Chapter 10.1 Meiosis (Glencoe Biology)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Heredity
Passing on of characteristics from parents to offspring.
Genetics
Branch of biology that studies heredity.
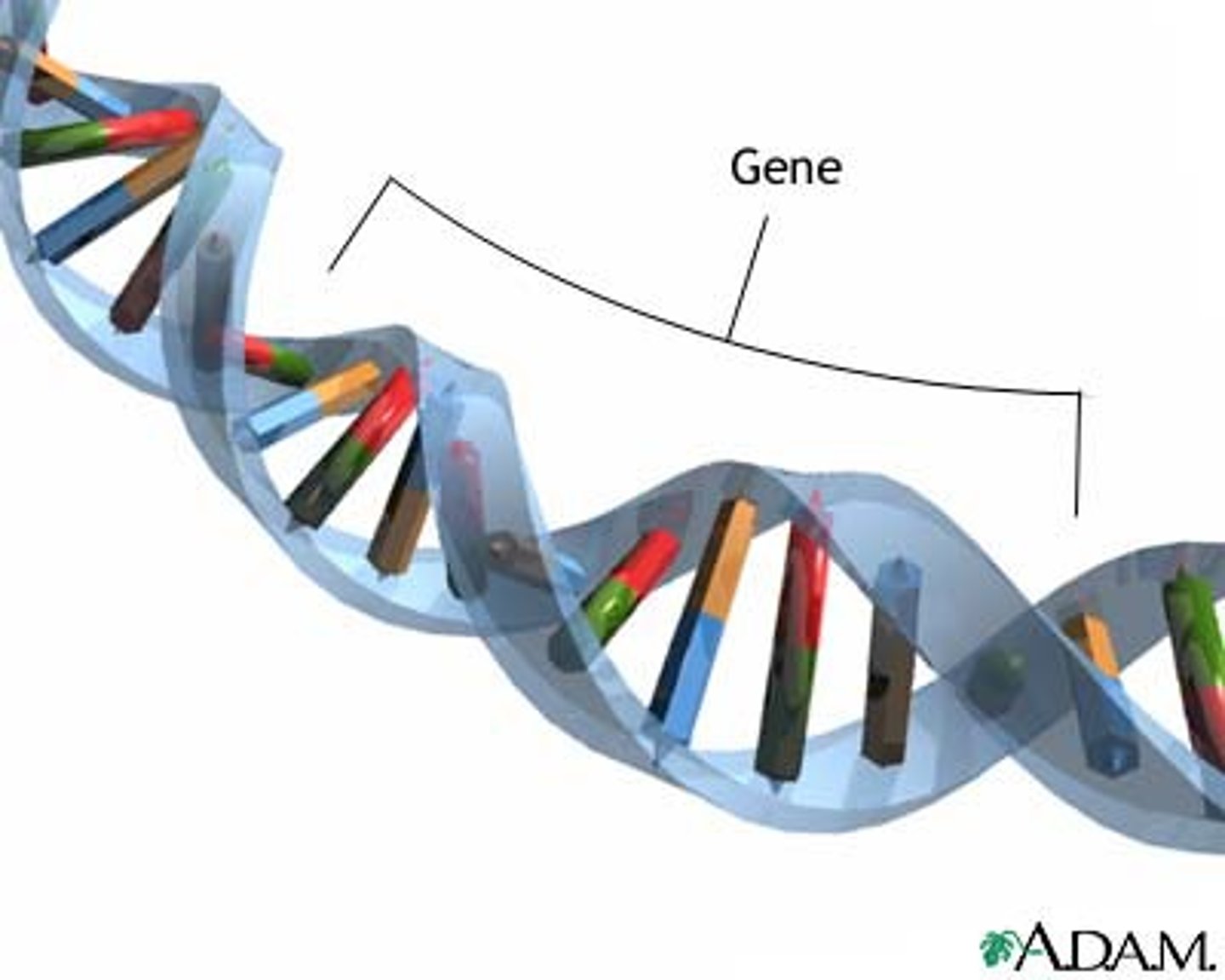
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
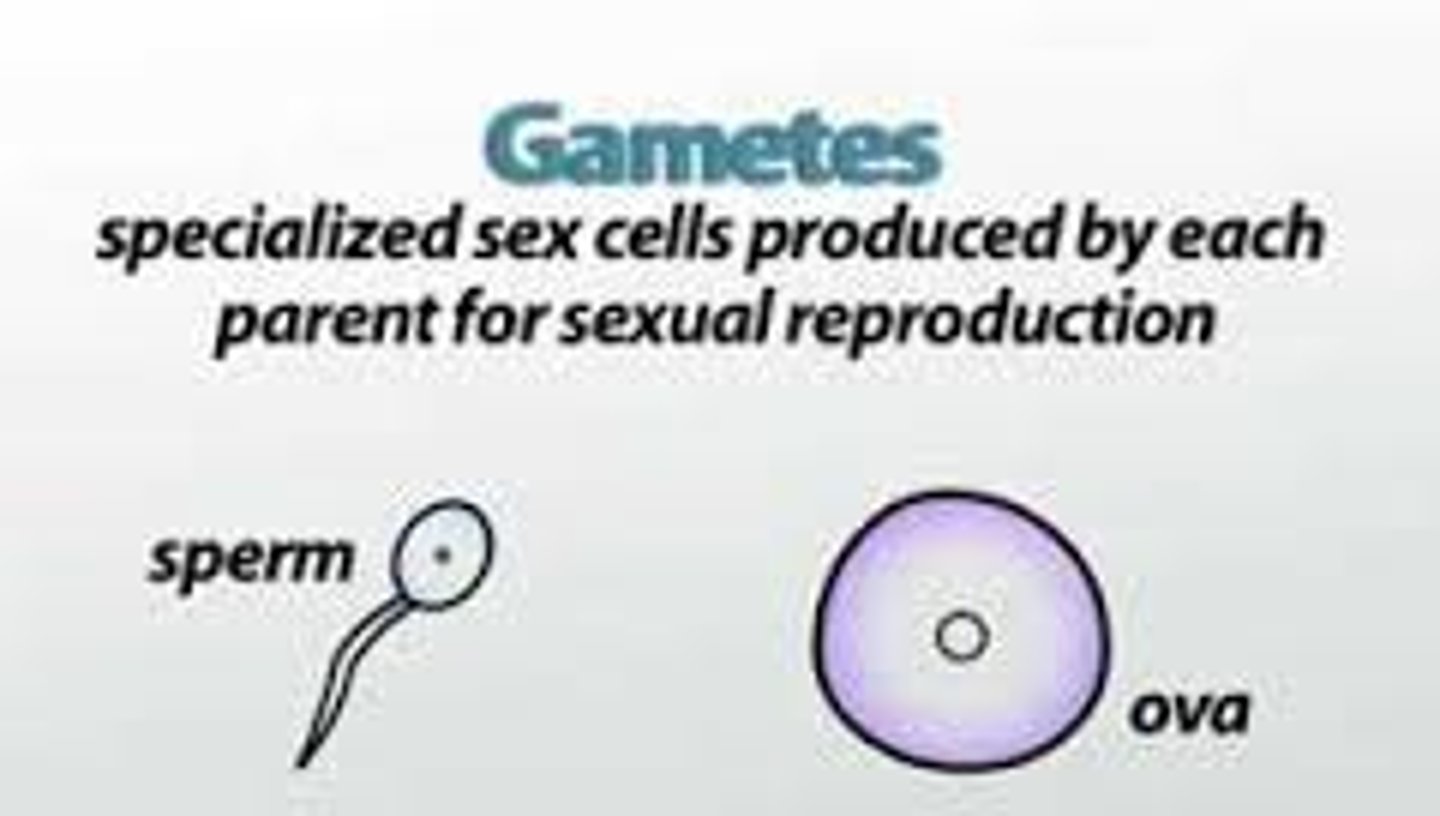
