Chapter 1-Hole's Human Anatomy & Physiology 16th Edition
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Appendicular
Upper and lower limbs
Pericardium
Membrane surrounding the heart
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain
Cranial
Pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain
Dorsal
Position toward the back of the body
Homeostasis
Maintenance of a stable internal environment. Contains 3 homeostatic mechanisms; Receptors(stimuli), Control Center(set point), and Effectors(muscles or glands) to get a response.
Physiology
The study of body function
Metabolism
The set of chemical changes in the body
Nasal
Pertaining to the nose
Orbital
Pertaining to the portion of the skull that encircles an eye
Parietal membrane
Membrane that lines the wall of a cavity
Pelvic cavity
Basin-shaped cavity enclosed by the pelvic bones.
Contains the terminal end of the large intestine, the urinary bladder, and the internal reproductive organs.
Pericardial membrane
Membrane that surrounds the heart
Pleural membrane
Membrane that encloses the lungs within the rib cage
Anatomy
Study of structure, which often involves cutting or removing body parts
Scientific Method
An approach to investigating the natural world
Subatomic particles
A particle that is smaller than an atom. Protons, neutrons, electrons
Atoms
Smallest unit of matter
Molecules
Groups of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
Macromolecules
A very large organic molecule composed of many smaller molecules
Cell
The basic unit of structure and function in living things
Organelles
Specialized structures that perform various jobs inside cells.
Tissue
Specialized cells assemble into layers or masses that have specific functions
Organ
Complex structures with specialized functions
Organ system
Groups of organs that function closely together
Organism
A living thing. Interacting organ systems.
Internal environment
The environment within the body in which the cells live
Cell membrane
The selectively permeable outer boundary of a cell consisting of a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins
Characteristics of life
Process Description
Growth Increase in cell number and size and increase in body size.
Reproduction Production of new cells and organisms.
Responsiveness Reaction to a change inside or outside of the body.
Movement Change in body position or location; motion of internal organs.
Metabolism The sum of all chemical reactions in a living system: Energy and nutrient cycling.
Respiration: Acquiring energy. Most organisms do it by taking in oxygen and giving off carbon dioxide
Digestion: Breaking down food into usable nutrients for absorption into the blood
