Chapter 56 Oral and Esophageal Disorders
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
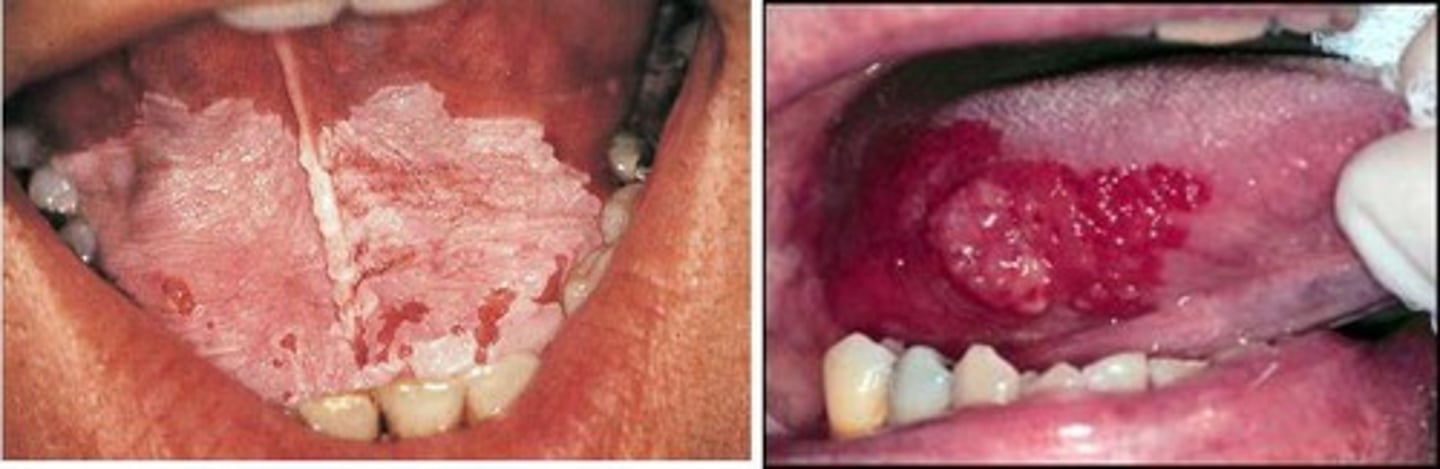
Leukoplakia/Erythroplakia
white and red patches on oral mucosa
- precursor to cancer
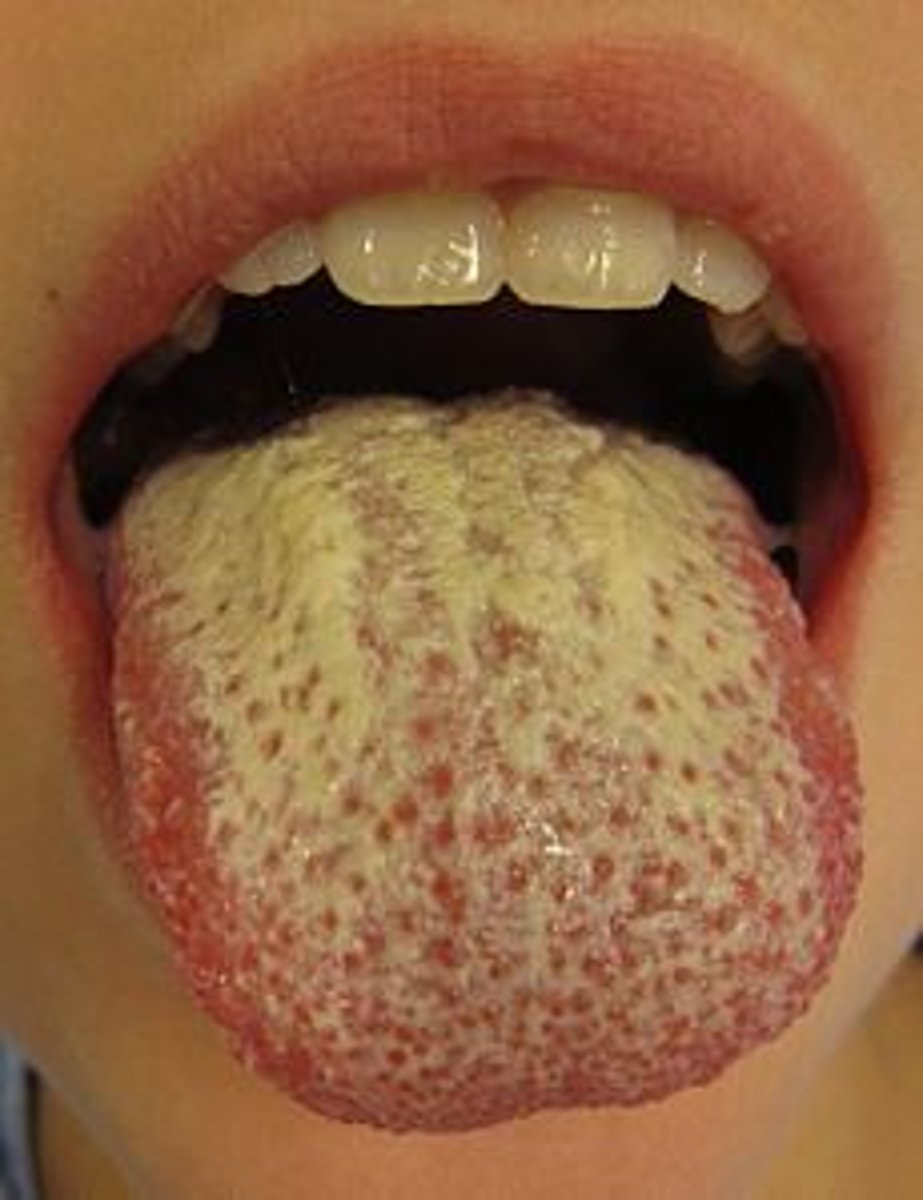
candidiasis
aka thrush
- yeast type fungal infection
- common from antibiotic use
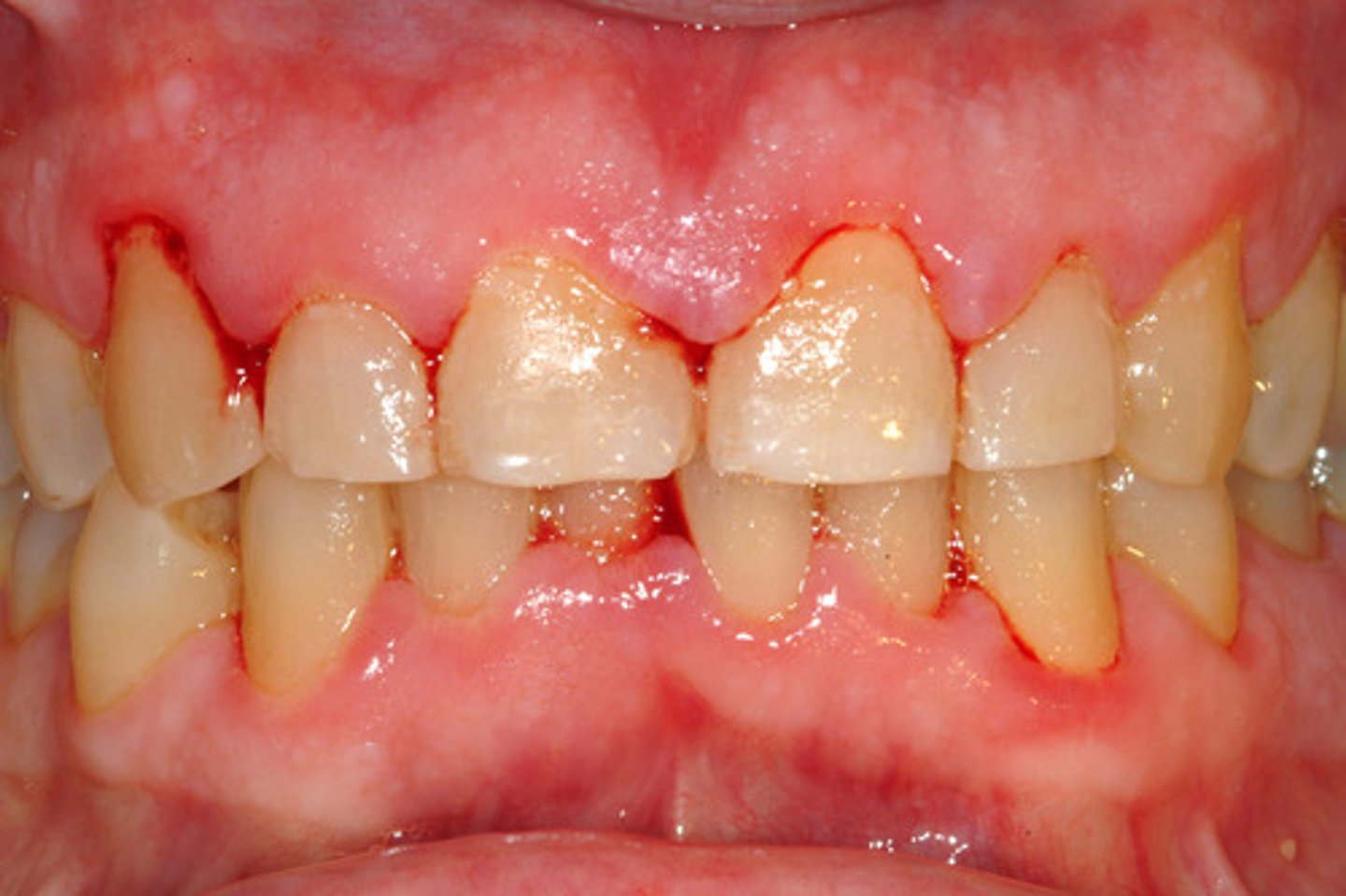
gingivitis
inflamed, painful, bleeding gums from poor oral hygiene
- why we do q4hr oral care
sialadenitis
inflammation of salivary glands from dehydration, stones, or poor oral hygiene
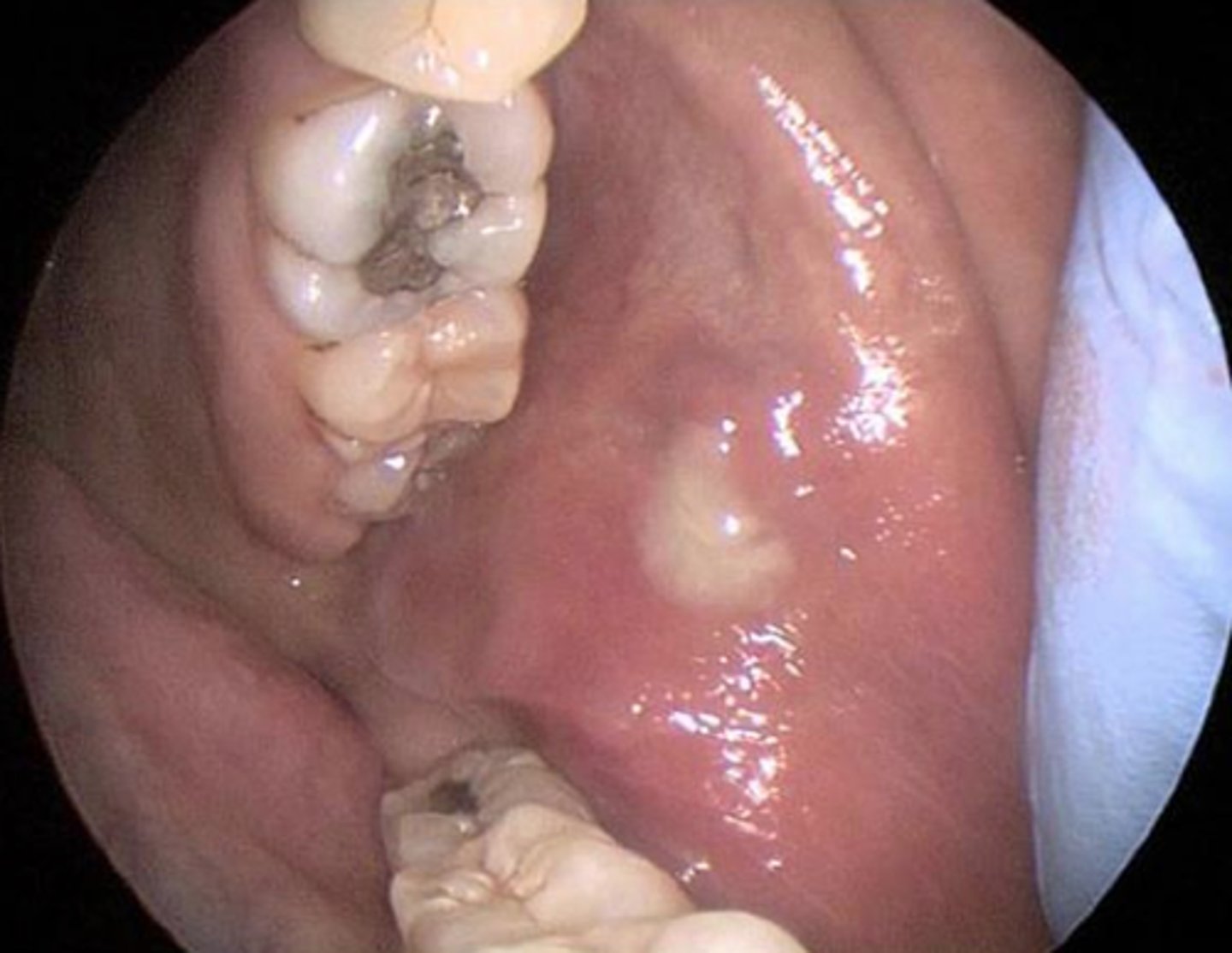
parotitis
inflammation of salivary gland due to decreased salivary flow from staph infection resulting in ear pain and fever
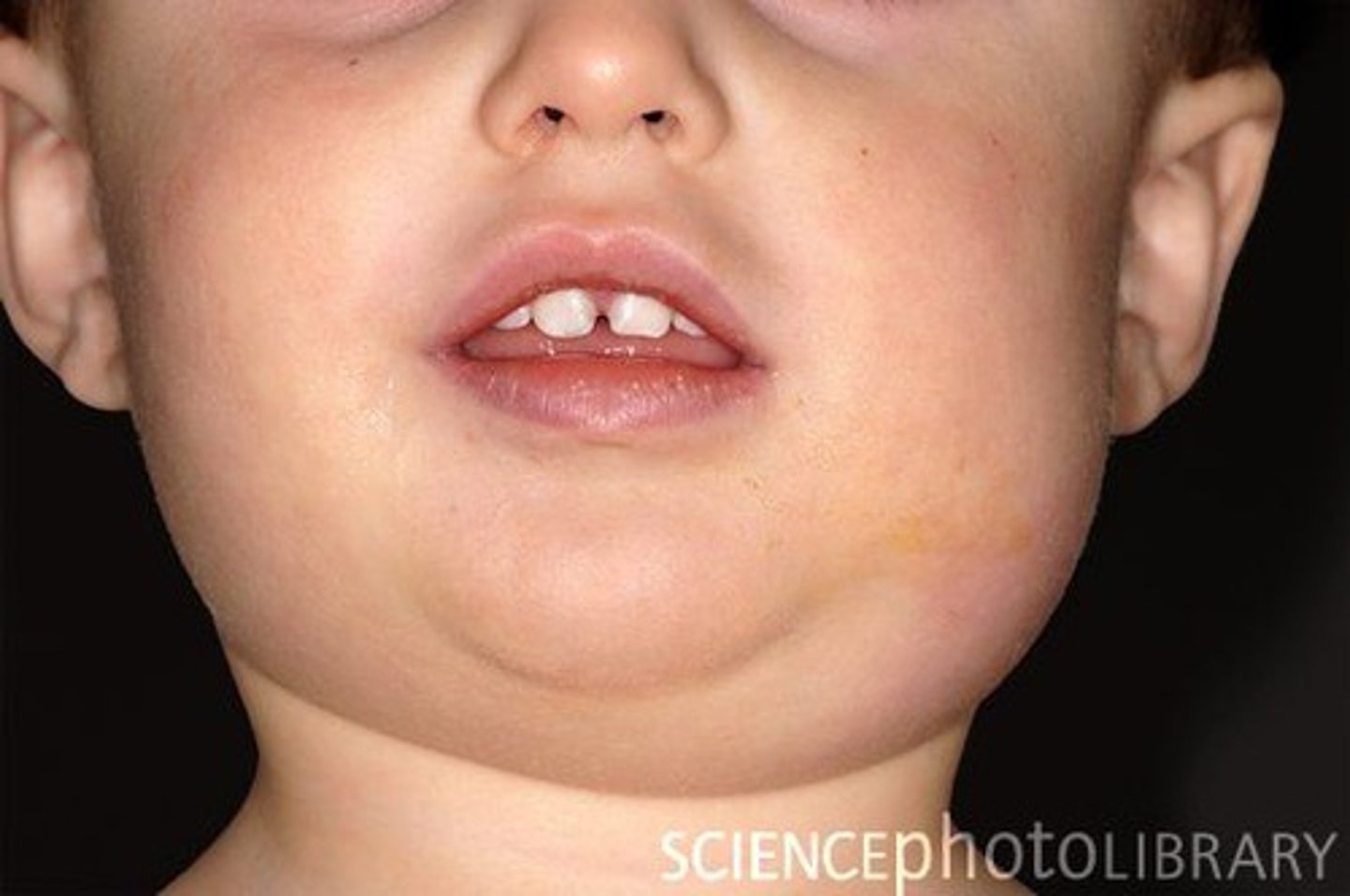
Stomatitis
epidemiology
patho
risk factors
complications
medical management
assessment
nursing actions
teaching
EPIDEMIOLOGY
- very common in pt with chemo or radiation
- age, nutrition, and oral hygiene play a role
PATHO
- inflammation and ulcers of the lining of the mouth
- most common on tongue and buccal area
RISK FACTORS
- radiation, chemotherapy, and oral hygiene
- viral, bacterial, fungal infections
- irritants like alcohol, tobacco, and mouth wash
-vitamin deficiencies like V b, folate, zinc, and iron
- Systemic diseases:chronic kidney and inflammatory bowel
COMPLICATIONS
- pain
-dysphagia(trouble swallow) and odynophagia (painful swallow) causing aspiration risk
- inflammation/open lesions that cause cause airway obstructions and infections
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
- assess oral cavity throughout chemo or radiation
- dental cleaning a month before