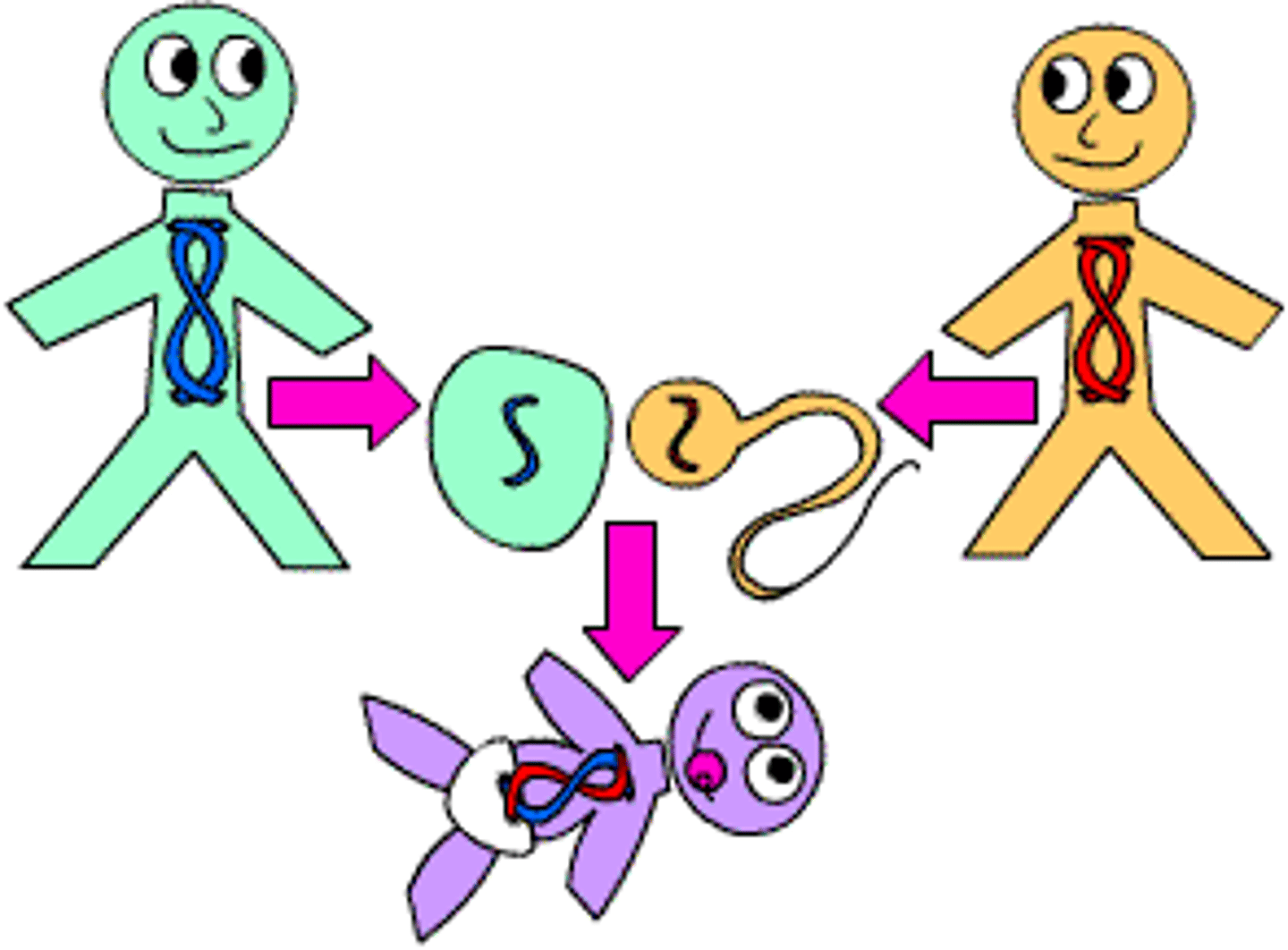
Gamete
Male and female sex cells; sperm and eggs.
Fertilization
Fusion of male and female gametes.
Zygote
Diploid cell formed when a sperm fertilizes an egg.
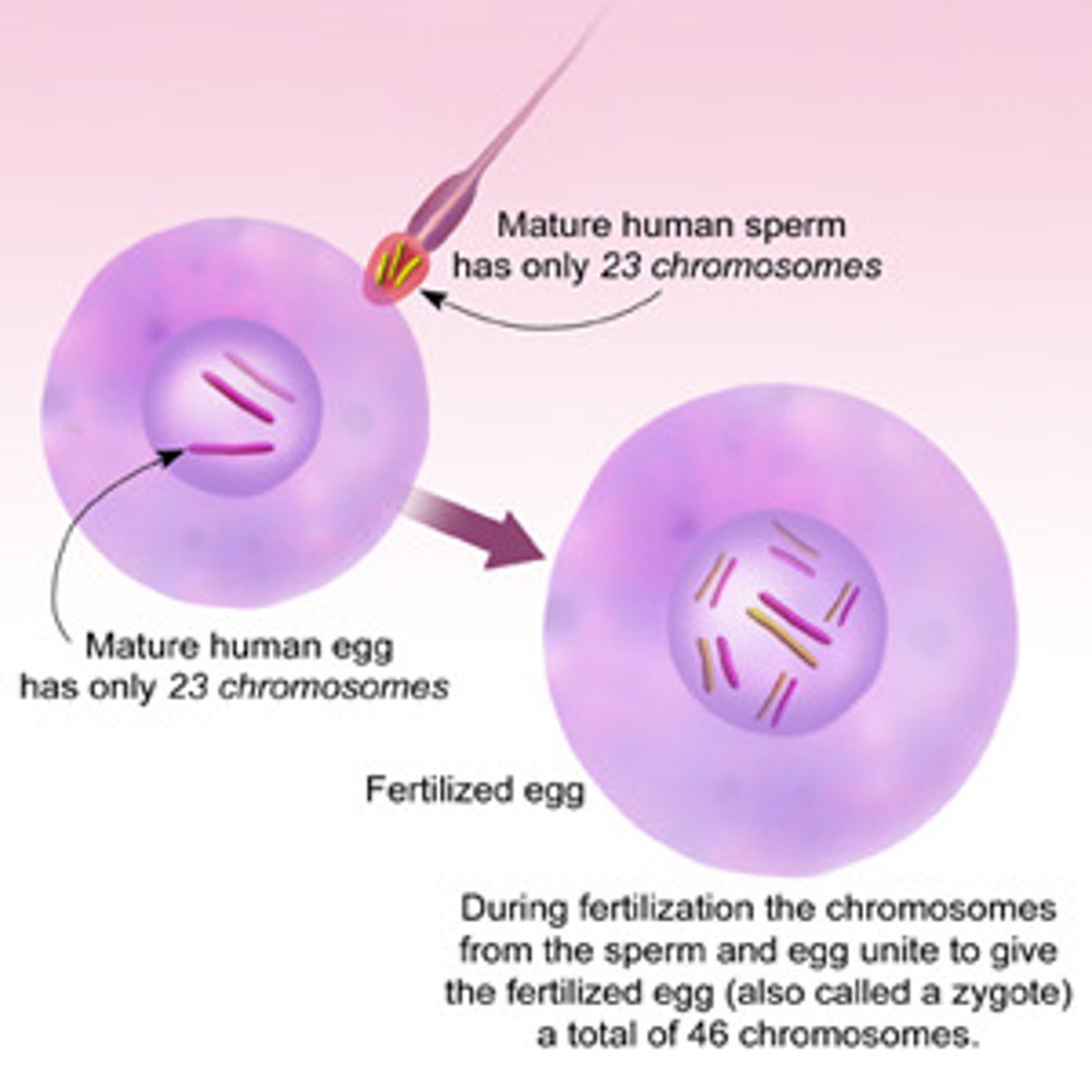
Diploid
Cell with two of each kind of chromosome; is said to contain a diploid, or 2n, number of chromosomes.
