Measuring economic activity and illustrating its variations: Circular Flow of Income + Calculations
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 3, Macroeconomics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
National income accounting
The services provided by a statistical entity in every country that measure the economy’s national income and output as well as other economic activity.
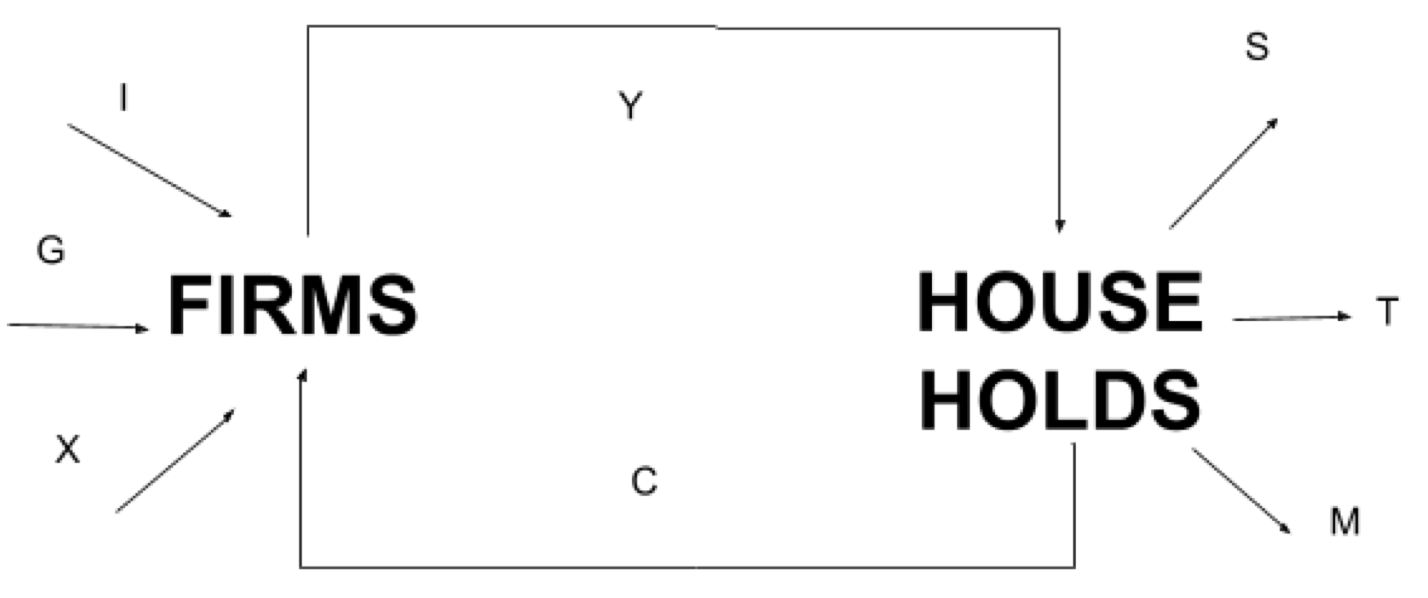
Households
Groups of individuals in the economy who share the same living accommodation, who pool their income and jointly decide the set of goods and services to consume.
Foreign sector
In an open economy the term refers to export revenues through selling domestic goods and services to foreigners and import expenditures through buying foreign goods and services.
Investment
Spending by firms on capital goods such as machines, tools, equipment and factories.
Net exports
(X - M): Export revenues minus import expenditure.
Circular Flow of Income Diagram
National income statistics
The statistical data used to measure a nation’s income and output, and perform national income accounting.
National income
The income earned by the factors of production of an economy, equal to wages plus interest, plus rents, plus profits.
Circular flow of income
A simplified illustration that shows the flows of income and expenditures in an economy.
Firms
Productive units that transform inputs (factors of production) into output (goods and services), usually aiming at earning profits
Leakage
Income not spent on domestic goods and services. It includes savings, taxes and import expenditure.
