Ionic Bonding
1/6
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
How are ions are formed by electron loss or gain?
Ions are electrically charged particles formed when atoms lose or gain electrons. (get a full outer shell)
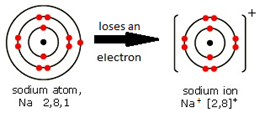
Metal atoms form positive ions (cations).
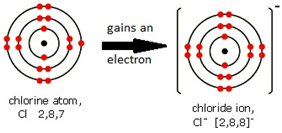
Non-metal atoms form negative ions (anions).
What are the charges of these ions:
• metals in Groups 1, 2 and 3
• non-metals in Groups 5, 6 and 7
• Ag, Cu, Fe, Fe, Pb, Zn
• hydrogen (H), hydroxide (OH), ammonium (NH4), carbonate (CO3), nitrate (NO3), sulfate (SO4).
When given this information of the following ions, it is possible to work out the formulae of ionic compounds which include these ions.
Name of Ion | Formula | Charge |
|---|---|---|
Sulfate | SO42- | -2 |
Carbonate | CO32- | -2 |
Nitrate | NO3- | -1 |
Hydroxide | OH- | -1 |
Ammonium | NH4+ | +1 |
Silver ion | Ag+ | +1 |
Zinc ion | Zn2+ | +2 |
Hydrogen ion | H+ | +1 |
Copper (II) ion | Cu2+ | +2 |
Iron (II) ion | Fe2+ | +2 |
Iron (III) ion | Fe3+ | +3 |
Lead (II) ion | Pb2+ | +2 |
Ion charges on the periodic table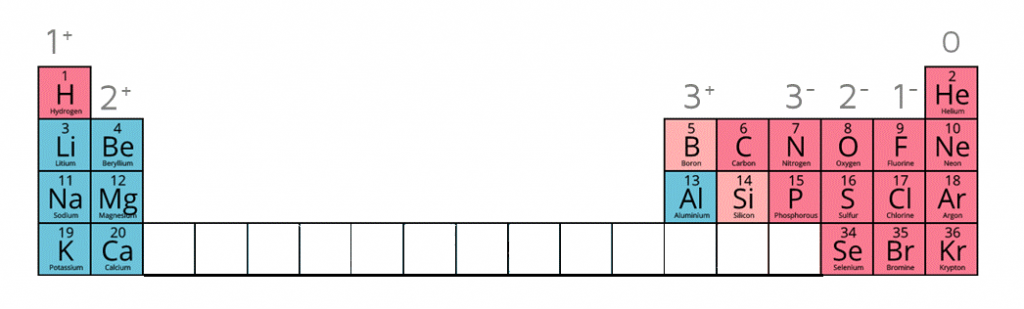
How do you write formulae for compounds formed between the ions listed before?
IONIC COMPOUNDS: Formed when Atoms of Metals transfer Electrons to atoms of Non - Metals to form Compounds made up of ions
FORMULAE FOR COMPOUNDS FORMED BETWEEN IONS
METALS: Loses Electrons to another atom and become Positively Charged Ions
NON - METALS: Gains Electrons from another atom to become Negatively Charged Ions
Example 1:
Sodium Chloride, NaCl (typical Ionic Bond)
SODIUM ATOM
Na 2 . 8 . 1 → Na+ 2 . 8 CHLORINE ATOM
Cl 2 . 8 . 7 → Cl- 2 . 8 . 8 FORMULAE OF IONIC COMPOUND: NaCl |
Example 2:
Magnesium Oxide, MgO (typical Ionic Bond)
MAGNESIUM ATOM
Mg 2 . 8 . 2 → Mg2+ 2 . 8 OXYGEN ATOM
O2 2 . 8 . 6 → O22- 2 . 8 . 8 FORMULAE OF IONIC COMPOUND: MgO |
How do you draw dot-and-cross diagrams to show the formation of ionic compounds by electron transfer, limited to combinations of elements from Groups 1, 2, 3 and 5, 6, 7?
(only outer electrons need be shown)
Sodium chloride, NaCl
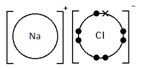
Magnesium chloride, MgCl2
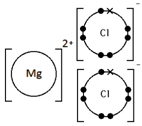
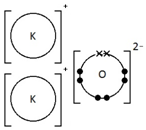
Potassium oxide, K2O
Calcium oxide, CaO
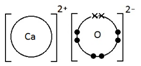
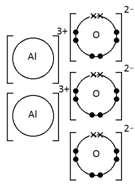
Aluminium oxide, Al2O3
Magnesium nitride, Mg3N2
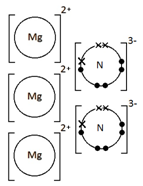
How can we comprehend ionic bonding through the lens of electrostatic attractions?
Ionic Bonds
As a general rule, metals are on the left of the periodic table and nonmetals are on the right-hand side
Ionic bonding involves the transfer of electrons from a metallic element to a non-metallic element
Transferring electrons usually leaves the metal and the non-metal with a full outer shell
Metals lose electrons from their valence shell forming positively charged cations
Non-metal atoms gain electrons forming negatively charged anions
Once the atoms become ions, their electronic configurations are the same as a noble gas
A potassium ion (K+) has the same electronic configuration as argon: [2,8,8]+
A chloride ion (Cl-) also has the same electronic configuration as argon: [2,8,8]-

Forming cations by the removal of electrons from metals

Forming anions by the addition of electrons to nonmetals
Cations and anions are oppositely charged and therefore attracted to each other
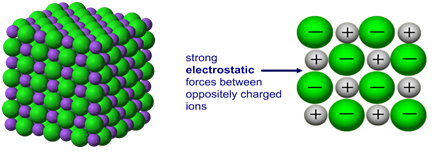
Electrostatic attractions are formed between the oppositely charged ions to form ionic compounds
The ionic bond is the electrostatic attraction formed between the oppositely charged ions, which occurs in all directions ( this called non-directional bonding)
This form of attraction is very strong and requires a lot of energy to overcome
This causes high melting points in ionic compounds

Cations and anions bond together using strong electrostatic forces, which require a lot of energy to overcome
The ions form a lattice structure which is an evenly distributed crystalline structure
Ions in a lattice are arranged in a regular repeating pattern so that positive charges cancel out negative charges
The attraction between the cations and anions is occurring in all directions
Each ion is attracted to all of the oppositely charged ions around it
Therefore the final lattice is overall electrically neutral

Ionic solids are arranged in lattice structures
Why do compounds with giant ionic lattices have high melting and boiling points?
Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points because they have a giant structure with strong electrostatic forces between oppositely charged ions that require a lot of energy to break.
Giant 3D lattice of sodium chloride (NaCl)
When do ionic compounds conduct electricity?
Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity when solid.
However, ionic compounds do conduct electricity if molten or in solution.