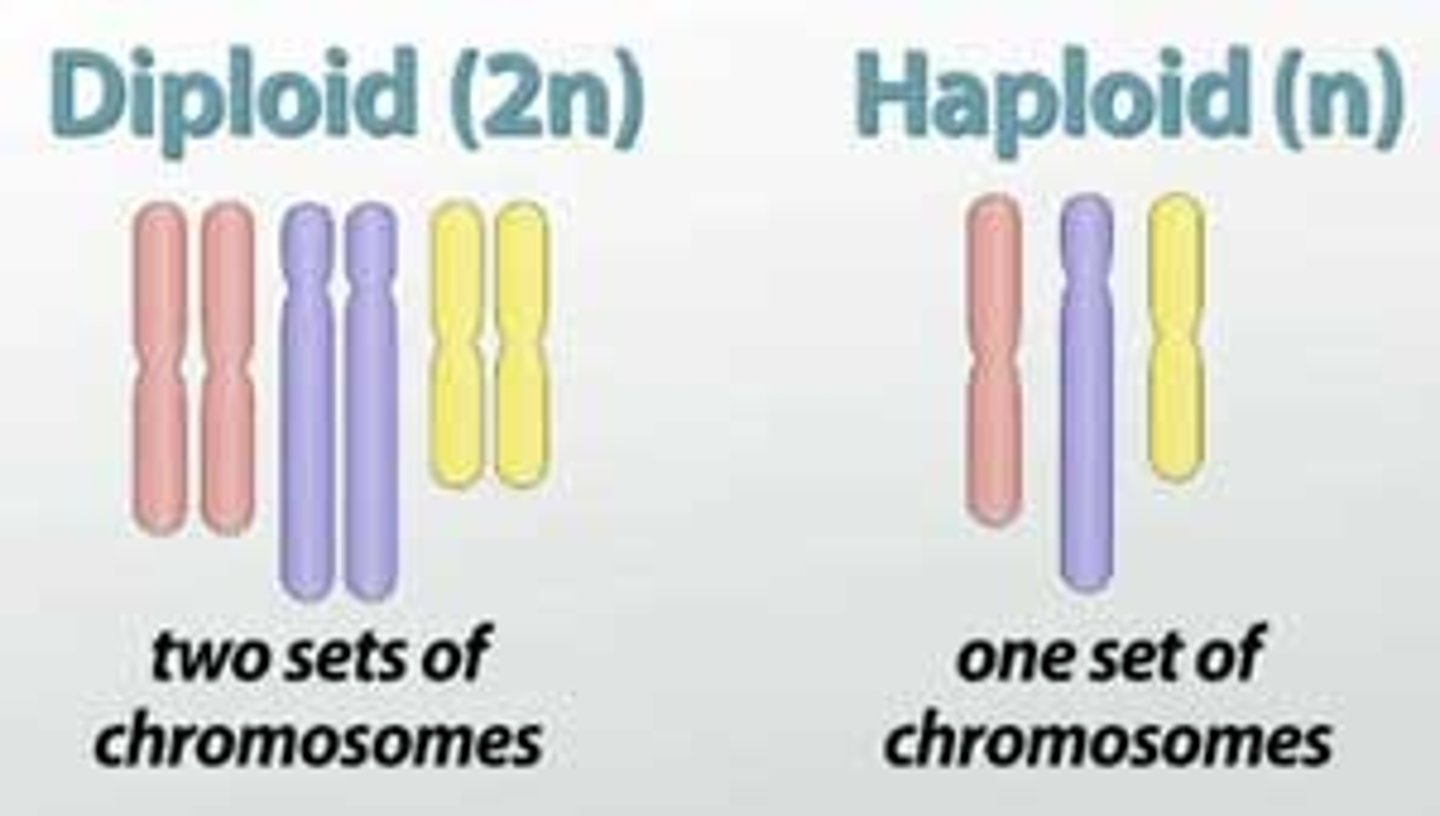
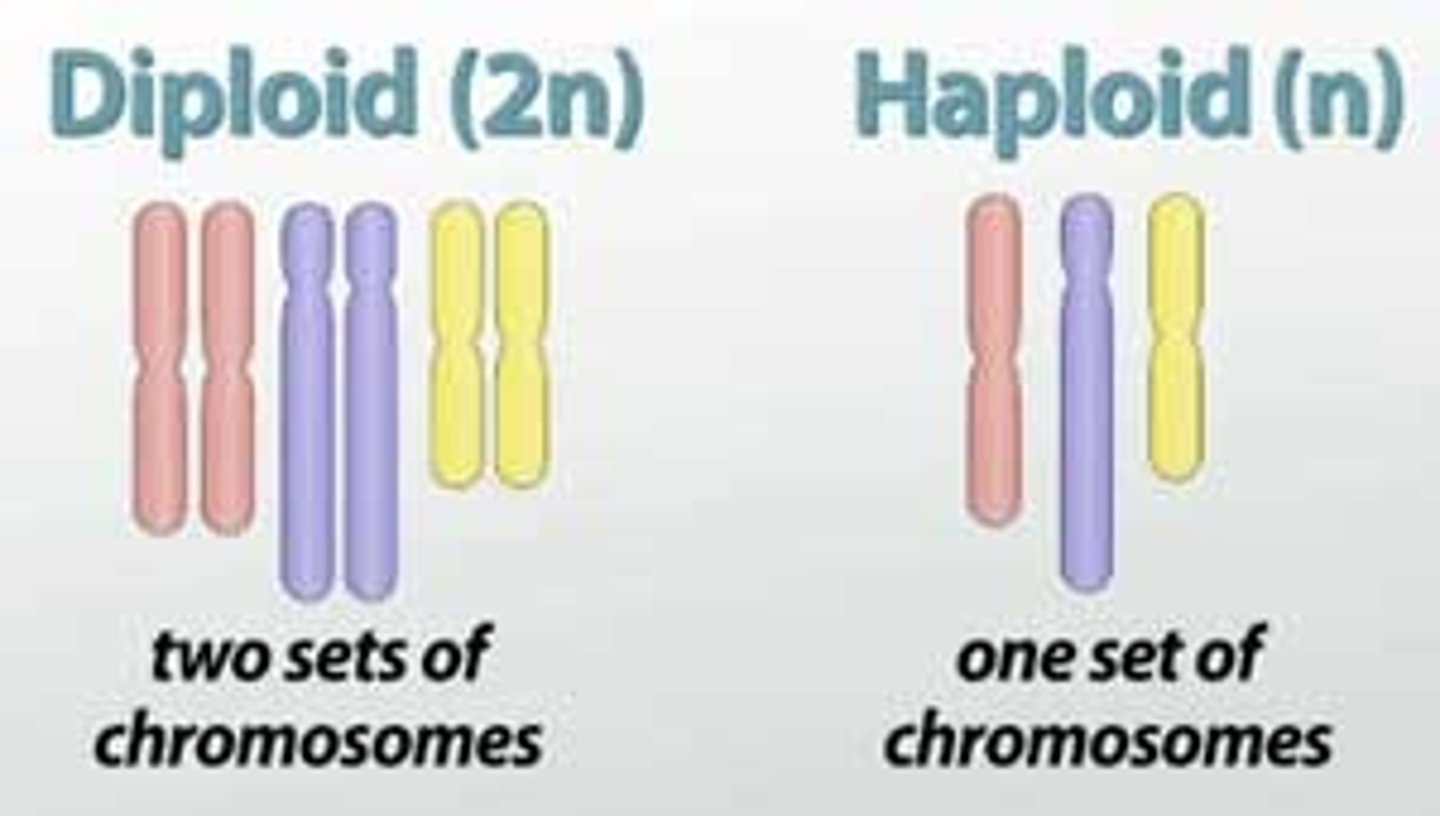
Haploid
Cell with one of each kind of chromosome; is said to contain a haploid or n, number of chromosomes.