Circulation: Moving chemicals and cells through the body fluids
Excretion: Removing waste products
Axial portion
head, neck, trunk
Appendicular portion
upper and lower limbs
Cranial cavity
houses the brain
Vertebral canal
contains the spinal cord and is surrounded by sections of the backbone
Thoracic cavity
cavity housing lungs and heart
Abdominopelvic cavity
contains both the abdominal and pelvic cavities.
Extends from the diaphragm to the floor of the pelvis. Its wall primarily consists of skin, skeletal muscles, and bones.
Viscera
The internal organs of the body.
Include the stomach, liver, spleen, gallbladder, kidneys, and the small and large intestines.
Diaphragm
A broad, thin muscle that separates the thoracic cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity.
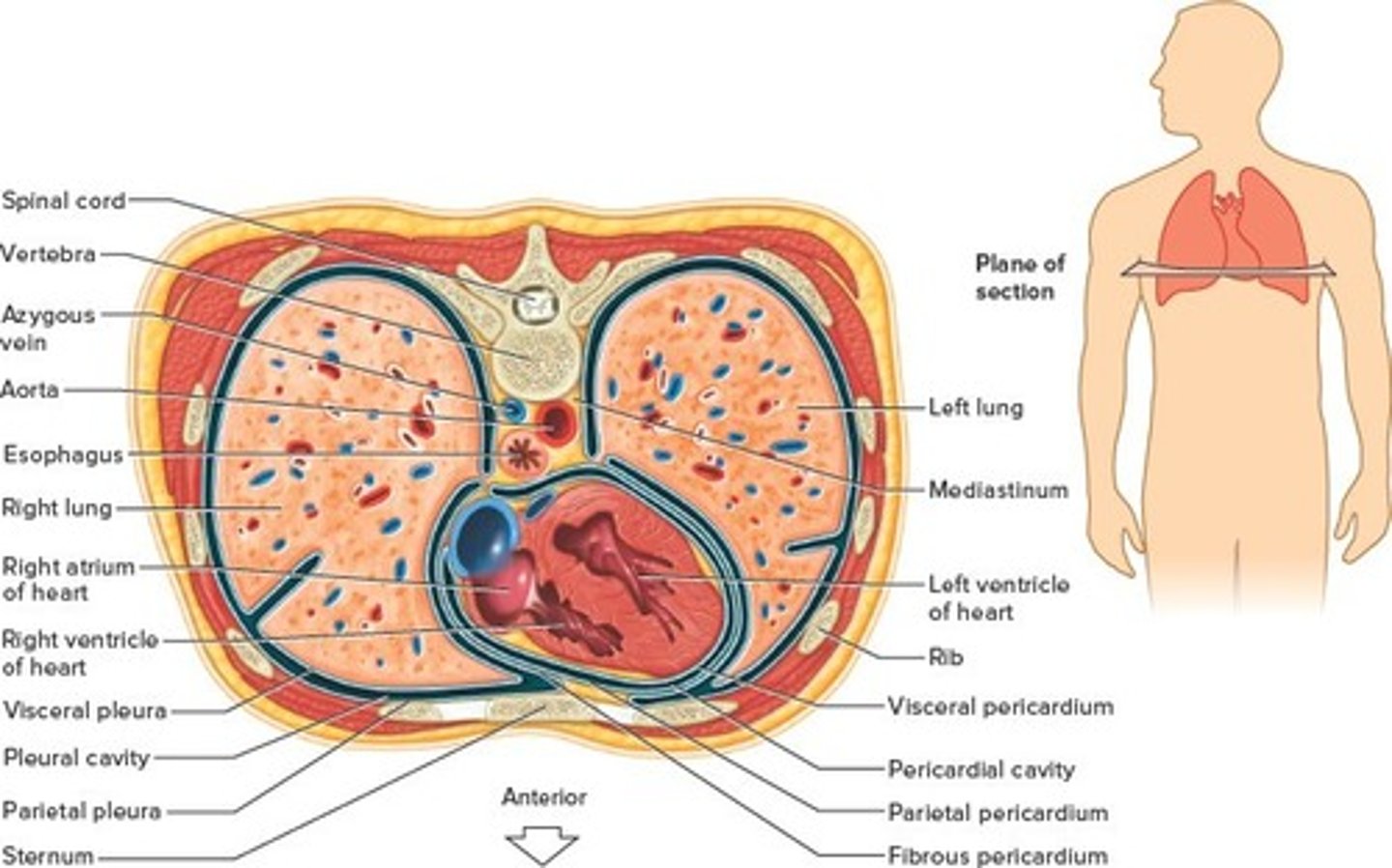
Mediastinum
(Space between the lungs)
Extends forward to the sternum and backward to the vertebral column. It forms a boundary between the right and left sides of the thoracic cavity. The mediastinum contains most of the thoracic cavity viscera (including the heart, esophagus, trachea, and thymus) except for the lungs. The right and left lungs are on either side of the mediastinum.
oral cavity
contains teeth and tongue
Nasal cavity
connecting with several air-filled sinuses
Orbital cavities
containing the eyes and associated skeletal muscles and nerves
Middle ear cavities
containing the middle ear bones
Serous membranes
Line the walls of the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities and fold back to cover the organs within these cavities. These membranes secrete a slippery serous fluid that separates the layer lining the wall of the cavity (parietal layer) from the layer covering an organ (visceral layer)
parietal pleura
lines the walls of the thoracic cavity
visceral pleura
inner layer of pleura lying closer to the lung tissue
pleural cavity
space between the folds of the pleura
pericardial membrane
membrane that surrounds the heart
visceral pericardium
covers the surface of the heart
parietal pericardium
outer layer of the pericardium
pericardial cavity
contains the heart
fibrous pericardium
The parietal pericardium is covered by a much thicker third layer
Thoracic Membranes
Abdominopelvic Membranes
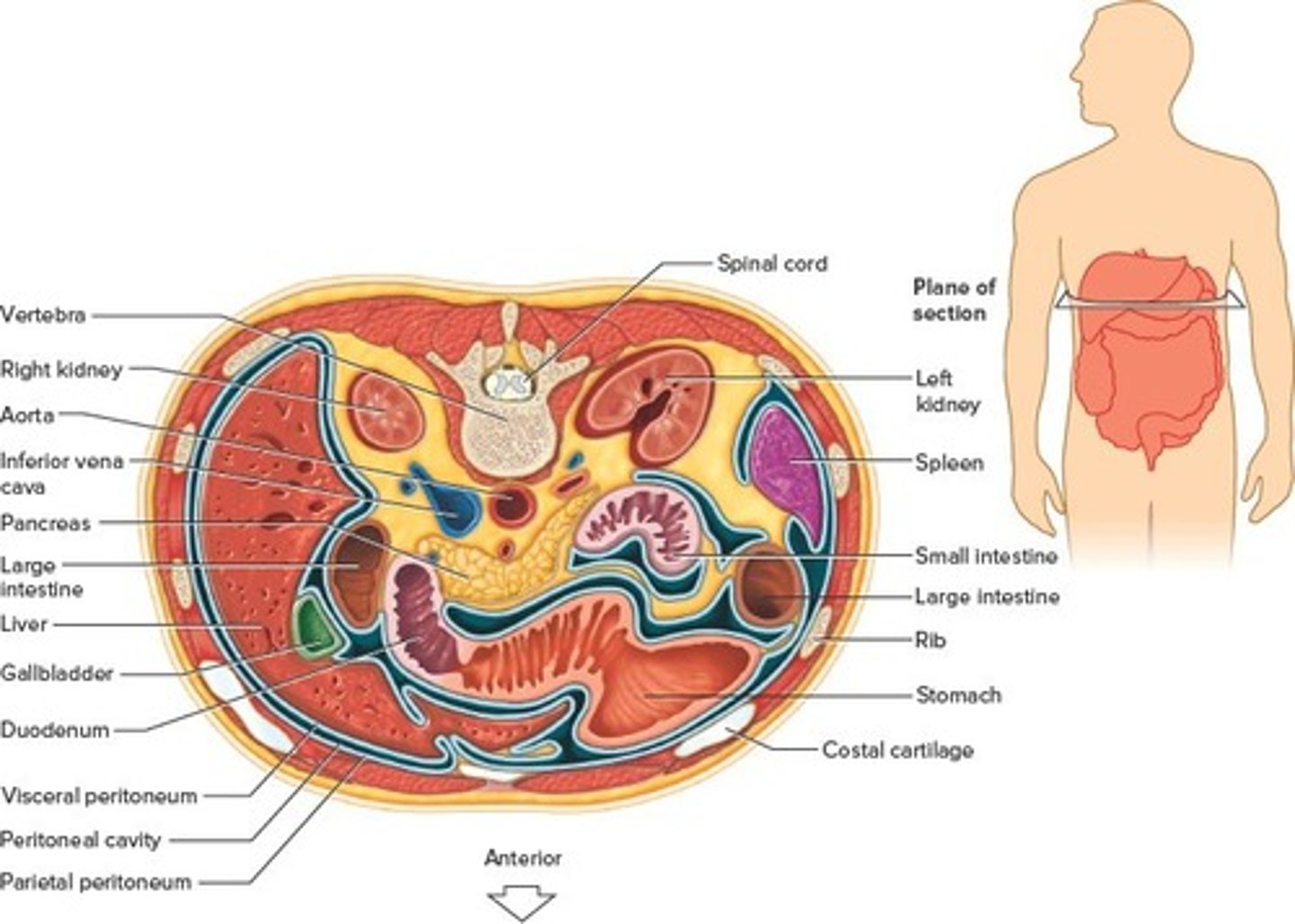
peritoneal membrane
lining of the abdominal cavity that protects the abdominal organs
parietal peritoneum
lines the wall of the abdominopelvic cavity
visceral peritoneum
the inner layer of the peritoneum that surrounds the organs of the abdominal cavity
integumentary system
include the skin and accessory organs such as the hair, nails, sweat glands, and sebaceous glands
