Higher Biology - Unit 1 - DNA and the genome
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/83
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
1
New cards
name the enzyme that joins fragments together in the lagging strand
ligase
2
New cards
describe how DNA is organised in prokaryotes
circular chromosomes, plasmids
3
New cards
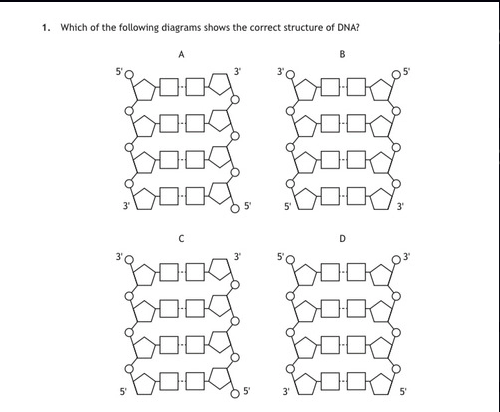
which of the following shows the correct structure of DNA
A
4
New cards
name the substance with which DNA is packaged in eukaryotes
histones
5
New cards
State why the antiparallel nature of the DNA molecule results in \n one of the strands being synthesised in short fragments.
polymerase works from the 5' end to the 3' end
6
New cards
What substances are required for DNA replicatiom
template DNA, enzymes and ATP, nucleotides
7
New cards
explain why primers are necessary for DNA replication
so that DNA polymerase can add nucleotides to the 3' end of the new strand
8
New cards
explain why only the leading strand can be replicated continuously
DNA __polymerase__ adds nucleotides to the 3’ end of the primer/new strand
9
New cards
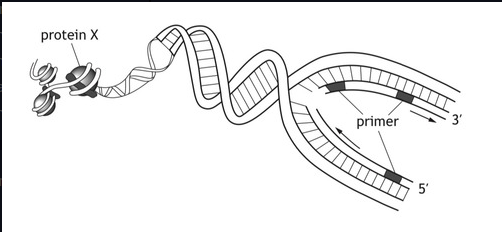
name protein X
histones
10
New cards
describe one organisational difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomal DNA
prokaryotic has circular chromosomes and eukaryotic has linear chromosomes
11
New cards
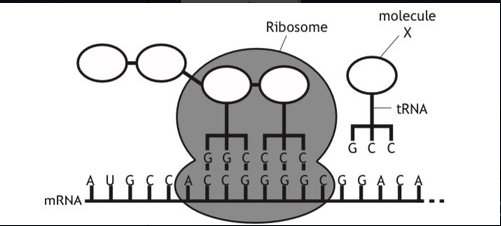
name molecule x
Amino acid
12
New cards
What is each DNA strand made up of
nucleotides
13
New cards
What are the three parts that make up a nucleotide
Phosphate, Deoxyribose sugar, base
14
New cards
The two strands of a DNA molecule run in opposite directions, this structure is said to be what
Antiparallel
15
New cards
Describe a prokaryotic cell
* no nucleus
* DNA is organised into circular chromosomes and plasmids
* DNA is organised into circular chromosomes and plasmids
16
New cards
Describe a eukaryotic cell
* nucleus
* linear chromosomes
* linear chromosomes
17
New cards
What type of cell is yeast
Eukaryote, however as it also has plasmids
18
New cards
State one location other than the nucleus where DNA is found in eukaryotic cells
Mitochondria, chloroplast and plasmid in yeast
19
New cards
Explain why cells need to carry out DNA replication
So that an exact copy of the genetic material is passed to each new cell
20
New cards
Describe what a polymerase chain reaction technique is
A technique used to create many copies of a fragment of DNA in an __in vintro__ laboratory setting
21
New cards
Name the six requirements for PCR
* Original DNA template
* primer
* nucleotides,
* heat tolerant DNA polymerase,
* thermal cycler,
* buffer solution
* primer
* nucleotides,
* heat tolerant DNA polymerase,
* thermal cycler,
* buffer solution
22
New cards
What is step one in PCR
Heating to 92-98°C which breaks the hydrogen bonds between the complementary base pairs
23
New cards
What is step two in PCR
Cooling to 50-65°C this allows for the primers to be added
24
New cards
What is step three in PCR
Heating to 70-80°C this allows for the DNA polymerase to be added
25
New cards
How is a cells genotype determined
By the sequence of bases in its gene
\
\
26
New cards
How is a cells phenotype determined
By the proteins that are synthesised when genes are expressed
27
New cards
What does gene expression involve
The transcription and translation of DNA sequences
28
New cards
Describe transcription in protein synthesis
The synthesis of mRNA from a section of DNA
29
New cards
In the structure of DNA how many strands does it have
Double strands
30
New cards
In the structure of RNA how many strands are there
It is single stranded
31
New cards
In the structure of DNA what type of sugar is there
Deoxyribose
32
New cards
In the structure of RNA what type of sugar is there
Ribose
33
New cards