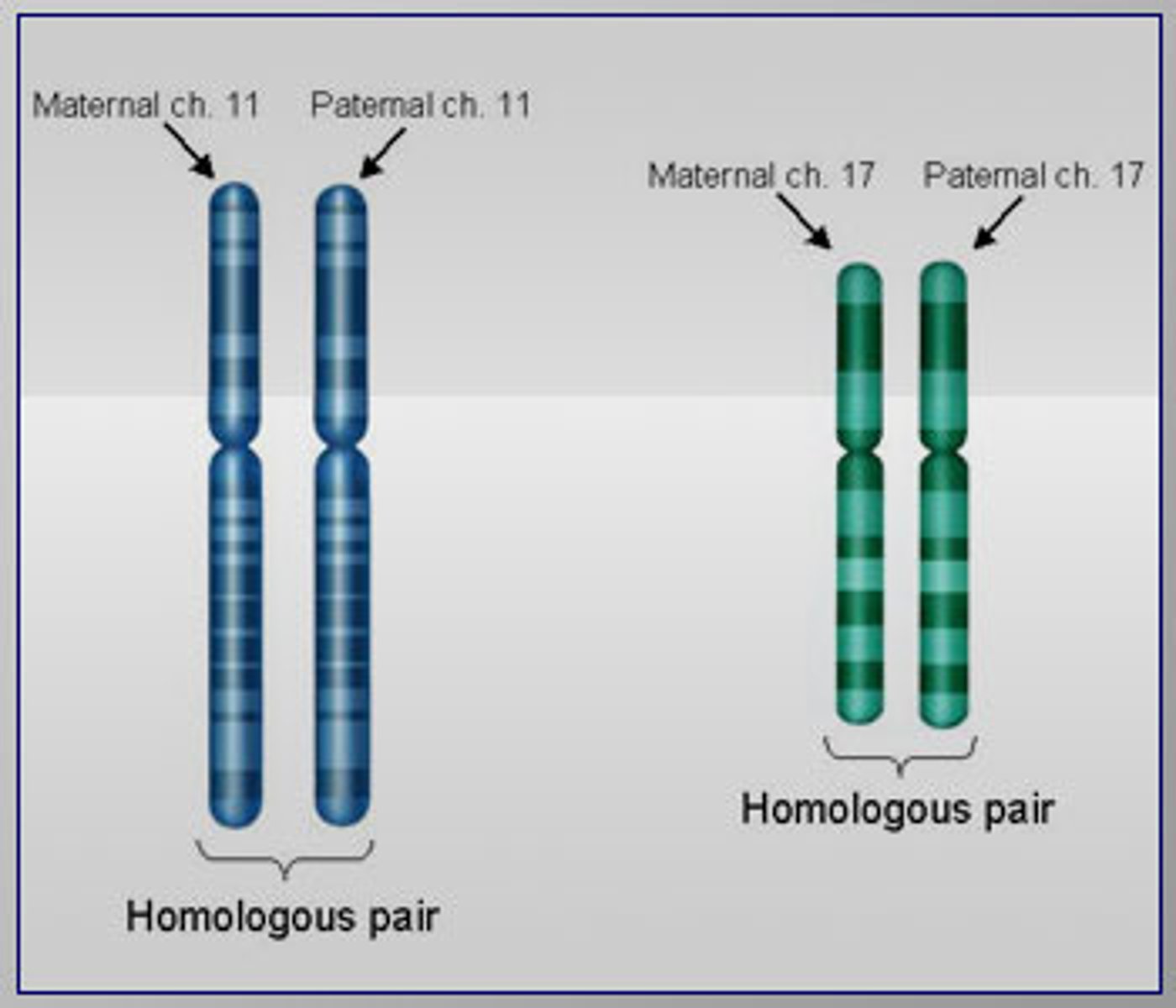
Homologous chromosome
Paired chromosomes with genes for the same traits arranged in the same order.
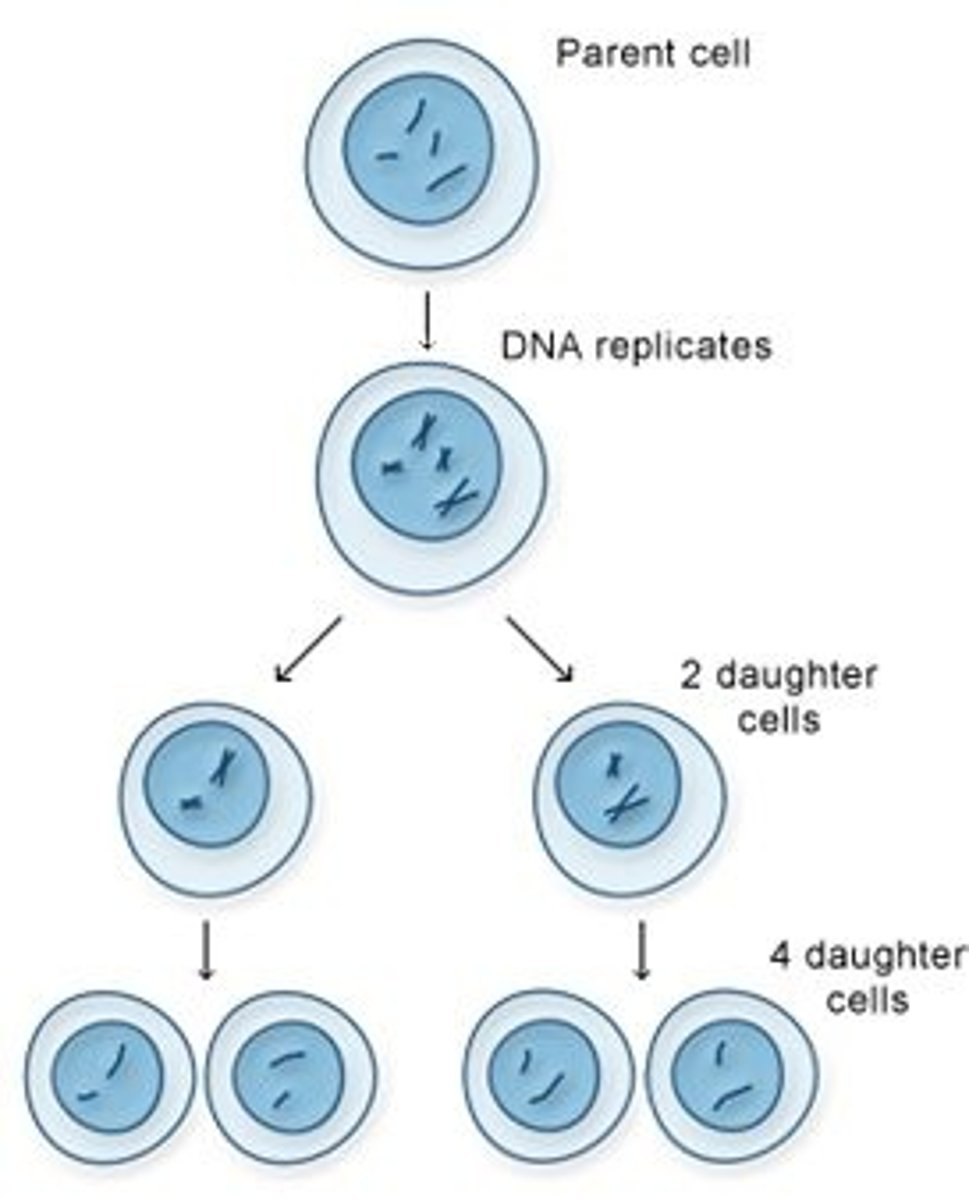
Meiosis
Type of cell division of body cell produces four gametes, each containing half the number of chromosomes as a parent's body cell.
Sperm
Haploid male sex cells produced by meiosis.
Egg
Haploid female sex cell produced by meiosis.
Sex cell
sperm or egg
Sexual reproduction
Pattern of reproduction that involves the production and subsequent fusion of haploid sex cells.
