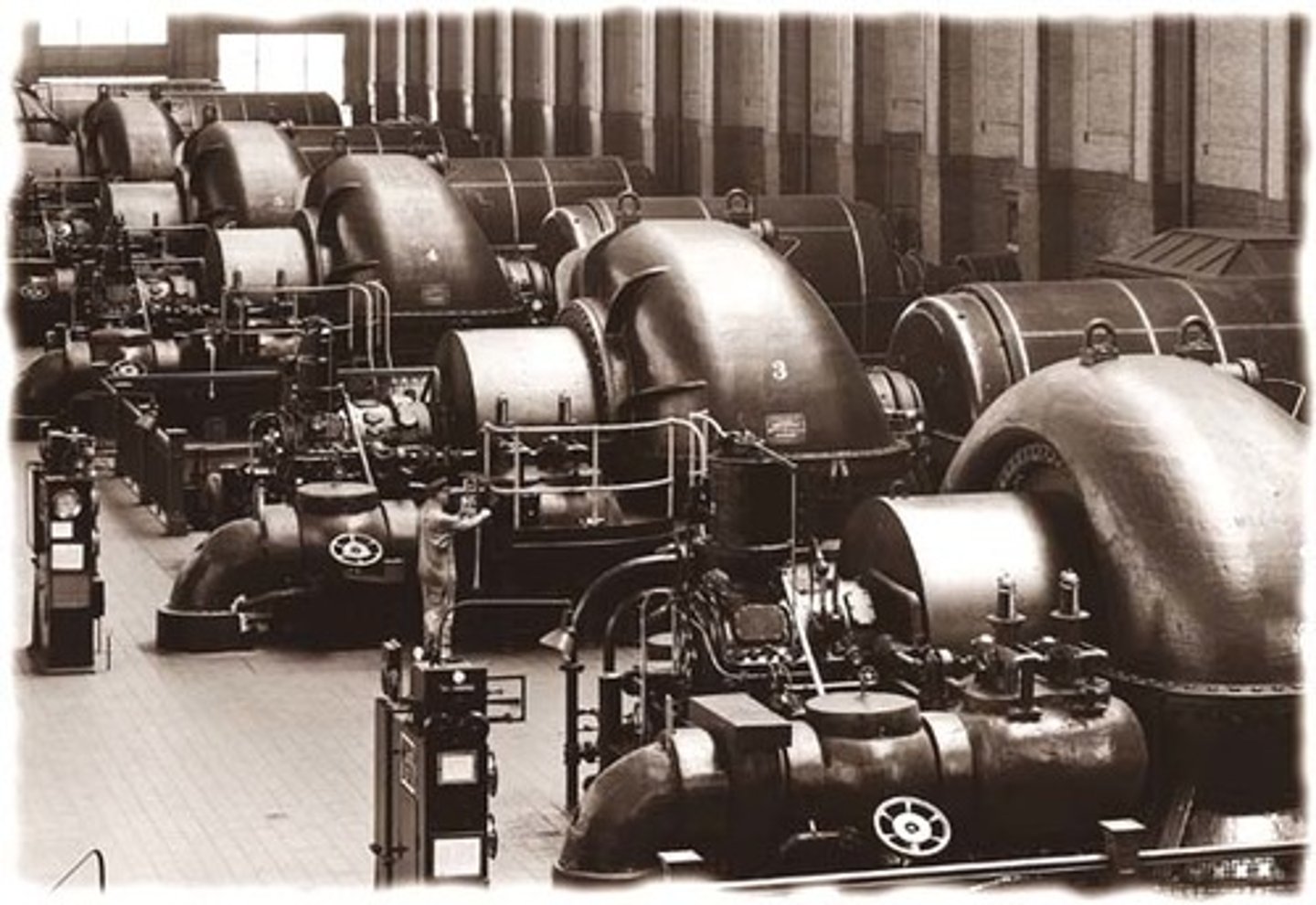
Second Industrial Revolution
A phase of rapid scientific discovery, mass production, and industrialization from 1870 to 1914 with innovations in steel production, chemicals, electricity, and precision machinery
Laissez-Faire Economics
A component of Free Market Capitalism in which the government is encouraged to have a relatively hands-off approach to the economy, abandoning tariffs, price controls, etc.

