Module 4
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Levels of organisation in the human body
Tissues
Epithelial tissue
Nervous tissue
Muscle tissue
Connective tissue
Tissues
Groups of similar cells and their extracellular products organized to perform a common function
Epithelial tissue
Covers body surfaces, lines cavities, forms glands, the internal and external lining of many organs and body tubes
Nervous tissue
Receives, transmits & integrates information to control body activities
Muscle tissue
Responsible for movement and support of body parts,
movement of materials within the body
3 Types of Muscle Tissue
Skeletal: helps move body segments
Smooth: helps move food along the digestive tract
Cardiac: Heart beat helps move blood around the body
Connective tissue
Protects other tissues, storage of fats and minerals, binds together other tissues, support organs structurally and functionally
4 Types of Connective tissue
Loose
Bone
Cartilage
Fibous
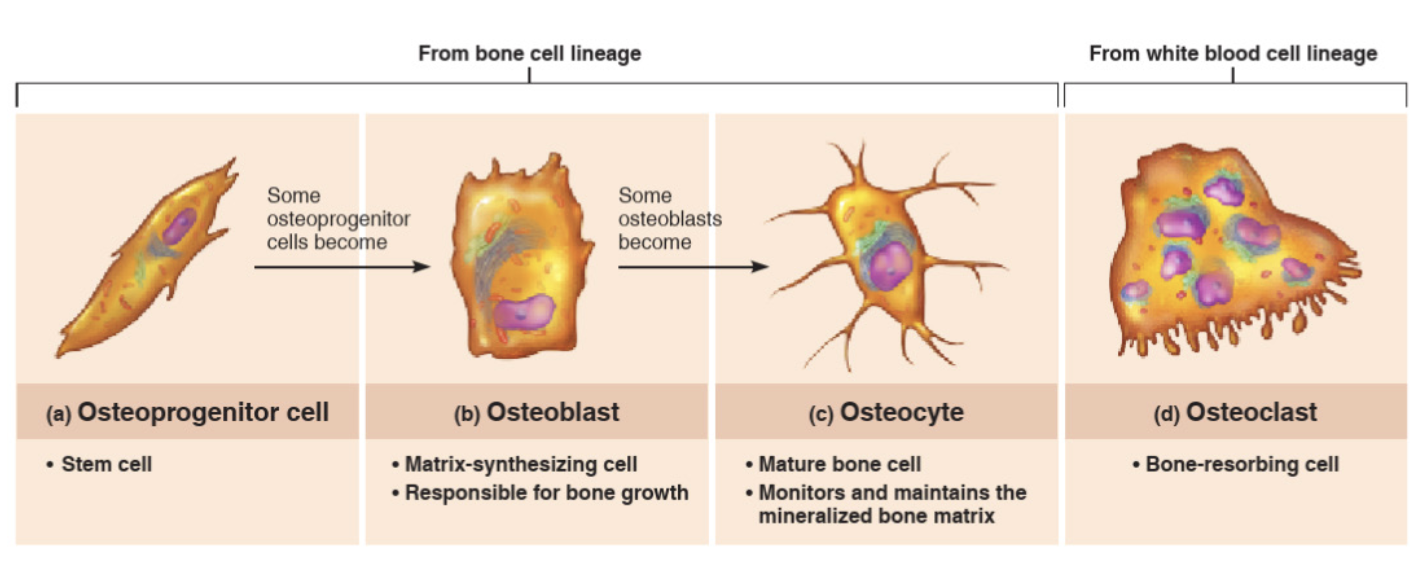
The cells of bone tissue
Muscle
Made up of a large number of bundles (fascicles) of muscle fibres (muscle cells), surrounded by connective tissue
Module 4: Lecture 3, Muscles in Action
Type 1:
Slow oxidative, slow twitch, low force, fatigue resistant
Type IIA:
Fast oxidative, Intermediate twitch and fatigability
Type IIB:
Fast Glycolytic, Fast twitch, more force, fatigues quickly
Types of contraction
Concentric – muscle shortening
during the contractionIsometric – whole muscle length stays the same
(or very close to) during the contractionEccentric – muscle lengthens
during the contraction
Module 4: Lecture 4,
7 Function of Skeletal System
Support
Protection
Anchorage
Minerals
Blood cell production
Triglycerides
Hormone