7. Part 2: Population Growth & Regulation
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Model used to model populations with negative density dependence
Logistic growth model
The shape of the logistic growth curve is
Sigmoidal / S-Shaped
The logistic growth rate is ______ when population size is small, and _____ as population gets large
exponential
slows
The growth rate is zero when a population reaches ______ _____ (K)
carrying capacity
The midpoint of the logistic curve (K/2) is the
inflection point
The inflection point is where the
instantaneous growth rate is maximized
Does carrying capacity change as the population size changes?
No
When resources (ex. food) is doubled, what would you expect the carrying capacity value to do?
Double
What growth model is this the equation for?
dN/dt = rN(1-N/K)
Logistic
dN/dt is the expression for
instantaneous growth rate
Logistic growth is used when population is limited by density-_____ factors, and the geometric growth model is used when population is limited by density-_____ factors
dependent
independent
Proportion of individuals that occurs in different age classes
Age structure
Population growth will likely slow if much of the population is ___(2 reasons)___
Over the reproductive age
In an age class with a higher risk of death
Stage structure uses ___ ____ _____ rather than specific age
life stage categories
(e.g. hatchling, juvenile, adult)
Plot that displays the likelihood of an individual surviving across age classes
Survivorship curve
Type I/II/III survivorship curve?
Low mortality early in life, high mortality later in life (K-selected)
Type I
Type I/II/III survivorship curve?
Consistent mortality throughout life
Type II
Type I/II/III survivorship curve?
High mortality early in life, lower mortality later in life (r-selected)
Type III
Organizes data on the birth rates, death rates, and fecundity for each age class in a population; typically, only females are used
Life table
Life table made of data collected by following a group of individuals born at the same time throughout their life
Cohort life table
Life table made of data collected from individuals that vary in age classes during a single time period
Static life table
Would you use a cohort or static life table for species that have minimal movement and relatively short life spans?
Cohort
(Easy to track the same individuals over time)
Would you use a cohort or static life table for species that are highly mobile, have long life spans, and for which age can be easily determined?
Static
What life table variable?
Average # of female offspring produced per female per time period
fecundity rate (b_x)
What life table variable?
The probability of surviving from birth to any later age class
Survivorship (I_x)
Survivorship at any given age class is the product of _______ and _____
prior age’s survivorship
prior age’s survival rate
What life table variable?
Total number of female offspring that we expect an average female to produce over the course of her life
Net reproductive rate (R_o)
What is this the equation for?
SUM(I_x * b_x)
Ro (net reproductive rate)
Average time between the birth of an individual and the birth of its offspring
generation time
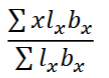
What is this the formula for?
Generation time
A population’s intrinsic growth rate can be calculated from the life table, depending upon _____ and _____
Net reproductive rate (Ro)
Generation time (T)
Population is growth when Ro >
1
The rate at which a population can change (increases/decreases) with shorter generation times
increases
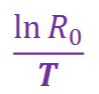
What is this the equation for?
Exponential intrinsic growth rate
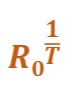
What is this the equation for?
Geometric intrinsic growth rate