- oral rinse (saline or sodium bicarb) every 4 hours
- room humidification
- topical analgesics and moisturizers
ASSESSMENT
- determine offending irritant like chemo, radiation, and steroids that can decrease immune function
- assess pt for opportunistic infections due to impaired immune function and inadequate nutrition
- vital signs: weight loss, dehydration (low BP and high HR), elevated temp if infection present
- nutritional intake most likely dehydrated and poor
- intake and output most likely low
NURSING ACTIONS
- aspiration precautions
- HOB 45 degrees
- suction equipment at bedside
- administer meds (antiviral like acyclovir/zovirax and antifungal like nystatin)
- viscous lidocaine to numb mouth and help with pain
- administer water-soluble lubricants for lips and mouth
TEACHING
- Mouth care after meals with soft bristle toothbrush
- Discourage use of alcohol mouthwash
- Remove dentures and clean after every meal and clean them
- Encourage regular dental check ups
- Saline mouth rinse q4 hours
- Dietary choices
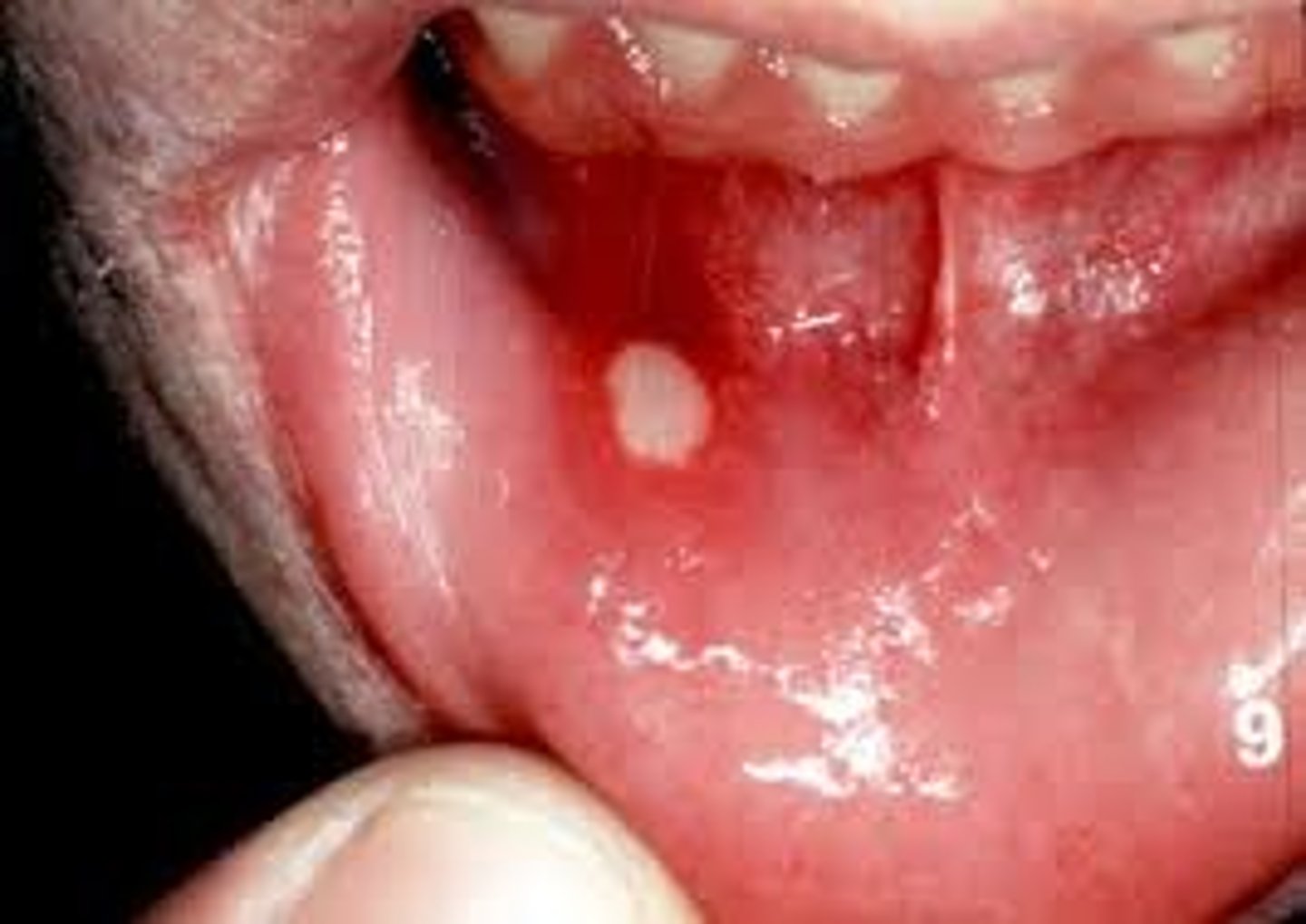
Primary vs secondary stomatitis
Primary results from painful oral ulcers, herpes simplex, and traumatic ulcers
Secondary results from viral, bacterial, or fungal infections in patients that are already suppressed immune system like from chemo or radiation
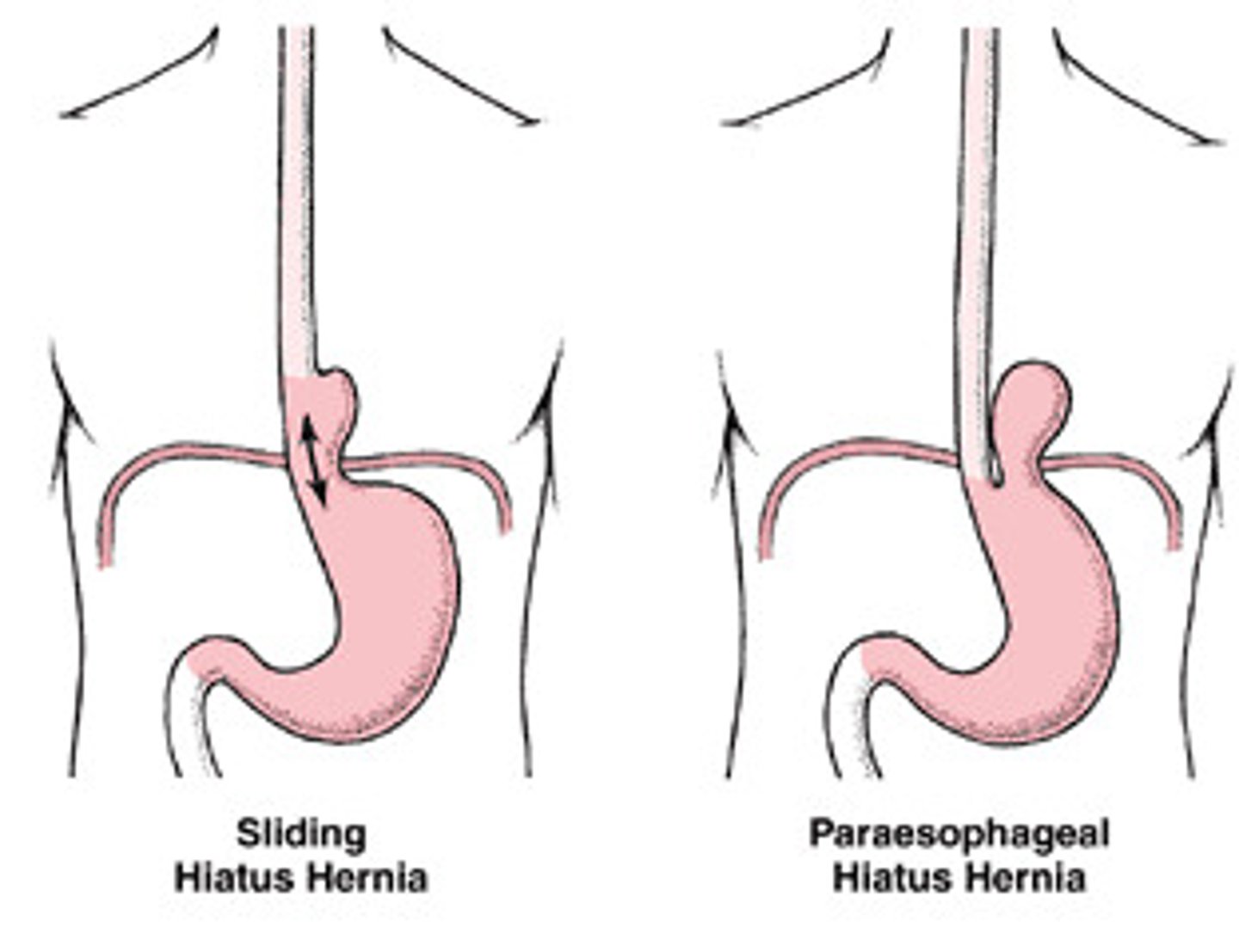
Hiatal Hernia
epidemiology
patho
diagnosis
medications
surgical
complications
assessment
action
teaching
EPI
- age over 50 due to weaken structures
- sliding is 95% and rolling 5%
- Barrett's esophagus is prone due to continued erosion of the esophagus from GERD
PATHO
- portion of the stomach protrudes upward through esophageal hiatus (opening) and can prevent proper closure
