Unit 1- Levels of Organization
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Anatomy
Study of internal and external structures
Physiology
How living organisms perform vital functions
Structure dictates…
Function
altering the structure will…
Alter function
ALL SPECIFIC FUNCTIONS ARE PERFORMED BY…
SPECIFIC STRUCTURES
Atoms
smallest stable unit of matter!!!! also the building blocks of everything we will discuss
Molecular (chemical) level
Atoms form molecules, properties determined by shape
Cellular Levels
smallest living structural and functional unit of the body
Tissue level
groups of cells working together to perform specific functions
Organ levels
2 of more tissues organized to perform several functions
Organ system level
Interaction of organs and tissues for common purposes (11 organ systems)
Whole organism
human being, need all 11 systems for life and health
Integumentary system
protect against environment, regulates temperature, and provides sensory info
A system that includes skin, hair, and nails
Skeletal system
supports and protects, and mineral function=calcium
main organs are bone, cartilage, and ligaments
Muscular system
Movement, protects and supports, body temperature
major organs are muscles and tendons
Nervous system
coordinates organ systems, responds to stimuli
major organs are brain, spinal cord, and nerves
Endocrine system
coordinates organ systems, metabolic activity and control development
major organs are pituitary glands, sex glands
Cardiovascular system
distributes blood
major organs are heart, vessels, blood
Lymphatic system
retains/ returns fluid, immune system
major organs are spleen and lymph nodes
Respiratory systems
Provides O2 to blood!!! communication, balance pH
Major organs are lungs, trachea
Digestive system
digest food, absorbs nutrients
major organs are stomach, liver, intestines
Urinary system
removes waste, controls water loss
major organs are kidney, bladder
Male reproductive system
produces sperm and male hormone
major organ is testes
Female reproductive system
produces egg/ produces female hormone/ support and nourish infant
major organs are ovaries, uterus
Homeostasis
Existence of relatively stable internal environment!
essential for life, maintaining homeostasis= the foundation of all physiology, all cells specializing and working in harmony to maintain homeostasis in spite of internal or external changes
( homeostatic imbalances) disorder and disease
disorder= any abnormality of structure or function
disease= a disorder characterized by a set of signs and systems (something is wrong, but the doctors do not know what)
(homeostasis mechanism) Autoregulation and extrinsic regulation
autoregulation= occurs when cells or systems adjust its activities automatically
Extrinsic regulation(on the outside) = hen the nervous or endocrine systems cause a change in activities
Homeostasis
Both the nervous and endocrine system regulate homeostasis
nervous system- reacts quicker- specific- short lived (ex. phone)
endocrine system-reacts slower-wide range- last longer (ex. 1000 post cards)
Receptor
Senses a change in a particular parameter, stimulus
Effector
Responds to command, can oppose or enhance stimulus
Negative Feedback
Stimulus Produces a response that opposes/ stops original stimulus
Temp, Blood sugar, most systems
Positive Feedback
Stimulus produces a response that increase/ enhances original stimulus
Dynamic Equilibrium
Body is continually adapting and ajusting
Sagittal
Front to back( lateral view)
frontal or coronal
Ear to Ear (Anterior to posterior)
Transverse or cross
Horizontal
superior
above
inferior
below
Anterior
Front
posterior
back
cranial or cephalic
head
Caudal
tail
Dorsal
back
Ventral
Belly
Proximal
Closer to attachment
Distal
distant from attachment
Medial
towards midline
lateral
away from midline
ipsilateral
same side
contralateral