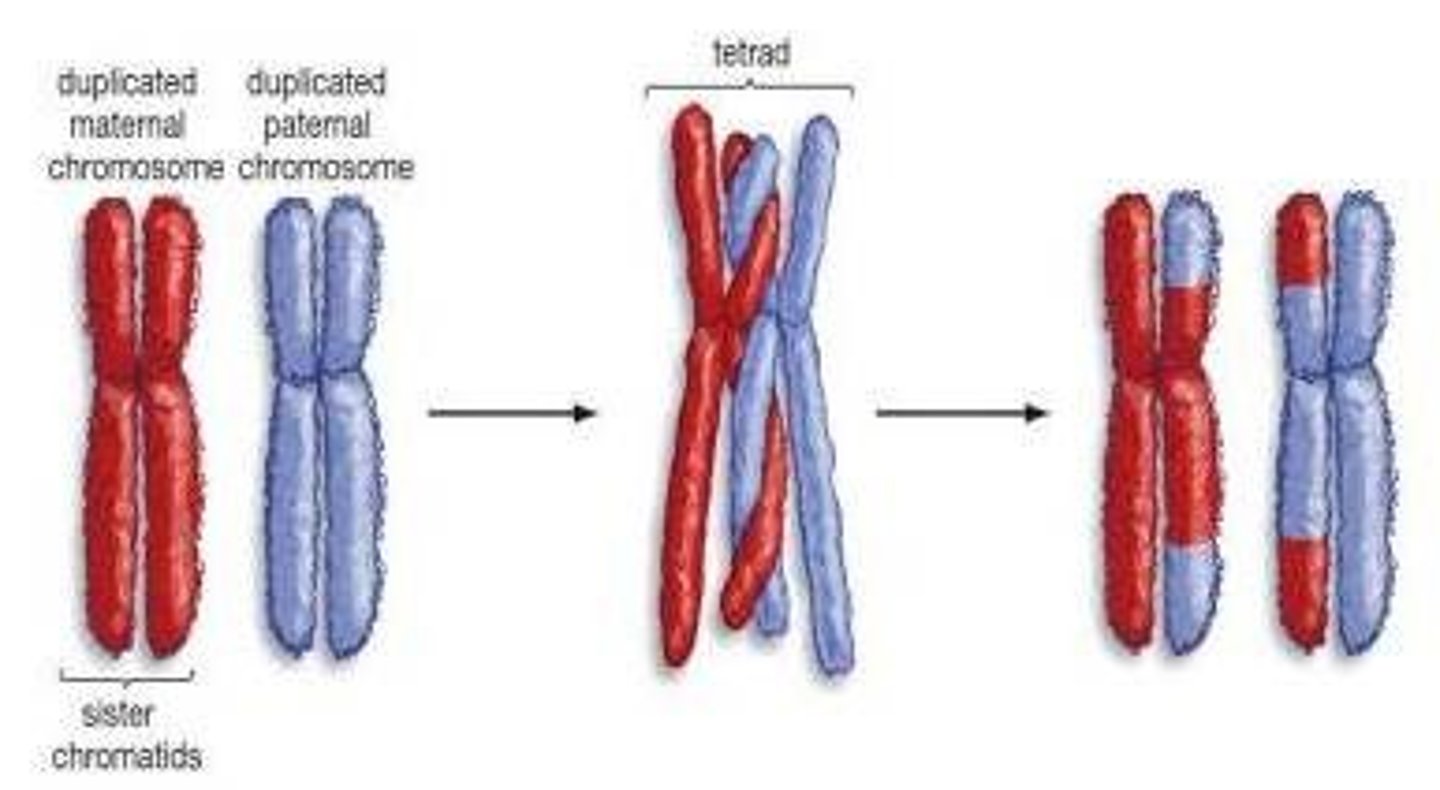
Crossing over
Exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids from homologous chromosomes during prophase I of meiosis; results in new allele combinations.
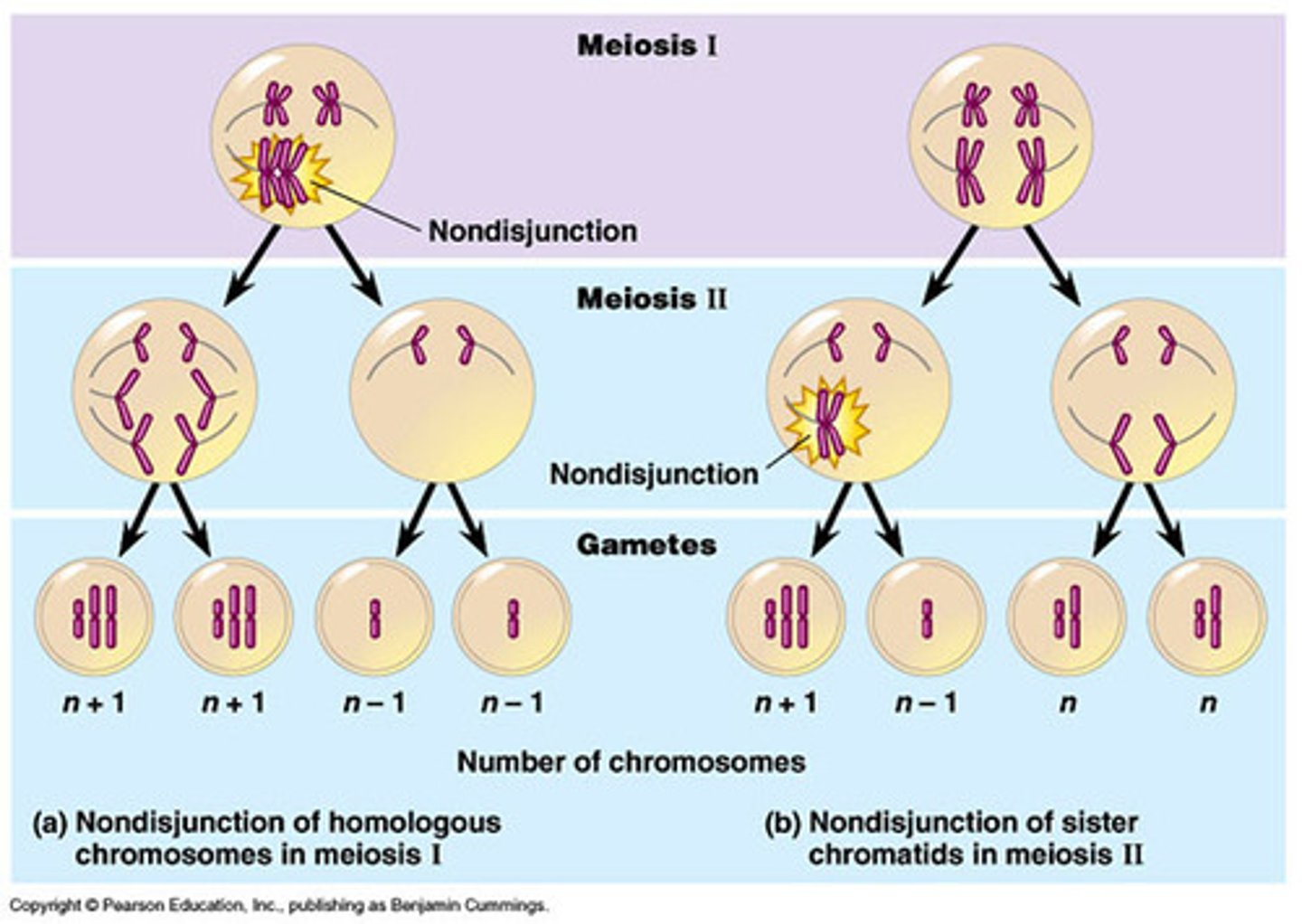
Non-disjunction
Failure of homologous chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis; results in gametes with too many or too few chromosomes.
2n
A full set of chromosomes. Found at the beginning and end of mitosis. Found at the beginning of meiosis. Also diploid. For humans 46 is the 2n number.
n
A 1/2 set of chromosomes. Found at the end of meiosis. Found in gametes/sex cells/sperm and eggs. In humans this number is 23.
