Antibacterial
1/223
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
224 Terms
Waksman
proposed the widely cited definition that “an antibiotic is a substance produced by microorganisms, which has the capacity of inhibiting the growth and even destroying other microorganisms
Waksman
isolated Streptomycin from Streptomyces griseus
Dubois
responsible for the isolation of the antibacterial antibiotic Tyrocidin
Bacillus brevis
Tyrocidin came from the soil bacterium
product of metabolism
synthetic product produced as a structural analog of a naturally occurring antibiotics
antagonizes growth or survival of one or more species of microorganisms
effective in low concentration
narrow spectrum
bactericidal
very selective mode of action
low serum protein binding
widely distributed especially in the CNS
excreted by the kidneys
A product is considered antibiotic if these conditions are met
bacteriostatic
bactericidal
types of activity of antibiotics
narrow spectrum
acting only on a single or limited group of microorganisms
broad spectrum
affects a wide variety of microorganism species
Beta lactam antibiotics
can be destroyed by acylases and beta lactases
penicillins
beta lactamase inhibitors
cephalosporins
monobactams
Classification of beta lactam antibiotics
penicilins
MOA: selective inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis
transpeptidase enzyme
catalyzes the nucleophilic carbonyl substitution process required for the cross-linking of the peptidoglycan in bacterial cell walls.
penicillin-binding proteins
the cross linking reaction if catalyzed by a class of transpeptidase known as
D-Ala-D-Ala
β-lactams mimic the structure of the__________ link and bind to the active site of PBPs, disrupting the cross-linking process.
rash or itching, delayed CV collapse or shock
allerginicity to penicillins can manifest as
allergy
______ to penicillin occurs due to penicilloic acid reacting with lysine-amino group forming of PENCILLOYL PROTEINS
natural
antistapylococcal
amino
extended-spectrum
classification of penicillins
natural penicillins
highly active against gram-positive cocci
very susceptible to B-lactamases
natural
identify the classification of the penicillin (natural, anti-staphylococcal, amino, extended-spectrum)
Pen G
natural
identify the classification of the penicillin (natural, anti-staphylococcal, amino, extended-spectrum)
Pen V
True
True or false
In natural penicillins, the inclusion of a side chain R-group that is Electron withdrawing group decreases the electron density of the side chain carbonyl and protects these penicillins from acid degradation.
V, G
Penicillin is more acid resistant than Penicillin __ since it contains an electronegative oxygen in the side chain
injection
if a ntural penicillin is not atleast partially acid resistant, then it can only be useful by
Pen G
benzylpenicillin
Pen V
phenoxymethylpenicillin
Pen V
natural penicillin that is administered orally
Pen G
natural penicillin that is administered through IV
Pen G
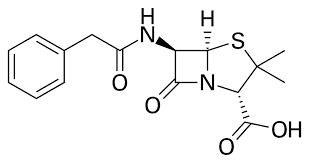
Pen V
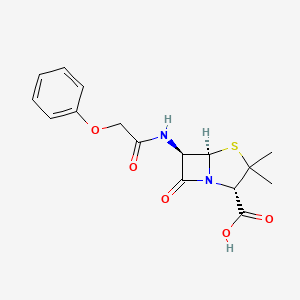
penicillin
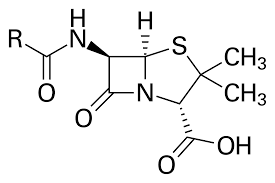
Pen G
Inactivated by the gastric juice and are not effective when administered orally unless antacid or buffer is taken along with
Penicillin G procaine
Penicillin G benzathine
Pen G salts
Pen V
Resistance to hydrolysis by gastric juice
It is able to form uniform concentration with blood
Very soluble in water
anti-staphylococcal
identify the classification of the penicillin (natural, anti-staphylococcal, amino, extended-spectrum)
methicillin
anti-staphylococcal
identify the classification of the penicillin (natural, anti-staphylococcal, amino, extended-spectrum)
oxacillin
anti-staphylococcal
identify the classification of the penicillin (natural, anti-staphylococcal, amino, extended-spectrum)
cloxacillin
anti-staphylococcal
identify the classification of the penicillin (natural, anti-staphylococcal, amino, extended-spectrum)
dicloxacillin
oxacillin
cloxacillin
dicloxacillin
isoxazolyl penicillins
anti-staphylococcal penicillins
resistant to B-lactamase enzymes
anti-staphylococcal
identify the classification of the penicillin (natural, anti-staphylococcal, amino, extended-spectrum)
nafcillin
methicillin
anti-staphylococcal penicillin that may cause nephrotoxicity and interstitial nephritis
nafcillin
may be used in infections caused solely by penicillin g-resistant staphylococci or when streptococci are also present
oxacillin
may be hepatotoxic and can cause bleeding
True
true or false
Penicillinase resistant penicillin, in general, there should be a increase in the steric hindrance at the α-carbon of the acyl group
True
true or false
Oxacillin, Cloxacillin, and Dicloxacillin, in which a substituted isoxazoyl ring, diortho-substituted aromatic rings, naphthyl ring systems are used as a bioisosteric replacement for the benzyl group in Penicillin G.