- type 1 is sliding
- type 2 is rolling
DX
- barium swallowing with fluoroscopy (most specific)
-Esophagogastroduodenoscopy/EGD to views the esophagus and stomach lining
- upper abdominal x-ray
- endoscopy
MEDICATIONS
- tx symptoms of heartburn and reflux
- antacids like tums, maalox, and mylanta
- PPI like Protonix/pantoprazole and Prilosec/omeprazole
- H2 receptor antagonists: pepcid/famotidine and Zantac/ranitidine
- Prokinetic agents: Reglan/metoclopramide to mobilize gut
SURGICAL
- Nissen fundoplication type 2
- hernia repair that will move it back in place and put mesh lining on top
COMPLICATIONS
- GERD/heartburn
- supradiaphragmatic volvulus: strangulation of hernia causing blood cut off
- intussusception: part of intestine is blocked and goes into itself
ASSESSMENT
- dysphagia
- GERD/heartburn
- n/v
- iron anemia
- symptoms worsen after eating
- regurgitation
- eructation/belching
- feeling of suffocation/SOB
- chest pain
ACTION
- position pt supine on the right side
- HOB above 30 after meals
- antacids to neutralize stomach acids
- histamines and PPI to reduce acid production
- prokinetics to increase gastric emptying
TEACHING
- limit foods like spicy/fatty, caffeine, chocolate, carbonated, acidic, peppermint, alcohol, and certain meds
- eat meals 2 hours before lying supine
- wear nonrestrictive clothing
- maintain normal weight
- proper positioning after eating
- when to seek medical care ie cardiac symptoms
- postoperative education
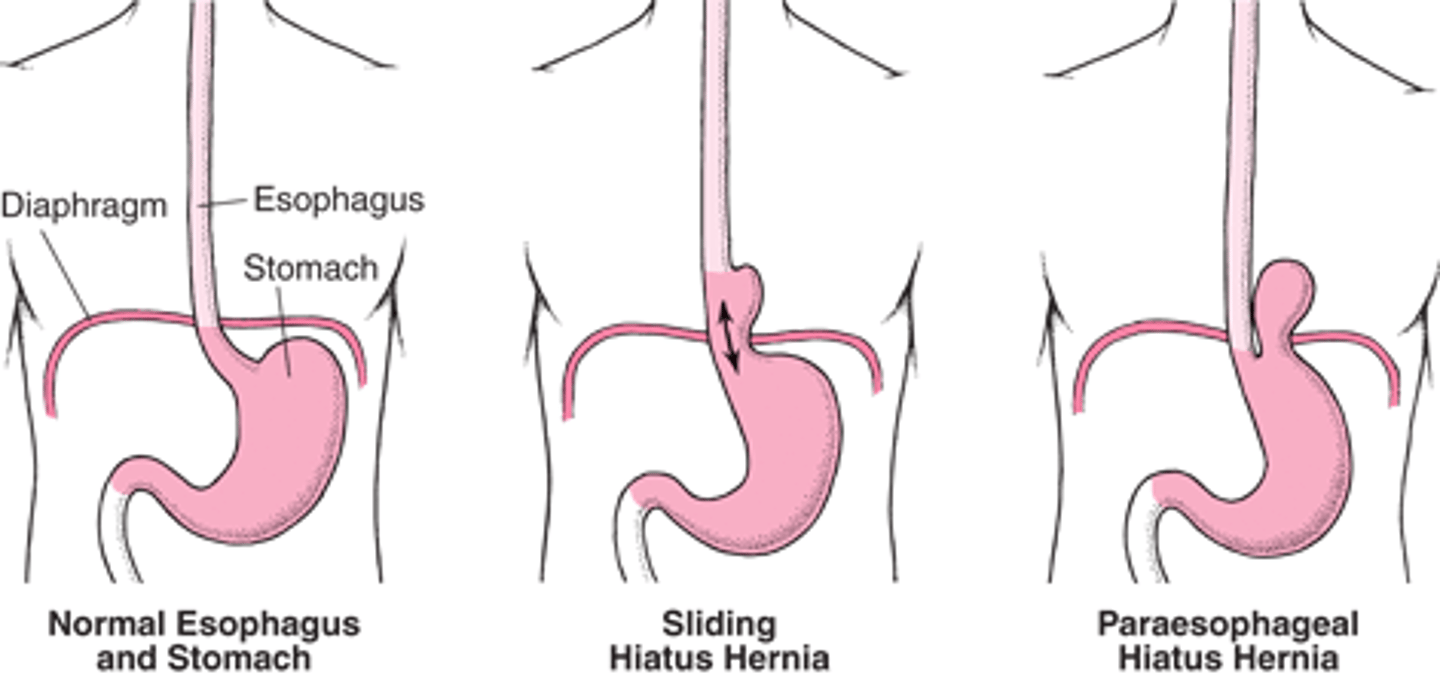
Sliding vs Rolling Hiatal Hernia
Sliding (1) is the constant wear and tear of the GEJ leading to widening of hiatal tunnel allowing sphincter and top part of the stomach upwards towards the chest
