Health Assessment Final Exam
1/373
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
374 Terms
Medical model
Health is the presence or absence of disease
Functional model
The ability to do things as a gauge of health
Wellness model
Health as a continuum which is always changing
System stability
Health related to levels of stress and the maintenance of homeostasis
Dimensions of wellness
physical, emotional, social, occupational, spiritual, environmental, intellectual, financial
Primary prevention
Efforts to prevent an injury or illness from ever occurring
Ex: lifestyle, immunizations
Secondary prevention
screening to identify diseases in the earliest stages, before the onset of signs and symptoms
Ex: mammogram, BP testing
Tertiary prevention
Actions that are taken after an adverse event that aims at reducing the harm or preventing disability
Ex: physical therapy, support groups
Effective communication
The act of sharing information between two people (or groups of people) so that the information is successfully understood.
Therapeutic communication
Verbal and nonverbal communication techniques that encourage patients to express their feelings and to achieve a positive relationship
Interpreter
A person who translates from one language to another (spoken)
Translater
a professional who works with written documents, moving words and meaning from one document into another
97.5-99.5
Normal temperature range
Hypothermic
Temperature below normal range
Hyperthermic
Temperature above normal range
Febrile
Temperature above 100.4
60-100
Normal pulse range
Bradycardia
Pulse below normal range
Tachycardia