Comparative Advantage
A concept of free market capitalism in which countries ought to produce and export only products which they can specialize in and produce more cheaply

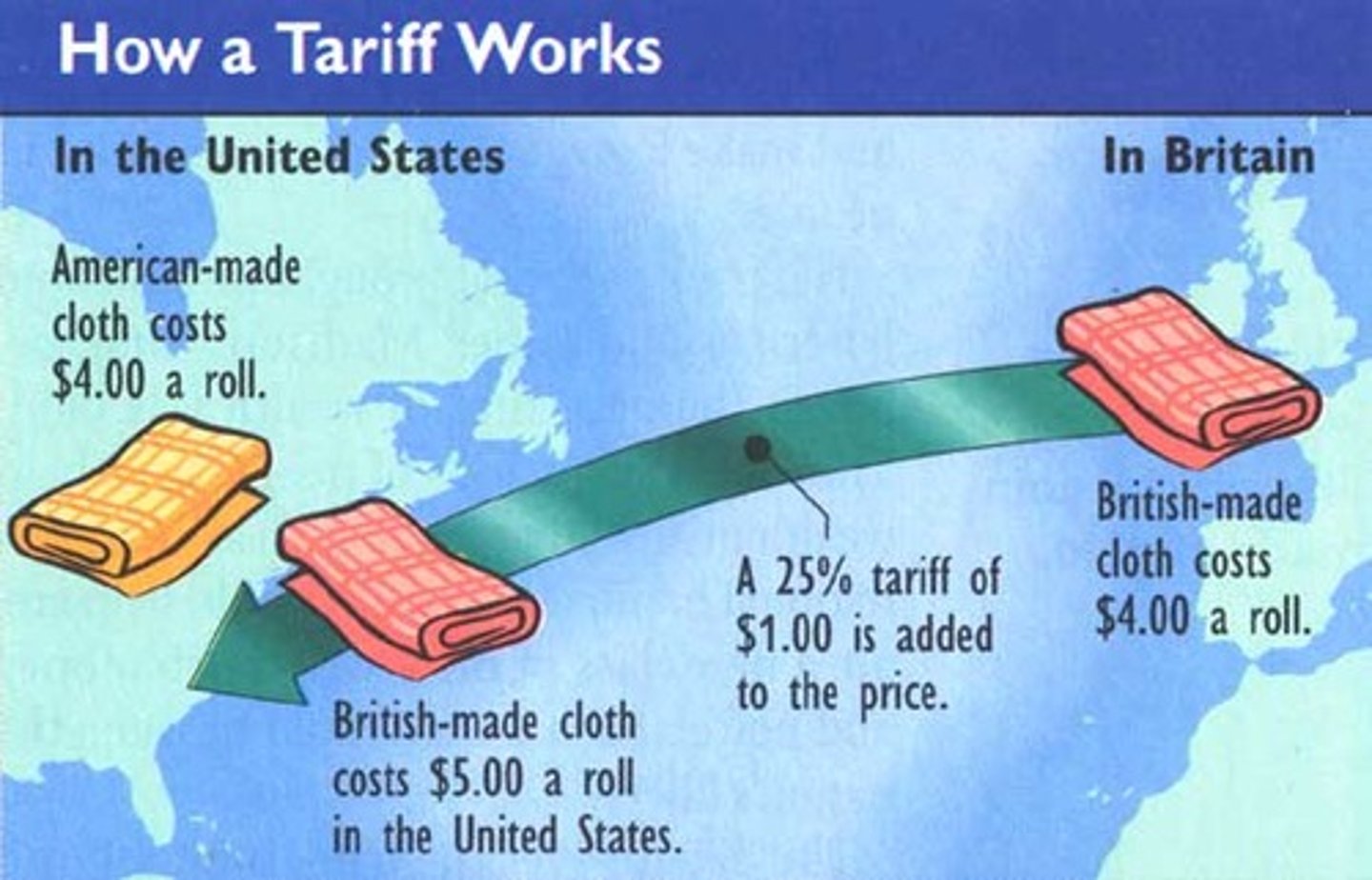
Tariff
A tax imposed on imports in order to increase government revenue and protect domestic jobs and profits; can result in counter-tariffs
Nationalism
The creation of a national identity that may align with a particular ethnicity

War Reparations
Compensation payments made at the conclusion of a war by the loser to the victor to cover damage or industry

Proletariat
In the context of Marxism, the factory workers who are exploited by the factory owners

Opiate of the Masses
A phrase attributed to Karl Marx in which he suggests that religion gives false comfort to people, discouraging them from seizing what is rightfully theirs during their lifetimes; will help shape anti-religious policies in communist states

Labor Union
An organization of workers in which they utilize collective bargaining in order to achieve gains such as increased wages, better working conditions, lower hours; may use strikes as a tool of the union

Bourgeoisie (Marxism)
In the context of Marxism, the factory owners who exploit the factory workers

Letter from Jamaica
Letter written by Simon Bolivar in which he denounces the restrictive mercantilist policies of Spain on the colonies and the Spanish policy that forbade Creoles from having any important colonial government positions; discusses the prospects of independence from Spain for Latin America