Rolling (2) is an anatomical defect causing improper anchoring of the stomach below the diaphragm
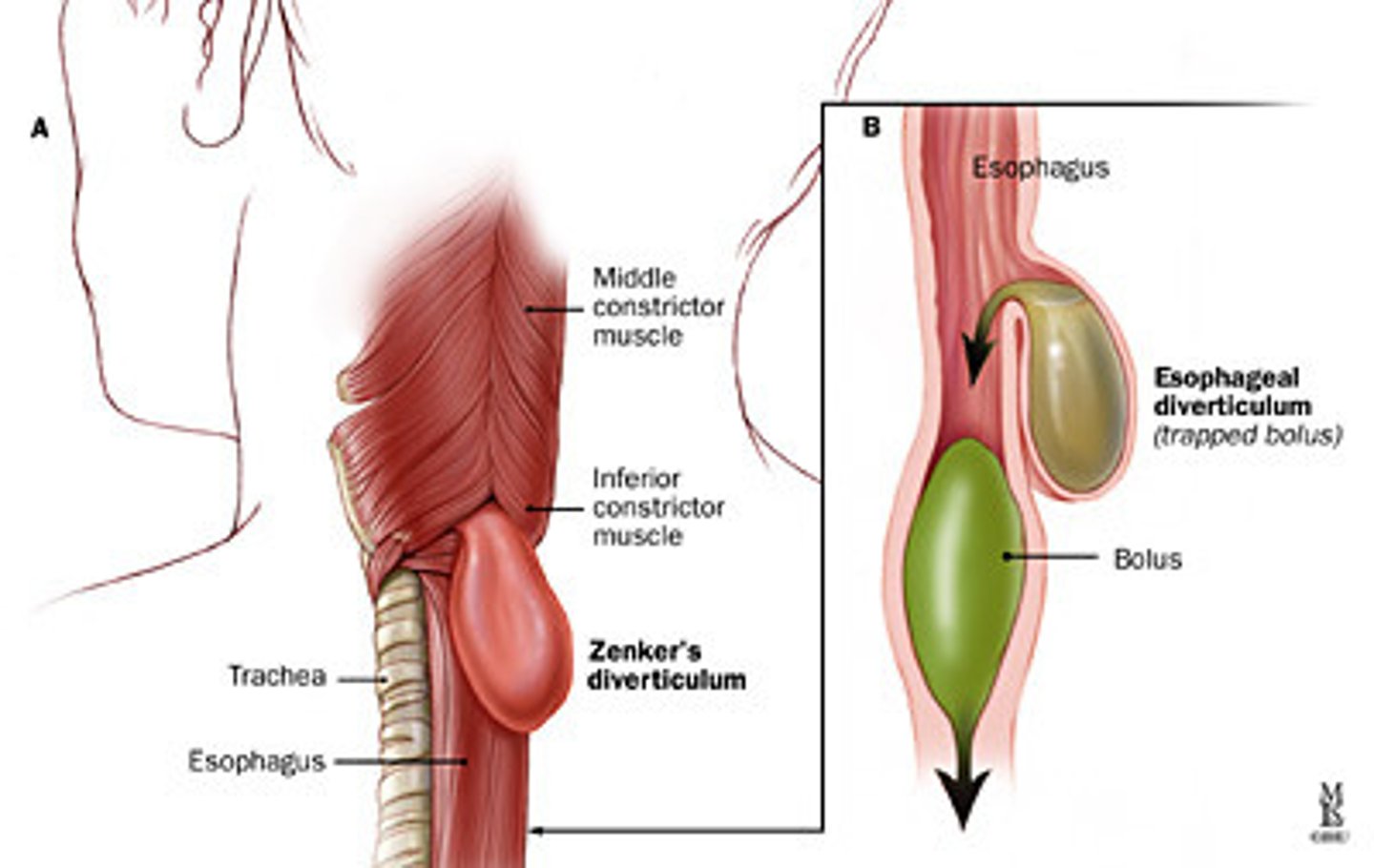
Zenker's Diverticulum and s/s
Food gets stuck in esophagus causing a pouch
- halitosis (bad breath)
- sour taste
- dysphagia
- neck fullness
- regurgitation
- belching
GERD
patho
risk factors
diagnosis
medications
surgical management
assessment
actions
teaching
PATHO
-Retrograde/backwards flow of GI contents into esophagus causing inflammation
- Each episode slows motility of the esophagus to clear material
- Erosion occurs and possible bleeding
RISK FACTORS
- Anything that weakens muscles or increases pressure
- Hiatal hernia
- LES hypotension
- Loss of esophageal motility
- Increased compliance of hiatal canal
- Increases gastric secretions
- Large meals
- Delayed emptying
- Obesity and pregnancy and ascites
- Tight belts
- NG tubes
- Smoking
- Genetic
DX
- *Esophageal manometry*: measures pressure in esophagus by water being inserted in nose or mouth and withdrawn slowly to read LES pressures and peristalsis
- Classic GERD symptoms with a trial of proton pump inhibits (PPI) with resolution of symptoms
- 24 hours ambulatory esophageal pH monitoring
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy/EGD
- Cardiac markers
MEDICATIONS
- Antacids to increase gastric pH
- Histamine receptors antagonists are shorted acting meds that decrease gastric acid production
- Prokinetic medications to increase gastric emptying
- PPI’s are longer acting meds that decrease gastric acid production
SURGERY
- Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication
ASSESSMENT
- Respiratory symptoms