Pulse above normal range
12-20
Normal respiration range
Bradypnea
Respirations below normal range
Tachypnea
Respirations above normal range
Under 120/80
Normal blood pressure range
Elevated blood pressure
120-129/<80
Stage I hypertension
130-139/80-89
Stage 2 hypertension
>140/>90
Hypertensive crisis
>180/>120
95-100%
Normal range for pulse ox
Hypoxia
Oxygen saturation below normal range
Bell
Smaller part of stethoscope used for children
Diaphragm
Larger part of stethoscope used for adults
80%
The bladder of a BP cuff should be what percent of arm circumference
40%
The bladder of a BP cuff should be what percent of arm vertically
Korotkoff sounds
Sounds heard while taking the blood pressure
Onset
O in old carts
Location
L in old carts
Duration
D in old carts
Charectoristics
C in old carts
Associated manifestation
A in old carts
Relieving factors
R in old carts
Treatments
T in old carts
Conduit
Brachial, femoral, and muscular arteries
Inspection
Looking and listening
Palaption
Touching patient
Percussion
Tapping/hitting patient to make sound
Auscultation
Listening with a stethoscope
Urgency
Strong feeling of having to urinate
Incontinence
Inability to hold urine
Enuresis
lack of control in urination; bed-wetting and incontinence
Oliguria
Small amount of urine (<30ml/hr)
Polyuria
Large amount of urine
Dysuria
Pain or burning with urination
Proteinuria
Protein present in urine
Hematuria
Blood present in urine
Nocturia
Waking up to urinate
Nephrolithiasis
Kidney stones
Renal calculus
Kidney stones; Made of salts and minerals
Renal artery stenosis
Narrowing of renal artery
ED
Erectile dysfunction
Dyspareunia