Autosome
Chromosome pairs 1-22. Body chromosomes, not sex chromosomes
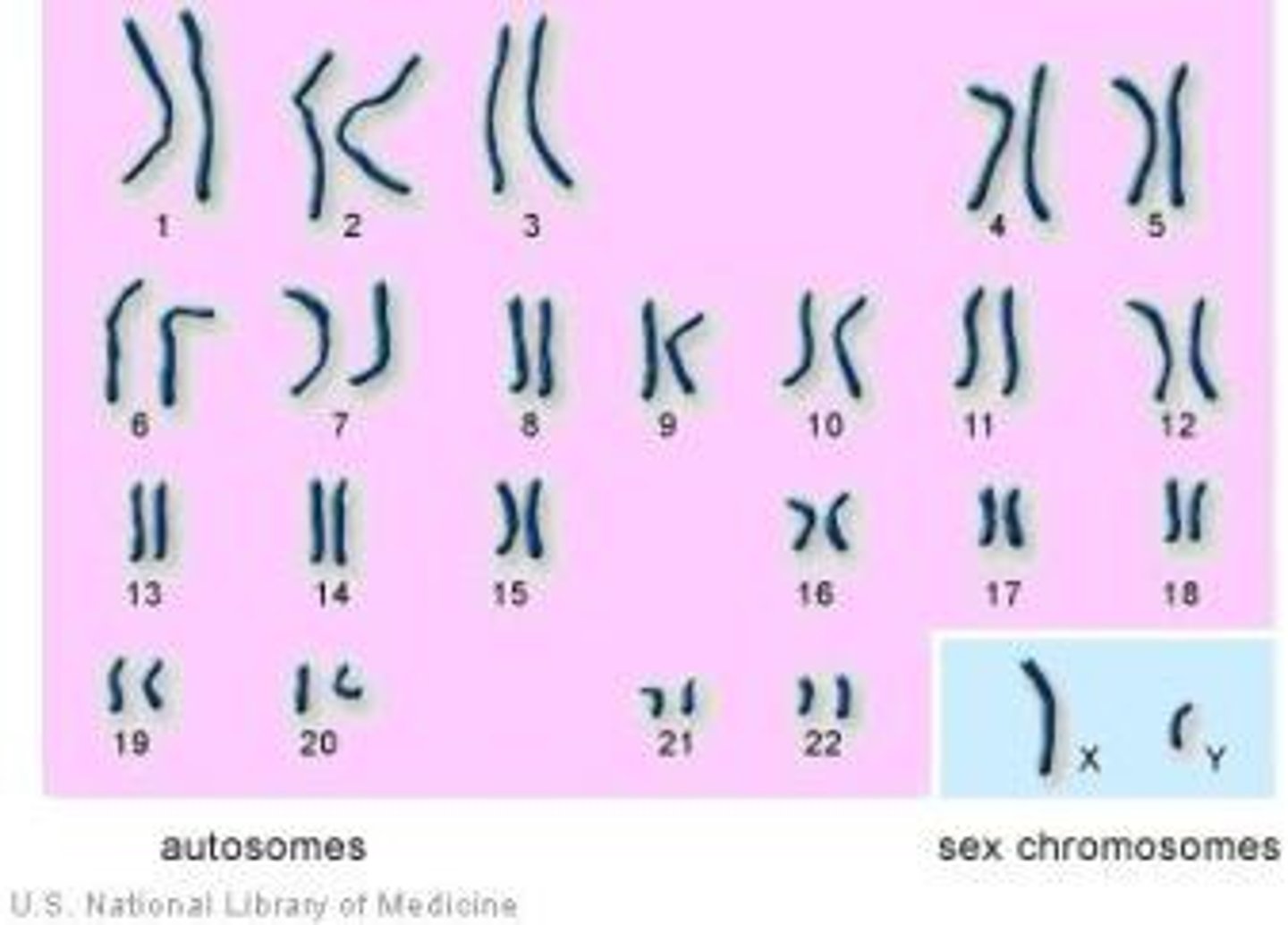
Sex chromosomes
Pair #23. XX or XY. determines gender.
Loci
A point on a chromosome that matches with a particular gene.
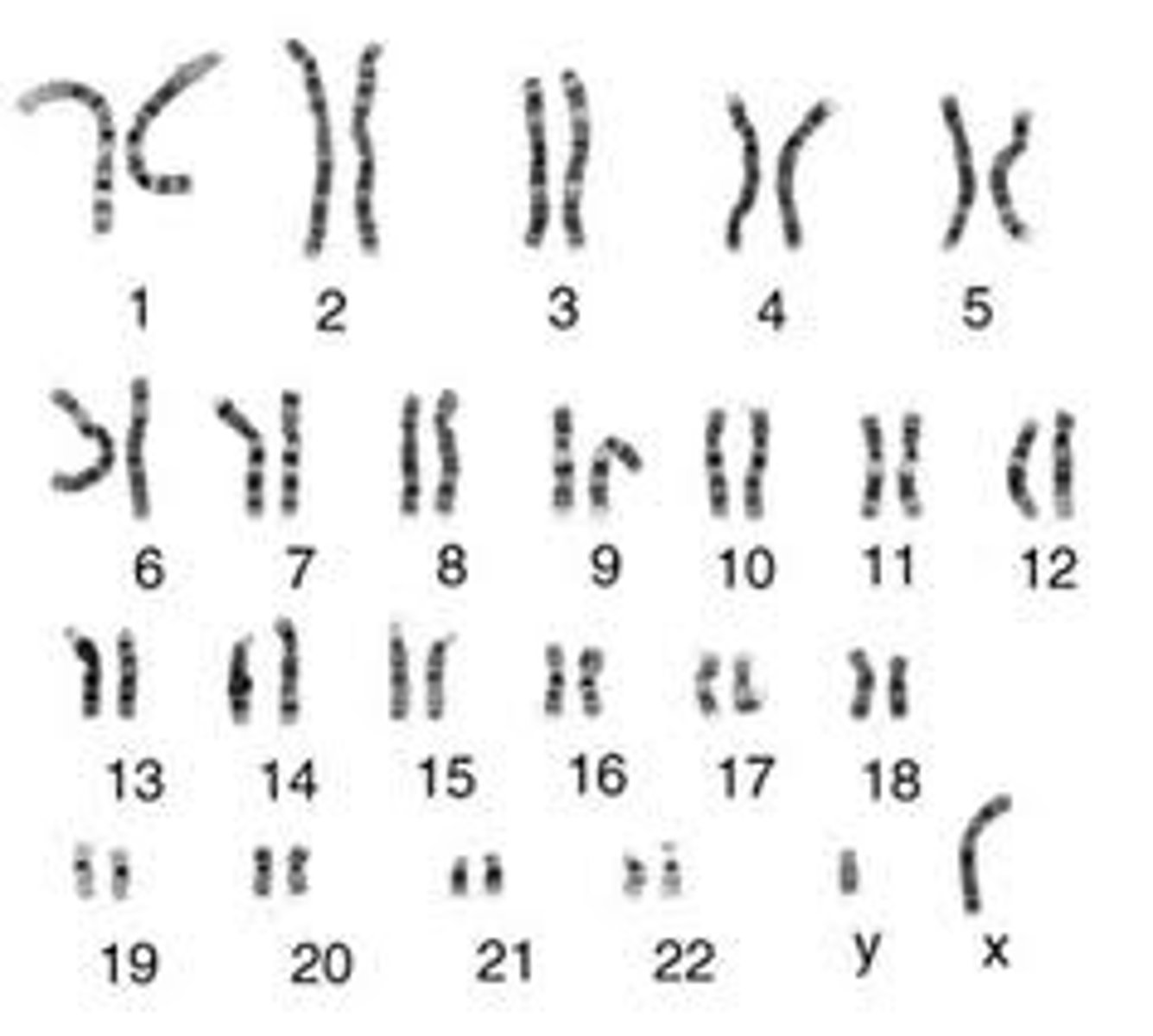
Karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape.