- Regurgitation
- Severe atypical chest pain
- Hemorrhage
- CBC
- Signs of Barrett’s esophagus
- Dental caries or erosions
- Eructation, flatulence, or bloating
- Nausea
- Globus
- pH of gastric aspirate, stomach is 1.5-2 while esophagus is 6-7
ACTIONS
- administer medications as ordered
- position patient on right side with HOB elevated 6-12 inches
- provide small, frequent meals
TEACHING
- limit irritating foods
- avoid smoking and alcohol
- eat meals 2 hours before laying supine
- wear nonrestrictive clothing
- maintain ideal body weight
- avoid NSAIDs and Aspirin since they can irritate lining of esophagus
Oral Cancer
patho
c/m
dx
tx
complications
assessments
action
teaching
PATHO
- Most are squamous cell carcinoma
- Malignancies of the lip are most common due to frequent carcinogen exposure
C/M
- Oral bleeding
- Raised area on the lip or in the mouth
- Oral ulcer with poorly defined margins, mucosal lesion, or nodule
- White and/or red patches
- Increasing pain that radiates to the ear or neck
- Dysarthria
- Dysphagia
- Difficulty chewing
- Oral fetor
- Regional lymph node involvement
- Weight loss
- Poor-fitting dentures
DX
- CBC
- Chemistry profile
- Liver function test
- CT scan
- PET scan
- MRI
- Chest X-ray t
TX
- Airway management
- Removal of source of irritation
- Radiotherapy, Chemotherapy, Chemoradiation
- Surgical removal
- Retinoids - vitamin A to help decrease issues with cancer and help fight infection
- Beta-carotene an antioxidant that converts to vitamin A
COMPLICATIONS
- Infection
- Facial edema
- Weight loss
- Difficulty/inability talking
- Dysphagia
- Hearing loss
- Osteoradionecrosis
- Trismus (difficulty opening mouth)
- Carotid artery rupture