Thus, these are less potent against bacteria that do not produce β lactamase, but are effective against those that do.
methicillin
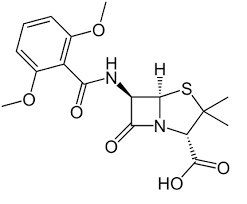
nafcillin
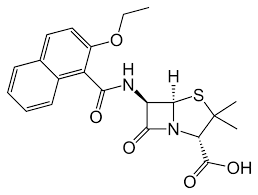
oxacillin
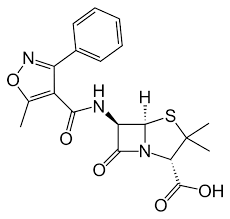
cloxacillin
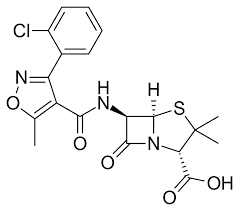
dicloxacillin
aminopenicillins
These antibiotics are orally active, and have a broader spectrum than Penicillin G, but are quite susceptible to β lactamases, they are often given with Clavulanic acid to avoid enzymatic degradation.
amino
identify the classification of the penicillin (natural, anti-staphylococcal, amino, extended-spectrum)
amoxcillin
amino
identify the classification of the penicillin (natural, anti-staphylococcal, amino, extended-spectrum)
ampicillin
ampicillin
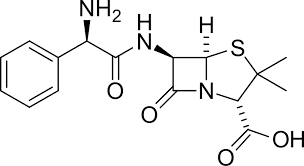
amoxicillin
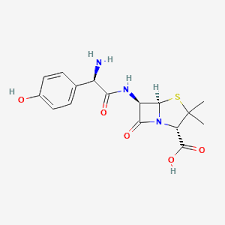
extended spectrum penicillins
They are susceptible to β lactamases that is why they are usually combined with another drug “β lactamase inhibitors”
Pseudomonas aerginosa
Enterobacter
Proteus
Klebsiella
other gram negative bacteria
extended spectrum penicillins have extended activity against what microorganisms
Carbenicillin
Ticarcillin
carboxypenicillins
extended spectrum
identify the classification of the penicillin (natural, anti-staphylococcal, amino, extended-spectrum)
carbenicillin
extended spectrum
identify the classification of the penicillin (natural, anti-staphylococcal, amino, extended-spectrum)
ticarcillin
extended spectrum
identify the classification of the penicillin (natural, anti-staphylococcal, amino, extended-spectrum)
mezlocillin
extended spectrum
identify the classification of the penicillin (natural, anti-staphylococcal, amino, extended-spectrum)
azlocillin
mezlocillin
azlocillin
ureidopenicillins
carboxypenicillin
contains Carboxylate moiety in the sidechain portion of the molecule that enhances their activity against gram negative bacteria
ureidopenicillin
contains the Acylureido group that mimics the peptidoglycan chain that enhances activity against gram negative bacteria
Class 1
Class 2
classification of beta lactamase inhibitors
Class 1 inhibitors
Prolongs inactivation of the enzyme
Commonly used with extended spectrum penicillin and beta lactamase-sensitive penicillins
Class 1
identify the classification of the beta-lactamase inhibitor
sulbactam
Class 1
identify the classification of the beta-lactamase inhibitor
clavulanic acid
Class 1
identify the classification of the beta-lactamase inhibitor
tazobactam
Augmentin
amoxicillin + clavulanic acid
Timentin
ticarcillin + clavulanic acid
unasyn
ampicillin + sulbactam
zosyn
piperacillin + tazobactam
Class 1
identify the classification of the beta-lactamase inhibitor
amoxicillin + clavulanic acid
Class 1
identify the classification of the beta-lactamase inhibitor
ticarcillin + clavulanic acid
Class 1
identify the classification of the beta-lactamase inhibitor
Ampicillin + sulbactam
Class 1
identify the classification of the beta-lactamase inhibitor
Piperacillin + tazobactam
Class 2 inhibitors
Possess potent antibacterial activity in addition to its ability to cause transient inhibition of some beta-lactamases
Class 2
identify the classification of the beta-lactamase inhibitor
carbapenems
Class 2
identify the classification of the beta-lactamase inhibitor
monobactam
Class 2
identify the classification of the beta-lactamase inhibitor
theinamycin
Class 2
identify the classification of the beta-lactamase inhibitor
meropenem
Class 2
identify the classification of the beta-lactamase inhibitor
biapenem
theinamycin
isolated from Streptomyces cattleya
Imipenem
first ever marketed theinamycin
meropenem
exhibits greater potency against gram negative and anaerobic bacteria than imipenem does, but is slightly less active against most gram positive
biapenem
the strongest for gram negative, gram positive, and anaerobes.
7-aminocephalosporanic acid
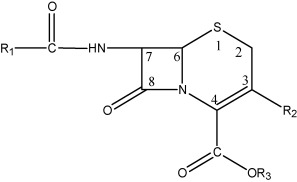
Cephalosporin
Isolated from Cephalosporium acremonium which inhibits the growth of a variety gram positive and gram negative
dihydrothiazine ring
Cephalosporin is a close congener of Pen, which contains the
3-acetoxylmethyl group
The most reactive site with acetoxyl group undergoing solvolysis inacid medium
Acylases
1st and 2nd gen
(cephalosporin)
gram +
3rd gen
(cephalosporin)
gram +, gram -
4th gen
(cephalosporin)
pseudomonas
5th gen
(cephalosporin)
MRSA
1st gen cephalosporin
The optimum activity of all first generation cephalosporin drugs is against gram-positive bacterias such as Staphylococci and Streptococci.
Cephradine
the ONLY cephalosporin derivative that is available in oral and parenteral preparation
Cefadroxil
prolonged DOA, Once a day dosing
Cephalexin
acid-stable