CIE AS Computer Science Hardware
1/198
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
199 Terms
memory cache
high speed memory external to processor which stores data which the processor will need again
primary memory
the part of computer memory which can be accessed directly from the CPU
what does primary memory contain?
the RAM and ROM memory chips
what does RAM stand for?
random access memory
what does ROM stand for?
read-only memory
is access time to locate data faster in RAM or in secondary devices?
RAM
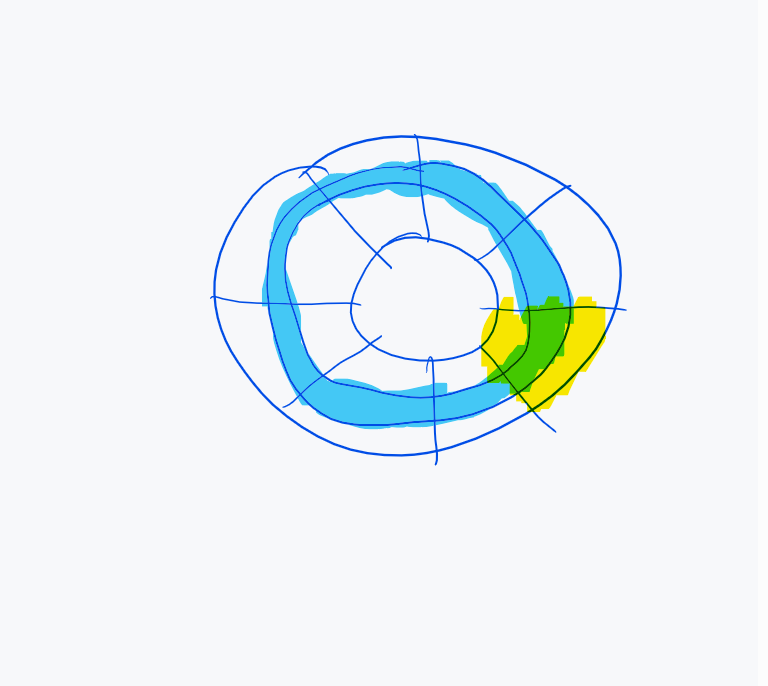
is the yellow part a track or sector?
sector
is the blue part a track or sector?
track
what is a removeable hard disk drive?
portable hard disk drive that is external to the computer, it can be connected via a USB port when required, often used as a device to back up files and data or as a way of transferring files between computers
what does SSD stand for?
solid state drive
what is an SSD?
storage media with no moving parts that relies on movement of electrons
is latency an issue in SSDs?
SSDs reduce the issue of latency considerably
is the data retrieved at the same or different rate in SSDs?
all data is retrieved at the same rate
do SSDs rely on magnetic properties?
no
how do the most common type of solid state drives storage devices store data?
by controlling the movement of electrons within NAND chips
how and where is data stored in SSDs?
the data is stored as 0s and 1s in millions of tiny transistors within the chip
are SSDs volatile or non-volatile?
non-volatile
are SSDs rewritable?
yes
what technology do a number of SSDs use?
EEPROM technology
what is the main difference between the most common types of SSDs compared to ones using EEPROM technology?
the use of NOR chips in ones using EEPROM rather than NAND chips
what effect does using EEPROM technology in SSDs have compared to the most common type of SSDs?
it makes them faster in operation but considerbaly more expensive
what difference does EEPROM technology in SSDs have in reading and erasing data?
EEPROM allows data to be read or erased in single bytes at a time, NAND usage only allows data blocks of data to be read or erased, this makes EEPROM more useful in certain applications where data needs to be accessed or erased in byte-size chunks
why do the majority of SSDs use NAND technology?
because of the cost of EEPROM
what kind of chips does flash memory use?
NAND
what are the advantages of SSD over HDD? (7)
more reliable - no moving parts to go wrong;
considerably lighter which makes them suitable for laptops;
do not have to get up to speed before they work properly;
have a lower power consumption;
run much cooler than HDDs;
are very thin because they have no moving parts;
access data considerably faster
what are the disadvantages of SSD over HDD? (1)
unknown longevity of the technology
what technology do memory sticks/flash memories/pen drives use?
solid state technology
how do memory sticks/flash memories/pen drives usually connect to the computer?
via the USB port
what is the main advantage of memory sticks/flash memories/pen drives?
they are small, lightweight devices which make them suitable for transferring files between computers and as small back-up devices
what is a dongle?
a small device that plugs into a computer and serves as an adapter or as a security measure to enable the use of the certain software
how do complex or expensive software (e.g. an expert system) often prevent illegal or unauthorised use of the software and prevent copying of the software?
using a memory stick as a dongle which contains additional files which are needed to run the software
what is optical storage?
CDs, DVDs and Blue-ray discs that use laser light to read and write data
how do CDs and DVDs store data?
using a thin layer of metal alloy or light-sensitive organic dye
what do CDs and DVDs contain?
a single, spiral track which runs from the centre of the disk to the edge
what happens when a CD or DVD disk spins?
the optical head moves to the point where the laser beam contacts the disk surface and follows the spiral track from the centre outwards
what is CD/DVD divided into? what does this allow for?
sectors, allowing direct access of data
which part of a CD disks /DVD disks/HDDs run faster?
the outer part
how is the data stored on the spiral track in CDs and DVDs?
in pits and bumps
how is data read and written in CDs and DVDs?
using a red laser