Painful intercourse
Menarche
Onset of menses during puberty
LMP
Last menstrual period; measured from the first day of bleeding
EDC
Estimated date of confinement (day a baby is expected to be born)
EDD
Estimated due date (day a baby is expected to be born)
Renal insufficiency (failure)
Loss of 25% of kidney function
End stage renal disease (ESRD)
Loss of 90% of kidney function
Yearly
How often is a physical exam recommended
50-74
Mammograms are recommended every 2 years between what ages
40
If there is a family history of breast cancer, what age should mammograms begin at
3
Pap smears should be conducted every ____ years between ages 21-29
5
Co-test of HPV and Pap smear should be conducted every ____ years at age 30
65
What age can cervical cancer screens (Pap smear and HPV test) stop at
Ovarian cancer
What cancer is there no screening available for the general population (Just for high risk patients)
Transvaginal ultrasound
Screening begins for high risk patients for ovarian cancer at age 30 by using what
Abdominal aortic aneurysm screening
Test conducted one time between ages 65-75 in men with a smoking history
20-34
Testicular cancer is most prevalent in white males ages:
Biopsy
What is the gold standard for testicular and prostate cancer diagnosis
Prostate
Which cancer is the 2nd leading cause of death in males and is common in males 50 and older
PSA
Routine screening for prostate cancer is not recommended, but ______ levels may be recommended for high risk males 50+ with a life expectancy of >10 years
Fecal occult test
Test of stool that can be done every year between ages of 45-75 to test for colon cancer