- Hypothyroidism, hyperparathyroidism
- Neck structure damage
ASSESSMENT
- Ability to swallow
- Fluid intake
- Nutritional intake
- Weight
- Albumin and total protein
- Oral mucosa irritation or infection
- Lymph nodes
- psychosocial adjustment
ACTIONS
- Airway management
- Aspiration precautions
- Maintain emergency bedside equipment aka trach kit
- Provide oral care
- Administer steroids as prescribed to help with swelling and inflammation
- Provide cool mist
- nutritional consult
- speech therapy
TEACHING
- aspiration precautions
- avoid tobacco and alcohol intake
- provide nutritional education
- oral hygiene
- management of xerostomia (dry mouth)
- frequent sips of water or saliva substitute
Oral trauma
patho
c/m
dx
surgery
complications
assessments
actions
teaching
PATHO
- directly related to location and severity of injury
- may occlude airway
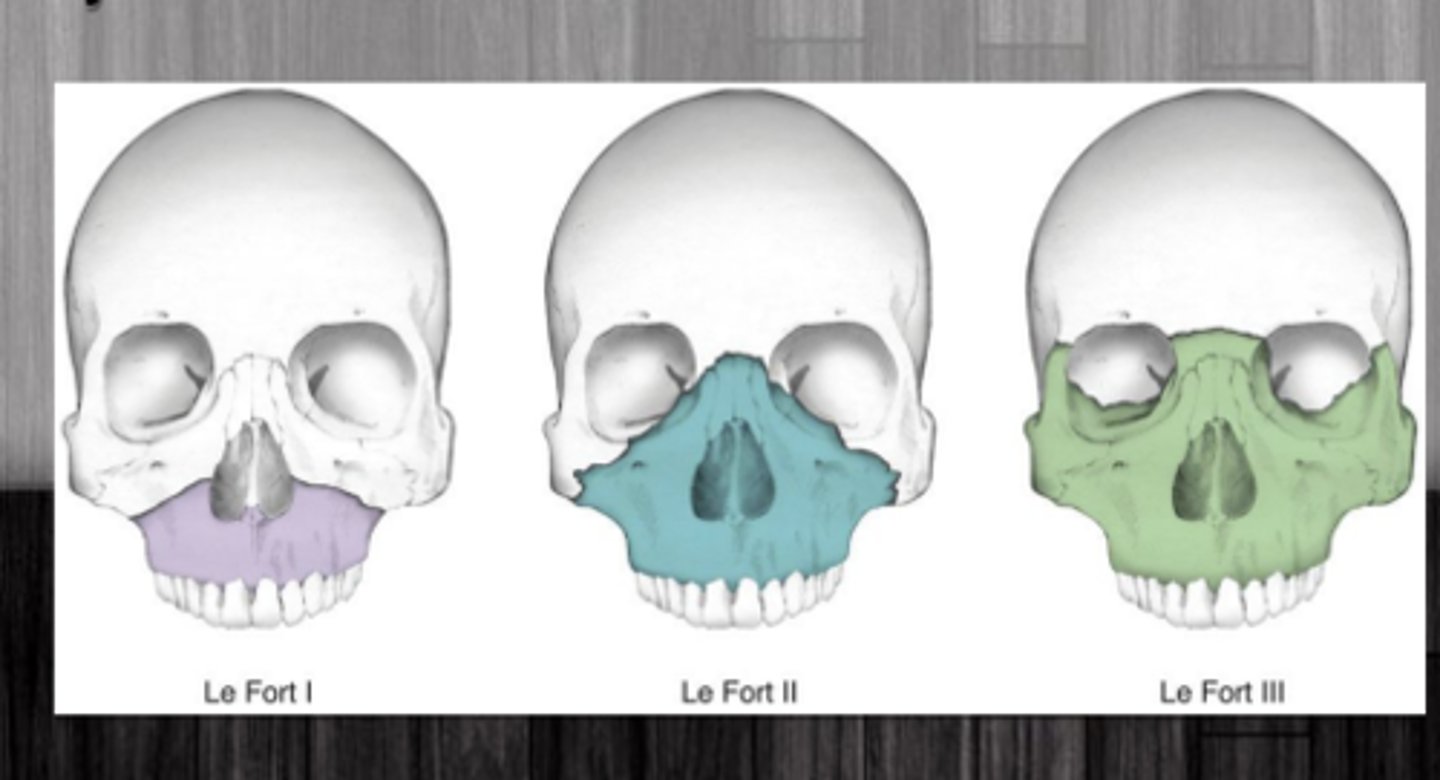
- LeForte fractures 1-3
C/M
- Increased RR (tachypnea)
- Stridor (noisy breathing) means airway obstruction
- SOB
- Decreased O2 stat
- Hypercarbia
- Tachycardia
- Changes in LOC
- Oral bleeding
- Swelling and edema
- Loss of teeth
- Pain
DX
- CBC
- Serum chemistry analysis
- Arterial blood gas
- Blood type and cross match
-Facial x ray or facial CT or MRI
SURGERY
- surgical stabilization
- fixed occlusion of fracture
- micro plating
- intermaxillary fixation
COMPICATIONS
- airway compromise
- aspiration of teeth
infection
inability to consume adequate diet
- meningitis
ASSESSMENT
- oral airway
- respiratory rate and quality
- oxygen saturation
- skin appearance
- ABGs
- CBCs
- electrolytes and daily weights
- temperature
ACTIONS
- wire cutters at all times