opposite side
Bilateral
both sides
Supine
face up
Prone
face down
Serous Membrane
Parietal
visceral
Lines cavities(layers)
lines body wall (cavity organ sits in)
viscera lubricant (in between layers)
Dorsal cavity
Cranial cavity
spinal cavity
brain
spinal cord
ventral cavity
thoracic cavity
pleural cavity
pericardial cavity
above the diaphragm
lungs
heart
diaphragm
abdominal cavity
peritoneum
pelvic cavity
x
abdominal organs(liver-largest)
connective tissue
bladder and rectum
The abdominal quadrant
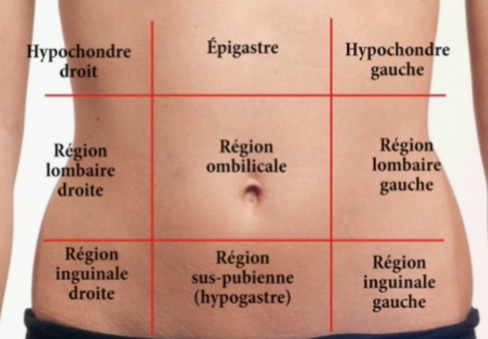

CHAPTER 2
proton
neutrons
electrons
(+) charged part of molecule
uncharged part of molecule
(-) charged part of molecule
Body is made up of…
oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen (96%)
molecule
when 2 or more atoms share electrons
ionic bonds
when opposite charged ions are attracted to each other (NaCl)
ions
an atom that has gained or lost electrons and becomes (+) (-) (Na+Cl)
Cations
anion
a (+) charged ion (Na)
a (-) charged ion (Cl-)
Covalent Bonds
when 2 or more atoms share electrons- much stronger than ionic bonds (H2O)
Nonpolar covalent bonds
2 atoms share the electrons equally
Polar covalent bonds
1 atom attracts the shared electron more- causes partial (+) (-) ( pulls more one way)
hydrogen bonds
(surface tension) water forms polar bonds, H is attracted to neighboring atoms (covalent bond/strong)
chemical reactions
reactants
products
starting substance of a reactions
ending substance after a reaction
activation energy
initial energy to start a reaction- increases in concentration &/or temperature cause atoms to collide
catalysis
speed up reaction by lowering the activation energy needed, not consumed
enzyme
special proteins to lower activation energy in living tissue, cannot tolerate high heat or concentration (body form)
exergonic!!!
reaction that releases more energy than they abords (produces energy)
Endergonic
reactions that require more energy than they release (absorb energy)
Decomposition Reaction
splitting up larger molecules into smaller ones, usually gives off energy
catabolism
the break downing of substances in the body
(break down of sugars)
lysis=
hydrolysis
break something apart/split
use of water split a substance
synthesis reaction
combining substances to produce new larger molecules, usually requires energy (A+B= AB)
Anabolism
the combing of substances in the body (amino acids= proteins)
dehydration synthesis
H2O is formed while joining reactants
Exchange reaction
when both compounds switch partners
reversible Reaction
when products can revert back to original reactants, surplus drives reactions (without energy)
Inorganic compounds
solubility
reactivity
big heat capacity
lubrication
molecule will break or dissolve in water
medium for reactions as well important reactants in many reactions
there is little friction between water molecules
electrolytes
soluble inorganic molecule whose ion will conducts an electric charge
neutral
acidic
basic
solution with a pH of 7
solution with a pH below 7
solution with a pH above 7
inorganic acids and bases
salts
Buffers
union of a cation(+) with an anion(-) *=(NaCl)
compounds that stabilize pH convert strong acids or bases into weak ones
Organic compound
based on carbon and hydrogen atoms,living
Carbohydrates
energy source
monosaccharides
simple single sugar
disaccharides
2 sugar molecules
sucrose,maltose,lactose
polysaccharides
long chain sugars
lipids
fat and oils
Fatty acids
long carbon chains with H’s,energy
glycerides
(mono,di,tri)energy source
steriods
hormones
cholesterol
structural component of cells, transport mechanism
Proteins
long chain of amino acids (peptide bonds)
fibrous proteins
structural, forms sheets or strands (hair, nails)
Globular Proteins
reactive, rounded, found in aqueous solution (blood)
Enzyme functions
facilitates most reactions in the body