Injections
Within the circular flow model these refer to spending on domestic output that does not originate from households and thus includes investment spending by firms, government expenditures and exports.
Consumption
Spending by households on durable and non-durable goods and on services over a period of time.
Government spending
Refers to all spending by the government that is distinguished into current expenditures, capital expenditures and transfer payments.
Income
A flow of earnings from using factors of production to produce goods and services. Wages and salaries are the factor reward to labour and interest is the flow of income for the ownership of capital.
Imports
The value of goods and services purchased domestically that are produced abroad.
Exports
Goods and services produced in one country and purchased by consumers in another country.
Income approach
One of the 3 equivalent ways that GDP can be measured, by adding all incomes generated in the production process (wages, profits, interest and rent) for a given period.
Expenditure approach
One of three analytically equivalent approaches of measuring GDP that adds all the expenditures made on final domestic goods and services over a period of time by households, firms, the government and foreigners.
Output approach
One of the three equivalent ways that GDP can be measured, it adds up the value of final goods and services produced in a given time period.
Aggregate demand (AD)
Planned spending on domestic goods and services at different average price levels, per period of time. Consists of consumption, investment and government expenditures plus net exports.
Economic growth
Refers to increases in real GDP over time. Potential economic growth and actual economic growth
Actual growth
Occurs when real output (real GDP) increases through time and is a result of greater or better use of existing resources. In the PPC model it can be illustrated by a movement from a point inside a PPC to another point in the northeast direction.
Per capita
Per person. Per capita values are found by dividing the variable by the size of the population.
Gross domestic product (GDP)
The value of all final goods and services produced within an economy over a period of time, usually a year or a quarter.
Gross national income (GNI)
The income earned by all national factors of production independently of where they are located over a period of time; it is equal to GDP plus factor income earned abroad minus factor income paid abroad
Real GDP
The total value of all final goods and services produced in an economy in a given time period, usually one year, adjusted for inflation.
Real GDP per person (per capita)
Real GDP divided by the population of the country.
Real GNI per person (per capita)
Real GNI divided by the population of the country.
Real interest rates
Payment for borrowing a sum of money or reward for saving expressed as a percentage of the principal sum, adjusted for inflation.
Nominal gross domestic product (GDP)
The total money value of all final goods and services produced in an economy in a given
time period, usually one year, at current values (not adjusted for inflation).
Nominal gross national income (GNI)
The total income earned by all the residents of a country (regardless of where their factors of production are located) in a given time period, usually a year, at current prices (not adjusted for inflation).
Nominal interest rates
Interest rates that have not been adjusted for inflation.
Price deflator
A price index that removes the impact of changes
Consumer price index (CPI)
The average of the prices of the goods and services that the typical consumer buys expressed as an index number. The CPI is used as a measure of the cost of living in a country and to calculate inflation.
Inflation
A sustained increase in the average level of prices.
Inflation rate
The percentage change between two periods of the average price level, usually measured through the CPI.
GDP using the expenditure method
AD = C + I + G + X-M
Real GDP formula
Real GDP = Nominal GDP / GDP deflator
Real GDP per capita formula
Real GDP per capita = GDP / population
Economic growth rate formula
Economic growth rate = percentage change in real GDP
Inflation rate formula
Inflation rate = percentage change in CPI
Nominal gross national income (GNI)
The total income earned by all the residents of a country (regardless of where their factors of production are located) in a given time period, usually a year, at current prices (not adjusted for inflation).
Purchasing power parity (PPP)
A method used to make the buying power of different currencies equal to the buying
power of US$1. PPP exchange rates are used to make comparisons of income or output
variables across countries while eliminating the influence of price level differences.
Consumer price index (CPI)
The average of the prices of the goods and services that the typical consumer buys
expressed as an index number. The CPI is used as a measure of the cost of living in a
country and to calculate inflation.
Inflation rate
The percentage change between two periods of the average price level, usually measured through the CPI.
Price deflator
A price index that removes the impact of changes in the price level when measuring nominal economic variables.