In the structure of DNA what are the names of the complementary base pairs
Cytosine, guanine, adenine, thymine
34
New cards
In the structure of RNA what are the names of the complementary base pairs
Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine
35
New cards
What is the function of mRNA(messenger RNA)
Carries a copy of the genetic code from the nucleus to the ribosome
36
New cards
What is the function of tRNA(transfer RNA)
Each tRNA molecule carries its specific amino acid to the ribosome
37
New cards
Describe the process of cellular differentiation
a cell expresses certain genes to produce proteins characteristics for the type of cell
* (this allows cells to carry out specialised functions)
* (this allows cells to carry out specialised functions)
38
New cards
Define meristems
Meristems are regions of unspecialised cells in plants that can divide (self-renew) and differentiate
39
New cards
Define general stem cells in animals
Stem cells are regions of unspecialised cells in animals that can divide (self-renew) and differentiate
40
New cards
Define embryonic stem cells in animals
Stem cells in the early embryo can differentiate into all the cell types that make up the organism and so are pluripotent
41
New cards
Define tissue stem cells in animals
Stem cells found in tissues throughout the body, involved in growth, repair and renewal of cells found in the tissue and so are multipoint
42
New cards
What does pluripotent mean
**these cells can differentiate into any type of cell**
43
New cards
What does multipotent mean
This means they can **differentiate** **into all** of the **types of cell found in that particular tissue type**
44
New cards
Describe therapeutic uses of stem cells
The repair of damaged or diseased organs and tissues,
45
New cards
examples of therapeutic uses of stem cells
corneal repair and the regeneration of damaged skin
46
New cards
Describe two research uses of stem cells
how disease develop or can be used in drug testing,
47
New cards
Describe the ethical issues surrounding the uses of embryonic stem cells
this involves the destruction of the embryo
48
New cards
Describe the role of non-coding sequences
Regulate transcription by turning genes on/off as regions of DNA activate RNA polymerase to bind to a coding region,
49
New cards
Define mutation
Mutation are random spontaneous changes to an organisms DNA
50
New cards
Describe a substitution mutation
A single nucleotide is replaced with a different nucleotide
51
New cards
Describe an insertion mutation
A single nucleotide is added into a DNA sequence
52
New cards
Describe a deletion mutation
A single nucleotide is removed from the DNA sequence
53
New cards
What is the effect of a substitution mutation
A single amino acid is changed when the protein is being made
54
New cards
What is the effect of an insertion mutation
All amino acids coded for after the mutation are affected as they are moved one base pair up (frameshift mutation)
55
New cards
What is the effect of a deletion mutation
All amino acids coded for after the mutation are affected as they moved one base pair down (frameshift mutation)
56
New cards
What is the effect of a missense mutation
One amino acid is changed for another
57
New cards
What is the effect of a nonsense mutation
A codon that is used to code for an amino acid is changed to a stop codon
58
New cards
Describe a chromosome duplication structure mutation
Genes from one chromosome duplicate and attach to its homologous partner
59
New cards
Describe a chromosome deletion structure mutation
The chromosome breaks in two places
60
New cards
Define evolution
Evolution is the change in organisms **over generations** as a result of genomic variations
61
New cards
Define natural selection
The non-random increase in frequency of DNA sequences that increase survival.