Skeletal system
consists of the bones as well as the ligaments and cartilages that bind bones together at joints
Muscular System
enables movement of the body and internal organs
Nervous System
consists of the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sense organs. Nerve cells within these organs use a bioelectrical signal called an impulse (an action potential) in combination with a chemical signal (a neurotransmitter) to communicate with one another and with muscles and glands
Endocrine System
includes all the glands that secrete chemical messengers, called hormones. Organs of the endocrine system include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, and adrenal glands, as well as the pancreas, ovaries, testes, pineal gland, and thymus
Hormones
Travel away from the glands in body fluids such as interstitial fluid and blood
cardiovascular system
Includes the heart, arteries, capillaries, veins, and blood. The heart is a muscular pump that helps force blood through the blood vessels. Blood carries gases, nutrients, hormones, and wastes. It carries oxygen from the lungs and nutrients from the digestive organs to all body cells, where these substances are used in metabolic processes.
lymphatic system
The other transport system and is closely associated with the cardiovascular system. It is composed of the lymphatic vessels, lymph fluid, lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen. This system transports some of the fluid from the spaces in tissues (interstitial fluid) back to the bloodstream and carries certain fatty substances away from the digestive organs.
digestive system
receive foods and then break down food molecules into simpler forms that can be absorbed into the internal environment
respiratory system
moves air in and out of the body and exchange gases between the blood and the air. Specifically, oxygen passes from air in the lungs into the blood, and carbon dioxide leaves the blood and enters the air in the lungs and then moves out of the body. The nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs are parts of this system
urinary system
consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys remove wastes from blood and assist in maintaining the body's water and electrolyte concentrations. (Electrolytes are chemicals, related to salts.) The product of these activities is urine. Other parts of the urinary system store urine and transport it to outside the body.
Excretion
removal of waste from the body
Reproduction
is the process of producing offspring (progeny)
reproductive system
of an organism, however, produces whole new organisms like itself