*Positive result: blue
Fecal immunochemical test (FIT)
Test that uses antibodies to detect colon cancer and can be done yearly between ages 45-75
Sigmoidoscopy
What is recommended every 5 years to test for colon cancer
Colonoscopy
What is recommended every 10 years to test for colon cancer
Lung
What type of cancer is the leading cause of death
50-80
People aged _____-_____ who have a 20 pack/year smoking history who currently smoke or quit in the past 15 years should have a Ct scan done annually to test for lung cancer
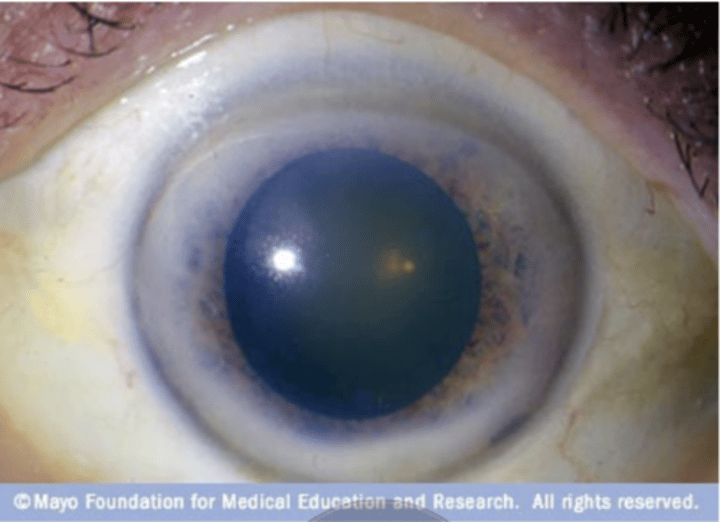
Arcus senilis
Gray ring around eye
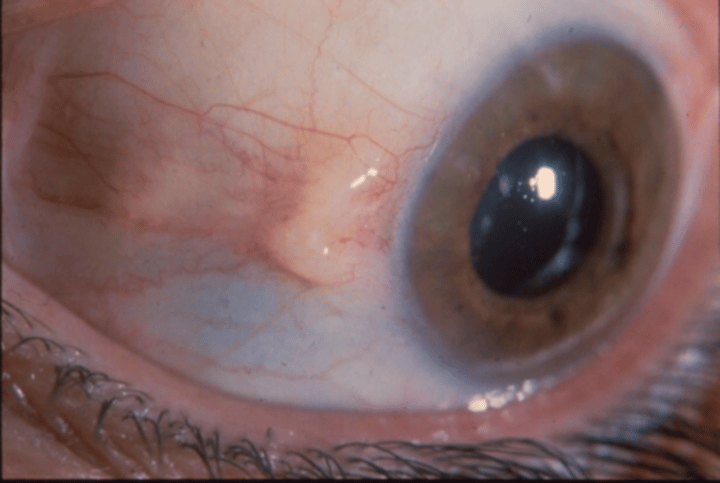
Pterygium
Bulging bump from eye
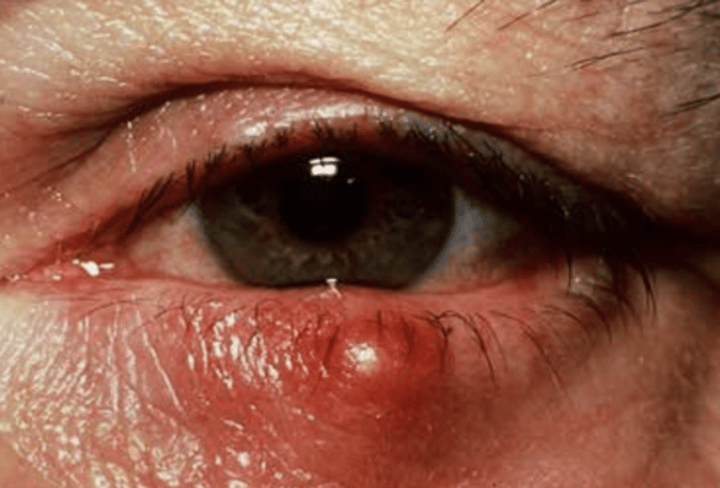
Stye (eclezion)
Clogged pore around eye
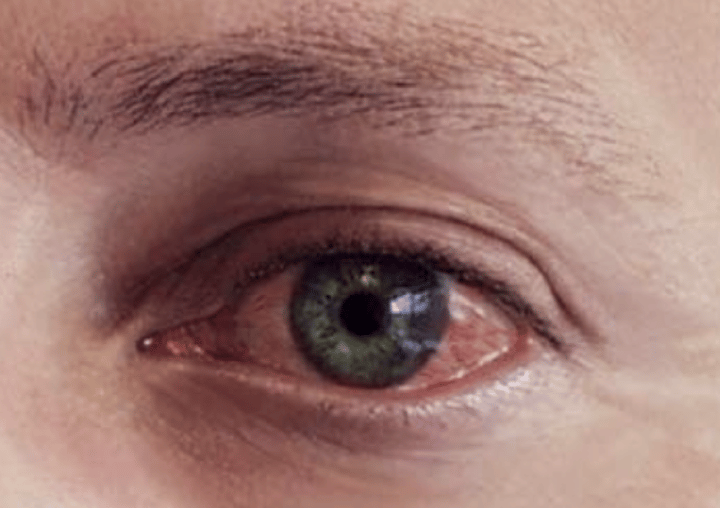
Conjunctivits
Pink eye

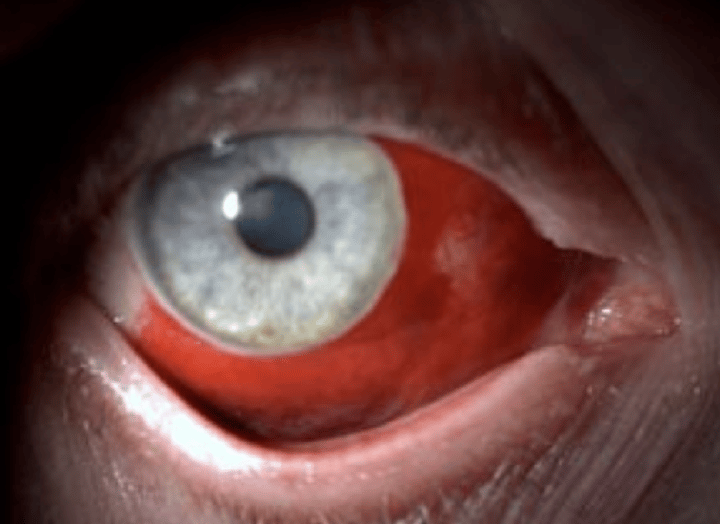
Subconjuctiva bleed
Blood in eye
Strabismus
One eye points inwards

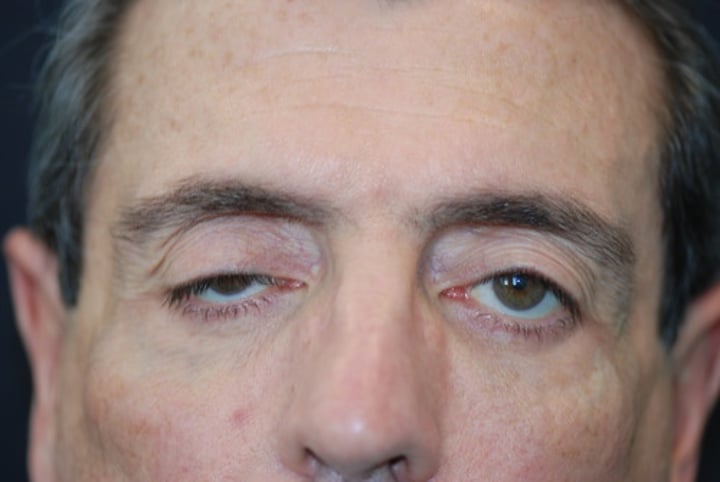
Ptosis
Drooping of eyelid
Iris
Colored part of the eye
Pupil
The opening through which light enters the eye (black part)
Schlera
white of the eye
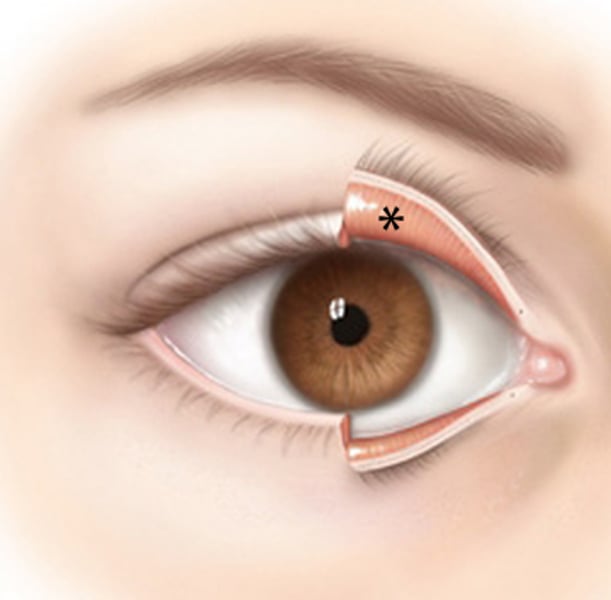
Conjunctiva
Delicate membrane lining the eyelids and covering the eyeball
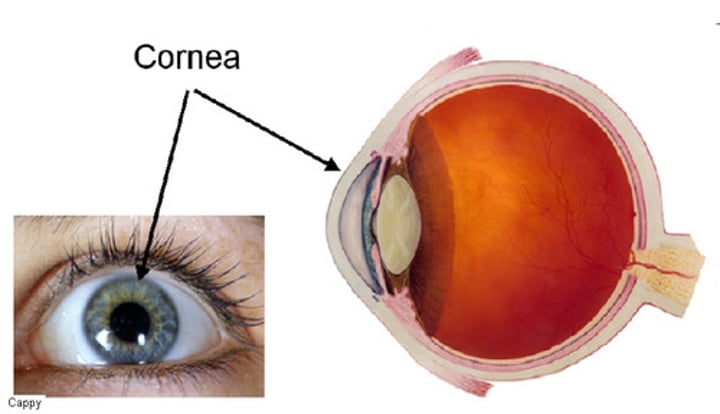
Cornea
The clear tissue that covers the front of the eye
Lens
the transparent structure behind the pupil that changes shape to help focus images on the retina
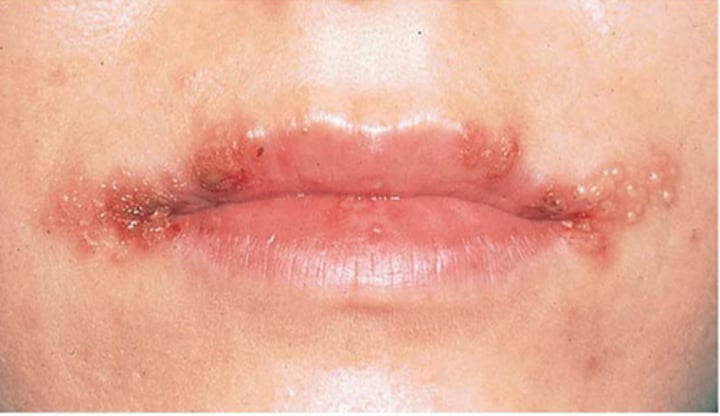
Herpes simplex
cold sores
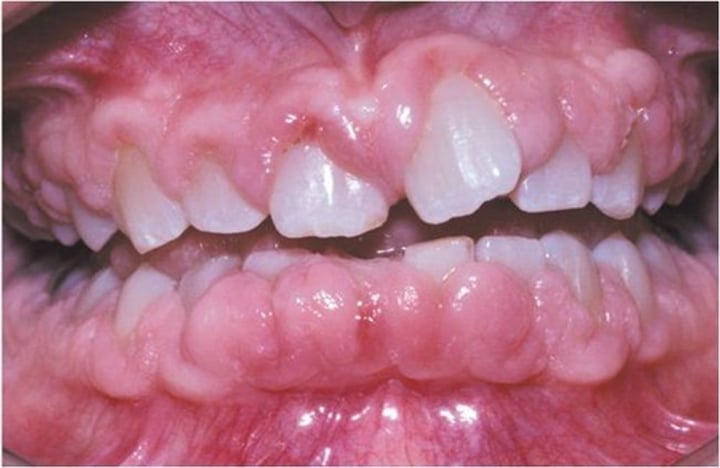
Gingival hypertrophy
Increased size of the gum encircling the teeth