- oral humidification
- elevate HOB 30-45 degrees
- administer antibiotics
- provide diet
- fq mouth care
TEACHING
- have wire cutters on them at all time
- mouth care after every meal
- s/s of infection
- finish antibiotics
- how to tube feed if necessary
Esophageal Cancer
patho
risk factors
c/m
dx
surgery
complications
assessment
actions
teaching
PATHO
- Rapidly growing squamous cell cancer, more than 50% metastasize
- Spreads to lymph nodes and into esophageal lumen
- No C/M until disease is advanced and recovery is unlikely
RISKS
- Barrets esophagus
- Nutritional deficiency
- GERD
- obesity
- lye stricture
- esophageal diverticula
- achalasia
- tylosis
C/M
- Progressive dysphagia
- Hemoptysis
- Burning sensation in middle of chest
- Painful swallowing
- Vomiting
- Weight loss/ anorexia
- Hoarseness / voice changes
- Melena
DX
- EGD is gold standard
- screenings
- barrium swallow
- CT scan
- PET scan
- Endoscopy
- Thoracoscopy and laparoscopy
SURGERY
- Esophagectomy
COMPLICATIONS
- Dysphagia
- Strictures
- Dumping syndrome - r/t surgery
- Stomatitis
- N/V
- Diarrhea
- heartburn
ASSESSMENTS
- n/v
- odynophagia
- dysphagia (with or without hiccups)
- weight loss
- H&H, CMC, blood glucose
- Serum calcium levels
- Liver enzymes and jaundice
- Psychosocial adjustment
ACTIONS
- HOB greater than 30 degrees
- Suction and Oxygen equipment
- Collaborate with nutritionist
- 6 small meals per day, BRAT diet, high in protein and fat
- Collaborate with speech
TEACHING
- lines, tubes, incisions
- preoperative care
- Coughing, deep breathing, incentive spirometry q2h, early ambulation
- Pain management
- enteral or parenteral feeding up to 3 weeks
- dental screenings and oral care