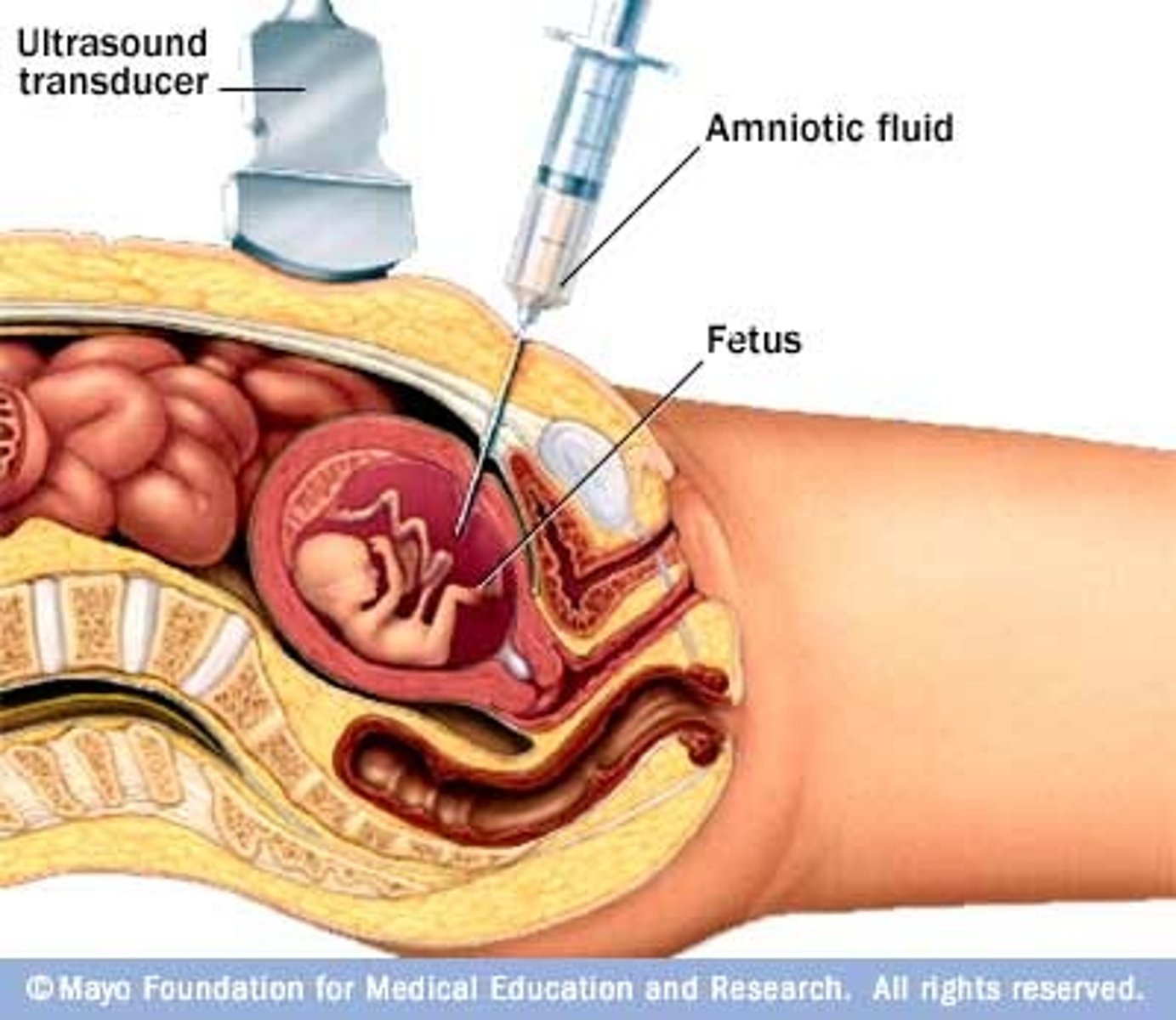
Amniocentesis
needle puncture of the amniotic sac to withdraw amniotic fluid for analysis of chromosomes or other fetal abnormalities
Deletion
A change to a chromosome in which a fragment of the chromosome is removed.
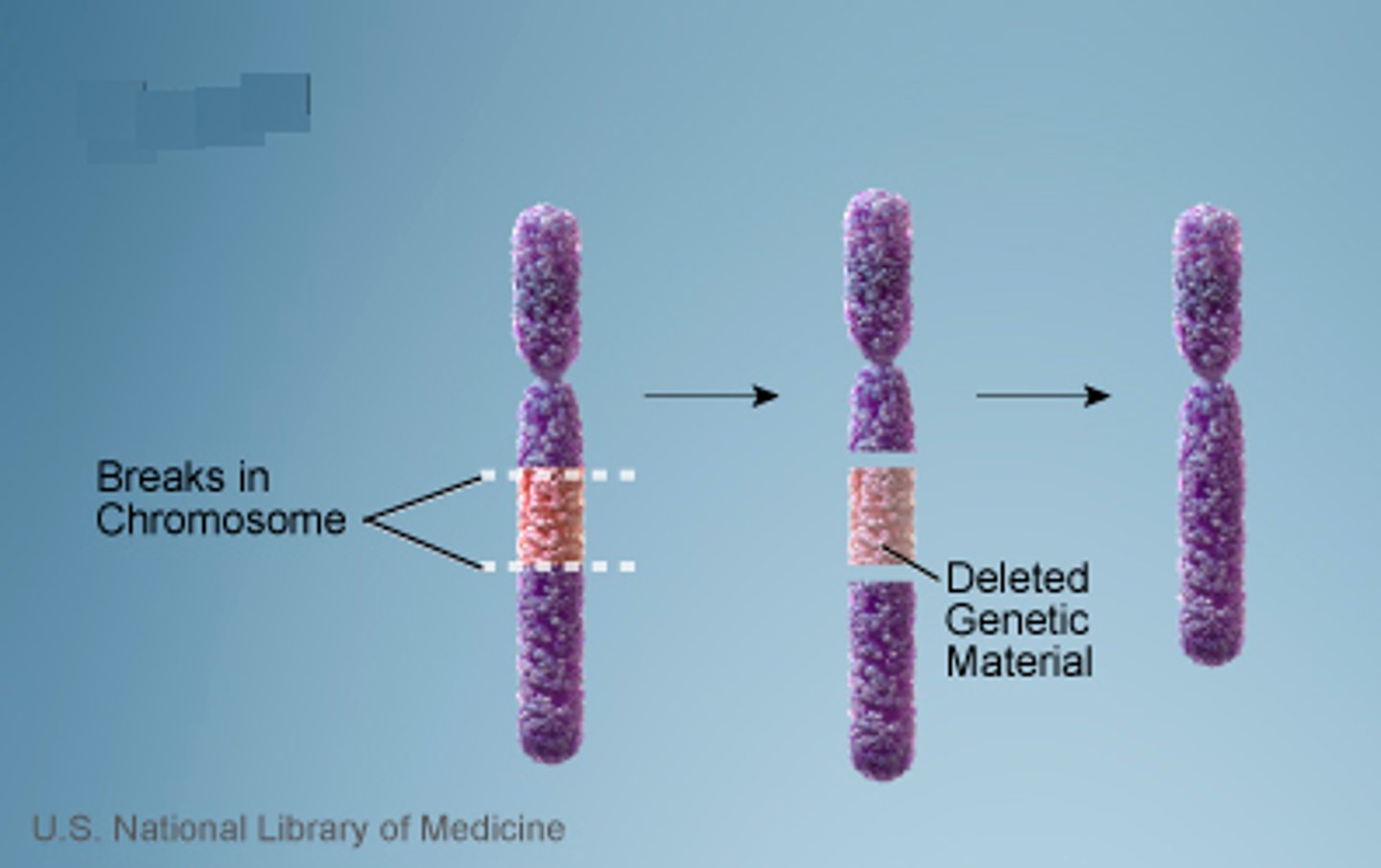
Duplication
change to a chromosome in which part of the chromosome is repeated