62
New cards
Describe stabilising natural selection
An **average phenotype is selected** for and extremes of the phenotype range are selected against
63
New cards
Describe horizontal gene transfer
Genes are transferred between individuals in the same generation. Prokaryotes and viruses exchange genetic material this way
64
New cards
Define speciation
Speciation is the generation of the new biological species by evolution as a result of isolation, mutation, natural selection
65
New cards
Describe the four step process of speciation
1. An isolation barrier splits a population into sub-populations
2. Mutations take place in each sub-population
3. Natural selection acts on both of the two new sub-populations
4. Speciation has taken place
66
New cards
Define isolation barriers
Isolation barriers **prevent gene flow** between sub-populations during speciation
67
New cards
Describe a geographical barrier
A barrier which physically separates a population by natural features e.g mountain or river
68
New cards
Describe a behavioural barrier
A barrier which separates two populations that are capable of interbreeding
69
New cards
Describe an ecological barrier
A barrier which causes separation by an ecological niche such as pH levels, salinity or breeding locations
70
New cards
Define allopatric speciation
isolated due to geographical barriers
71
New cards
Define sympatric speciation
isolated due to behavioural and ecological barriers
72
New cards
What is the use for bioinformatics
The use of computer and statistical analysis to identify and compare sequence data
73
New cards
What is a molecular clock used for
To estimate when species diverged
74
New cards
By analysing an individuals genome what can be predicted
The individuals likelihood of developing certain diseases
75
New cards
Define pharmacogenetics
This is the study of the genetic variation between individual’s that affect their response to drugs/pharmaceuticals
76
New cards
Describe the use of pharmacogenetics in personal medicine
An individuals personal genome can be used to select the most effective drugs and dosage to treat their disease
77
New cards
Where does transcription take place
The nucleus
78
New cards
Where does translation take place
The ribosome
79
New cards
Describe the process of translation
* gene copied into mRNA strand using RNA polymerase
* primary mRNA transcript is spliced into mature mRNA transcript
* primary mRNA transcript is spliced into mature mRNA transcript
80
New cards
Describe the process of transcription
\- mRNA attaches to ribosome \n - tRNA anticodons bind with mRNA codons bringing amino acids together \n - peptide bonds form between amino acids to create a protein
81
New cards
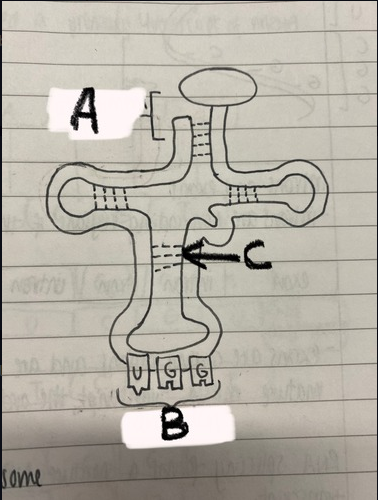
Label points A and B and name the bonds at point C
A: amino acid attachment site B: anticodon C: hydrogen bonds
82
New cards
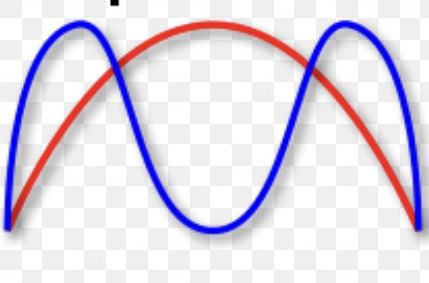
Which graph is this: directional, stabilising or disruptive?
Disruptive
83
New cards
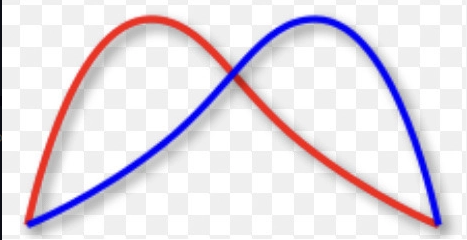
Which graph is this: directional, stabilising or disruptive?
Directional
84
New cards
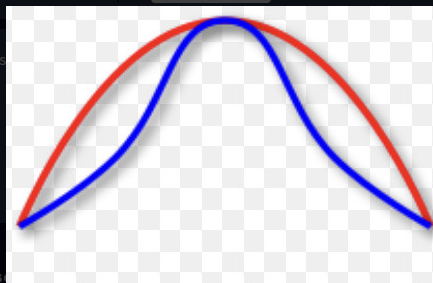
Which graph is this: directional, stabilising or disruptive?
Stabilising