Tropical Storms
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What is a tropical storm?
Intense low pressure weather systems that develop in the tropics
What are the different names for tropical storms?
Hurricanes, cyclones, typhoons or willy-willys
What conditions are needed for tropics storms?
Sea temperature
Ocean depth
Location
Wind sheer
Sea temperature of ≥27°C
Ocean depth of at least 60-70m
A location of at least 5°N/S of the equator
Low wind sheer
Why is the condition “Sea temperature of ≥27°C” required?
Heat energy (fuel) for the storm
Why is the condition “Ocean depth of at least 60-70m” required?
Rising warm air takes moisture in to the atmosphere from the hot ocean, which then condenses to form huge towering cumulonimbus clouds, which eventually burst, releasing large quantities of rainfall
Why is the condition “A location of at least 5°N/S of the equator” required?
In order for the Coriolis effect to make the storm spin, which is too weak over the equator
Coriolis effect
Created by the Earth’s rotation and makes winds bend
Why is the condition “Low wind sheer” required?
If the winds in the upper atmosphere are too strong (ie strong wind sheer) the rising warm moist air gets blown away / blown off course and the storm cannot form properly
What are the main characteristics of tropical storms?
Size
Hazards
Movement
Structure
Where they form
Direction of movement
Climax and nadir
600/700km across
They bring heavy rain, high wind speeds, storm surges and landslides
They spin or rotate as they move. The spin is created by the Earth spinning (Coriolis effect)
When they reach a certain size, they develop an eye (80 mph). Also consist of eye wall and rain bands
They develop in tropical areas between 5-20°N/S of the equator
They move westwards
Over hot oceans they are their worst, but burn out if they pass over land surfaces or move towards the poles
What are the conditions of the eye like?
Calm, high pressure, descending air
What is the difference between high pressure and low pressure?
Low pressure areas are characterised by rising air and are often associated with cloudy, wet, and windy weather, while high pressure areas are associated with sinking air and typically bring clear, dry, and calm conditions
How do tropical storms form? (sequence of events)
A strong upward movement of air draws water vapour up from the ocean surface
This evaporated air cools as it rises and condenses to form towering thunderstorm clouds
Several small thunderstorms join together to form a giant spinning storm. When it reaches 120km per hour it is classified as a tropical storm
The storm develops an eye at its centre where air descends rapidly (high pressure). The outer edge is where the stronger most intense winds and rain are felt
As the storm grows it is carried across the ocean it gathers strength
On reaching the shore the storms energy supply is cut off and friction from the land slows it down and begins to weaken
What makes the tropical storms spin?
Wind blows from areas of high pressure to low pressure
As the Earth rotates it causes the wind to bend and sends warm air rising
At what location is the effect of the Coriolis effect the strongest?
At 5°N/S of the equator the effect of the Coriolis force brings about the maximum rotation of the air
What direction do the storms spin in the different hemispheres?
Storms spin anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere, and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere
How long do tropical storms generally last?