- postoperative education
Esophageal Trauma
patho
dx
meds
surgery
complications
assessments
actions
teaching
PATHO
Common causes are
- Ingestion
- Blunt injury
- Open penetrating wounds
- Foreign body ingestion
- Spontaneous rupture
- Tube placement
- Smoke or chemical inhalation
DX
- Chest x-ray
- Chest CT
- Esophagography
MEDS
- Broad spectrum antibiotics
- High dose corticosteroids
- Opioid or nonopioid analgesics
- Topical analgesics
SURGERY
- Control bleeding
- Remove damaged tissue
- Repair wounds
- Resect esophagus
- Replace esophagus with bowel segment
- Glucagon for esophagus to relax muscle
COMPLICATIONS
- Infections
- Abscesses
- Subcutaneous emphysema in neck
- Pneumothorax
- Shock
- Sepsis
- Respiratory impairment
- Esophageal mucosal burns
- Esophageal strictures
- Aspiration pneumonia
- Hemorrhage
ASSESSMENTS
- vital signs
- chest pain
- LOC
- serum electrolytes
- CBC
- Daily weights
ACTIONS
- Low intermittent esophageal and gastric suction
- Keep pt NPO
- Provide nutrition
- Administer antibiotics
- High dose corticosteroids
- Pain management
TEACHING
- Explain procedures, tests, medications, and discharge instructions
- Signs of infection
- Monitor weight
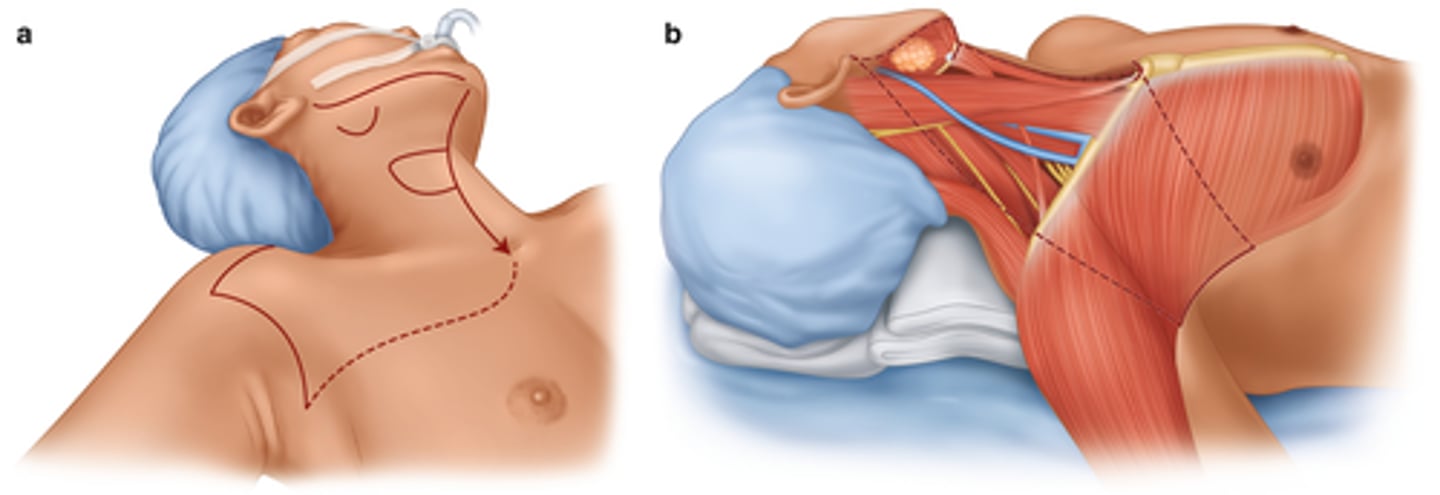
Head and Neck cancer
patho
Related to metastasis of cancer through local lymph nodes
All cervical lymph nodes from mandible to clavicle, internal jugular veins, spinal accessory muscles, and may include bone, muscles, and veins
radial neck dissection considerations and complications
- Airway compromise
- Speech and swallowing
- Trach insertion tray at bedside
- Bleeding
- Carotid artery rupture
- Nerve injury
- Splint surgical site if coughing
- PT/OT/Speech consults