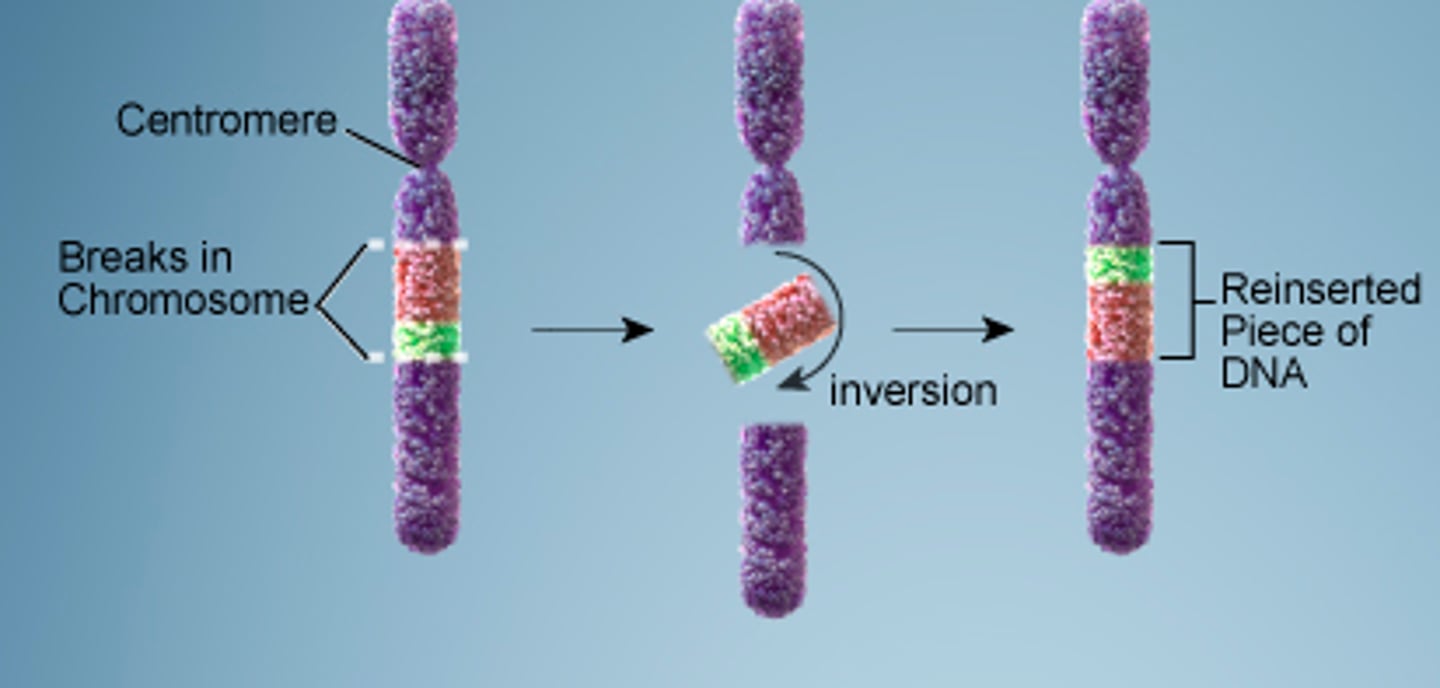
Inversion
A mutation that occurs when a chromosome piece breaks off and reattaches in reverse orientation
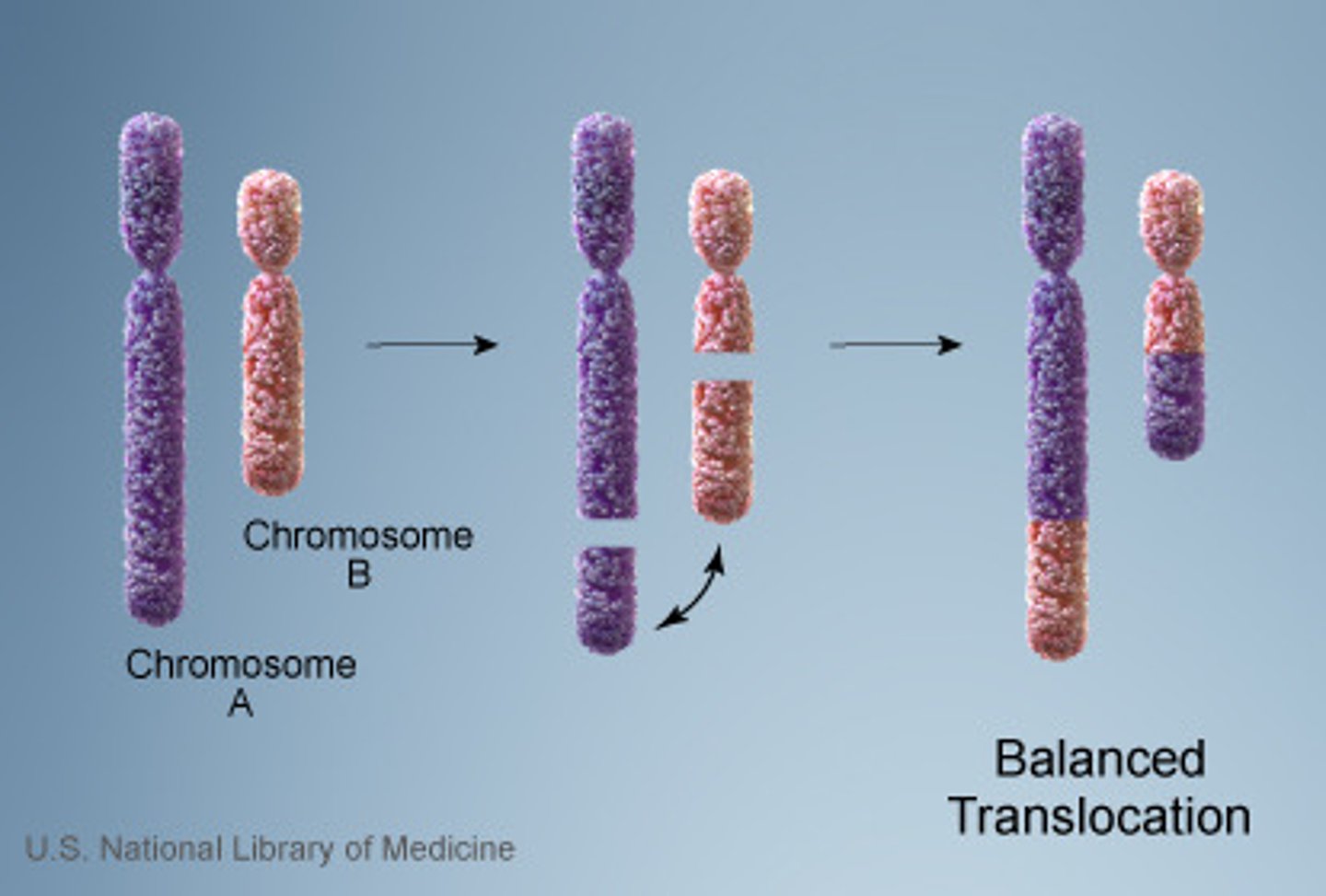
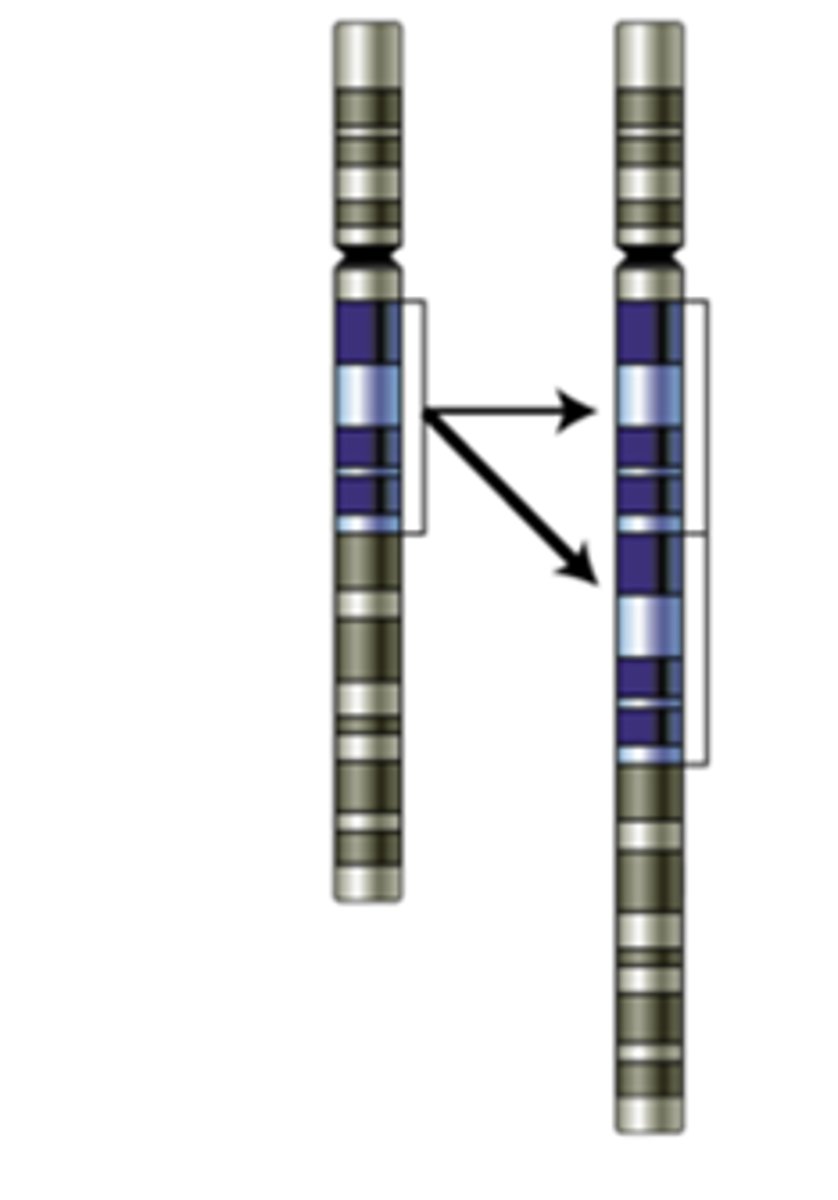
Translocation
Change to a chromosome in which a fragment of one chromosome attaches to a nonhomologous chromosome.