7-14 days
Saffir-Simpson Scale
Estimates storm damage when it hits land, although many storms never make landfall
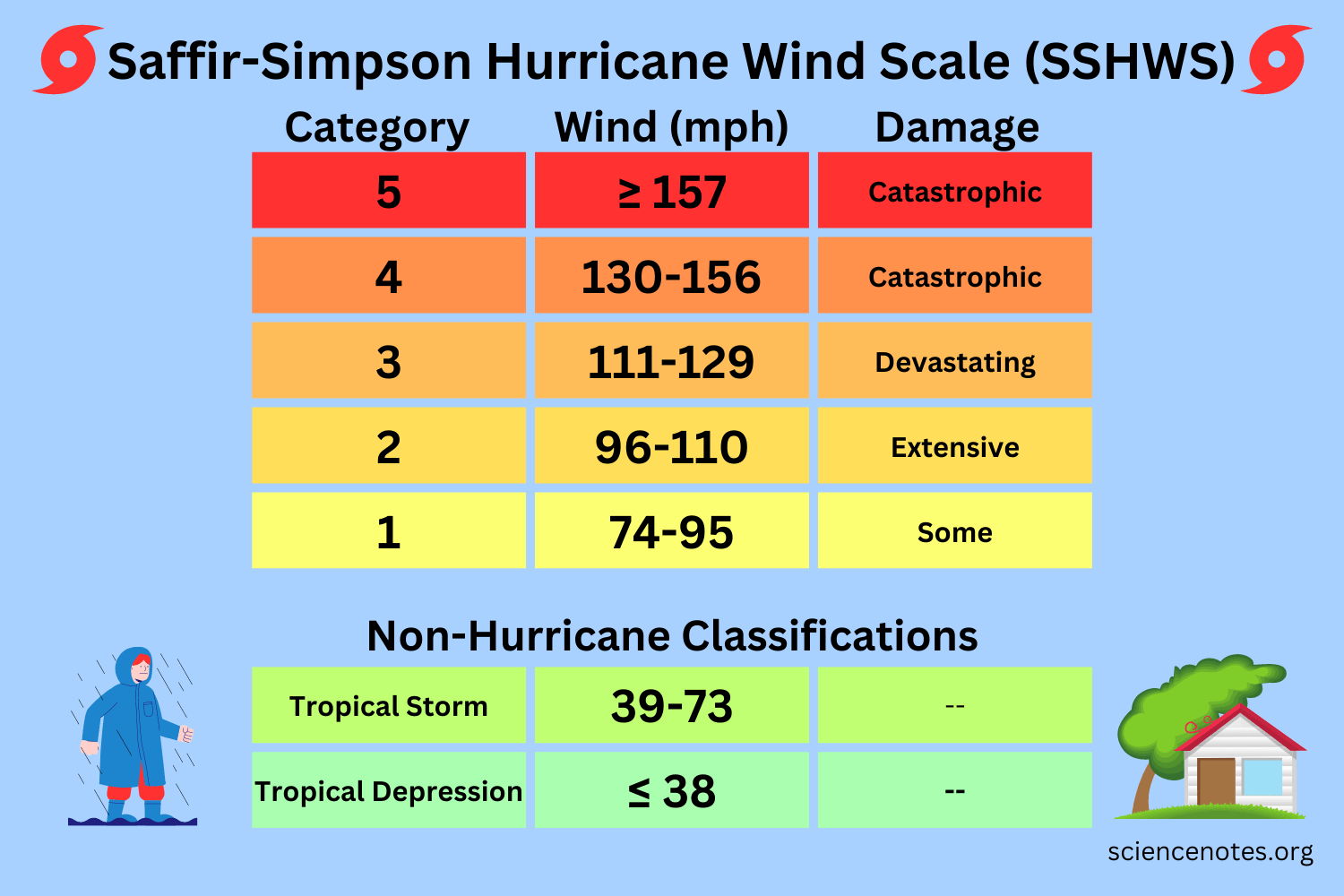
What wind speeds are classified as a tropical depression?
≤38mph
What wind speeds are classified as a tropical storm?
39-73mph
What wind speeds are classified as Category 1?
74-95mph
What wind speeds are classified as Category 2?
96-110mph
What wind speeds are classified as Category 3?
111-129mph
What wind speeds are classified as Category 4?
130-156mph
What wind speeds are classified as Category 5?
≥157mph
What is a flaw of the Saffir-Simpson scale?
In assessing impact, it does not take into account rainfall and storm surges
What is the frequency of tropical storms?
Tropical storms happen frequently. Over 100 tropical storms are formed each year.
Why do most tropical storms not develop into a major hazard?
Most tropical storms will never reach land, so they do not develop into a major hazard
Hurricane season in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres
Storms are more frequent in the Northern Hemisphere between June and November, and in the Southern Hemisphere between November and April
Storm surge
An abnormal rise of water generated by a storm, over and above the predicted astronomical tides
Storm tide
The water level rise due to the combination of storm surge and the astronomical tide
What does “razed” mean?
To destroy to the ground : demolish
e.g. buildings razed to the ground